中国组织工程研究 ›› 2019, Vol. 23 ›› Issue (18): 2822-2826.doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-4344.1194
• 组织工程骨及软骨材料 tissue-engineered bone and cartilage materials • 上一篇 下一篇
不同材料赋值方法下踝关节三维有限元模型的应力及位移变化
骆 健1,王立华1,王 涛2,温 辉2
- 1昆明理工大学机电工程学院,云南省昆明市 650500;2昆明市中医医院呈贡医院,云南省昆明市 650500
Changes of stress and displacement of three-dimensional finite element model of ankle joint using different material assignment methods
Luo Jian1, Wang Lihua1, Wang Tao2, Wen Hui2
- 1School of Mechanic and Electronic Engineering, Kunming University of Science and Technology, Kunming 650500, Yunnan Province, China; 2Chenggong Branch of Kunming Municipal Hospital of Traditional Chinese Medicine, Kunming 650500, Yunnan Province, China
摘要:
文章快速阅读:
.jpg)
文题释义:
灰度值赋值法:通过参考以往文献中的经验公式建立灰度值、密度、弹性模量之间的关系进行骨骼材料属性的赋予,材料赋值方式比较简单、自动化程度较高并且满足个体多样性有限元分析的需求。由于CT图像质量和数据来源等因素决定着材料赋值的准确性,这也导致了灰度值赋值法的局限性。但是,近年来随着加工制造业的飞速发展和CT技术越来越成熟,能够很好的确保数据的准确性和图像质量的精度,这也打破了以往灰度值赋值法的一些局限性。
生物力学:在骨头相关的力学问题研究上主要涉及到生物固体力学与运动生物力学,都是运用基本的力学原理和方法研究各组织之间相关的力学问题。
背景:人体三维有限元仿真分析由于其自身的优越性,被广泛应用于人体生物力学研究,但对骨骼材料属性的赋值并未有确切的定论。
目的:对踝关节进行力学有限元分析,探索出更符合临床实际情况的材料属性赋值方法。
方法:对1例正常男性志愿者踝关节CT断层数据进行三维重建并进行曲面拟合,然后进行有限元网格划分,分别运用均一赋值法与灰度值赋值法2种方式对骨骼进行材料属性的赋予,模拟双腿站立、单足站立、正常步态、上楼梯、下楼梯等5种工况下踝关节的生物力学响应。
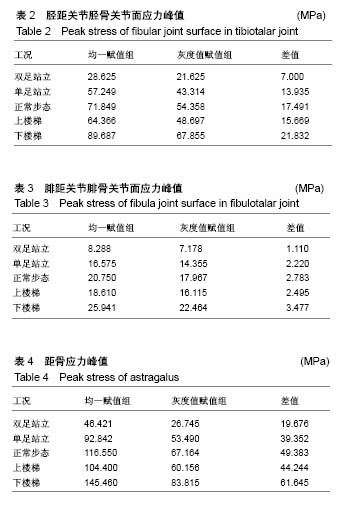
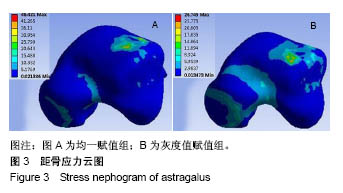
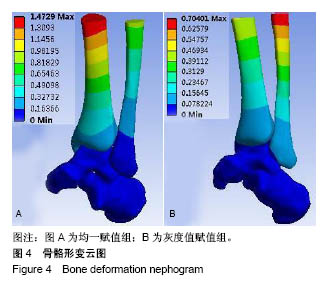
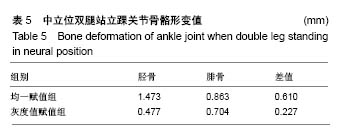
结果与结论:①在5种工况下胫骨关节面、距骨体的应力峰值均一赋值组明显高于灰度值赋值组,2种赋值方法下腓骨关节面上的应力峰值相差不大;②均一赋值组在距骨颈处应力分布较为集中且分布区域面积较小,灰度值赋值组在距骨颈处应力分布较为均匀且分布区域面积覆盖整个距骨颈处;③均一赋值组形变量胫骨大于腓骨,灰度值赋值组腓骨大于胫骨;④均一赋值组胫骨与腓骨形变量的差值大于灰度值赋值组;⑤说明在对踝关节进行生物力学有限元分析中,灰度值赋值法更符合临床实际情况,具有更高的准确性且能在一定程度上解决由于个体差异性带来的建模误差。
中图分类号:
R445
.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)