中国组织工程研究 ›› 2026, Vol. 30 ›› Issue (3): 701-710.doi: 10.12307/2026.013
• 骨与关节综述 bone and joint review • 上一篇 下一篇
免疫微环境调节骨再生
杨 虎1,郑 宇2,贾承明2,王 通1,张广飞1,纪垚垚1
- 1陕西中医药大学,陕西省咸阳市 712000;2陕西省中医医院,陕西省西安市 710000
-
收稿日期:2024-12-02接受日期:2025-02-06出版日期:2026-01-28发布日期:2025-07-07 -
通讯作者:郑宇,博士,副主任医师,硕士生导师,陕西省中医医院,陕西省西安市 710000 共同通讯作者:贾承明,硕士,主治医师,陕西省中医医院,陕西省西安市 710000 -
作者简介:杨虎,男,1991年生,湖北省十堰市人,汉族,陕西中医药大学中西医结合学院在读硕士,主治医师,主要从事中西医结合骨科疾病的基础与临床研究。 -
基金资助:陕西省自然科学基础研究青年项目(2024JC-YBQN-0948),项目负责人:贾承明;陕西省中医药管理局共建类项目(2019-GJ-JC011),项目负责人:郑宇;陕西省自然科学基础研究青年项目(2019JQ-557),项目负责人:郑宇
Immune microenvironment regulates bone regeneration
Yang Hu1, Zheng Yu2, Jia Chengming2, Wang Tong1, Zhang Guangfei1, Ji Yaoyao1
- 1Shaanxi University of Chinese Medicine, Xianyang 712000, Shaanxi Province, China; 2Shaanxi Provincial Chinese Medicine Hospital, Xi’an 710000, Shaanxi Province, China
-
Received:2024-12-02Accepted:2025-02-06Online:2026-01-28Published:2025-07-07 -
Contact:Zheng Yu, MD, Associate chief physician, Master’s supervisor, Shaanxi Provincial Chinese Medicine Hospital, Xi’an 710000, Shaanxi Province, China Co-corresponding author: Jia Chengming, MS, Attending physician, Shaanxi Provincial Chinese Medicine Hospital, Xi’an 710000, Shaanxi Province, China -
About author:Yang Hu, Master candidate, Attending physician, Shaanxi University of Chinese Medicine, Xianyang 712000, Shaanxi Province, China -
Supported by:Shaanxi Province Natural Science Basic Research Youth Project, No. 2024JC-YBQN-0948 (to JCM) ; Shaanxi Provincial Administration of Chinese Medicine, No. 2019-GJ-JC011 (to ZY); Shaanxi Province Natural Science Basic Research Youth Project, No. 2019JQ-557 (to ZY)
摘要:
文题释义:
免疫微环境:由骨髓间充质干细胞、成骨细胞、破骨细胞、各种免疫细胞、造血细胞和分泌的细胞因子共同组成的微环境,在骨再生过程中发挥着重要的调节作用。骨再生:是一个复杂的、精心策划的骨形成生理过程,涉及多种细胞类型以及细胞内和细胞外分子信号传导途径,以促进骨骼修复和恢复骨骼功能,最常见的骨再生形式是骨折愈合。
摘要
背景:局部免疫微环境在骨生成过程中起着重要的调节作用,免疫系统与骨骼系统有着千丝万缕的联系。
目的:从免疫细胞调节微环境、小细胞外囊泡调节免疫反应和骨生物材料诱导免疫反应3个方面促进骨再生进行系统综述,阐明骨再生过程中的免疫调节机制。
方法:检索PubMed数据库、中国知网、万方数据库及维普数据库中免疫微环境影响骨再生或骨组织修复的相关文献,以“骨免疫学,免疫微环境,小细胞外囊泡,骨再生,骨组织修复,生物材料,组织工程”为中文检索词,以“Osteoimmunology,Immune Microenvironment,Small Extracellular Vesicles,Bone Regeneration,Bone Tissue Repair,Biomaterials,Tissue Engineering”为英文检索词,删除重复和与研究目的无关文献,最后筛选出符合标准的92篇文献进行精读和综述。
结果与结论:多种免疫细胞和骨细胞处于同一微环境,免疫细胞能够调控骨细胞的分化和活性,共同组成影响骨再生的免疫微环境。中性粒细胞在骨损伤初期能够显著降低局部炎症反应,为骨再生形成有利的微环境。M1型巨噬细胞能够清除异物和降低早期炎症反应,M2型巨噬细胞能够促进成骨标志物和因子的表达,共同在骨损伤的修复过程中发挥重要作用。B细胞和T细胞可直接或间接影响成骨细胞和破骨细胞的生成和活性,调节骨代谢,促进骨再生。小细胞外囊泡以旁分泌方式调节局部免疫微环境,促进骨损伤部位的骨生成和血管生成。生物材料表面的金属离子、表面亲水性、孔隙度、孔径、表面形态和表面粗糙度均能直接调节局部免疫反应,具有抗炎、促进血管生成和成骨的作用,从而加速骨再生。
中国组织工程研究杂志出版内容重点:人工关节;骨植入物;脊柱;骨折;内固定;数字化骨科;组织工程
中图分类号:
引用本文
杨 虎, 郑 宇, 贾承明, 王 通, 张广飞, 纪垚垚. 免疫微环境调节骨再生[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2026, 30(3): 701-710.
