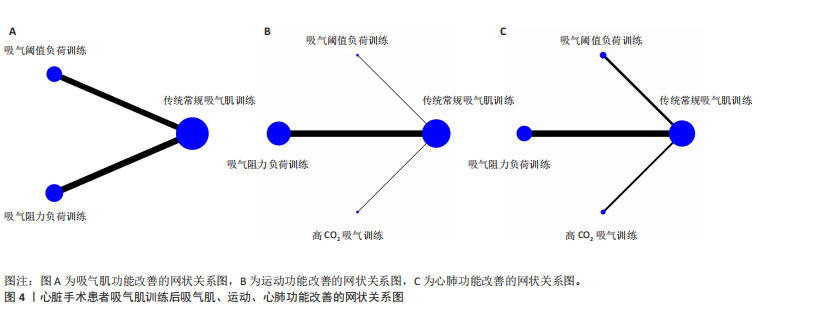
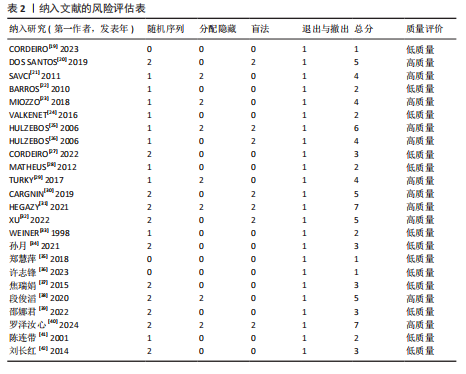
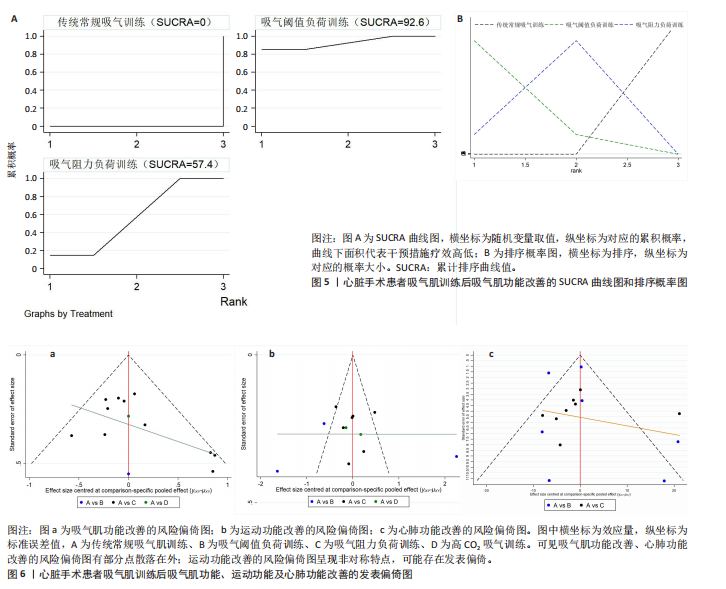
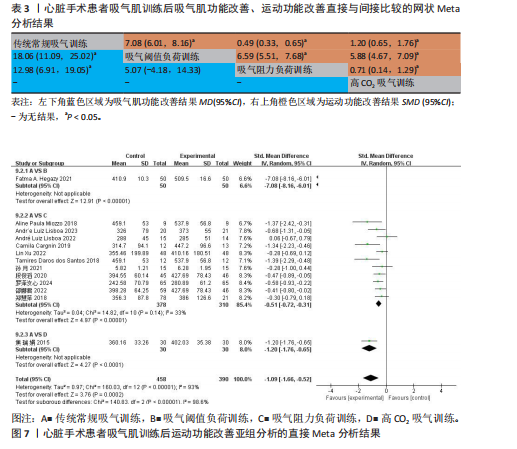
[1] ROTH GA, MENSAH GA, JOHNSON CO, et al. Global Burden of Cardiovascular Diseases and Risk Factors, 1990–2019: Update From the GBD 2019 Study. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2020;76(25):2982-3021.
