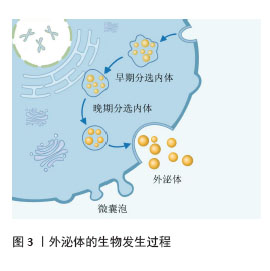
[1] 褚厚斌,谢云博,宋国华.外泌体介导的细胞间通讯在动脉粥样硬化中的研究进展[J].中国动脉硬化杂志,2025,33(9): 815-822.
[2] ZHAO Y, TANG J, JIANG K, et al. Liquid biopsy in pancreatic cancer - Current perspective and future outlook. Biochim Biophys Acta Rev Cancer. 2023;1878(3):188868.
[3] FREITAS AJA, CAUSIN RL, VARUZZA MB, et al. Liquid Biopsy as a Tool for the Diagnosis, Treatment, and Monitoring of Breast Cancer. Int J Mol Sci. 2022;23(17):9952.
[4] HOFMAN P. Liquid biopsy for lung cancer screening: Usefulness of circulating tumor cells and other circulating blood biomarkers. Cancer Cytopathol. 2021; 129(5):341-346.
[5] KIM Y, SHIN S, LEE KA. Exosome-based detection of EGFR T790M in plasma and pleural fluid of prospectively enrolled non-small cell lung cancer patients after first-line tyrosine kinase inhibitor therapy. Cancer Cell Int. 2021;21(1):50.
[6] 张咪,吴赛璇,董明,等.新型纳米递送系统:工程化小细胞外囊泡[J].中国组织工程研究,2022,26(27):4417-4422.
[7] 王季然,谷颖之,白玉兴.外泌体在牙周炎中组织修复及免疫调控作用的研究进展[J].北京口腔医学,2024,32(6):425-428.
[8] KALLURI R, LEBLEU VS. The biology, function, and biomedical applications of exosomes. Science. 2020;367(6478):eaau6977.
[9] CAI R, WANG L, ZHANG W, et al. The role of extracellular vesicles in periodontitis: pathogenesis, diagnosis, and therapy. Front Immunol. 2023;14:1151322.
[10] 张旭,刘法昱,范杰.HERC5对口腔鳞癌顺铂耐药性的影响[J].医药论坛杂志, 2025,46(6):568-573+580.
[11] JÄWERT F, NYMAN J, OLSSON E, et al. Regular clinical follow-up of oral potentially malignant disorders results in improved survival for patients who develop oral cancer. Oral Oncol. 2021;121:105469.
[12] 周梦缘,卢杨,许益敏,等.口腔鳞状细胞癌及口腔潜在恶性病变早期诊断研究进展[J].医药前沿,2024,14(28):40-43.
[13] 徐英娇,王姗.唾液外泌体在口腔鳞状细胞癌的研究进展[J].口腔医学,2022,42(7): 664-667+672.
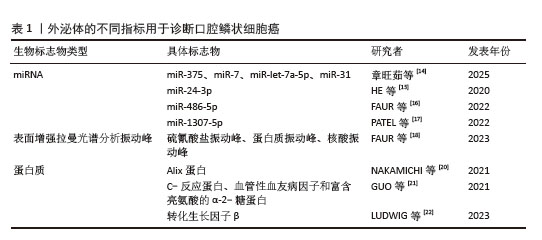
[14] 章旺茹,陈媛媛,李志萍,等.口腔鳞状细胞癌淋巴结转移机制及相关研究模型进展[J].中华老年口腔医学杂志,2025, 23(2):155-160.
[15] HE L, PING F, FAN Z, et al. Salivary exosomal miR-24-3p serves as a potential detective biomarker for oral squamous cell carcinoma screening. Biomed Pharmacother. 2020;121: 109553.
[16] FAUR CI, ROMAN RC, JURJ A, et al. Salivary Exosomal MicroRNA-486-5p and MicroRNA-10b-5p in Oral and Oropharyngeal Squamous Cell Carcinoma. Medicina (Kaunas). 2022;58(10):1478.
[17] PATEL A, PATEL S, PATEL P, et al. Salivary Exosomal miRNA-1307-5p Predicts Disease Aggressiveness and Poor Prognosis in Oral Squamous Cell Carcinoma Patients. Int J Mol Sci. 2022;23(18):10639.
[18] FAUR CI, DINU C, TOMA V, et al. A New Detection Method of Oral and Oropharyngeal Squamous Cell Carcinoma Based on Multivariate Analysis of Surface Enhanced Raman Spectra of Salivary Exosomes. J Pers Med. 2023;13(5):762.
[19] ZLOTOGORSKI-HURVITZ A, DEKEL BZ, MALONEK D, et al. FTIR-based spectrum of salivary exosomes coupled with computational-aided discriminating analysis in the diagnosis of oral cancer. J Cancer Res Clin Oncol. 2019;145(3):685-694.