Yang Hu, Zheng Yu, Jia Chengming, Wang Tong, Zhang Guangfei, Ji Yaoyao. Immune microenvironment regulates bone regeneration[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(3): 701-710.
免疫微环境调节骨再生发展的关键时间点及重要内容,见表1。
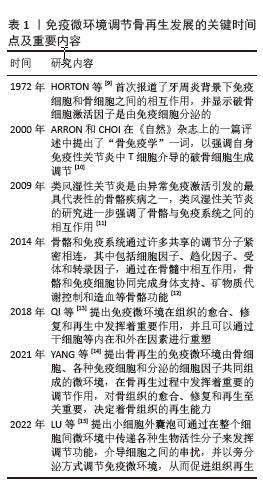
2.2 免疫微环境调节骨再生的机制 见图3。
2.2.1 中性粒细胞 中性粒细胞是由造血干细胞衍生而来,在骨髓中发育成熟,然后迁移到血液和组织中。在骨损伤时,中性粒细胞会第一时间在骨损伤处聚集和浸润,对骨修复过程的初期阶段至关重要[16-17]。对小鼠骨折模型的研究发现,骨折后炎症细胞因子水平升高,单核细胞和巨噬细胞在骨折处募集,而中性粒细胞被过度消耗则导致骨折愈合延迟,表明中性粒细胞在启动骨修复过程中起着至关重要的作用[18]。中性粒细胞可通过与先天免疫系统和适应性免疫系统的细胞相互作用来调节免疫反应,积极协调炎症的消退,帮助组织修复[19]。中性粒细胞最早到达损伤部位并招募骨髓间充质干细胞和巨噬细胞,然后巨噬细胞调节骨髓间充质干细胞向软骨和成骨分化[20]。在骨再生的早期炎症阶段,高水平的白细胞介素8诱导促炎环境,中性粒细胞为促炎N1亚型,招募其他类型的免疫细胞(如M1巨噬细胞、辅助性T细胞1和辅助性T细胞17)积极减少炎症,为骨再生准备环境。炎症消退后,白细胞介素8水平下降,这一阶段募集的中性粒细胞是表达抗炎因子的N2亚型,促进骨再生[21]。PAPAGORAS
等[22]研究发现,在炎症部位表达白细胞介素17a的中性粒细胞可以介导骨髓间充质干细胞向成骨细胞分化,并且白细胞介素17a的表达受白细胞介素1β正向调控。BASTIAN等[23]研究表明,在基质细胞浸润骨折血肿并合成最终骨组织之前,中性粒细胞通过合成纤维连接蛋白+细胞外基质来促进骨再生。因此,在骨折早期,中性粒细胞不仅能够启动急性炎症反应、清除病原微生物,还可以调节免疫反应,介导骨髓间充质干细胞向成骨细胞的分化,促进骨形成。
2.2.2 巨噬细胞 巨噬细胞由单核细胞衍生而来,广泛分布于各种组织中,作为专业的吞噬细胞能够抵御病原体的侵入,并且高效地清除体内的坏死组织及细胞残骸[24]。
骨损伤后,血浆蛋白和异物吸引巨噬细胞到骨缺损处,在炎症早期,巨噬细胞转化为M1型,具有很强的吞噬能力,可以吞噬凋亡的中性粒细胞,清除局部组织中的病原体和碎片;随后,巨噬细胞转化为M2型,能够调节血管生成、成纤维细胞再生和骨再生,启动骨组织再生过程[25]。巨噬细胞通过释放骨形态发生蛋白2、骨形态发生蛋白4和转化生长因子β等细胞因子促进成骨细胞的分化和增殖,并参与骨损伤、愈合和再生的各个阶段[26]。