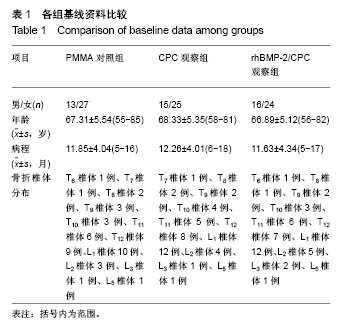
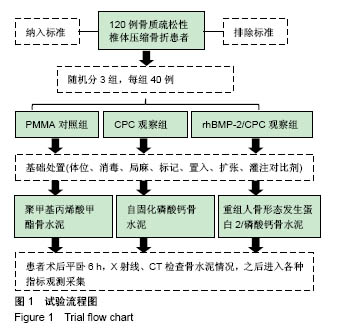
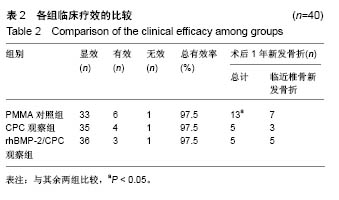
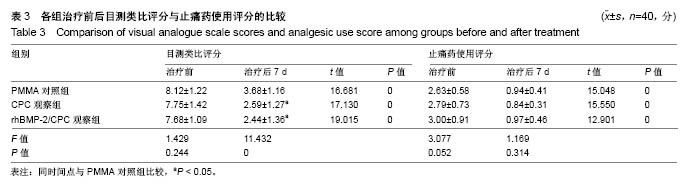
| [1] Han SL,Wan SL,Li QT,et al.Is vertebroplasty a risk factor for subsequent vertebral fracture, meta-analysis of published evidence.Osteoporos Int.2015;26(1):113-122.[2] Li YB,Zheng X,Wang R,et al.SPECT-CT versus MRI in localizing active lesions in patients with osteoporotic vertebral compression fractures.Nucl Med Commun. 2018;39(7): 610-617.[3] 陈小兵,赵洪普.骨质疏松性椎体压缩骨折不同时期保守和微创治疗的疗效比较[J].中国全科医学,2015,18(35):4320-4324.[4] 杨富国,杨波,尹飚,等.椎体成形结合抗骨质疏松治疗减少再骨折发生率[J].中国组织工程研究,2016,20(33):4905-4912.[5] 褚定坤,陶晓冰,郜顺兴,等.改良椎体成形术治疗骨质疏松性多发椎体压缩性骨折的临床效果[J].中国医药导报, 2016,13(6): 91-94.[6] He CJ,Liu GD.Comparison of the Efficacy and Safety of Bone-filling Mesh Container and Simple Percutaneous Balloon Kyphoplasty in the Treatment of Osteoporotic Vertebral Compression Fractures.Pain Physician. 2018;21(3): 259-268.[7] Xing D,Ma JX,Ma XL,et al.A meta-analysis of balloon kyphoplasty compared to percutaneous vertebroplasty for treating osteoporotic vertebral compression fractures.J Clin Neurosci.2013;20(6):795-803.[8] 李涛,张延,杨妮,等.微创经皮椎体成形术治疗脊柱转移性肿瘤的临床疗效分析[J].现代生物医学进展, 2017,17(28):5582-5584, 5488.[9] Zhang L,Li J,Yang H,et al.Histological evaluation of bone biopsy results during PVP or PKP of vertebral compression fractures.Oncol Lett.2013;5(1):135-138. [10] Boattini M,Francisco AR,Cavaco R,et al.Shock following subcutaneous injections of polymethylmethacrylate.Med Intensiva.2015;39(4):256-257.[11] Matsumoto G,Sugita Y,Kubo K,et al.Gelatin powders accelerate the resorption of calcium phosphate cement and improve healing in the alveolar ridge.J Biomater Appl. 2014; 28(9):1316-1324.[12] 赵国权.PVP治疗骨质疏松性椎体压缩骨折的研究进展[J].中国骨与关节损伤杂志,2015,30(1):106-109.[13] Martins PC,Couto TE,Gama AC.Auditory-perceptual evaluation of the degree of vocal deviation: correlation between the Visual Analogue Scale and Numerical Scale. Codas.2015;27(3):279-284.[14] Monticone M,Baiardi P,Vanti C,et al.Responsiveness of the Oswestry Disability Index and the Roland Morris Disability Questionnaire in Italian subjects with sub-acute and chronic low back pain.Eur Spine J.2012;21(1):122-129.[15] de Oliveira Ferreira N,Arthuso M,da Silva RB,et al.Validation of the Portuguese version of the quality of life questionnaire of the European foundation for osteoporosis (QUALEFFO-41) in Brazilian women with postmenopausal osteoporosis with vertebral fracture.Clin Rheumatol.2013;32(11):1585-1592.[16] 印平,马远征,马迅,等.骨质疏松性椎体压缩性骨折的治疗指南[J].中国骨质疏松杂志,2015,21(6):643-648.