[2] World Health Organization (WHO). Cardiovascular Disease [Internet]. 2018. [cited 2019 Mar. 1]. Available from:http://www.who.int/en/ news-room/fact-sheets/detail/cardiovascular-diseases-(cvds).
[3] PARK JW, OH JC, LEE JW, et al. The effect of 5Hz high-frequency rTMS over contralesional pharyngeal motor cortex in post-stroke oropharyngeal dysphagia: a randomized controlled study. Neurogastroenterol Motil. 2013;25(4): 250-324.
[4] LAOHACHAI K, WINLAW D, SELVADURAI H, et al. Inspiratory muscle training is associated with improved inspiratory muscle strength, resting cardiac output, and the ventilatory efficiency of exercise in patients with a fontan circulation. J Am Heart Assoc. 2017;6(8): e005750
[5] NISSINEN J, BIANCARI F, WISTBACKA JO, et al. Safe time limits of aortic cross-clamping and cardiopulmonary bypass in adult cardiac surgery. Perfusion. 2009;24(5):297-305.
[6] GUIZILINI S, GOMES WJ, FARESIN SM, et al. Evaluation of pulmonary function in patients following on and off-pump coronary artery bypass grafting. Braz J Cardiovasc Surg. 2005;20(3). doi: 10.1590/s1678-97412005000300013.
[7] MISKOVIC A, LUMB AB. Postoperative pulmonary complications. Br J Anaesth. 2017;118(3):317-334.
[8] 冯梦月. 吸气肌训练对肺移植患者肺功能、膈肌功能和运动能力的影响[D]. 南京:南京体育学院,2023.
[9] STEIN R, MAIA CP, SILVEIRA AD, et al. Inspiratory muscle strength as a determinant of functional capacity early after coronary artery bypass graft surgery. Arch Phys Med Rehabil. 2009;90(10):1685-1691.
[10] 罗泽汝心, 王渝强, 周亚馨, 等. 术前吸气肌训练预防成人心脏手术患者术后肺部并发症的最新进展[J]. 中国胸心血管外科临床杂志,2023,30(10):1519-1523.
[11] 郑静, 李宝宝, 杨丽娟. 吸气肌训练预防心脏手术后患者肺部并发症的研究进展[J]. 上海护理,2020,20(9):62-65.
[12] KENDALL F, OLIVEIRA J, PELETEIRO B, et al. Inspiratory muscle training is effective to reduce postoperative pulmonary complications and length of hospital stay: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Disabil Rehabil. 2018;40(8):864-882.
[13] ZHANG S, LI B, MENG X, et al. The Effects of Inspiratory Muscle Training (IMT) on Patients Undergoing Coronary Artery Bypass Graft (CABG) Surgery: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Rev Cardiovasc Med. 2023;24(1):16.
[14] XIANG Y, ZHAO Q, LUO T, et al. Inspiratory muscle training to reduce risk of pulmonary complications after coronary artery bypass grafting: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Front Cardiovasc Med. 2023;10: 1223619.
[15] AQUINO TN, PRADO JP, CRISAFULLI E, et al. Efficacy of Respiratory Muscle Training in the Immediate Postoperative Period of Cardiac Surgery: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Braz J Cardiovasc Surg. 2024;39(1):e20220165.
[16] LISBOA CAL, OLIVEIRA SL, MANSUETO G, et al. Inspiratory Muscle Training in Patients in the Postoperative Phase of Cardiac Surgery: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Ann Rehabil Med. 2023;47(3):162-172.
[17] Higgins JP, Altman DG, Gøtzsche PC, et al. The Cochrane Collaboration’s tool for assessing risk of bias in randomised trials. BMJ. 2011;343:d5928.
[18] 柳青, 翟伟, 谭亚芹, 等. 临床研究文献质量评价工具浅析[J]. 中国针灸,2014, 34(9):919-922.
