| [1] Neo M, Fujibayashi S, Miyata M, et al. Vertebral artery injury during cervical spine surgery: a survey of more than 5600 operations. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2008;33(7):779-785. [2] Lunardini DJ, Eskander MS, Even JL, et al. Vertebral artery injuries in cervical spine surgery. Spine J. 2014;14(8): 1520-1525. [3] Wright NM. Posterior C2 fixation using bilateral, crossing C2 laminar screws: case series and technical note. J Spinal Disord Tech. 2004;17(2):158-162.[4] Ma W, Feng L, Xu R, et al. Clinical application of C2 laminar screw technique. Eur Spine J. 2010;19(8):1312-1317. [5] Vanek P, Homolkova H, Benes V, et al. Occipitocervical stabilization using bilateral laminar C2 screws in children with mucopolysaccharidosis IVA. Eur Spine J. 2015;24(12): 2756-2762. [6] Sinha S, Jagetia A, Aher RB, et al. Occiput/C1-C2 fixations using intra-laminar screw of axis - A long-term follow-up. Br J Neurosurg. 2015;29(2):260-264. [7] Dorward IG, Wright NM. Seven years of experience with C2 translaminar screw fixation: clinical series and review of the literature. Neurosurgery. 2011;68(6):1491-1499; discussion 1499.[8] Bhatnagar R, Yu WD, Bergin PF, et al. The anatomic suitability of the C2 vertebra for intralaminar and pedicular fixation: a computed tomography study. Spine J. 2010;10(10): 896-899.[9] 马维虎,刘观燚,徐荣明.枢椎经椎板螺钉固定的研究进展[J].中华外科杂志,2008,46(19):1511-1513.[10] Kim S, Kwak DS, Kim IB. Morphometric analysis and classification of the cross-sectional shape of the C2 lamina. Biomed Res Int. 2017;2017:7276946. [11] Yue B, Kwak DS, Kim MK, et al. Morphometric trajectory analysis for the C2 crossing laminar screw technique. Eur Spine J. 2010;19(5):828-832. [12] Ma XY, Yin QS, Wu ZH, et al. C2 anatomy and dimensions relative to translaminar screw placement in an Asian population. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2010;35(6):704-708.[13] Chytas D, Korres DS, Babis GC, et al. Anatomical considerations of C2 lamina for the placement of translaminar screw: a review of the literature. Eur J Orthop Surg Traumatol. 2017. doi: 10.1007/s00590-017-2072-z. [14] 黄师,赵鑫,侯铁胜,等.枢椎交叉椎板螺钉置钉的应用解剖[J].解剖学杂志,2009,32(1):110-111.[15] 王建,孙玛骥,张星晨,等.枢椎椎板螺钉出针点的解剖学测量分析[J].医药卫生(文摘版),2016,1:277.[16] 陈科,陈仲, 靳安民,等.3种不同枕-寰-枢固定技术的生物力学比较[J].广东医学,2011,32(21):2764-2767.[17] 黄师,侯铁胜,赵鑫,等.C1侧块C2椎板螺钉固定与C1-2关节螺钉固定的生物力学性能比较[J].