| [1] Hochrein A, Zinser W, Spahn G, et al. What parameters affect knee function in patients with untreated cartilage defects: baseline data from the German Cartilage Registry. Int Orthop. 2018. doi: 10. 1007/s00264-018-4125-2. [2] Jones KJ, Mosich GM, Williams RJ. Fresh precut osteochondral allograft core transplantation for the treatment of femoral cartilage defects. Arthrosc Tech. 2018;7(8):e791-e795. [3] Kreuz PC, Kalkreuth RH, Niemeyer P, et al. Treatment of a focal articular cartilage defect of the talus with polymer-based autologous chondrocyte implantation: a 12-year follow-up period. J Foot Ankle Surg. 2017;56(4):45-46. [4] Lee BH, Park JN, Lee EJ, et al. Therapeutic efficacy of spherical aggregated human bone marrow-derived mesenchymal stem cells cultured for osteochondral defects of rabbit knee joints. Am J Sports Med. 2018; 46(9):2242-2252. [5] Zhao Z, Zhou X, Guan J, et al. Co-implantation of bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells and chondrocytes increase the viability of chondrocytes in rat osteo-chondral defects. Oncol Lett. 2018;15(5):7021-7027. [6] Böck T, Schill V, Krähnke M, et al. TGF-β1-modified hyaluronic acid/poly(glycidol) hydrogels for chondrogenic differentiation of human mesenchymal stromal cells. Macromol Biosci. 2018:e1700390. [7] Choukroun J, Diss A, Simonpieri A, et al. Platelet-rich fibrin: a second generation platelet concentrate. Part Ⅴ: histologic evaluations of PRF effects on bone allograft maturation in sinus lift. Oral Surg Oral Med Oral Pathol Oral Radiol Endod. 2006;101(3)299-303. [8] Mosesson MW, Siebenlist KR, Meh DA. The structure and biological features of fibrinogen and fibrin. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 2001;936:11-30. [9] Honda H, Tamai N, Naka N, et al. Bone tissue engineering with bone marrowderived stromal cells integrated with concentrasted growth factor in Rattus norvegicus calvaria defect model. J Artificial Organs. 2013;16(3):305-315. [10] Lohan A, Marzahn U, El SK, et al. Osteochondral articular defect repair using auricle-derived autologous chondrocytes in a rabbit model. Ann Anat. 2014;196(5):317-326. [11] Zhou Q, Wei B, Liu S, et al. Cartilage matrix changes in contralateral mobile knees in a rabbit model of osteoarthritis induced by immobilization. Bmc Musculoskeletal Disorders. 