GONG等[27]研究发现,在巨噬细胞和间充质干细胞系统共培养体系中,M2巨噬细胞通过促进血管内皮生长因子、胰岛素样生长因子1和转化生长因子β等再生细胞因子的表达,增加碱性磷酸酶水平、骨矿化和成骨标志物,从而促进骨再生。ZHANG等[28]研究发现,M2巨噬细胞通过释放肿瘤抑素M和骨形态发生蛋白2因子增强骨髓间充质干细胞的增殖和成骨分化。VALLéS等[29]对促炎或抗炎巨噬细胞的成骨作用进行研究,发现抗炎巨噬细胞通过增加骨矿化和碱性磷酸酶活性来增强骨髓间充质干细胞向成骨细胞分化,并且抗炎巨噬细胞分泌的白细胞介素10调控成骨标志物RUNX2、Ⅰ型胶原和碱性磷酸酶的表达以促进成骨。也有研究发现,巨噬细胞不同亚群(M0、M1和M2)都具有促进骨髓间充质干细胞向成骨细胞分化的能力,但其相关性可能在不同的生理条件下发生变化[30]。因此,巨噬细胞在骨再生的各个阶段均具有重要作用。在骨再生初期,M1巨噬细胞通过吞噬病原体和碎片清除异物;在骨再生中后期,M2巨噬细胞通过促进成骨标志物的生成、成骨细胞生成相关因子的表达和骨髓间充质干细胞向成骨细胞分化,促进成骨和骨再生。
2.2.3 T细胞 T细胞来源于骨髓中的造血干细胞,在胸腺中发育成熟,然后迁移到周围淋巴器官,主要包括CD4+T细胞和CD8+T细胞,是适应性免疫系统中最重要的淋巴细胞。T细胞可以分为3个不同的亚型:辅助性T细胞(包括辅助性T细胞1、辅助性T细胞2和辅助性T细胞17)、细胞毒性T细胞及调节性T细胞[31]。在骨修复过程中,中性粒细胞通过产生C-C基序趋化因子配体2将辅助性T细胞17细胞招募到骨缺损处,促进骨形成[32]。然而,CD4+调节性T细胞通过分泌细胞因子(如转化生长因子β和白细胞介素4等),以细胞因子依赖的方式抑制破骨细胞的分化和功能。在去卵巢骨质疏松模型中,调节性T细胞通过分泌白细胞介素10和转化生长因子β等因子抑制破骨细胞的活性,减少骨吸收。CD8+T细胞具有骨保护作用,可通过分泌骨保护素抑制破骨细胞生成。研究发现,将CD8+ T细胞介导的促炎症期的初始“抗再生”状态重塑为调节性T细胞介导的免疫调节期的“促再生”状态,可以促进骨愈合[33]。辅助性T细胞1和辅助性T细胞2细胞分别通过分泌其标志性细胞因子干扰素γ和白细胞介素4来抑制破骨细胞的形成。辅助性T细胞1和辅助性T细胞2产生的干扰素γ和白细胞介素4通过降解肿瘤坏死因子受体相关因子6抑制破骨细胞分化,促进骨生成[34]。活化的辅助性T细胞2可分泌白细胞介素4,白细胞介素4可诱导巨噬细胞向M2型极化,M2巨噬细胞是骨再生的重要因素。辅助性T细胞1细胞可通过肿瘤坏死因子α诱导破骨细胞的生成,增加破骨细胞的活性,导致骨吸收的增多和骨质流失[35]。当处于炎症状态或雌激素水平较低时,辅助性T细胞1的破骨作用占主导地位[36]。因此,T细胞通过促进骨髓间充质干细胞向成骨细胞分化和骨生成抑制破骨细胞的活性,促进骨再生。