[19] CORDEIRO ALL, ALMEIDA DE BRITO J, RODRIGUES PEREIRA L, et al. Inspiratory muscle training on quality of life and functional capacity after hospital discharge in patients submitted to coronary artery bypass grafting: A controlled clinical trial. J Bodyw Mov Ther. 2023;35:202-207.
[20] DOS SANTOS TD, PEREIRA SN, PORTELA LOC, et al. Moderate-to-high intensity inspiratory muscle training improves the effects of combined training on exercise capacity in patients after coronary artery bypass graft surgery: A randomized clinical trial. Int J Cardiol. 2019;279:40-46.
[21] SAVCI S, DEGIRMENCI B, SAGLAM M, et al. Short-term effects of inspiratory muscle training in coronary artery bypass graft surgery: a randomized controlled trial. Scand Cardiovasc J. 2011;45(5):286-293.
[22] BARROS GF, SANTOS CDA S, GRANADO FB, et al. Respiratory muscle training in patients submitted to coronary arterial bypass graft. Rev Bras Cir Cardiovasc. 2010;25(4):483-490.
[23] MIOZZO AP, STEIN C, MARCOLINO MZ, et al. Effects of High-Intensity Inspiratory Muscle Training Associated with Aerobic Exercise in Patients Undergoing CABG: Randomized Clinical Trial. Braz J Cardiovasc Surg. 2018; 33(4):376-383.
[24] VALKENET K, TRAPPENBURG JCA, HULZEBOS EH, et al. Effects of a pre-operative home-based inspiratory muscle training programme on perceived health-related quality of life in patients undergoing coronary artery bypass graft surgery. Physiotherapy. 2017;103(3):276-282.
[25] HULZEBOS EH, HELDERS PJ, FAVIÉ NJ, et al. Preoperative intensive inspiratory muscle training to prevent postoperative pulmonary complications in high-risk patients undergoing CABG surgery: a randomized clinical trial. JAMA. 2006;296(15): 1851-1857.
[26] HULZEBOS EH, VAN MEETEREN NL, VAN DEN BUIJS BJ, et al. Feasibility of preoperative inspiratory muscle training in patients undergoing coronary artery bypass surgery with a high risk of postoperative pulmonary complications: a randomized controlled pilot study. Clin Rehabil. 2006;20(11):949-959.
[27] CORDEIRO ALL, CARVALHO BSC, SILVA EGD, et al. Inspiratory muscle training and functional capacity following coronary artery bypass grafting in high-risk patients: A pilot randomized and controlled trial. J Clin Transl Res. 2022;8(4):266-271.
[28] MATHEUS GB, DRAGOSAVAC D, TREVISAN P, et al. Treinamento muscular melhora o volume corrente e a capacidade vital no pós-operatório de revascularização do miocárdio Inspiratory muscle training improves tidal volume and vital capacity after CABG surgery. Braz J Cardiovasc Surg. 2012;27(3):362-369.
[29] TURKY K, AFIFY AMA. Effect of Preoperative Inspiratory Muscle Training on Alveolar-Arterial Oxygen Gradients After Coronary Artery Bypass Surgery. J Cardiopulm Rehabil Prev. 2017;37(4):290-294.
[30] CARGNIN C, KARSTEN M, GUARAGNA JCVDC, et al. Inspiratory Muscle Training After Heart Valve Replacement Surgery Improves Inspiratory Muscle Strength, Lung Function, and Functional Capacity: A randomized controlled trial. J Cardiopulm Rehabil Prev. 2019;39(5):E1-E7.
[31] HEGAZY FA, MOHAMED KAMEL SM, ABDELHAMID AS, et al. Effect of postoperative high load long duration inspiratory muscle training on pulmonary function and functional capacity after mitral valve replacement surgery: A randomized controlled trial with follow-up. PLoS One. 2021;16(8):e0256609.
[32] XU L, WEI J, LIU J, et al. Inspiratory muscle training improves cardiopulmonary function in patients after transcatheter aortic valve replacement: a randomized clinical trial. Eur J Prev Cardiol. 2023;30(2):191-202.