2015;16(1):224. [12] Yamaguchi S, Aoyama T, Ito A, et al. The effect of exercise on the early stages of mesenchymal stromal cell-induced cartilage repair in a rat osteochondral defect model. PLoS One. 2016;11(3):e0151580. [13] Zhang F, Liu D, Wang G, et al. Experimental research of articular cartilage defect repair using micro-fracture and insulin-like growth factor 1 in rabbits. Zhongguo Xiu Fu Chong Jian Wai Ke Za Zhi. 2014;28(5):591-596.[14] Yeo Y, Geng W, Ito T, et al. Photocrosslinkable hydrogel for myocyte cell culture and injection. Journal of biomedical matericals research. J Biomed Mater Res B Appl Biomater. 2007;81(2):312-322. [15] Shinojima N, Hossain A, Takezaki T, et al. TGF-β mediates homing of bone marrow-derived human mesenchymal stem cells to glioma stem cells. Cancer Res. 2013;73(7): 2333-2344. [16] Tang X, Chen F, Lin Q, et al. Bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells repair the hippocampal neurons and increase the expression of IGF-1 after cardiac arrest in rats. Exp Ther Med. 2017;14(5):4312-4320. [17] Ju X, Xue D, Wang T, et al. Catalpol promotes the survival and vegf secretion of bone marrow-derived stem cells and their role in myocardial repair after myocardial infarction in rats. Cardiovasc Toxicol. 2018. doi: 10. 1007/s12012-018-9460-4. [18] 张文丽,李淑慧,陈诚,等.富血小板纤维蛋白复合自体骨髓间充质干细胞修复兔牙槽骨缺损的研究[J].口腔医学研究, 2015,31(4): 336-339.[19] 杨勇,杨涛,刘斌,等.自体ADSCs复合富血小板纤维蛋白修复家兔耳软骨缺损的实验研究[J].现代生物医学进展,2013,13(12): 2210-2214.[20] Bahmanpour S, Ghasemi M, Sadeghi-Naini M, et al. Effects of platelet-rich plasma & platelet-rich fibrin with and without stromal cell-derived factor-1 on repairing full-thickness cartilage defects in knees of rabbits. Iran J Med Sci. 2016; 41(6):507-517. [21] Permuy M, Guede D, Lópezpeña M, et al. Effects of glucosamine and risedronate alone or in combination in an experimental rabbit model of osteoarthritis. BMC Vet Res. 2014;10(1):97. [22] Permuy M, Guede D, López-Peña M, et al. Effects of diacerein on cartilage and subchondral bone in early stages of osteoarthritis in a rabbit model. BMC Vet Res. 2015;11(1): 1-11. [23] SM Pagura, Thomas SG, Woodhouse LJ, et al. Circulating and synovial levels of IGF-I, cytokines, physical function and anthropometry differ in women awaiting total knee arthroplasty when compared to men. J Orthop Res. 2005; 23(2):397-405. [24] Nesic D, Whiteside R, Brittberg M, et al. Cartilage tissue engineering for degenerative joint disease.Adv Drug Deliv Rev. 2006;58(2):300-322. [25] Ni GX. Development and Prevention of Running-Related Osteoarthritis. Curr Sports Med Rep. 2016;15(5):342. [26] Felson DT. Clinical practice. Osteoarthritis of the knee. N Engl J Med. 2006;354(8):841-848. [27] Critchley