[20] NAKAMICHI E, SAKAKURA H, MII S, et al. Detection of serum/salivary exosomal Alix in patients with oral squamous cell carcinoma. Oral Dis. 2021;27(3):439-447.
[21] GUO H, JIANG W, HUANG S, et al. Serum exosome-derived biomarkers for the early detection of oral squamous cell carcinoma. Mol Cell Biochem. 2021;476(12):4435-4447.
[22] LUDWIG N, YERNENI SS, HARASYMCZUK M, et al. TGFβ carrying exosomes in plasma: potential biomarkers of cancer progression in patients with head and neck squamous cell carcinoma. Br J Cancer. 2023; 128(9):1733-1741.
[23] 崔莹莹,丁传扬,彭超然,等.口腔潜在恶性病变的临床病理学诊断研究进展[J].华西口腔医学杂志,2025,43(3): 314-324.
[24] WARNAKULASURIYA S, KUJAN O, AGUIRRE-URIZAR JM, et al. Oral potentially malignant disorders: A consensus report from an international seminar on nomenclature and classification, convened by the WHO Collaborating Centre for Oral Cancer. Oral Dis. 2021;27(8):1862-1880.
[25] 韩莹,赵璞,刘宏伟.细针扣刺预处理联合光动力疗法治疗口腔白斑[J].北京大学学报(医学版),2025,57(1):91-96.
[26] 魏子豪,曾昕,陈谦明.口腔白斑病的规范性临床诊疗[J].中华口腔医学杂志, 2022,57(8):884-889.
[27] WANG X, NIE X, XU G, et al. miR-450b promotes cell migration and invasion by inhibiting SERPINB2 in oral squamous cell carcinoma. Oral Dis. 2024;30(2):376-389.
[28] YU X, DENG J, ZHANG H, et al. Effects of BRCA1 overexpression via the NRF2/HO1/NQO1 pathway on oral cancer cells proliferation, migration, and apoptosis. Heliyon. 2024;10(20):e38977.
[29] 夏倩,王嘉祺,王紫钰,等.外泌体miR-185作为口腔白斑恶变诊断标志物的可行性研究[C]//中华口腔医学会口腔粘膜病专业委员会,中华口腔医学会中西医结合专业委员会.中华口腔医学会第十三次全国口腔粘膜病学暨第十一次全国口腔中西医结合学术大会论文汇编.首都医科大学附属北京口腔医院黏膜科,2021:95.
[30] 柴娟华,李阳,梁冰,等.口腔黏膜下纤维化患者血清miR-204和miR-200b水平与临床疗效的关系研究[J].国际检验医学杂志,2024,45(10):1212-1217.
[31] ZHOU S, ZHU Y, LI Z, et al. Exosome-derived long non-coding RNA ADAMTS9-AS2 suppresses progression of oral submucous fibrosis via AKT signalling pathway. J Cell Mol Med. 2021;25(4):2262-2273.
[32] 黄永祺.槟榔碱通过巨噬细胞外泌体miR-155促进口腔黏膜下纤维化[D].广州:南方医科大学,2024.
[33] ABDELSAMIE M, ZAHRAN F, HUSSINE AA, et al. Clinical and biochemical assessment of the effect of topical use of coenzyme Q10 versus topical corticosteroid in management of symptomatic oral lichen planus: randomized controlled clinical trial. BMC Oral Health. 2023;23(1):506.
[34] ZHAO Z, WANG L, ZHANG M, et al. Reveals of quercetin’s therapeutic effects on oral lichen planus based on network pharmacology approach and experimental validation. Sci Rep. 2022;12(1):1162.
[35] SALINAS-GILABERT C, GÓMEZ GARCÍA F, GALERA MOLERO F, et al. Photodynamic Therapy, Photobiomodulation and Acetonide Triamcinolone 0.1% in the Treatment of Oral Lichen Planus: A Randomized Clinical Trial. Pharmaceutics. 2022;15(1):30.
[36] PENG Q, ZHANG J, ZHOU G. Differentially circulating exosomal microRNAs expression profiling in oral lichen planus. Am J Transl Res. 2018;10(9):2848-2858.
[37] BYUN JS, HONG SH, CHOI JK, et al. Diagnostic profiling of salivary exosomal microRNAs in oral lichen planus patients. Oral Dis. 2015;21(8):987-993.
[38] 娜密牙,白丽娜,冯美玲,等.通过龈沟液SERS检测早期诊断牙周炎的研究进展[J].光散射学报,2025,37(1):1-7.
