| [1]Louis DN, Perry A, Reifenberger G, et al. The 2016 World Health Organization Classification of Tumors of the Central Nervous System: a summary. Acta Neuropathol. 2016;131(6):803-820.[2]Lapointe S, Perry A, Butowski NA. Primary brain tumours in adults. Lancet. 2018;392(10145):432-446. [3]Lee JH, Lee JE, Kahng JY, et al. Human glioblastoma arises from subventricular zone cells with low-level driver mutations. Nature. 2018; 560(7717):243-247. [4]Wick W, Gorlia T, Bendszus M, et al. Lomustine and Bevacizumab in Progressive Glioblastoma. N Engl J Med. 2017;377(20):1954-1963.[5]Najafi M, Goradel NH, Farhood B, et al. Tumor microenvironment: Interactions and therapy. J Cell Physiol. 2019;234(5):5700-5721. [6]Hoshino A, Costa-Silva B, Shen TL, et al. Tumour exosome integrins determine organotropic metastasis. Nature. 2015;527(7578):329-335. [7]Novikova MV, Khromova NV, Kopnin PB. Components of the Hepatocellular Carcinoma Microenvironment and Their Role in Tumor Progression. Biochemistry (Mosc). 2017;82(8):861-873.[8]Witz IP. The tumor microenvironment: the making of a paradigm. Cancer Microenviron. 2009;2 Suppl 1:9-17.[9]Yang M, Reynoso J, Jiang P, et al. Transgenic nude mouse with ubiquitous green fluorescent protein expression as a host for human tumors. Cancer Res. 2004;64(23):8651-8656.[10]Suetsugu A, Katz M, Fleming J, et al. Multi-color palette of fluorescent proteins for imaging the tumor microenvironment of orthotopic tumorgraft mouse models of clinical pancreatic cancer specimens. J Cell Biochem. 2012;113(7):2290-2295. [11]Wang A, Dai X, Cui B, et al. Experimental research of host macrophage canceration induced by glioma stem progenitor cells. Mol Med Rep. 2015;11(4):2435-2442. [12]Dai X, Chen H, Chen Y, et al. Malignant transformation of host stromal ?broblasts derived from the bone marrow traced in a dual-color fluorescence xenograft tumor model. Oncol Rep. 2015;34(6):2997-3006.