[1] 曲文庆,李文亮.踝关节骨关节炎的保踝治疗新进展[J].中华创伤骨科杂志,2018,20(8):732-736.
[2] VAN HEEST TJ, LAFFERTY PM.Injuries to the ankle syndesmosis.J Bone Joint Surg Am.2014;96(7):603-613.
[3] SCHEPERS T.Acute distal tibiofibular syndesmosis injury: a systematic review of suture-button versus syndesmotic screw repair. Int Orthop.2012;36(6):1199-1206.
[4] ZHANG P, LIANG Y, HE J, et al.A systematic review of suture-button versus syndesmotic screw in the treatment of distal tibiofibular syndesmosis injury.BMC Musculoskelet Disord.2017; 18(1):286.
[5] 牟风云,胡章勇,刘陵.三种螺钉固定方式治疗下胫腓联合分离对踝关节功能影响的比较研究[J].创伤外科杂志,2017,19(10):777-780.
[6] SCHEPERS T, VAN LIESHOUT EM, VAN DER LINDEN HJ, et al. Aftercare following syndesmotic screw placement: a systematic review.J Foot Ankle Surg.2013;52(4):491-494.
[7] VAN DEN BEKEROM MP, KLOEN P, LUITSE JS, et al. Complications of Distal Tibiofibular Syndesmotic Screw Stabilization: Analysis of 236 Patients.J Foot Ankle Surg.2013; 52(4):456-459.
[8] 毕刚,陈大伟,李春光,等.下胫腓联合损伤对踝关节稳定性影响的生物力学研究[J].中国矫形外科杂志,2017,25(20):1881-1885.