2.2.4 B细胞 B细胞来源于造血干细胞,其成熟过程与骨细胞之间存在紧密联系,骨髓腔中的骨髓间充质干细胞为B细胞的分化成熟提供有利微环境。B细胞可通过产生多种细胞因子和趋化因子直接作用于骨细胞和调节免疫微环境来调节骨再生和骨重塑[37]。B细胞和B细胞来源的浆细胞均可以表达核因子κB受体激活因子配体(receptor activator of nuclear factor-κB ligand,RANKL)、诱饵受体3或白细胞介素7分泌间接调节破骨细胞的生成[38]。对绝经后骨质疏松症的研究发现,B细胞通过分泌RANKL增加破骨细胞的生成和活性,从而促进骨吸收和骨质流失,导致骨密度降低。骨保护素是维持骨量稳态的重要因子,通过竞争性与核因子κB受体激活因子结合,拮抗RANKL与其结合,从而抑制破骨细胞的分化和活性,减少骨吸收,促进骨形成。骨骼中的骨保护素主要来源于B细胞,因此,B细胞可通过分泌骨保护素加速骨形成和骨重塑。在炎症环境中,被激活的T细胞通过CD40/CD40L通路诱导B细胞分泌骨保护素,促进骨再生[39]。体外实验发现,B细胞产生的转化生长因子β能够抑制破骨细胞的活性并加速其凋亡,转化生长因子β还能诱导B细胞分泌骨保护素,促进骨形成,进一步说明B细胞在骨再生过程中发挥至关重要的作用[40]。
综上所述,B细胞通过分泌各种因子促进骨再生,然而部分B细胞通过产生RANKL增加破骨细胞的活性,导致骨质流失,因此,B细胞在骨修复中具有双重调节作用,需要进一步的研究明确其具体作用及机制。
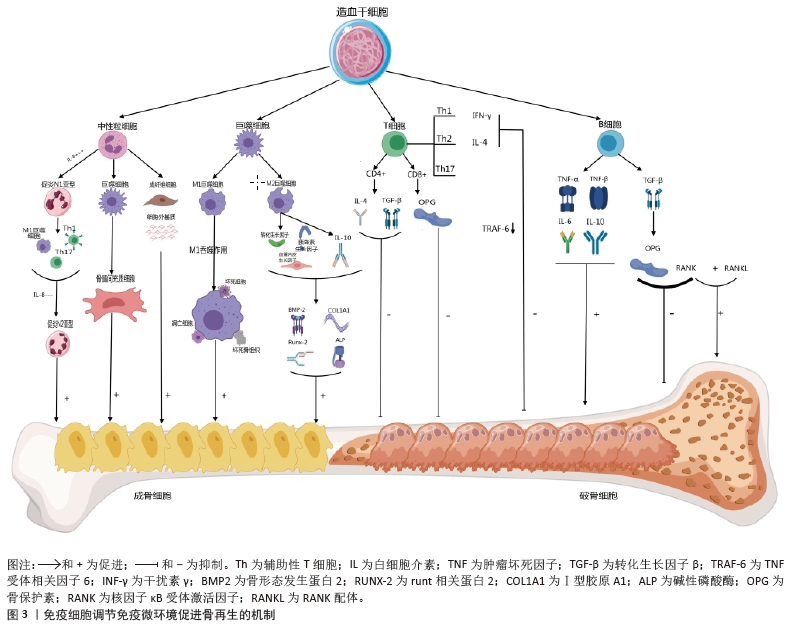
2.3 小细胞外囊泡介导免疫微环境与骨再生 细胞外囊泡是一种小型囊泡结构,直径为30-150 nm,由脂质双分子层构成,源自内吞过程,并且在各种体液中普遍存在[41]。根据细胞外囊泡的起源和物理特性,可以将其分为多个亚型,其中小型细胞外囊泡是近年来研究最广泛的亚型之一。小型细胞外囊泡由于大小、水平、含量和来源的不同,具有很大的异质性,并针对特定的器官或细胞,从而导致不同的生物学功能[42]。小型细胞外囊泡是细胞间通讯的一种新模式的介质,通过细胞胞吐作用释放小型细胞外囊泡后,它们与靶细胞相互作用,并通过胞吞作用将包括蛋白质、脂质、信使RNA(mRNA)和microRNA
(miRNA)在内的细胞内成分转运到靶细胞的胞浆中,参与细胞间信号传导,导致健康和疾病状态下基因表达和细胞功能的变化[43-44]。细胞外囊泡还可以介导与分泌细胞和细胞外基质的信号级联,或者可以释放到血液和淋巴管中以发挥长距离通讯功能。小型细胞外囊泡是骨相关疾病和骨再生的无细胞治疗策略,具有纳米尺寸、无毒性、低免疫原性、生物相容性良好和使用灵活性等独特优势[45]。小型细胞外囊泡介导细胞之间的串扰,并以旁分泌方式调节免疫微环境,通过在整个细胞间微环境中传递各种生物活性分子来发挥调节功能,是骨免疫学中细胞间信号网络的重要部分[15]。最近的研究表明,源自巨噬细胞的小型细胞外囊泡在免疫应答、信号转导、细胞增殖和血管生成等不同的生物过程中发挥着至关重要的作用[46]。干细胞衍生的小型细胞外囊泡可以通过创造有益的免疫微环境,在很少的免疫反应下增强细胞增殖和功能,而来自间充质干细胞衍生的小型细胞外囊泡可以增强组织再生和免疫调节[47]。
