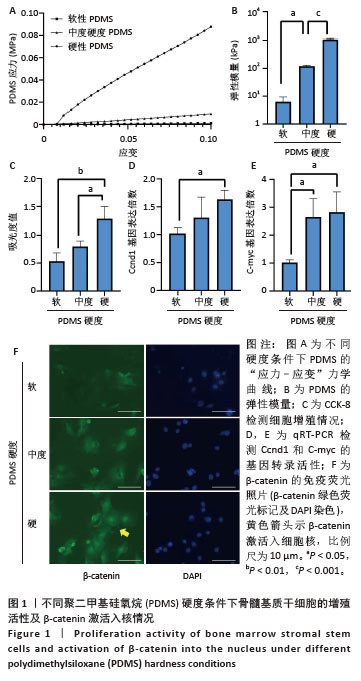
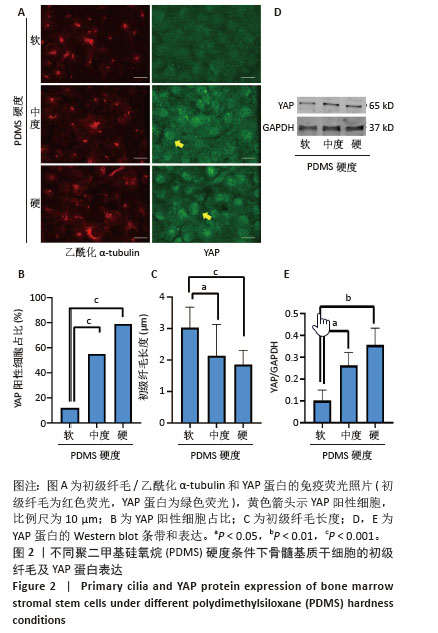
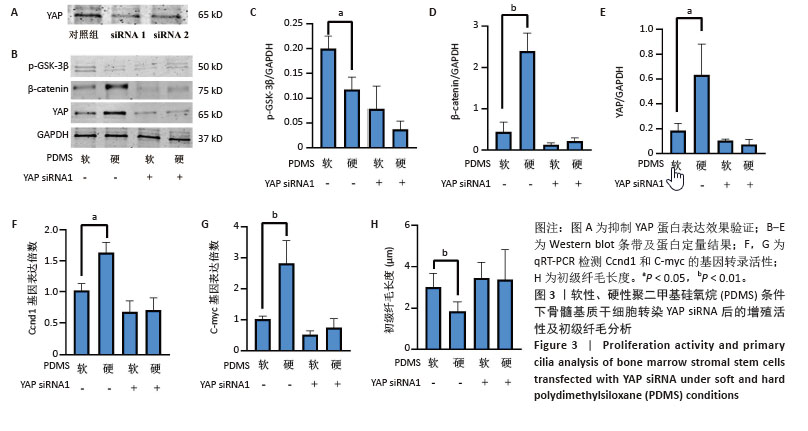
[1] 侯建飞,王福科,杨桂然,等.羟基磷灰石表面改性作为组织工程骨支架的应用优势[J].中国组织工程研究,2022,26(10):1610-1614.
[2] 钟思扬,廖晴,周星宇,等.骨微环境对组织工程骨再生过程的影响[J].中国组织工程研究,2024,28(15):2452-2460.
[3] 马春燕,潘清,何磊,等.细胞外基质PDMS硬度对牙髓干细胞增殖和成骨分化的影响[J].上海口腔医学,2021,30(3):253-257.
[4] 郑力恒,吴昊,尚玉攀,等.组织工程支架材料性质对干细胞分化的影响[J].中国组织工程研究,2017,21(14):2274-2279.
[5] HE S, LEI P, KANG W, et al. Stiffness Restricts the Stemness of the Intestinal Stem Cells and Skews Their Differentiation Toward Goblet Cells. Gastroenterology. 2023;164(7):1137-1151.e15.
[6] PAN JX, XIONG L, ZHAO K, et al. YAP promotes osteogenesis and suppresses adipogenic differentiation by regulating β-catenin signaling. Bone Res. 2018;6:18.
[7] SUN K, GUO J, GUO Z, et al. The roles of the Hippo-YAP signalling pathway in Cartilage and Osteoarthritis. Ageing Res Rev. 2023;90: 102015.
[8] MENG H, FU S, FERREIRA MB, et al. YAP activation inhibits inflammatory signalling and cartilage breakdown associated with reduced primary cilia expression. Osteoarthritis Cartilage. 2023;31(5):600-612.
[9] MELI VS, ATCHA H, VEERASUBRAMANIAN PK, et al. YAP-mediated mechanotransduction tunes the macrophage inflammatory response. Sci Adv. 2020;6(49):eabb8471.
[10] SALES FCP, ARIATI RM, NORONHA VT, et al. Mechanical Characterization of PDMS with Different Mixing Ratios. Procedia Structural Integrity. 2022;37:383-388.
[11] LEE M, CHU K, CHAKRABORTY M, et al. PDMS hydrogel-coated tissue culture plates for studying the impact of substrate stiffness on dendritic cell function. STAR Protoc. 2022;3(2):101233.
[12] KRETSCHMER M, MAMISTVALOV R, SPRINZAK D, et al. Matrix stiffness regulates Notch signaling activity in endothelial cells. J Cell Sci. 2023; 136(2):jcs260442.
[13] KONG MJ, HAN SJ, SEU SY, et al. Shortening of primary cilia length is associated with urine concentration in the kidneys. Kidney Res Clin Pract. 2023;42(3):312-324.
