| [1] Turan T,Kuran I,Sadikoglu B,et al. Eversion with four sutures: an easy, fast, and reliable technique for microvascular anastomosis. Plast Reconstr Surg.2001;107(2):463-470. [2] Cordeiro PG.Re: combined microvascular anastomosis.Ann Plast Surg. 2002;49(2):217. [3] Zeebregts CJ,Heijmen RH,van den Dungen JJ.Non-suture methods of vascular anastomosis.Br J Surg.2003;90(3):261-271. [4] Jab?onska B.End-to-end ductal anastomosis in biliary reconstruction: indications and limitations.Can J Surg. 2014;57(4):271-277. [5] 王欢,顾玉东,董震,等.大鼠断尾再植模型[J].中国手外科志, 1998, 14(2):108-109. [6] Assersen K,Sørensen J.Intravascular stenting in microvascular anastomoses.J Reconstr Microsurg.2015;31(2):113-118. [7] 范启申.断指再植新进展与展望[J].实用手外科杂志, 2006,20(3): 131-137. [8] 宋建星,郭恩覃.微型血管吻合夹与针线吻合方法的比较研究[J].中国修复重建外科杂志,2001,15(5): 312-314. [9] 宋建星,郭恩覃.机械血管吻合技术[J].中华整形外科杂志, 2002, 18(3):184-185. [10] Senthil-Kumar P,Ng-Glazier JH,Randolph MA,et al.An intraluminal stent facilitates light-activated vascular anastomosis.J Trauma Acute Care Surg.2017;83(1 Suppl 1):S43-S49. [11] 张怡五,郭云玲,刘萍,等.Nakayama血管吻合器在四肢主要血管损伤修复中的运用[J].实用骨科杂志, 2002,8(6):455. [12] Schohn T,Lequint T,Naito K,et al. A trick to improve the technique of the IntraVascular Stent (IVaS): "Clip Stent".Ann Chir Plast Esthet. 2011;56(6):512-517. [13] 曾宪森,张保贵,高雅,等.可溶性血管内支架辅助小血管缝合的实验研究[J].中华显微外科杂志,1998,21(2):129-131. [14] 郝永玉,梁向党,孙赓.血管黏合吻合用速溶支架血液相容性实验研究[J].医疗卫生装备,2012,33(4):7-9. [15] Sadeghi-Avalshahr AR,Khorsand-Ghayeni M,Nokhasteh S.Physical and mechanical characterization of PLLA interference screws produced by two stage injection molding method.Prog Biomater. 2016;5(3-4):183-191. [16] Lizundia E,Petisco S,Sarasua JR.Phase-structure and mechanical properties of isothermally melt-and cold-crystallized poly (L-lactide).J Mech Behav Biomed Mater.2013;17:242-251. [17] Agrawal CM,Haas KF,Leopold DA,et al.Evaluation of poly(L-lactic acid) as a material for intravascular polymeric stents.Biomaterials. 1992;13:176-182. [18] 肖越勇,张金山.崔福斋,等.生物可降解性血管内支架的制备及其性能研究[J].中华放射学杂,2003,37(11):1136-1142. [19] Tamai H,Igaki K,Kyo E,et al.Initial and 6-month results of biodegradable poly-l-lactic acid coronary stents in humans. Circulation. 2000;102:399-404. [20] Nakano Y,Hori Y,Sato A,et al.Evaluation of a poly(L-lactic acid) stent for sutureless vascular anastomosis.Ann Vasc Surg. 2009; 23(2):231-238.. [21] Bünger CM,Grabow N,Sternberg K,et al.Iliac anastomotic stenting with a biodegradable poly-L-lactide stent: a preliminary study after 1 and 6 weeks.J Endovasc Ther.2006;13(4):539-548. [22] Khorgami Z,Shoar SAminian A,et al. Stent-and-glue sutureless vascular anastomosis.Med Hypotheses. 2011;77(1):94-96. [23] 张金山.现代腹部介入放射学[M].北京:科学出版社,2000:239-241. [24] Grabow N,Schlun M,Sternberg K,et al.Mechanical properties of laser cut poly(L-lactide) micro-specimens: implications for stent design, manufacture, and sterilization. J Biomech Eng. 2005;127: 25-31. [25] 粟爽,李万甫.三种不同材料血管内支架的生物相容性[J].中国组织工程研究与临床康复,2008,12(17):3293-3232. [26] 姚军燕,秦能,杨青芳.生物医用高分子材料聚乳酸的成型方法研究[J].塑料工业,2004,32(10):6-8. [27] Younes B,Fotheringham A,El-Dessouky HM,et al.Factorial optimization of the effects of melt-spinning conditions on as-spun aliphatic-aromatic copolyester fibers I. Spin draw ratio,overall orientation and drawability.Int J Polym Mater.2011;60:316-339. [28] Maria P,Sung-Woo C,Mikael S.The effect of process variables on the properties of melt-spun poly(lactic acid) fibres for potential use as scaffold matrix materials.J Mater Sci.2013;48:3055-3066. [29] Kim MS,Kim JC,Kim YH.Effects of take-up speed on the structure and properties of melt-spun poly(L-lactic acid) fibers.Polym Adv Technol. 2008;19:748-755. [30] Moskovtz MJ,Browne E,Kononov A.Microvascular anastomosis ulilizing new intravascular stents.Ann Plast Sury.1994;32(6): 44-49. [31] Miyamoto S,Sakuraba M,Asano T,et al.Optimal technique or microvascular anastomosis of very small vessels: Comparative study of three techniques in a rat superficial inferior epigastric arterial flap model.J Plast Reconstr Aesthet Surg. 2010;63(7): 1196-1201. [32] Bauer F,Fichter AM,Loeffelbein DJ,et al.Microvascular anastomosis using modified micro-stents: a pilot in vivo study.J Craniomaxillofac Surg.2015;43(2):204-207. [33] Narushima M,Koshima I,Mihara M,et al.Intravascular stenting (IVaS) for safe and precise supermicrosurgery.Ann Plast Surg. 2008;60(1):41-44. [34] Bossut C,Barbier O.Exploration of the intravascular stenting method for sub 1-mm vessels. J Reconstr Microsurg. 2011; 27(8):461-468. [35] Narushima M,Mihara M,Koshima I,et al.Intravascular stenting (IVaS) method for fingertip replantation.Ann Plast Surg. 2009; 62(1):38-41. [36] 高洪,何鹤皋,曾炳芳,等.血管吻合技术与微栓子形成关系的实验研究[J].上海第二医科大学学报,2002,22(6):509-510. |
.jpg)

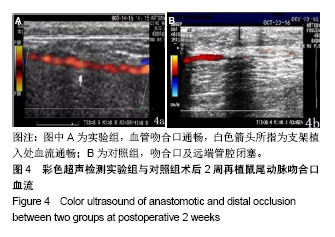
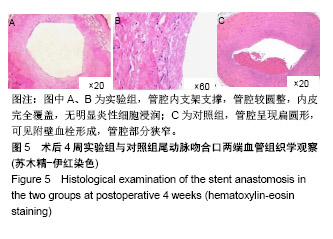



.jpg)