[39] HU H, LEUNG WK. Mass Spectrometry-Based Proteomics for Discovering Salivary Biomarkers in Periodontitis: A Systematic Review. Int J Mol Sci. 2023;24(19):14599.
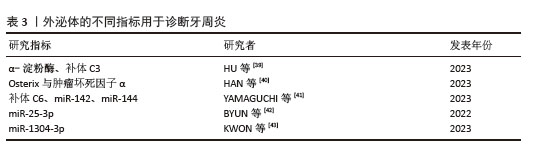
[40] HAN P, JIAO K, MORAN CS, et al. TNF-α and OSX mRNA of Salivary Small Extracellular Vesicles in Periodontitis: A Pilot Study. Tissue Eng Part C Methods. 2023;29(7):298-306.
[41] YAMAGUCHI A, TSURUYA Y, IGARASHI K, et al. Changes in the components of salivary exosomes due to initial periodontal therapy. J Periodontal Implant Sci. 2023;53(5):347-361.
[42] BYUN JS, LEE HY, TIAN J, et al. Effect of Salivary Exosomal miR-25-3p on Periodontitis With Insulin Resistance. Front Immunol. 2022;12:775046.
[43] KWON EJ, KIM HJ, WOO BH, et al. Profiling of plasma-derived exosomal RNA expression in patients with periodontitis: A pilot study. Oral Dis. 2023;29(4):1726-1737.
[44] MALTHA JC, KUIJPERS-JAGTMAN AM. Mechanobiology of orthodontic tooth movement: An update. J World Fed Orthod. 2023;12(4):156-160.
[45] 管佳妮,严斌.龈沟液内正畸牙移动相关生物标志物的研究进展[J].口腔医学研究,2022,38(5):400-403.
[46] KAPOOR P, CHOWDHRY A, BAGGA DK, et al. MicroRNAs in oral fluids (saliva and gingival crevicular fluid) as biomarkers in orthodontics: systematic review and integrated bioinformatic analysis. Prog Orthod. 2021;22(1):31.
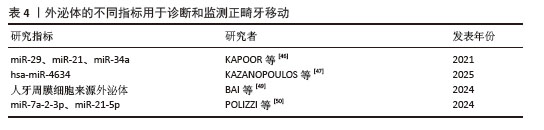
[47] KAZANOPOULOS N, SIDERIS CD, XU Y, et al. Identification of Salivary Exosome-Derived miRNAs as Potential Biomarkers of Bone Remodeling During Orthodontic Tooth Movement. Int J Mol Sci. 2025;26(3):1228.
[48] JEON HH, TEIXEIRA H, TSAI A. Mechanistic Insight into Orthodontic Tooth Movement Based on Animal Studies: A Critical Review. J Clin Med. 2021;10(8):1733.
[49] BAI X, WANG Y, MA X, et al. Periodontal ligament cells-derived exosomes promote osteoclast differentiation via modulating macrophage polarization. Sci Rep. 2024; 14(1):1465.
[50] POLIZZI A, ALIBRANDI A, LO GIUDICE A, et al. Impact of periodontal microRNAs associated with alveolar bone remodeling during orthodontic tooth movement: a randomized clinical trial. J Transl Med. 2024;22(1):1155.
[51] NAGI R, KUMAR SS, SHETH M, et al. Association between oral microbiome dysbiosis and Sjogren Syndrome. A systematic review of clinical studies. Arch Oral Biol. 2025;172:106167.
[52] ZHAO T, ZHANG R, LI Z, et al. A comprehensive review of Sjögren’s syndrome: Classification criteria, risk factors, and signaling pathways. Heliyon. 2024;10(17):e36220.
[53] VEENBERGEN S, KOZMAR A, VAN DAELE PLA, et al. Autoantibodies in Sjögren’s syndrome and its classification criteria. J Transl Autoimmun. 2021;5:100138.
[54] FERRANT J, PONTIS A, ZIMMERMANN F, et al. Phenotypic and proteomic analysis of plasma extracellular vesicles highlights them as potential biomarkers of primary Sjögren syndrome. Front Immunol. 2023; 14:1207545.
[55] PENG X, HOU L, WU X, et al. The plasma exosomes from patients with primary Sjögren’s syndrome contain epithelial cell-derived proteins involved in ferroptosis. J Mol Med (Berl). 2023;101(10):1289-1304.
[56] CROSS T, HAUG KBF, BRUSLETTO BS, et al. Non-Coding RNA in Salivary Extracellular Vesicles: A New Frontier in Sjögren’s Syndrome Diagnostics? Int J Mol Sci. 2023; 24(17):13409.
[57] YAMASHIRO K, HAMADA T, MORI K, et al. Exosome-Derived microRNAs from Mouthrinse Have the Potential to Be Novel Biomarkers for Sjögren Syndrome. J Pers Med. 2022;12(9):1483.