[14] MACARELLI V, LEVENTEA E, MERKLE FT. Regulation of the length of neuronal primary cilia and its potential effects on signalling. Trends Cell Biol. 2023;33(11):979-990.
[15] 闵子洋,穆妮热·艾力,郑耘昊,等.细胞外基质力学微环境与细胞间相互作用的机制与特征[J].中国组织工程研究,2022,26(25): 4034-4045.
[16] AREFIN AME, LAHOWETZ M, EGAN PF. Simulated tissue growth in tetragonal lattices with mechanical stiffness tuned for bone tissue engineering. Comput Biol Med. 2021;138:104913.
[17] ZHANG J, WEHRLE E, ADAMEK P, et al. Optimization of mechanical stiffness and cell density of 3D bioprinted cell-laden scaffolds improves extracellular matrix mineralization and cellular organization for bone tissue engineering. Acta Biomater. 2020;114:307-322.
[18] MA C, DU T, NIU X, et al. Biomechanics and mechanobiology of the bone matrix. Bone Res. 2022;10(1):59.
[19] WU D, ISAKSSON P, FERGUSON SJ, et al. Young’s modulus of trabecular bone at the tissue level: A review. Acta Biomater. 2018;78:1-12.
[20] CLAUSING RJ, STILLER A, KUHN F, et al. Measuring Young’s modulus of single trabeculae in cancellous bone using a two-point bending test. Clin Biomech (Bristol). 2023;102:105875.
[21] FAN L, CHEN S, YANG M, et al. Metallic Materials for Bone Repair. Adv Healthc Mater. 2024;13(3):e2302132.
[22] CHEN G, DONG C, YANG L, et al. 3D Scaffolds with Different Stiffness but the Same Microstructure for Bone Tissue Engineering. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces. 2015;7(29):15790-15802.
[23] HILGENDORF KI, MYERS BR, REITER JF. Emerging mechanistic understanding of cilia function in cellular signalling. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 2024;25(7):555-573.
[24] VERBRUGGEN SW, SITTICHOKECHAIWUT A, REILLY GC. Osteocytes and Primary Cilia. Curr Osteoporos Rep. 2023;21(6):719-730.
[25] WANG W, JACK BM, WANG HH, et al. Intraflagellar Transport Proteins as Regulators of Primary Cilia Length. Front Cell Dev Biol. 2021;9:661350.
[26] LACEY SE, PIGINO G. The intraflagellar transport cycle. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 2025;26(3):175-192.
[27] ZHOU H, WU S, LING H, et al. Primary Cilia: A Cellular Regulator of Articular Cartilage Degeneration. Stem Cells Int. 2022;2022:2560441.
[28] 王巧玲,吴志卯,完迪迪,等.初级纤毛发生起始的分子机制[J].中国细胞生物学学报,2023,45(11):1731-1744.
[29] RIDDLE RC, TAYLOR AF, ROGERS JR, et al. ATP release mediates fluid flow-induced proliferation of human bone marrow stromal cells. J Bone Miner Res. 2007;22(4):589-600.
[30] MANSINI AP, PEIXOTO E, JIN S, et al. The Chemosensory Function of Primary Cilia Regulates Cholangiocyte Migration, Invasion, and Tumor Growth. Hepatology. 2019;69(4):1582-1598.
[31] MA W, WEI L, JIN L, et al. YAP/Aurora A-mediated ciliogenesis regulates ionizing radiation-induced senescence via Hedgehog pathway in tumor cells. Biochim Biophys Acta Mol Basis Dis. 2024;1870(4):167062.
[32] CHEN H, XIAO H, WU B, et al. The effects of primary cilia-mediated mechanical stimulation on nestin+-BMSCs during bone-tendon healing. J Adv Res. 2024. doi: 10.1016/j.jare.2024.09.012.
[33] CROZET F, LEVAYER R. Emerging roles and mechanisms of ERK pathway mechanosensing. Cell Mol Life Sci. 2023;80(12):355.
[34] LIU L, GUO J, TONG X, et al. Mechanical strain regulates osteogenesis via Antxr1/LncRNA H19/Wnt/β-catenin axis. J Cell Physiol. 2024;239(5): e31214.
[35] CAI S, ZOU Y, ZHAO Y, et al. Mechanical stress reduces secreted frizzled-related protein expression and promotes temporomandibular joint osteoarthritis via Wnt/β-catenin signaling. Bone. 2022;161:116445.
[36] KAMETANI Y, TANAKA S, WADA Y, et al. Yes-associated protein activation potentiates glycogen synthase kinase-3 inhibitor-induced proliferation of neonatal cardiomyocytes and iPS cell-derived cardiomyocytes. J Cell Physiol. 2022;237(5):2539-2549.
[37] BERNATIK O, PACLIKOVA P, KOTRBOVA A, et al. Primary Cilia Formation Does Not Rely on WNT/β-Catenin Signaling. Front Cell Dev Biol. 2021;9: 623753.
[38] NIEHRS C, DA SILVA F, SEIDL C. Cilia as Wnt signaling organelles. Trends Cell Biol. 2025;35(1):24-32.
[39] Berbari NF, O’Connor AK, Haycraft CJ, et al. The primary cilium as a complex signaling center. Curr Biol. 2009;19(13):R526-535.
[40] ZHANG K, DA SILVA F, SEIDL C, et al. Primary cilia are WNT-transducing organelles whose biogenesis is controlled by a WNT-PP1 axis. Dev Cell. 2023;58(2):139-154.e8.
|