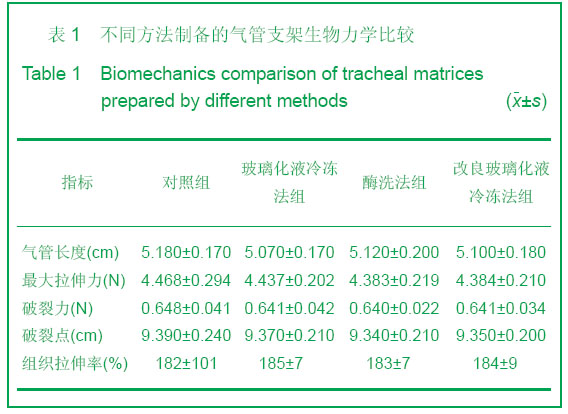
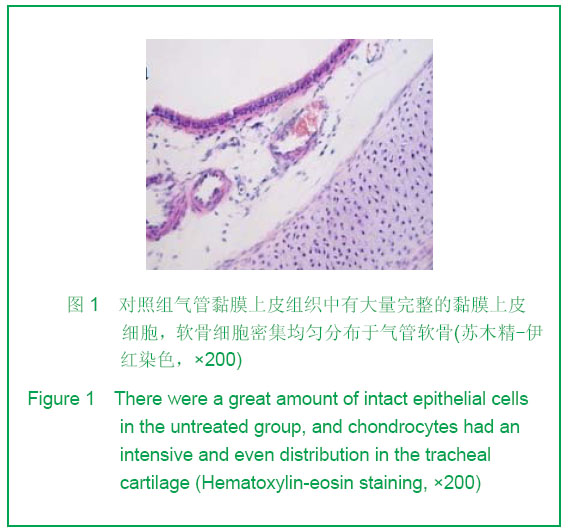
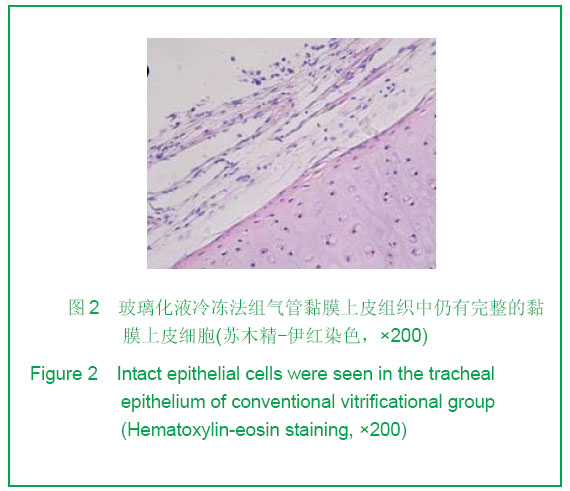
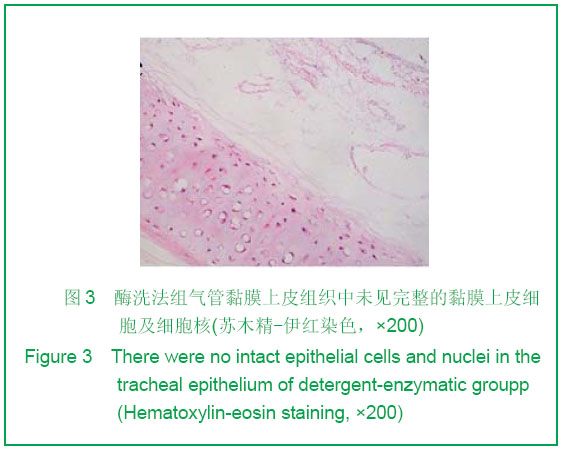
| [1] Teng Z, Trabelsi O, Ochoa I, et al. Anisotropic material behaviours of soft tissues in human trachea: An experiment alstudy. J Biomech. 2012; 45(9):1717-1723.[2] Badylak SF, Weiss DJ, Caplan A, et al. Engineered whole organs and complex tissues. J Lancet. 2012;379(9819): 943-952.[3] Baiguera S, Del Gaudio C, Jaus MO, et al. Long-term changes to in vitro preserved bioengineered human trachea and their implications for decellularized tissues. J Biomaterials. 2012;33(14):3662- 3672.[4] Yang B, Zhou L, Peng B, et al. Stem cells in a tissue-engineered human airway. J Lancet. 2012; 379(9825): 1487.[5] Jungebluth P, Bader A, Baiguera S,et al. The concept of in vivo airway tissue engineering. J Biomaterials. 2012;33(17): 4319-4326.[6] Liang ZB, Li XF, Liu K. Zhongguo Zuzhi Gongcheng Yanjiu yu Linchuang Kangfu. 200;12(5):929-932.梁志波,李小飞,刘锟.同种异体气管移植的研究及展望[J].中国组织工程研究与临床康复,2008,12(5):929-932.[7] Xiaofei Li, Jian Wang, Yunfeng Ni, et al. Bone morphogenetic protein-2 stimulation of cartilage regeneration in canine tracheal graft. J Journal of Lung and Heart Transplantation. 2009;28(3):285- 289. [8] Hinderer S, Schesny M, Bayrak A, et al. Engineering of fibrillar decorin matrices for a tissue-engineered trachea. J Biomaterials. 2012;33(21):5259-5266.[9] Daly AB, Wallis JM, Borg ZD, et al. Initial binding and recellularization of decellularized mouse lung scaffolds with bone marrow-derived mesenchymal stromal cells. J Tissue Eng Part A. 2012; 18(2):1-16.[10] Shi HC, Xu H, Wu J, et al. Zhonghua Waike Zazhi. 2008; 46(20):1589-1590.史宏灿,徐洪,吴俊,等. 玻璃化冷冻同种异体气管移植动物模型的建立[J].中华外科杂志,2008,46(20):1589-1590.[11] Go T, Jungebluth P, Baiguero S, et al. Both epithelial cells and mesenchymal stem cell-derived chondrocytes contribute to the survival of tissue-engineered airway transplants in pigs. J Thorac Cardiovasc Surg. 2010;139(2):437-443.[12] Zhang WH, Huo R, Li SB, et al. Zhongguo Meirong Yixue. 2010;7(19):1015-1017.张文浩,霍然,李尚滨, 等.组织工程化犬气管的生物力学研究[J].中国美容医学,2010,7(19):1015-1017.[13] Macchiarini P, Baiguera S , Jungebluth P, et al. Tissue engineered human tracheas for in vivo implantation. J Biomaterials. 2010;31(34):8931-8938.[14] Macchiarini P, Jungebluth P, Go T, et al. Clinical transplantation of a tissue- engineered airway. J Lancet. 2008; 372(9655):2023-2030. [15] Xu H, Shi HC, Zang WF, et al. An experimental research on cryopreserving rabbit trachea by vitrification. J Cryobiology. 2009;58(2):225-231.[16] Yavin S, Arav A. Measurement of essential physical properties of vitrification solutions. J Theriogenology.2007; 67(1):81-89. [17] Guan J, Urban JP, Li ZH, et al.Effects of rapid cooling on articular cartilage. J Cryobiology. 2006;52(3):430-439. [18] Dahl SL, Chen Z, Solan AK, et al. Feasibility of vitrification as a storage method for tissue-engineered blood vessels. J Tissue Eng.2006;12(2):291-300. |