[58] KAKAN SS, JANGA SR, COOPERMAN B, et al. Small RNA Deep Sequencing Identifies a Unique miRNA Signature Released in Serum Exosomes in a Mouse Model of Sjögren’s Syndrome. Front Immunol. 2020;11:1475.
[59] YAMAL JM, MOFLEH D, CHUANG RJ, et al. Training protocol and calibration of the International Caries Detection and Assessment System in a school-based clinical trial of elementary school-age children. J Public Health Dent. 2025;85(1):13-20.
[60] 杜民权.早期龋的临床诊断和治疗[C]//中华口腔医学会口腔预防医学专业委员会.中华口腔医学会口腔预防医学专业委员会第24次口腔预防学术年会论文集.武汉大学口腔医院,2024:15.
[61] SHAFAIE E, BADRI Z, SALEHINIYA H, et al. Comparison the salivary streptococcus mutans levels between caries-active and caries-free children from Birjand, Iran: A case-control study. Heliyon. 2024;10(3):e25663.
[62] SALTOS ROSERO N, SEOANE PRADO R, et al. Molecular and serological typing of Streptococcus mutans strains isolated from young Galician population: relationship with the oral health status. Int Microbiol. 2020;23(4):589-596.
[63] BENDER O, KHOURY J, HIRSCH G, et al. Immunorecognition of Streptococcus mutans secreted proteins protects against caries by limiting tooth adhesion. J Dent. 2024;141:104805.
[64] PALLAVI P, SAHOO PP, SEN SK, et al. Comparative evaluation of anti-biofilm and anti- adherence potential of plant extracts against Streptococcus mutans: A therapeutic approach for oral health. Microb Pathog. 2024;188:106514.
[65] ELLEPOLA K, SHIELDS RC, KAJFASZ JK, et al. MecA in Streptococcus mutans is a multi-functional protein. mSphere. 2024;9(12): e0030824.
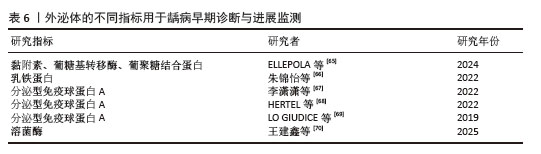
[66] 朱锦怡,樊琪,周媛,等.唾液蛋白作为低龄儿童龋预测标志物的研究进展[J].国际口腔医学杂志,2022,49(2):212-219.
[67] 李潇潇,李芝香,董宁,等.儿童龋病唾液氧化应激和免疫 指标与龋病严重程度的相关性[J].疑难病杂志,2022,21(1): 69-73.
[68] HERTEL S, HANNIG M, HANNIG C, et al. Mucins 5b and 7 and secretory IgA in the oral acquired pellicle of children with caries and caries-free children. Arch Oral Biol. 2022;134:105314.
[69] LO GIUDICE G, NICITA F, MILITI A, et al. Correlation of s-IgA and IL-6 Salivary with Caries Disease and Oral Hygiene Parameters in Children. Dent J (Basel). 2019;8(1):3.
[70] 王建鑫,王舒婷,马雷,等.牙面黑色素沉着与铁、龋病关系的研究进展[J].国际口腔医学杂志,2025,52(4):456-465.
[71] OH SY, KIM DY, LEE KY, et al. Streptococcus mutans-derived extracellular vesicles promote skin wound healing via tRNA cargo. J Nanobiotechnology. 2025;23(1):322.
[72] 郑思颖,王诗怡,虞千瑶,等.唇腭裂伴牙槽突裂患者裂隙邻近牙的发育异常和错位特征及治疗进展[J].口腔疾病防治, 2025,33(10):908-918.
[73] WU N, YAN J, HAN T, et al. Integrated assessment of differentially expressed plasma microRNAs in subtypes of nonsyndromic orofacial clefts. Medicine (Baltimore). 2018;97(25):e11224.
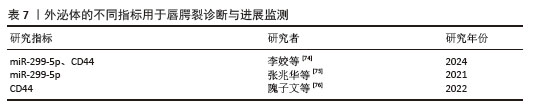
[74] 李姣,张楠,朱艳艳.miR-299-5p联合CD44对儿童非综合征型唇腭裂的诊断价值[J].河南医学研究,2024,33(17):3113-3116.
[75] 张兆华,高雨蔚,宋红权,等.外周血miR-299-5p和miR-127-3p的表达水平与非综合征型唇腭裂相关性研究[J].口腔生物医学,2021,12(1):30-33.
[76] 隗子文,李佳兴,张兆华,等.非综合征型唇腭裂中SMAD7和CD44表达水平及其临床意义[J].哈尔滨医科大学学报, 2022,56(1):55-58. |