中国组织工程研究 ›› 2019, Vol. 23 ›› Issue (27): 4315-4320.doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-4344.1378
• 肌肉肌腱韧带组织构建 tissue construction of the muscle, tendon and ligament • 上一篇 下一篇
核心区力量训练和电针干预对大学生腰肌劳损有协同治疗作用
蒋满意1,许思毛2,宾恩明3
- (1浙江经贸职业技术学院,浙江省杭州市 310018;2广西师范大学体育学院,广西壮族自治区桂林市 541004;3桂林电子科技大学信息科技学院,广西壮族自治区桂林市 541004)
Synergistic effect of core strength training and electropuncture for treating lumbar muscle strain in college students
Jiang Manyi1, Xu Simao2, Bin Enming3
- (1Zhejiang Vocational and Technical College of Economics and Trade, Hangzhou 310018, Zhejiang Province, China; 2College of Physical Education, Guangxi Normal University, Guilin 541004, Guangxi Zhuang Autonomous Region, China; 3College of Information Science and Technology, Guilin University of Electronic Science and Technology, Guilin 541004, Guangxi Zhuang Autonomous Region, China)
摘要:
文章快速阅读:
.jpg)
文题释义:
核心区:对于核心区的概念虽有不同的描述方法,国际上接受最多的一种概念是:核心区被描述为一个肌肉区域,即前方是腹部肌群,后方是脊柱后部肌群,上方是膈肌,下方是盆底肌及髋部周围肌群。
腰肌劳损:又称功能性腰痛、慢性下腰损伤、腰臀肌筋膜炎等,实为腰部肌肉及其附着点筋膜或骨膜的慢性损伤性炎症,是腰痛的常见原因之一,主要症状是腰或腰骶部胀痛、酸痛,反复发作,疼痛可随气候变化或劳累程度而变化,如日间劳累加重,休息后可减轻时轻时重,为临床常见病,多发病,发病因素较多。其日积月累,可使肌纤维变性,甚而少量撕裂,形成瘢痕、纤维索条或粘连,遗留长期慢性腰背痛。
.jpg)
文题释义:
核心区:对于核心区的概念虽有不同的描述方法,国际上接受最多的一种概念是:核心区被描述为一个肌肉区域,即前方是腹部肌群,后方是脊柱后部肌群,上方是膈肌,下方是盆底肌及髋部周围肌群。
腰肌劳损:又称功能性腰痛、慢性下腰损伤、腰臀肌筋膜炎等,实为腰部肌肉及其附着点筋膜或骨膜的慢性损伤性炎症,是腰痛的常见原因之一,主要症状是腰或腰骶部胀痛、酸痛,反复发作,疼痛可随气候变化或劳累程度而变化,如日间劳累加重,休息后可减轻时轻时重,为临床常见病,多发病,发病因素较多。其日积月累,可使肌纤维变性,甚而少量撕裂,形成瘢痕、纤维索条或粘连,遗留长期慢性腰背痛。
摘要
背景:腰肌劳损病因不明,属于非特异性腰痛,其不仅影响生活与工作,也造成沉重医疗负担与间接社会成本。
目的:探讨核心区力量训练与电针对大学生腰肌劳损的干预作用。
方法:研究方案的实施符合广西师范大学对研究的相关伦理要求。选择 80名大学生腰肌劳损志愿者,所有受试者对试验方案均知情同意并签署了知情同意书。随机将80名受试者分为对照组、电针组、核心区力量组、电针核心区力量组。对照组不采取任何干预措施,电针组采用电针干预,核心区力量组采用核心区力量训练干预,电针核心区力量组采用电针和核心区力量的联合干预。干预时间为7周,记录治疗前、治疗后的目测类比评分与疼痛症状积分,并追踪4 个月观察其复发率。