[33] WEINER P, ZEIDAN F, ZAMIR D, et al. Prophylactic inspiratory muscle training in patients undergoing coronary artery bypass graft. World J Surg. 1998;22(5):427-431.
[34] 孙月, 田妍卉, 林碧莹, 等. 使用POWER-breathe进行吸气肌训练对PCI术后患者心肺功能的影响[J]. 中国老年保健医学, 2021,19(3):21-23.
[35] 郑慧萍, 鲁胜男, 张喆. 术前呼吸肌训练对吸气肌无力者冠状动脉旁路移植术预后的影响[J]. 临床心血管病杂志,2018, 34(3):272-275.
[36] 许志锋, 吴桂琴, 吴永前, 等. 术前呼吸肌训练对心脏瓣膜置换术吸气肌无力患者预后的影响[J]. 岭南心血管病杂志, 2023,29(4):380-384.
[37] 焦瑞娟, 马亚飞, 史素玲, 等. 吸气肌训练对冠状动脉旁路移植术后心肺功能和生活质量的影响: 中国转化医学和整合医学学术交流会(上海站),中国上海, 2015[C].
[38] 段俊滔, 刘聪颖, 于桂香, 等. 吸气肌训练对经皮冠状动脉介入治疗术后患者的影响研究[J]. 中华护理杂志,2020,55(4): 519-523.
[39] 邵娜君, 吴惠霞, 黄贞敏, 等. 吸气肌训练在经皮冠状动脉介入治疗术患者中的应用效果[J]. 当代护士(上旬刊),2022, 29(6):123-126.
[40] 罗泽汝心, 王渝强, 周亚馨, 等. 有限资源下创新性吸气肌训练方案对心脏瓣膜疾病患者术后肺部并发症的影响[J]. 中国康复医学杂志,2024,39(1):39-44.
[41] 陈连带,叶庆新. 呼吸训练器对心脏瓣膜置换术后康复作用的探讨[J]. 现代康复,2001(8):151.
[42] 刘长红, 张一明. 深呼吸训练器在高龄冠状动脉旁路移植术患者围术期中的应用[J]. 中国康复医学杂志,2014,29(11):1077-1078.
[43] 郭佳宝, 朱毅. 吸气肌训练的临床研究进展[J]. 中国康复医学杂志, 2014,29(9): 888-892.
[44] 岳明叶, 王慧华, 胡玉婷, 等. 吸气肌训练促进心脏手术病人肺康复的研究进展[J]. 护理研究,2022,36(5):858-863.
[45] CAVAYAS YA, ELJAIEK R, RODRIGUE É, et al. Preoperative Diaphragm Function Is Associated With Postoperative Pulmonary Complications After Cardiac Surgery. Crit Care Med. 2019;47(12):e966-e974.
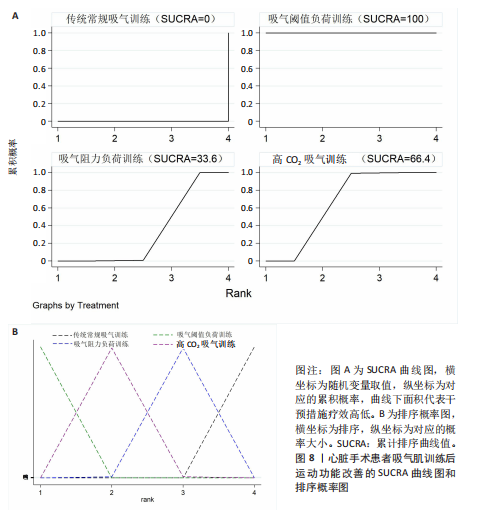
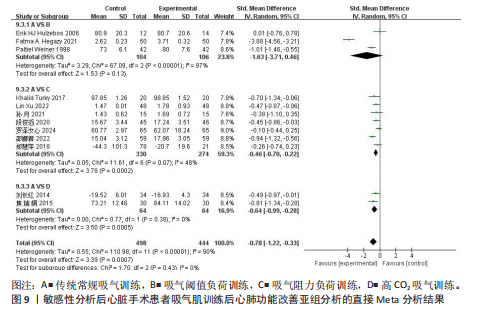
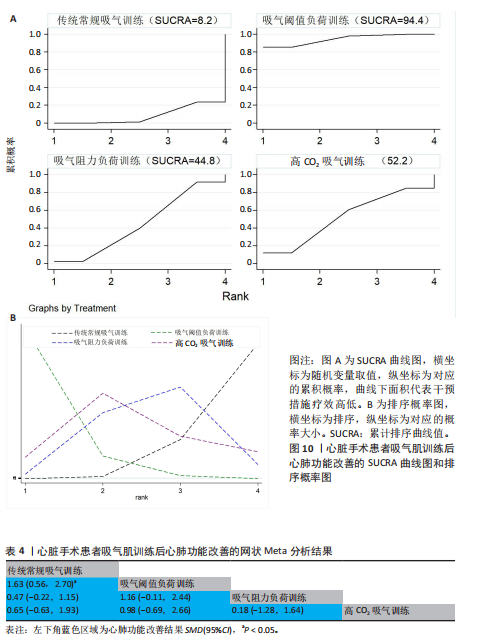