骨髓间充质干细胞的成骨分化是骨折愈合的重要过程,骨髓间充质干细胞介导的治疗活性是免疫调节的一个重要方面,包括骨髓间充质干细胞衍生的小型细胞外囊泡。JOHNSON等[48]发现单核细胞来源的小型细胞外囊泡通过诱导骨髓间充质干细胞的成骨分化,增加RUNX2和骨形态发生蛋白2的表达,促进骨形成。骨髓间充质干细胞衍生的小型细胞外囊泡通过表达miR-136-5p抑制低密度脂蛋白受体相关蛋白4的表达,并激活Wnt/β-catenin通路,促进成骨细胞的生成,加速骨折愈合[49]。在促炎反应早期,M1来源的小型细胞外囊泡过表达miRNA-21a-5p可促进骨髓间充质干细胞的成骨分化[50]。在骨愈合晚期发生的抗炎反应中,过表达miRNA-5106的M2来源小型细胞外囊泡可抑制盐诱导激酶2,3的表达,促进成骨细胞分化和骨矿物质沉积,加速骨折愈合[51]。M2来源的小型细胞外囊泡携带的MiR-26a-5p可促进骨髓间充质干细胞中骨生成相关蛋白骨桥蛋白、碱性磷酸酶、RUNX2和Ⅱ型胶原的表达,诱导成骨细胞分化,积极促进骨再生[52]。由于成骨和血管生成密切相关,小型细胞外囊泡通过调节整个成骨-血管生成过程或巨噬细胞极化-血管生成耦合来促进骨再生。M2在促进血管生成和创面愈合中发挥重要作用,巨噬细胞来源的小型细胞外囊泡在体外和体内均具有血管生成潜能,可促进骨折部位血管的生成,从而增加血管化和营养供应[53]。
综上所述,小型细胞外囊泡在骨髓间充质干细胞和免疫细胞的细胞调控中起着至关重要的作用,从而积极影响骨再生(图4)。然而,需要更多的研究来精确地确定骨再生中外泌体免疫调节的机制以及骨骼细胞和免疫细胞之间的双边相互作用。
2.4 生物材料调节免疫微环境与骨再生
2.4.1 化学特性 骨生物材料在植入后通常会发生不同程度的降解并释放出金属离子,改变局部微环境。随着生物材料的发展,金属离子展现出多种生物学效能,包括增加成骨细胞活性、促进骨新生血管的生成以及抑制破骨细胞的分化等,在组织工程中有着重要的应用[54]。例如,镁离子(Mg2+)、锌离子(Zn2+)和钙离子(Ca2+)具有促进骨骼生长的能力,而铜离子(Cu2+)和钴离子(Co2+)具有促进血管生长的能力[55-57]。对于骨质疏松的骨缺损,锶离子(Sr2+)可以抑制破骨细胞、促进成骨[58]。各种金属离子可以通过直接调节巨噬细胞对免疫和炎症反应产生至关重要的影响,从而改善骨缺损微环境,促进骨修复和骨血管生成[59]。这些金属离子促进成骨的机制是众多而复杂的,该文将从金属离子在调节免疫微环境中的作用和机制等方面探讨金属离子在骨再生中的重要作用。
