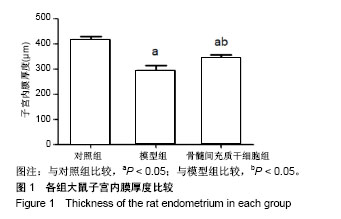
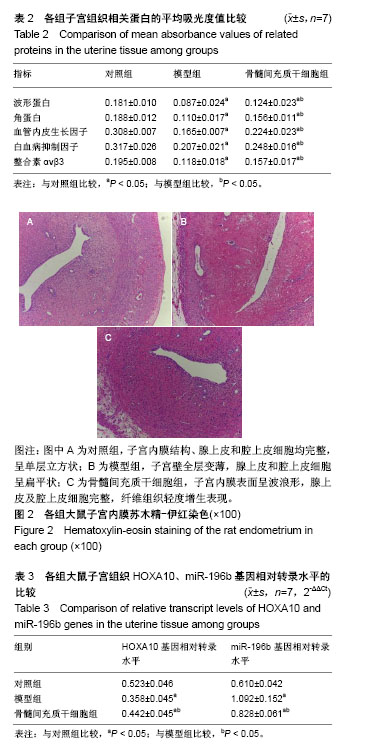
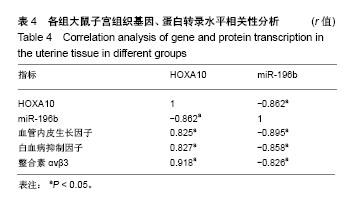
| [1] Mahajan N, Sharma S.The endometrium in assisted reproductive technology: How thin is thin. J Hum Reprod Sci. 2016;9(1):3-8.[2] 黎雪茹,王中海.薄型子宫内膜的研究进展[J].中华妇幼临床医学杂志, 2015,11(1):109-112.[3] Kasius A, Smit JG, Torrance HL, et al. Endometrial thickness and pregnancy rates after IVF: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Hum Reprod Update. 2014;20(4):530-541.[4] 尹晓丹,何军琴,王景尚,等.补肾活血方对肾虚血瘀薄型子宫内膜大鼠子宫内膜容受性的影响研究[J].中国全科医学, 2018,21(6):683-685.[5] Grow DR, Iromloo K. Oral contraceptives maintain a very thin endometrium before operative hysteroscopy. Fertil Steril. 2006; 85(1):204-207.[6] Kumbak B, Erden HF, Tosun S, et al. Outcome of assisted reproduction treatment in patients with endometrial thickness less than 7 mm. Reprod Biomed Online. 2009;18(1):79-84.[7] 魏丽坤,张雷,王蔼明,等.子宫内膜微创术对薄型子宫内膜容受性的影响[J].山东医药,2015,55(25):66-68. [8] 郭欢欢,孙蓬明,林元.薄型子宫内膜的临床处理进展[J].国际妇产科学杂志,2015,42(4):417-420. [9] Gilman AR, Dewar KM, Rhone SA, et al. Intrauterine Adhesions Following Miscarriage: Look and Learn. J Obstet Gynaecol Can. 2016;38(5):453-457.[10] Chen L, Zhang H, Wang Q, et al. Reproductive Outcomes in Patients With Intrauterine Adhesions Following Hysteroscopic Adhesiolysis: Experience From the Largest Women's Hospital in China. J Minim Invasive Gynecol. 2017;24(2):299-304.[11] Lebovitz O, Orvieto R. Treating patients with "thin" endometrium - an ongoing challenge. Gynecol Endocrinol. 2014;30(6):409-414.[12] 覃桂荣,熊艳敏,李柳铭,等.宫腔镜子宫内膜微创术对子宫内膜容受性影响的研究[J].实用妇产科杂志,2014,30(2):128-131.[13] 刘子霞,赵华,王兴玲,等.种植窗口期人子宫内膜组织中ER、PR及 HOXA-11的表达[J].郑州大学学报(医学版), 2014,9(2):215-218.[14] 赵诗艺,刘英,杨晓葵,等.薄型子宫内膜冻融胚胎移植周期中应用雌二醇/雌二醇地屈孕酮的疗效观察[J].实用妇产科杂志,2015, 31(4): 270-273. [15] 程龙凤,王蔼明,赵勇.粒细胞集落刺激因子与子宫内膜修复的研究进展[J].生殖医学杂志,2015,24(4):334-337. [16] 张蔚苓,常淑华.补肾活血周期治疗联合西药对宫腔粘连术后子宫内膜影响的临床研究[J].中华中医药学刊, 2016,34(5):1169-1172. [17] Fetih AN, Habib DM, Abdelaal II, et al. Adding sildenafil vaginal gel to clomiphene citrate in infertile women with prior clomiphene citrate failure due to thin endometrium: a prospective self-controlled clinical trial. Facts Views Vis Obgyn. 2017;9(1):21-27.[18] Du H, Taylor HS. Contribution of bone marrow-derived stem cells to endometrium and endometriosis. Stem Cells. 2007;25(8): 2082-2086.[19] 朱淑霞,宋治远,梁光萍,等.鼠龄与骨髓间充质干细胞生物特性的关系研究[J].中国全科医学,2005,8(6):465-467.[20] 夏良君,胡玉姣,姚兵,等.电针及骨髓间充质干细胞移植对大鼠薄型子宫内膜的影响[J].医学研究生学报,2018,31(2):129-136.[21] Lim JY, Yoon SO, Seol SY, et al. Overexpression of miR-196b and HOXA10 characterize a poor-prognosis gastric cancer subtype. World J Gastroenterol. 2013;19(41):7078-7088.[22] 许春艳,宋阳,李坤寅,等.薄型子宫内膜模型的动物选择及其造模方法改进[J].中国实验动物学报,2016,24(2):217-220.[23] 罗卓野,杨爱敏,崔娜,等.辅助生殖中薄型子宫内膜治疗的研究进展[J].中华生殖与避孕杂志,2018, 38(1):49-56.[24] Cicinelli E, Matteo M, Tinelli R, et al. Prevalence of chronic endometritis in repeated unexplained implantation failure and the IVF success rate after antibiotic therapy. Hum Reprod. 2015;30(2): 323-330.