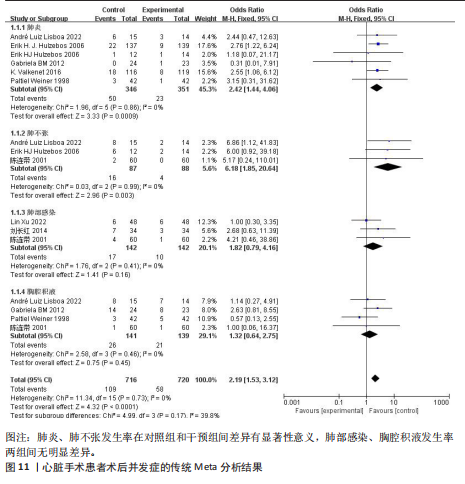
[46] 王一木, 王灵雨, 刘靖宇, 等. 吸气肌训练对心脏外科手术患者干预效果的Meta分析[J]. 实用心脑肺血管病杂志, 2025,33(5):101-109.
[47] MONERUZZAMAN M, SUN WZ, CHANGWE GJ, et al. Efficacy of Multiple Exercise Therapy after Coronary Artery Bypass Graft: A Systematic Review of Randomized Control Trials. Rev Cardiovasc Med. 2023;24(5):141.
[48] 梅桃桃, 刘扣英. 慢性阻塞性肺疾病患者吸气肌训练的研究进展[J]. 护理学杂志, 2013,28(23):72-75.
[49] GEDDES EL, O’BRIEN K, REID WD, et al. Inspiratory muscle training in adults with chronic obstructive pulmonary disease: an update of a systematic review. Respir Med. 2008;102(12):1715-1729.
[50] 常影, 刘泽雄, 季晓鹏, 等. 体外循环肺损伤机制与肺保护策略研究进展[J]. 长春中医药大学学报,2023,39(7):817-821.
[51] MONERUZZAMAN M, SUN WZ, CHANGWE GJ, et al. Efficacy of Multiple Exercise Therapy after Coronary Artery Bypass Graft: A Systematic Review of Randomized Control Trials. Rev Cardiovasc Med. 2023;24(5):141.
[52] SAMEED M, CHOI H, AURON M, et al. Preoperative Pulmonary Risk Assessment. Respir Care. 2021;66(7):1150-1166.
[53] JEONG BH, SHIN B, EOM JS, et al. Development of a prediction rule for estimating postoperative pulmonary complications. PLoS One. 2014;9(12): e113656.
[54] WINKELMANN ER, STEFFENS É, WINDMÖLLER P, et al. Preoperative expiratory and inspiratory muscle weakness to predict postoperative outcomes in patients undergoing elective cardiac surgery. J Card Surg. 2020;35(1):128-134.
|