[17] 许正伟,贺宝荣,郝定均,等.胸腰椎骨质疏松性骨折经皮椎体成形术后骨水泥渗漏的研究进展[J].中华骨科杂志, 2016,36(17): 1142-1148.[18] 白明,银和平,吴一民,等.骨水泥复合人工骨修复材料在经皮穿刺球囊扩张椎体后凸成形术中的应用[J].中国矫形外科杂志, 2016, 24(22):2022-2026.[19] 崔冠宇,田伟,刘波,等.椎体强化后椎弓根螺钉内固定术治疗骨质疏松性胸腰椎爆裂骨折[J].中华创伤骨科杂志, 2015,17(6): 502-508.[20] Nawasrah A,Gad MM,El Zayat M.Effect of Henna Addition on the Surface Roughness and Hardness of Polymethylmethacrylate Denture Base Material: An in vitro Study.J Contemp Dent Pract.2018;19(6):732-738.[21] 梅平均,姜志强,李颖,等.聚甲基丙烯酸甲酯与自固化磷酸钙骨水泥治疗胸腰椎骨质疏松性骨折的疗效对比[J].西部医学, 2017, 29(8):1088-1091.[22] Carli AV,Bhimani S,Yang X,et al.Vancomycin-Loaded Polymethylmethacrylate Spacers Fail to Eradicate Periprosthetic Joint Infection in a Clinically Representative Mouse Model.J Bone Joint Surg Am.2018;100(11):e76. [23] Sheikh Z,Abdallah MN,Hanafi AA,et al.Mechanisms of in Vivo Degradation and Resorption of Calcium Phosphate Based Biomaterials.Materials(Basel).2015;8(11):7913-7925[24] Samavedi S,Whittington AR,Goldstein AS.Calcium phosphate ceramics in bone tissue engineering: a review of properties and their influence on cell behavior.Acta Biomater. 2013;9(9): 8037-8045. [25] 郭新辉,吕扬阳,范积平,等.磷酸钙与聚甲基丙烯酸甲酯制备复合型骨水泥的生物安全性研究[J].中国骨与关节损伤杂志, 2016, 31(5):506-510.[26] 徐爱敬,樊安未,李海冰.2种材料治疗胸腰椎骨质疏松性骨折的疗效对比研究[J].检验医学与临床,2018,15(4):561-563. [27] 张福恒,陈德喜,郎继孝,等.聚甲基丙烯酸甲酯与磷酸钙骨水泥在骨质疏松性胸腰椎压缩骨折中的临床疗效分析[J].中国骨与关节损伤杂志,2015,30(1):21-23.[28] Yuan W,He X,Zhang J,et al. Calcium Phosphate Silicate and Calcium Silicate Cements Suppressing Osteoclasts Activity Through Cytokine Regulation.J Nanosci Nanotechnol. 2018; 18(10):6799-6804.[29] Ahmad HI,Ahmad MJ,Adeel MM,et al.Positive selection drives the evolution of endocrine regulatory bone morphogenetic protein system in mammals. Oncotarget. 2018;9(26):18435-18445. [30] Yao Q,Liu Y,Sun H.Heparin-dopamine functionalized graphene foam for sustained release of bone morphogenetic protein-2.J Tissue Eng Regen Med.2018;12(6):1519-1529.[31] 陈晓敏,马霄,邵南齐,等.负载重组人骨形态发生蛋白2的纳米羟基磷灰石/丝素蛋白复合材料重建脊柱稳定性[J].中国组织工程研究,2017,21(18):2802-2807. [32] 张波,韦冰丹,甘坤宁,等.富血小板血浆联合骨髓间充质干细胞对兔股骨头坏死BMP-2/Smads通路的影响[J].中国骨质疏松杂志, 2016,22(2):131-134,227.[33] 张群慧,于锋,张浩亮,等.磷酸钙骨水泥/rhBMP-7修复兔上颌窦上壁骨折的实验研究[J].临床耳鼻咽喉头颈外科杂志, 2015, 29(21):1890-1893. [34] 厉孟,刘旭东,刘兴炎,等.明胶微球/rhBMP-2/CPC的制备及其异位成骨效应研究[J].中国骨伤,2011,24(5):411-415.[35] 金林峰,范顺武,赵兴.经皮椎体后凸成形术治疗椎体后凸成形术后相邻椎体骨折[J].中国老年学杂志,2016,36(6):1503-1504. [36] Liu BM,Li M,Yin BS,et al.Effects of Incorporating Carboxymethyl Chitosan into PMMA Bone Cement Containing Methotrexate.PLoS One.2015;10(12):e0144407.[37] 唐政杰,侯宇,张亘瑷,等.椎体后凸成形术后再发骨折的相关危险因素分析[J].中国矫形外科杂志,2015,23(2):124-131. |
.jpg)
.jpg)