| [1] Shen LL, Mañucat-Tan NB, Gao SH, et al. The ProNGF/p75NTR pathway induces tau pathology and is a therapeutic target for FTLD-tau. Mol Psychiatry. 2018;23(8):1813-1824.[2] Zhao M, Wen X, Li G, et al. The spatiotemporal expression and mineralization regulation of p75 neurotrophin receptor in the early tooth development. Cell Prolif. 2019;52(1):e12523.[3] 吴小莹,杨斌. 脑源性神经营养因子与骨/牙组织发育代谢:促成或抑制细胞的增殖与分化[J].中国组织工程研究, 2015,19(2):283-288.[4] 熊静,李志伟,韩剑虹,等. proBDNF-p75NTR通路抑制C6细胞增殖[J]. 医学研究杂志, 2015, 44(3): 89-93.[5] Lv GH, Jiang L, Man C, et al. The effect of nerve growth factor on the expression of BMP-2 in the healing of rabbits' mandibular fracture with partial nerve injury. Lin Chung Er Bi Yan Hou Tou Jing Wai Ke Za Zhi. 2016;30(7):535-537.[6] Su YW, Zhou XF, Foster BK, et al. Roles of neurotrophins in skeletal tissue formation and healing. J Cell Physiol. 2018;233(3): 2133-2145.[7] 崔国胜,曾剑玉,张婧,等.神经生长因子对2型糖尿病小鼠骨髓基质细胞体外成骨能力的影响[J].中华口腔医学杂志, 2018, 53(2): 97-102.[8] 刘建军,黄亮,韩庆斌,等.神经生长因子对大鼠胫骨骨折愈合的影响及其机制[J].山东医药,2016,56(32): 27-29.[9] 刘强和,王亮亮,王翔,等.人β-NGF重组质粒转染GFP转基因小鼠BMSC的实验研究[J].重庆医学,2014,43(10): 1161-1163,1167.[10] 马乐园,赵岩,乔万庆,等.创伤性脑损伤合并骨折中加速骨折愈合过程中相关因子的表达[J].中国组织工程研究,2017, 21(32): 5115-5121.[11] Becker K, Cana A, Baumgärtner W, et al. p75 Neurotrophin Receptor: A Double-Edged Sword in Pathology and Regeneration of the Central Nervous System. Vet Pathol. 2018;55(6):786-801.[12] Chakraborty S, Castranova V, Perez MK, et al. Nanoparticles-induced apoptosis of human airway epithelium is mediated by proNGF/p75NTR signaling. J Toxicol Environ Health A. 2017;80(1):53-68.[13] Mitsiadis TA, Pagella P. Expression of Nerve Growth Factor (NGF), TrkA, and p75(NTR) in Developing Human Fetal Teeth. Front Physiol. 2016;7:338.[14] 李俊峰,陈莲香,吕霞,等. p75NTR蛋白体外通过TrkANGFR/p75NTR异源二聚体信号途径促进L02细胞增殖[J].中华消化杂志, 2012, 32(4): 256-261.[15] Mukai J, Hachiya T, Shoji-Hoshino S, et al. NADE, a p75NTR-associated cell death executor, is involved in signal transduction mediated by the common neurotrophin receptor p75NTR. J Biol Chem. 2000;275(23):17566-17570.