[13]Shultz LD, Goodwin N, Ishikawa F, et al. Human cancer growth and therapy in immunodeficient mouse models. Cold Spring Harb Protoc. 2014;2014(7):694-708. [14]Lai Y, Wei X, Lin S, et al. Current status and perspectives of patient-derived xenograft models in cancer research. J Hematol Oncol. 2017;10(1):106. [15]Roque-Lima B, Roque CCTA, Begnami MD, et al. Development of patient-derived orthotopic xenografts from metastatic colorectal cancer in nude mice. J Drug Target. 2018. doi: 10.1080/1061186X. 2018.1509983. [Epub ahead of print][16]Ye D, Zhou C, Wang S, et al. Tumor suppression effect of targeting periostin with siRNA in a nude mouse model of human laryngeal squamous cell carcinoma. J Clin Lab Anal. 2019;33(1):e22622. [17]Jacobsen BM, Harrell JC, Jedlicka P, et al. Spontaneous fusion with, and transformation of mouse stroma by, malignant human breast cancer epithelium. Cancer Res. 2006;66(16):8274-8279.[18]Goldenberg DM, Zagzag D, Heselmeyer-Haddad KM, et al. Horizontal transmission and retention of malignancy, as well as functional human genes, after spontaneous fusion of human glioblastoma and hamster host cells in vivo. Int J Cancer. 2012;131(1):49-58. [19]Liu J, Zhang Y, Bai L, et al. Rat bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells undergo malignant transformation via indirect co-cultured with tumour cells. Cell Biochem Funct. 2012;30(8):650-656. [20]Chen Y, Wang Z, Dai X, et al. Glioma initiating cells contribute to malignant transformation of host glial cells during tumor tissue remodeling via PDGF signaling. Cancer Lett. 2015;365(2):174-181. [21]Wan Y, Fei XF, Wang ZM, et al. Expression of miR-125b in the new, highly invasive glioma stem cell and progenitor cell line SU3. Chin J Cancer. 2012;31(4):207-214.[22]Dong J, Dai XL, Lu ZH, et al. Incubation and application of transgenic green fluorescent nude mice in visualization studies on glioma tissue remodeling. Chin Med J (Engl). 