SE, Eswaramoorthy R, Kelly DJ. Low-oxygen conditions promote synergistic increases in chondrogenesis during co-culture of human osteoarthritic stem cells and chondrocytes.J Tissue Eng Regen Med. 2018;12(4): 1074-1084. [28] Chen MJ, Whiteley JP, Please CP, et al. Inducing chondrogenesis inMSC/chondrocyte co-cultures using exogenous TGF-β: a mathematical model. J Theor Biol. 2018;439:1-13. [29] Thorstensson CA, Garellick G, Rystedt H, et al. Better management of patients with osteoarthritis: development and nationwide implementation of an evidence-based supported osteoarthritis self-management programme. Musculoskeletal Care. 2015;13(2):67-75. [30] Jing L, Zhang J, Leng H, et al. Repair of articular cartilage defects in the knee with autologous iliac crest cartilage in a rabbit model. Knee Surg Sports Traumatol Arthrosc. 2015; 23(4):1119-1127. |
.jpg) 文题释义:
富血小板纤维蛋白:是一种被纤维蛋白紧密包裹的血小板聚合物,内部疏松多孔,并且含有多种可以促进软骨细胞分化增殖的细胞生长因子,如:肿瘤生长因子β1、胰岛素类生长因子1、血管内皮生长因子。目前研究发现,这些细胞因子是促进骨髓间充质干细胞向软骨分化的重要因素,同时其可以加速软骨细胞的增殖、生长。
陈旧性负重位软骨缺损:膝关节内侧副韧带、前交叉韧带和内侧半月板切除改变膝关节应力,同时在股骨内侧髁关节面钻孔破坏关节软骨,建立的创伤性关节炎承重面关节软骨缺损模型可在较短时间内形成作为研究膝关节损伤致骨关节炎的实验模型。
文题释义:
富血小板纤维蛋白:是一种被纤维蛋白紧密包裹的血小板聚合物,内部疏松多孔,并且含有多种可以促进软骨细胞分化增殖的细胞生长因子,如:肿瘤生长因子β1、胰岛素类生长因子1、血管内皮生长因子。目前研究发现,这些细胞因子是促进骨髓间充质干细胞向软骨分化的重要因素,同时其可以加速软骨细胞的增殖、生长。
陈旧性负重位软骨缺损:膝关节内侧副韧带、前交叉韧带和内侧半月板切除改变膝关节应力,同时在股骨内侧髁关节面钻孔破坏关节软骨,建立的创伤性关节炎承重面关节软骨缺损模型可在较短时间内形成作为研究膝关节损伤致骨关节炎的实验模型。.jpg) 文题释义:
富血小板纤维蛋白:是一种被纤维蛋白紧密包裹的血小板聚合物,内部疏松多孔,并且含有多种可以促进软骨细胞分化增殖的细胞生长因子,如:肿瘤生长因子β1、胰岛素类生长因子1、血管内皮生长因子。目前研究发现,这些细胞因子是促进骨髓间充质干细胞向软骨分化的重要因素,同时其可以加速软骨细胞的增殖、生长。
陈旧性负重位软骨缺损:膝关节内侧副韧带、前交叉韧带和内侧半月板切除改变膝关节应力,同时在股骨内侧髁关节面钻孔破坏关节软骨,建立的创伤性关节炎承重面关节软骨缺损模型可在较短时间内形成作为研究膝关节损伤致骨关节炎的实验模型。
文题释义:
富血小板纤维蛋白:是一种被纤维蛋白紧密包裹的血小板聚合物,内部疏松多孔,并且含有多种可以促进软骨细胞分化增殖的细胞生长因子,如:肿瘤生长因子β1、胰岛素类生长因子1、血管内皮生长因子。目前研究发现,这些细胞因子是促进骨髓间充质干细胞向软骨分化的重要因素,同时其可以加速软骨细胞的增殖、生长。
陈旧性负重位软骨缺损:膝关节内侧副韧带、前交叉韧带和内侧半月板切除改变膝关节应力,同时在股骨内侧髁关节面钻孔破坏关节软骨,建立的创伤性关节炎承重面关节软骨缺损模型可在较短时间内形成作为研究膝关节损伤致骨关节炎的实验模型。
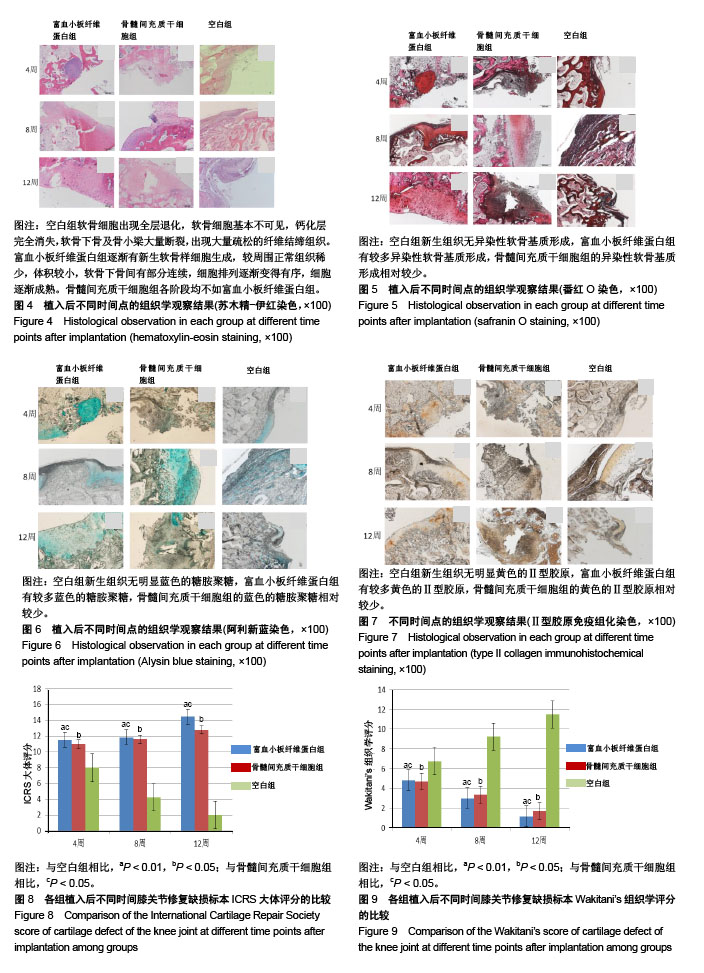
.jpg) 文题释义:
富血小板纤维蛋白:是一种被纤维蛋白紧密包裹的血小板聚合物,内部疏松多孔,并且含有多种可以促进软骨细胞分化增殖的细胞生长因子,如:肿瘤生长因子β1、胰岛素类生长因子1、血管内皮生长因子。目前研究发现,这些细胞因子是促进骨髓间充质干细胞向软骨分化的重要因素,同时其可以加速软骨细胞的增殖、生长。
陈旧性负重位软骨缺损:膝关节内侧副韧带、前交叉韧带和内侧半月板切除改变膝关节应力,同时在股骨内侧髁关节面钻孔破坏关节软骨,建立的创伤性关节炎承重面关节软骨缺损模型可在较短时间内形成作为研究膝关节损伤致骨关节炎的实验模型。
文题释义:
富血小板纤维蛋白:是一种被纤维蛋白紧密包裹的血小板聚合物,内部疏松多孔,并且含有多种可以促进软骨细胞分化增殖的细胞生长因子,如:肿瘤生长因子β1、胰岛素类生长因子1、血管内皮生长因子。目前研究发现,这些细胞因子是促进骨髓间充质干细胞向软骨分化的重要因素,同时其可以加速软骨细胞的增殖、生长。
陈旧性负重位软骨缺损:膝关节内侧副韧带、前交叉韧带和内侧半月板切除改变膝关节应力,同时在股骨内侧髁关节面钻孔破坏关节软骨,建立的创伤性关节炎承重面关节软骨缺损模型可在较短时间内形成作为研究膝关节损伤致骨关节炎的实验模型。