[9] SCHON JM, WILLIAMS BT, VENDERLEY MB, et al. A 3D CT analysis of screw and suture button fixation of the syndesmosis. Foot Ankle Int. 2017,38(2):208-214.
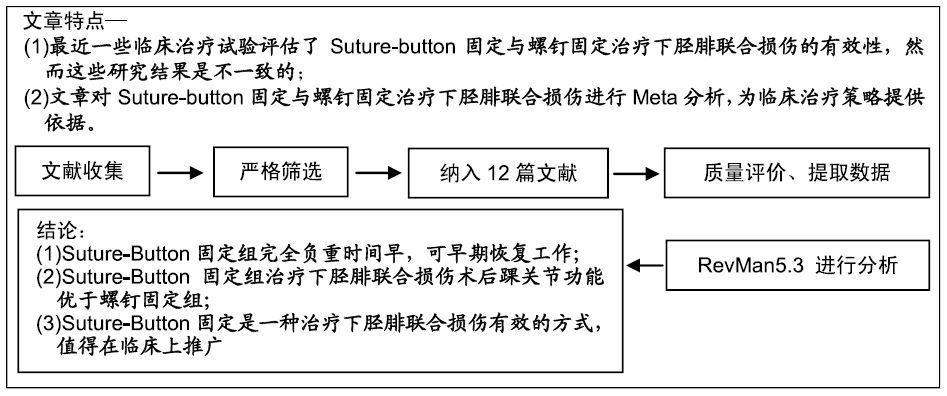
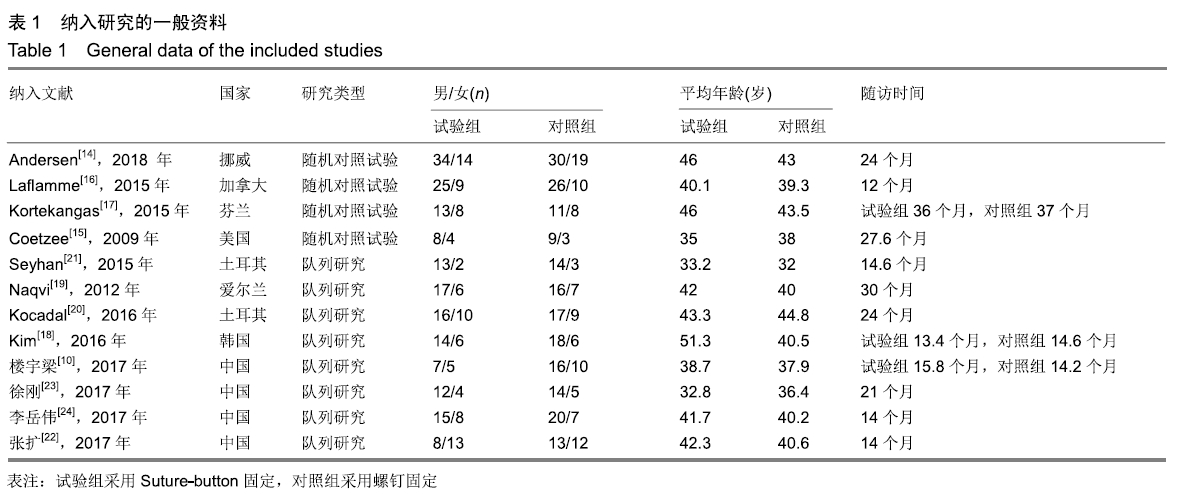
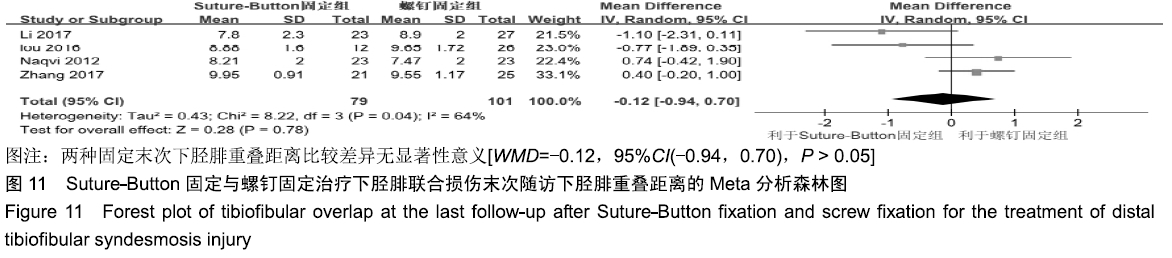
[10] 楼宇梁,洪建军,邵希文,等.Endobutton与螺钉内固定治疗下胫腓联合分离的临床疗效分析[J].中国骨伤,2016,29(8):729-733.
[11] KLITZMAN R, ZHAO H, ZHANG LQ, et a1.Suture-button versus screw fixation of the syndesmosis:A biomechanicalanalysis.Foot Ankle Int. 2010;31(1):69-75.
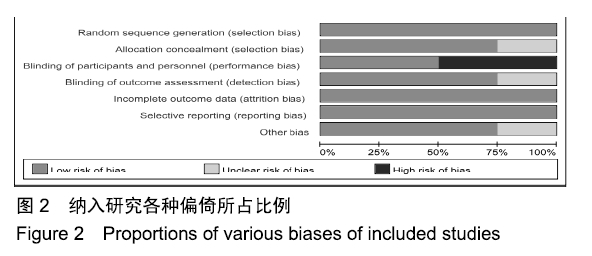
[12] GREEN S.Cochrane Handbook for Systematic Reviews of Interventions: Cochrane Book Series.Naunyn-Schmiedebergs Archiv für experimentelle Pathologie und Pharmakologie.2011, 5(2):S38.
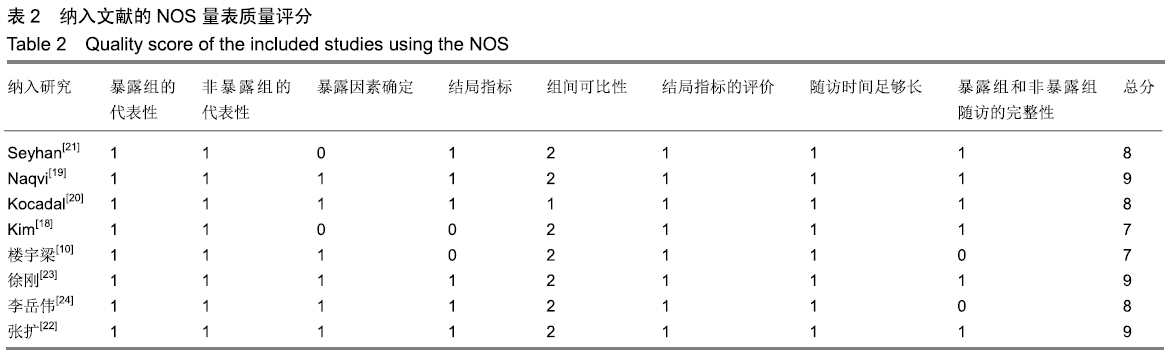
[13] WELLS GA, SHEA BJ, O'CONNELL D, et al.The newcastle- ottawa scale (NOS) for assessing the quality of non-randomized studies in meta-analysis.Appl Eng Agric.2014;18:727-734.