[16] Hickman FE, Stanley EM, Carter BD. Neurotrophin Responsiveness of Sympathetic Neurons Is Regulated by Rapid Mobilization of the p75 Receptor to the Cell Surface through TrkA Activation of Arf6. J Neurosci. 2018;38(24):5606-5619.[17] Stabile A, Pistilli A, Crispoltoni L, et al. A role for NGF and its receptors TrKA and p75NTR in the progression of COPD. Biol Chem. 2016;397(2):157-163.[18] Douillard T, Martinelli-Kläy CP, Lombardi T. Nerve Growth Factor Expression and Its Receptors TrkA and p75NTR in Peri-Implantitis Lesions. Implant Dent. 2016;25(3):373-379.[19] Amoras Eda S, Gomes ST, Freitas FB, et al. NGF and P75NTR gene expression is associated with the hepatic fibrosis stage due to viral and non-viral causes. PLoS One. 2015;10(3):e0121754.[20] 李家勇,王铭,彭称飞,等. P75NTR在兔骨折不愈合局部组织中的表达及意义[J].中国骨质疏松杂志,2017,23(4):437-440.[21] 刘宇鹏,赵德伟,王卫明,等.神经生长因子对骨折愈合中骨形态发生蛋白表达的影响[J].中华医学杂志,2014,94(23): 1825-1828.[22] Liu Y, Zhao D, Wang W, et al. Nerve growth factor modulates bone morphogenetic protein expression in rabbit fracture. Zhonghua Yi Xue Za Zhi. 2014;94(23):1825-1828.[23] Zhuang YF, Li J. Serum EGF and NGF levels of patients with brain injury and limb fracture. Asian Pac J Trop Med. 2013;6(5):383-386.[24] Sang XG, Wang ZY, Cheng L, et al. Analysis of the mechanism by which nerve growth factor promotes callus formation in mice with tibial fracture. Exp Ther Med. 2017;13(4):1376-1380.[25] Bei C, Lin Z, Yang Z, et al. Study on effect of NGF on fracture healing. Zhongguo Xiu Fu Chong Jian Wai Ke Za Zhi. 2009;23(5): 570-576.[26] 吴永超,郑启新,谢宗平,等.骨髓间充质干细胞表达神经营养因子及治疗脊髓损伤的研究[J].中华实验外科杂志, 2005,22(2):139-141.[27] 卢莎,谭文杰,张玲,等.脂质体转染法与电转染法在丙型肝炎病毒RNA 转染人肝癌细胞中的应用效果比较[J].山东医药, 2016,56(19):15-18.[28] 张禾璇,单可人,何燕,等.脂质体法与电穿孔法转染两种细胞效率的比较[J].重庆医学,2014,43(33):4432-4433.[29] 纪玉婷,杨燕,郑荣生,等.慢病毒介导稳定高表达Cx32的Huh7细胞系建立及其对细胞增殖的影响[J].中国药理学通报, 2018, 34(2): 284-289.[30] 李诗鹏,李强,石正松,等.基因重组腺病毒载体与慢病毒载体转染兔骨髓间充质干细胞的对比[J].中国组织工程研究, 2017, 21(9): 1340-1345. |
.jpg)
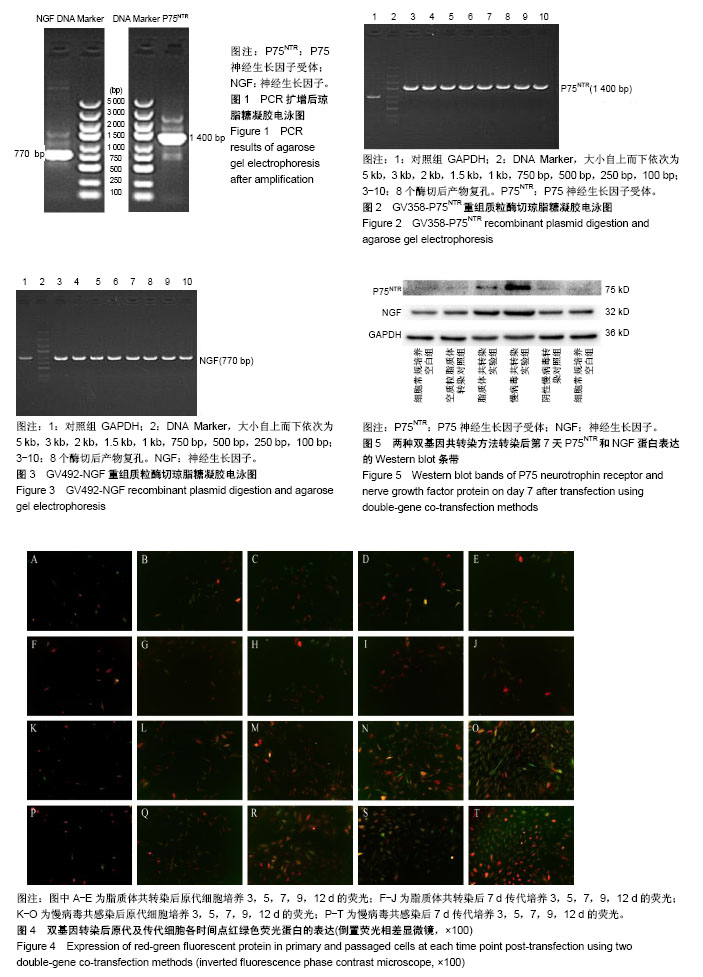
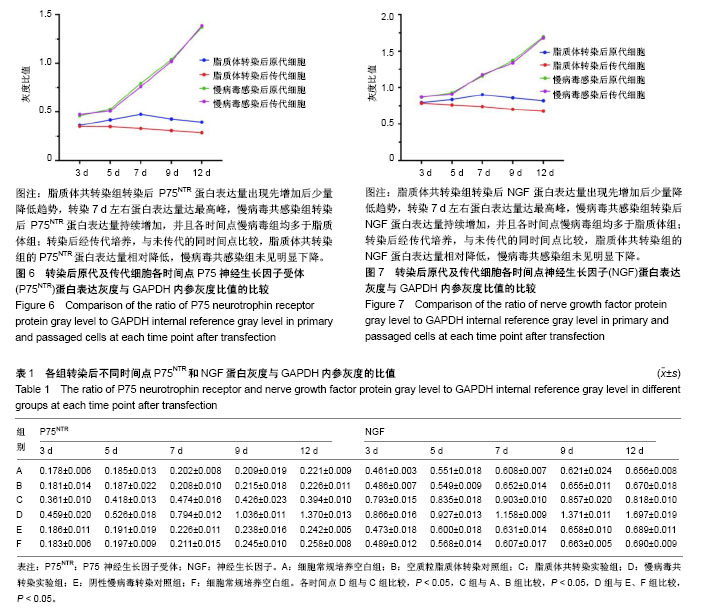
.jpg)
.jpg)