2012;125(24):4349-4354.[23]Chen Z, Guo P, Xie X, et al. The role of tumour microenvironment: a new vision for cholangiocarcinoma. J Cell Mol Med. 2019;23(1):59-69. [24]Gentilini A, Pastore M, Marra F, et al. The Role of Stroma in Cholangiocarcinoma: The Intriguing Interplay between Fibroblastic Component, Immune Cell Subsets and Tumor Epithelium. Int J Mol Sci. 2018;19(10):E2885. [25]Weniger M, Honselmann KC, Liss AS. The Extracellular Matrix and Pancreatic Cancer: A Complex Relationship. Cancers (Basel). 2018; 10(9):E316.[26]Zhang X, Ding K, Wang J, et al. Chemoresistance caused by the microenvironment of glioblastoma and the corresponding solutions. Biomed Pharmacother. 2019;109:39-46. [27]Agorku DJ, Tomiuk S, Klingner K, et al. Depletion of Mouse Cells from Human Tumor Xenografts Significantly Improves Downstream Analysis of Target Cells. J Vis Exp. 2016;(113). [28]Rycaj K, Li H, Zhou J, et al. Cellular determinants and microenvironmental regulation of prostate cancer metastasis. Semin Cancer Biol. 2017;44:83-97. [29]López-Soto A, Gonzalez S, Smyth MJ, et al. Control of Metastasis by NK Cells. Cancer Cell. 2017;32(2):135-154.[30]Chen K, Liu Q, Tsang LL, et al. Human MSCs promotes colorectal cancer epithelial-mesenchymal transition and progression via CCL5/β-catenin/Slug pathway. Cell Death Dis. 2017;8(5):e2819. [31]Yu Y, Zhang Q, Ma C, et al. Mesenchymal stem cells recruited by castration-induced inflammation activation accelerate prostate cancer hormone resistance via chemokine ligand 5 secretion. Stem Cell Res Ther. 2018;9(1):242. [32]Dasari S, Fang Y, Mitra AK. Cancer Associated Fibroblasts: Naughty Neighbors That Drive Ovarian Cancer Progression. Cancers (Basel). 2018;10:E406.[33]Tome Y, Tsuchiya H, Hayashi K, et al. In vivo gene transfer between interacting human osteosarcoma cell lines is associated with acquisition of enhanced metastatic potential. J Cell Biochem. 