Mg2+是细胞中仅次于钾离子的第二大阳离子,镁在人体内主要存在于骨骼中,是骨组织的基本元素[60]。在炎症的早期阶段,Mg2+能够增加瞬时受体电位阳离子通道成员7的表达水平,并且Mg2+进入单核-巨噬细胞细胞系的过程依赖于瞬时受体电位阳离子通道成员7通道,从而促进有利于骨生成免疫微环境的形成[61]。中等浓度的Mg2+通过抑制Toll样受体-核因子κB信号通路诱导巨噬细胞向M2表型极化,促进白细胞介素10和白细胞介素1a的表达,抑制白细胞介素6、白细胞介素1β和肿瘤坏死因子α的表达,从而抑制炎症反应。Mg2+也刺激巨噬细胞中骨生成分子的表达,并通过骨形态发生蛋白/SMAD信号通路促进骨髓间充质干细胞的成骨分化,促进骨形成[62]。钙是骨骼健康所必需的,因为它是骨骼中最丰富的元素,提供力量和支持运动。在微观水平上,Ca2+也广泛参与多种信号通路,植入物表面Ca2+的存在可以促进纤维蛋白生物聚合和血小板活化,促进临时骨基质的形成,Ca2+修饰的种植体表面不仅可以增强骨整合,还可以减少炎症反应并促进血管化[63-64]。ZHANG等[65]研究了植入磷酸钙基生物材料后Ca2+、巨噬细胞极化和新骨形成之间的相关性,结果显示,Ca2+通过激活Wnt/β-catenin信号通路促进巨噬细胞中精氨酸酶1和白细胞介素10的转录,进而促进骨生成。Sr2+主要储存在骨组织中,特别是在新鲜骨小梁活跃生长和再生的区域。锶修饰的生物活性材料和Sr2+都具有抗炎特性,可使巨噬细胞向M2表型极化[66]。锶还调节中性粒细胞极化,导致抗炎细胞因子的产生,间接使巨噬细胞向M2表型极化[67]。Sr2+在组织工程骨中能够上调血管内皮生长因子水平,通过激活血小板衍生生长因子BB/磷脂酰肌醇3激酶/蛋白激酶B信号通路促进骨组织血管生成[68]。GUO等[69]发现,锶诱导的M2表型巨噬细胞极化促进了血小板内皮细胞黏附分子1的血管生成以及更高水平的血小板衍生生长因子BB,从而促进骨血管生成和骨再生。
锌是一种必需的微量营养素,人体中大约30%的锌储存在骨骼中,对骨骼的生长和稳定起着至关重要的作用。Zn2+促进成骨细胞的黏附、增殖和分化,促进骨钙素、Ⅰ型胶原、碱性磷酸酶、RUNX2等成骨标志物的表达[70]。Zn2+可以通过调节某些信号通路来调节炎症细胞的分化,同时,机体需要足够的锌水平来维持适当强度的免疫反应[71]。Zn2+具有通过磷脂酰肌醇3激酶/蛋白激酶B/雷帕霉素靶蛋白信号通路调节巨噬细胞向M2表型极化的能力,从而促进骨膜源性祖细胞的成骨分化[72]。LI等[73]发现氯化锂可以通过Wnt通路诱导骨髓间充质干细胞的成骨分化,促进骨再生。在巨噬细胞中,氯化锂可以抑制丝裂原活化蛋白激酶和细胞外信号调节激酶通路的磷酸化,导致M2型巨噬细胞占主导地位[74]。富含锰涂层的生物材料促进了成骨细胞的黏附,显示出增强成骨作用。YANG等[75]对锰离子抗炎特性的化学机制进行研究,发现二价锰离子向三价锰离子的转化促进了M1巨噬细胞中活性氧的消耗,使其向抗炎M2表型极化。Cu2+具有有效和有益的免疫调节特性,有助于减少炎症反应和促炎细胞因子的表达。Cu2+可以增强巨噬细胞的分泌和吞噬能力,有助于形成有益的免疫微环境[76]。XU等[77]的研究表明,铜可以在骨缺损部位招募M2型巨噬细胞,有助于形成利于H型血管生成的微环境。