中华实验外科杂志, 2008,25(12): 1646-1648.[18] 王向阳,徐华梓,池永龙,等.改良枢椎椎板螺钉置钉方法的临床应用[J].脊柱外科杂志,2016,14(4):216-219.[19] Engler JA, Smith ML. Use of intraoperative fluoroscopy for the safe placement of C2 laminar screws: technical note. Eur Spine J. 2015;24(12):2771-2775.[20] Kaneyama S, Sugawara T, Sumi M, et al. A novel screw guiding method with a screw guide template system for posterior C-2 fixation: clinical article. J Neurosurg Spine. 2014;21(2):231-238. [21] 胡勇,袁振山,谢辉,等.快速成型导向模板技术在枢椎椎板交叉螺钉置钉中的应用[J].中华骨科杂志,2013,33(6):640-648.[22] Geck MJ, Truumees E, Hawthorne D, et al. Feasibility of rigid upper cervical instrumentation in children: tomographic analysis of children aged 2-6. J Spinal Disord Tech. 2014; 27(3):E110-117. [23] Savage JG, Fulkerson DH, Sen AN, et al. Fixation with C-2 laminar screws in occipitocervical or C1-2 constructs in children 5 years of age or younger: a series of 18 patients. J Neurosurg Pediatr. 2014;14(1):87-93. [24] Chamoun RB, Relyea KM, Johnson KK, et al. Use of axial and subaxial translaminar screw fixation in the management of upper cervical spinal instability in a series of 7 children. Neurosurgery. 2009;64(4):734-739; discussion 739. [25] Vanek P, Homolkova H, Benes V, et al. Occipitocervical stabilization using bilateral laminar C2 screws in children with mucopolysaccharidosis IVA. Eur Spine J. 2015;24(12): 2756-2762. [26] Cristante AF, Torelli AG, Kohlmann RB, et al. Feasibility of intralaminar, lateral mass, or pedicle axis vertebra screws in children under 10 years of age: a tomographic study. Neurosurgery. 2012;70(4):835-838; discussion 838-839. [27] Hwang SW, Gressot LV, Chern JJ, et al. Complications of occipital screw placement for occipitocervical fusion in children. J Neurosurg Pediatr. 2012;9(6):586-593. [28] Klimo P Jr, Astur N, Gabrick K, et al. Occipitocervical fusion using a contoured rod and wire construct in children: a reappraisal of a vintage technique. J Neurosurg Pediatr. 2013;11(2):160-169. [29] Singh B, Cree A. Laminar screw fixation of the axis in the pediatric population: a series of eight patients. Spine J. 2015 1;15(2):e17-25.[30] Xia DD, Lin SL, Chen W, et al. Computed tomography morphometric analysis of C2 translaminar screw fixation of Wright's technique and a modified technique in the pediatric cervical spine. Eur Spine J. 2014;23(3):606-612. |
.jpg)
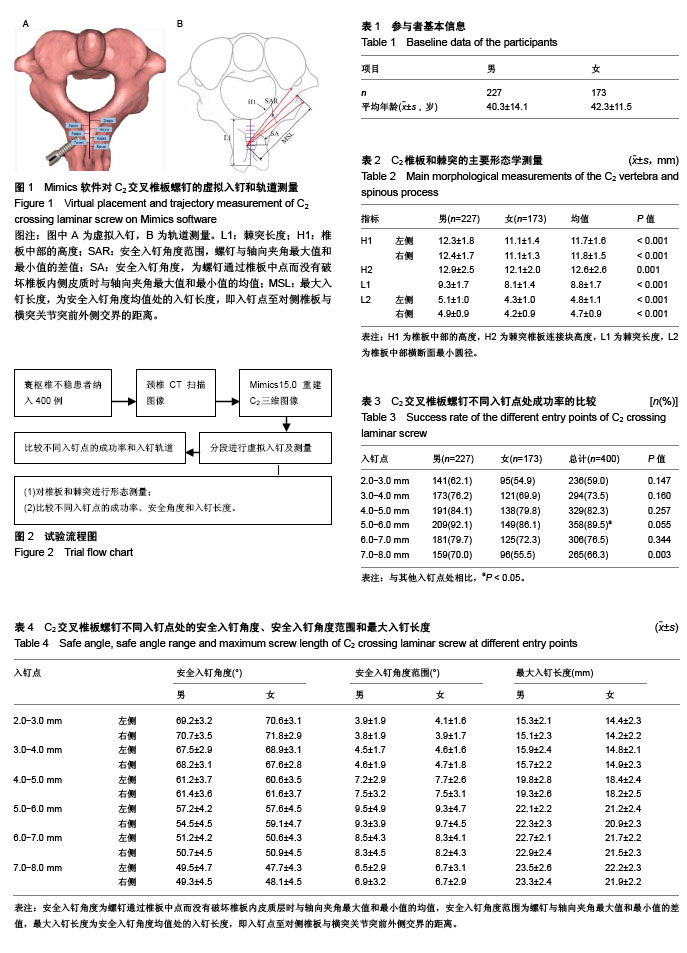
.jpg)