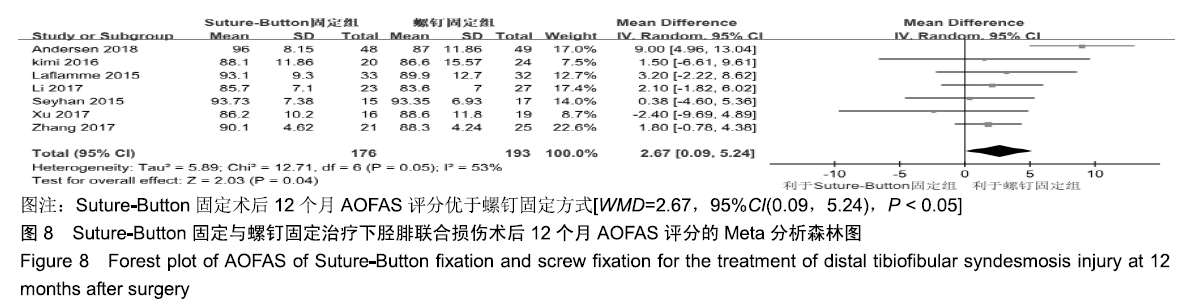
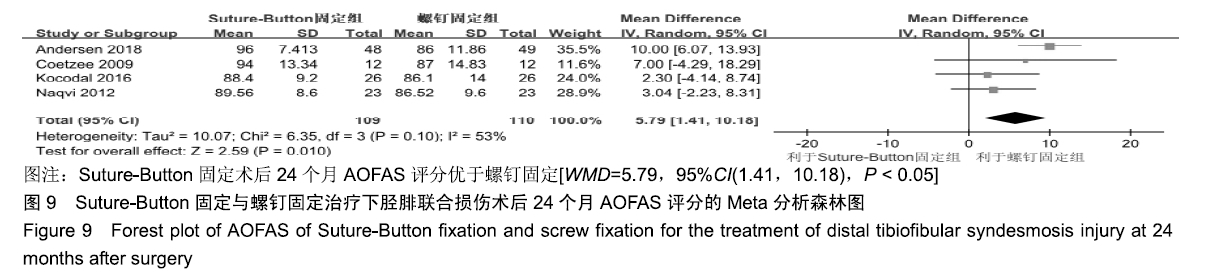
[14] ANDERSEN MR, FRIHAGEN F, HELLUND JC, et al.Randomized Trial Comparing Suture Button with Single Syndesmotic Screw for Syndesmosis Injury.J Bone Joint Surg Am.2018;100(1):2-12.
[15] COETZEE JC, EBELING P.Treatment of Syndesmosis Disruptions With TightRope Fixation.J Foot Ankle Surg.2009;7(3):196-202.
[16] LAFLAMME M, BELZILE EL, BEDARD L, et al.A prospective randomized multicenter trial comparing clinical outcomes of patients treated surgically with a static or dynamic implant for acute ankle syndesmosis rupture.J Orthop Trauma.2015;29(5): 216-223.
[17] KORTEKANGAS T, SAVOLA O, FLINKKILA T, et al.A prospective randomised study comparing TightRope and syndesmotic screw fixation for accuracy and maintenance of syndesmotic reduction assessed with bilateral computed tomography.Injury.2015; 46(6): 1119-1126.
[18] KIM JH, GWAK HC, LEE CR, et al.A Comparison of Screw Fixation and Suture-Button Fixation in a Syndesmosis Injury in an Ankle Fracture. J Foot Ankle Surg.2016;55(5):985-990.