2009;108(2):362-367. [34]Durgan J, Florey O. Cancer cell cannibalism: Multiple triggers emerge for entosis. Biochim Biophys Acta Mol Cell Res. 2018;1865(6):831-841. [35]Martins I, Raza SQ, Voisin L, et al. Entosis: The emerging face of non-cell-autonomous type IV programmed death. Biomed J. 2017; 40(3):133-140. [36]Khalkar P, Díaz-Argelich N, Antonio Palop J, et al. Novel Methylselenoesters Induce Programed Cell Death via Entosis in Pancreatic Cancer Cells. Int J Mol Sci. 2018;19(10):E2849.[37]Lapitz A, Arbelaiz A, Olaizola P, et al. Extracellular Vesicles in Hepatobiliary Malignancies. Front Immunol. 2018;9:2270. [38]Nawaz M, Shah N, Zanetti BR, et al. Extracellular Vesicles and Matrix Remodeling Enzymes: The Emerging Roles in Extracellular Matrix Remodeling, Progression of Diseases and Tissue Repair. Cells. 2018; 7(10):E167. [39]Choi D, Lee TH, Spinelli C, et al. Extracellular vesicle communication pathways as regulatory targets of oncogenic transformation. Semin Cell Dev Biol. 2017;67:11-22.[40]Suetsugu A, Honma K, Saji S, et al. Imaging exosome transfer from breast cancer cells to stroma at metastatic sites in orthotopic nude-mouse models. Adv Drug Deliv Rev. 2013;65(3):383-390. [41]Wang Z, Chen JQ, Liu JL, et al. Exosomes in tumor microenvironment: novel transporters and biomarkers. J Transl Med. 2016;14(1):297.[42]Zhao H, Yang L, Baddour J, et al. Tumor microenvironment derived exosomes pleiotropically modulate cancer cell metabolism. Elife. 2016; 5:e10250. [43]Rackov G, Garcia-Romero N, Esteban-Rubio S, et al. Vesicle-Mediated Control of Cell Function: The Role of Extracellular Matrix and Microenvironment. Front Physiol. 2018;9:651. |
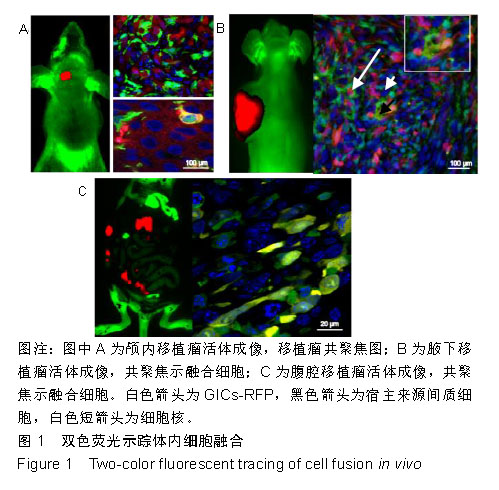
.jpg)
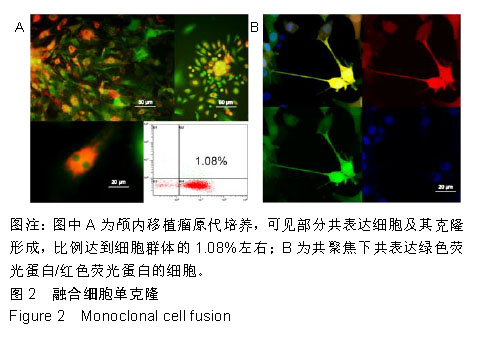
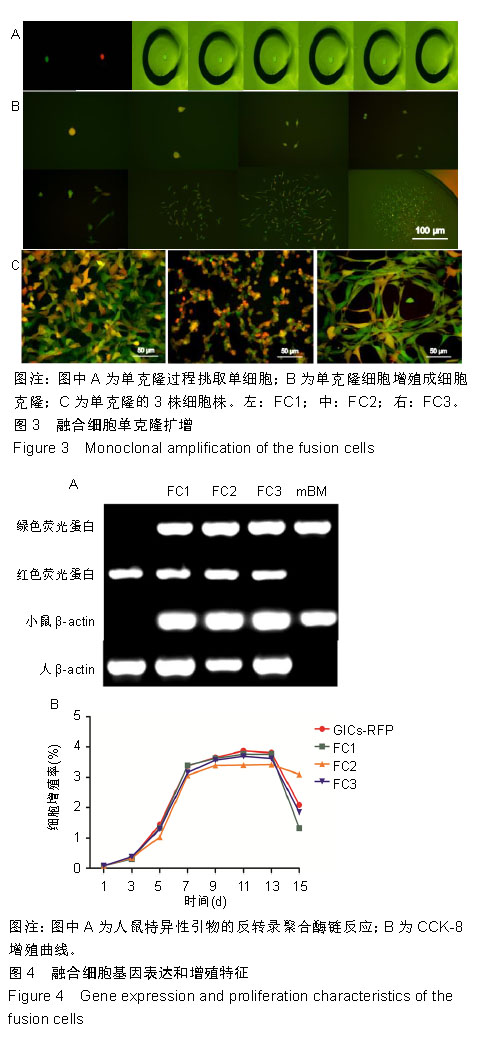
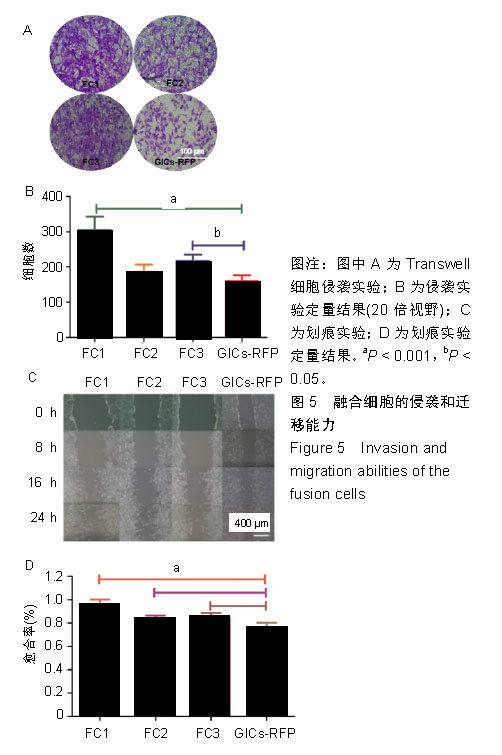

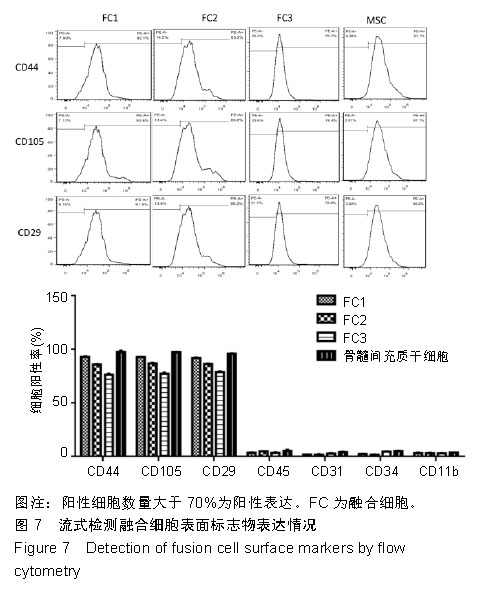
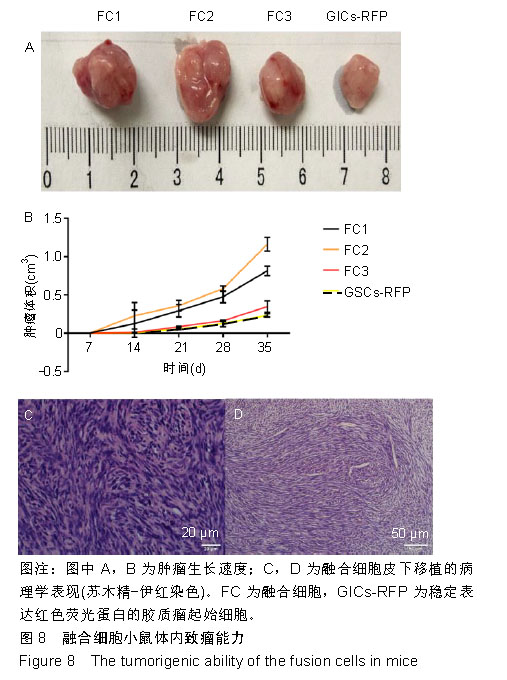
.jpg)
.jpg)