[25] Du H, Naqvi H, Taylor HS. Ischemia/reperfusion injury promotes and granulocyte-colony stimulating factor inhibits migration of bone marrow-derived stem cells to endometrium. Stem Cells Dev. 2012; 21(18): 3324-3331.[26] Jing Z, Qiong Z, Yonggang W, et al. Rat bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells improve regeneration of thin endometrium in rat. Fertil Steril. 2014;101(2):587-594. [27] 马黔红.辅助生殖技术的新进展[J].中国计划生育和妇产科, 2017,9(1): 73-76.[28] Kunicki M, ?ukaszuk K, Woclawek-Potocka I, et al. Evaluation of granulocyte colony-stimulating factor effects on treatment-resistant thin endometrium in women undergoing in vitro fertilization. Biomed Res Int. 2014;2014:913235.[29] Senturk LM, Erel CT. Thin endometrium in assisted reproductive technology. Curr Opin Obstet Gynecol. 2008;20(3):221-228.[30] Nagori CB, Panchal SY, Patel H. Endometrial regeneration using autologous adult stem cells followed by conception by in vitro fertilization in a patient of severe Asherman's syndrome. J Hum Reprod Sci. 2011; 4(1):43-48.[31] Zhao G, Cao Y, Zhu X, et al. Transplantation of collagen scaffold with autologous bone marrow mononuclear cells promotes functional endometrium reconstruction via downregulating ΔNp63 expression in Asherman's syndrome. Sci China Life Sci. 2017; 60(4):404-416.[32] 赵小萱,陈璐,姜月蓬,等.薄型子宫内膜的中西医研究进展[J].湖南中医药大学学报,2017,37(12):1425-1430.[33] 曹蕾,罗颂平,欧汝强.补肾健脾法对复发性流产患者子宫内膜容受性的干预作用[J].广州中医药大学学报,2010,27(6): 562-565.[34] Su X, Liao L, Shuai Y, et al. MiR-26a functions oppositely in osteogenic differentiation of BMSCs and ADSCs depending on distinct activation and roles of Wnt and BMP signaling pathway. Cell Death Dis. 2015;6: e1851.[35] Candini O, Spano C, Murgia A, et al. Mesenchymal progenitors aging highlights a miR-196 switch targeting HOXB7 as master regulator of proliferation and osteogenesis. Stem Cells. 2015;33(3): 939-950.[36] Szczepańska M, Wirstlein P, Luczak M, et al. Expression of HOXA-10 and HOXA-11 in the endometria of women with idiopathic infertility. Folia Histochem Cytobiol. 2011;49(1):111-118.[37] Smith CC, Taylor HS. Xenoestrogen exposure imprints expression of genes (Hoxa10) required for normal uterine development. FASEB J. 2007;21(1):239-246.[38] Popovic R, Riesbeck LE, Velu CS, et al. Regulation of mir-196b by MLL and its overexpression by MLL fusions contributes to immortalization. Blood. 2009;113(14):3314-3322.[39] 余晓芬.滋肾育胎丸对肾虚-薄型子宫内膜机制的研究[D].广州:广州中医药大学,2017.[40] 刘梅梅,丁慧,尹晓静,等.多囊卵巢综合征患者血清血管内皮生长因子、内皮抑素水平及对卵巢间质血流的影响研究[J].中国全科医学, 2017, 20(4): 448-453.[41] 张雪洛,陈艳花,夏红,等.人子宫内膜容受性研究进展[J].临床医药实践, 2016, 25(3):210-213.[42] Tapia A, Salamonsen LA, Manuelpillai U, et al. Leukemia inhibitory factor promotes human first trimester extravillous trophoblast adhesion to extracellular matrix and secretion of tissue inhibitor of metalloproteinases-1 and -2. Hum Reprod. 2008;23(8):1724-1732.[43] 马彩辉,张清学,李予,等.子宫内膜HOXA10及白血病抑制因子mRNA表达水平与体外受精-胚胎移植妊娠结局的关系[J].临床医学,2012, 32(4):1-4. |
.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)