[19] NAQVI GA, CUNNINGHAM P, LYNCH B, et al.Fixation of Ankle Syndesmotic Injuries: Comparison of TightRope Fixation and Syndesmotic Screw Fixation for Accuracy of Syndesmotic Reduction. Am J Sport Med.2012;40(12):2828-2835.
[20] KOCADAL O, YUCEL M, PEPE M, et al.Evaluation of Reduction Accuracy of Suture-Button and Screw Fixation Techniques for Syndesmotic Injuries.Foot Ankle Int.2016;37(12):1317.
[21] SEYHAN M, DONMEZ F, MAHIROGULLARI M, et al.Comparison of screw fixation with elastic fixation methods in the treatment of syndesmosis injuries in ankle fractures.Injury.2015;46:S19-S23.
[22] 张扩,卢全忠,沈林华,等.TightRope与金属螺钉内固定治疗下胫腓联合分离的临床疗效对比[J]. 中国骨与关节损伤杂志,2017,32(10): 1037-1040.
[23] 徐刚,李小飞,史东平,等.动态与静态固定 2 种方式在治疗伴下胫腓联合损伤的踝关节骨折中的疗效比较[J].中国骨与关节损伤杂志, 2017, 32(4):1672-9935.
[24] 李岳伟,张茗慧,李小荣,等.弹性固定及坚强固定治疗踝关节旋前-外旋型骨折合并下胫腓联合分离的疗效比较[J].骨与关节修复重建, 2017, 31(7):1002-1892
[25] VALKERING KP, VERGROESEN DA, Nolte PA.Isolated syndesmosis ankle injury.Orthopedics.2012;35(12):1705-1710.
[26] PAKARINEN H.Stability-based classification for ankle fracture management and the syndesmosis injury in ankle fractures due to a supination external rotation mechanism of injury.Acta Orthop Suppl. 2012;83(347):1-26.
[27] THORNES B, SHANNON F, GUINEY AM, et al.Suture-Button Syndesmosis Fixation.Clin Orthop Relat Res.2005;(431):207-212.
[28] COTTOM JM, HYER CF, PHILBIN TM, et al.Transosseous Fixation of the Distal Tibiofibular Syndesmosis: Comparison of an Interosseous Suture and Endobutton to Traditional Screw Fixation in 50 Cases.J Foot Ankle Surg.2009;48(6):620-630.
[29] TERAMOTO A, SUZUKI D, KAMIYA T, et al.Comparison of Different Fixation Methods of the Suture-Button Implant for Tibiofibular Syndesmosis Injuries.Am J Sport Med.2011;39(10): 2226-2232.
[30] LITTLE MILTION MT, BERKES MB, SCHOTTEL PC, et al. Anatomic Fixation of Supination External Rotation Type IV Equivalent Ankle Fractures.J Orthop Trauma.2015;29(5):250-255.
[31] KAFTANDZIEV I, SPASOV M, TRPESKI S, et al.Fate of the syndesmotic screw-Search for a prudent solution.Injury.2015;46: S125-S129.
[32] ANDERSEN MR, FRIHAGEN F, MADSEN JE, et al.High complication rate after syndesmotic screw removal.Injury.2015; 46(11):2283-2287.
[33] LALLI TA, MATTHEWS LJ, HANSELMAN AE, et al.Economic impact of syndesmosis hardware removal. Foot.2015;25:131-133.
[34] SCHEPERS T, VAN LIESHOUT EM, DE VRIES MR, et al. Complications of Syndesmotic Screw Removal.Foot Ankle Int. 2011;32(11):1040-1044.
[35] SCHEPERS T.To retain or remove the syndesmotic screw: a review of literature. Arch Orthop Trauma Surg.2011;131(7): 879-883.
[36] MANJOO A, SANDERS DW, TIESZER C, et al.Functional and Radiographic Results of Patients with Syndesmotic Screw Fixation: Implications for Screw Removal.J Orthop Trauma.2010; 24(1):2-6.
[37] HODGSON P, THOMAS R.Avoiding suture knot prominence with suture button along distal fibula: technical tip.Foot Ankle Int. 2011; 32:908-909.
|