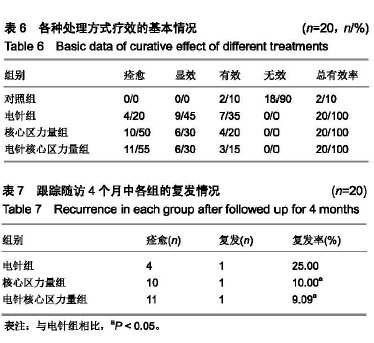
结果与结论:①与干预前相比,电针组、核心区力量组、电针核心区力量组的目测类比评分、疼痛症状综合评分均显著下降(P < 0.05);②干预后电针组、核心区力量组、电针核心区力量组的目测类比评分及疼痛症状综合评分均显著小于对照组,其中电针核心区力量组疼痛症状综合评分又显著小于电针组、核心区力量组(P < 0.05);③核心区力量组、电针核心区力量组的痊愈率高于电针组,核心区力量组、电针核心区力量组的疗效优于电针组(P < 0.05);④核心区力量组、电针核心区力量组的复发率低于电针组(P < 0.05);⑤结果说明,电针与核心区力量训练对大学生腰肌劳损均有治疗作用,但核心区力量训练的疗效优于电针,复发率也低于电针;电针联合核心区力量训练对大学生腰肌劳损具有协同治疗作用。
背景:腰肌劳损病因不明,属于非特异性腰痛,其不仅影响生活与工作,也造成沉重医疗负担与间接社会成本。
目的:探讨核心区力量训练与电针对大学生腰肌劳损的干预作用。
方法:研究方案的实施符合广西师范大学对研究的相关伦理要求。选择 80名大学生腰肌劳损志愿者,所有受试者对试验方案均知情同意并签署了知情同意书。随机将80名受试者分为对照组、电针组、核心区力量组、电针核心区力量组。对照组不采取任何干预措施,电针组采用电针干预,核心区力量组采用核心区力量训练干预,电针核心区力量组采用电针和核心区力量的联合干预。干预时间为7周,记录治疗前、治疗后的目测类比评分与疼痛症状积分,并追踪4 个月观察其复发率。
结果与结论:①与干预前相比,电针组、核心区力量组、电针核心区力量组的目测类比评分、疼痛症状综合评分均显著下降(P < 0.05);②干预后电针组、核心区力量组、电针核心区力量组的目测类比评分及疼痛症状综合评分均显著小于对照组,其中电针核心区力量组疼痛症状综合评分又显著小于电针组、核心区力量组(P < 0.05);③核心区力量组、电针核心区力量组的痊愈率高于电针组,核心区力量组、电针核心区力量组的疗效优于电针组(P < 0.05);④核心区力量组、电针核心区力量组的复发率低于电针组(P < 0.05);⑤结果说明,电针与核心区力量训练对大学生腰肌劳损均有治疗作用,但核心区力量训练的疗效优于电针,复发率也低于电针;电针联合核心区力量训练对大学生腰肌劳损具有协同治疗作用。
中图分类号:


.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg) #br#
文题释义:#br#
核心区:对于核心区的概念虽有不同的描述方法,国际上接受最多的一种概念是:核心区被描述为一个肌肉区域,即前方是腹部肌群,后方是脊柱后部肌群,上方是膈肌,下方是盆底肌及髋部周围肌群。#br#
腰肌劳损:又称功能性腰痛、慢性下腰损伤、腰臀肌筋膜炎等,实为腰部肌肉及其附着点筋膜或骨膜的慢性损伤性炎症,是腰痛的常见原因之一,主要症状是腰或腰骶部胀痛、酸痛,反复发作,疼痛可随气候变化或劳累程度而变化,如日间劳累加重,休息后可减轻时轻时重,为临床常见病,多发病,发病因素较多。其日积月累,可使肌纤维变性,甚而少量撕裂,形成瘢痕、纤维索条或粘连,遗留长期慢性腰背痛。
#br#
文题释义:#br#
核心区:对于核心区的概念虽有不同的描述方法,国际上接受最多的一种概念是:核心区被描述为一个肌肉区域,即前方是腹部肌群,后方是脊柱后部肌群,上方是膈肌,下方是盆底肌及髋部周围肌群。#br#
腰肌劳损:又称功能性腰痛、慢性下腰损伤、腰臀肌筋膜炎等,实为腰部肌肉及其附着点筋膜或骨膜的慢性损伤性炎症,是腰痛的常见原因之一,主要症状是腰或腰骶部胀痛、酸痛,反复发作,疼痛可随气候变化或劳累程度而变化,如日间劳累加重,休息后可减轻时轻时重,为临床常见病,多发病,发病因素较多。其日积月累,可使肌纤维变性,甚而少量撕裂,形成瘢痕、纤维索条或粘连,遗留长期慢性腰背痛。