综上所述,金属离子通过促进巨噬细胞向M2表型极化降低炎症反应、调节免疫微环境,促进骨血管生成和骨再生(表2)。

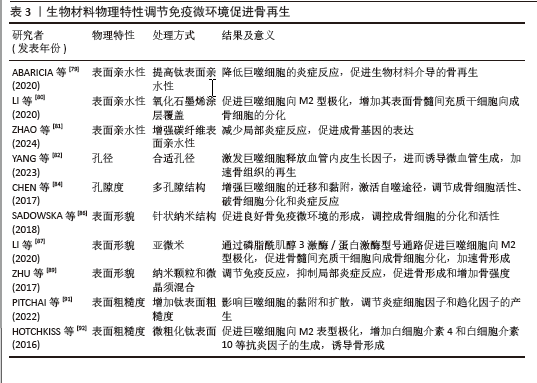
2.4.2 物理特性 成骨生物材料的表面与周围免疫环境直接接触并发生反应,免疫细胞在周围环境中受亲水性、孔隙度、孔径、表面形态和粗糙度的影响。生物材料表面的亲疏水性能够影响非特异性蛋白与生物材料的结合,进而影响骨形成的免疫微环境。疏水性表面相较于亲水性表面更能促进单核-巨噬细胞在其上的黏附,并诱发局部产生炎症反应[78]。亲水生物材料表面可减少蛋白质吸附和白细胞活化,从而降低对异物的排斥反应,通过增加生物材料的亲水性可使植入物更有效地融入骨骼。ABARICIA等[79]发现适度提高钛表面亲水性可降低巨噬细胞的炎症反应,从而促进生物材料介导的骨再生。将氧化石墨烯均匀覆盖于经过喷砂预处理及酸蚀刻加工的钛板表层,可显著增强钛板的亲水性,促进巨噬细胞向M2型极化,增加材料表面骨髓间充质干细胞向成骨细胞的分化[80]。ZHAO等[81]发现,通过特殊技术增强碳纤维聚醚醚酮材料的表面亲水性,不仅可以减少局部炎症反应,还能促进成骨基因的表达。因此,可通过增加生物材料的表面亲水性调节骨免疫微环境,促进成骨细胞分化、加速骨再生。
骨生物材料的孔隙度和孔径能够调节局部免疫反应,影响巨噬细胞极化和成骨细胞的活性。恰当微孔尺寸的生物材料能够通过营造一个微缺氧的外部环境,激发巨噬细胞释放血管内皮生长因子,进而诱导微血管生成,加速骨组织的再生[82]。孔径过小会阻碍血液运输营养物质和氧气,从而增强局部炎症反应,导致肉芽组织形成,完全堵塞微毛孔,堵塞阻止骨细胞向内生长,最终导致骨再生不良和种植体失败[83]。另有研究发现,多孔结构能够显著增强巨噬细胞的迁移和黏附,通过激活自噬途径,调节成骨细胞的活性、破骨细胞的分化和炎症反应[84]。较高的孔隙率有助于成骨细胞更好地附着和生长,促使形成紧密且结构稳固的细胞外基质,进而提升生物体在早期阶段的固定效果[85]。因此,适当大小孔隙度和孔径的生物材料通过调节免疫反应,促进骨血管生成和骨再生。
生物材料的表面形貌是另一个影响材料与免疫细胞相互作用的重要因素。
SADOWSKA等[86]认为针状纳米结构的仿生钙缺乏羟基磷灰石能够产生良好的骨免疫微环境,调控成骨细胞的分化和活性。LI等[87]比较了亚微米和微米表面形貌生物材料对免疫微环境的影响,发现亚微米表面的生物材料在体外可通过磷脂酰肌醇3激酶/蛋白激酶信号通路促进巨噬细胞向M2型极化,从而促进骨髓间充质干细胞向成骨细胞分化,加速骨形成。POSADA等[88]发现,通过特定技术在镁支架表面创造纳米结构可以增加表面面积,促进磷灰石成核,提高多孔镁支架的生物活性和耐蚀性,增强骨整合。ZHU等[89]通过对比格犬骨缺损模型研究发现,由纳米颗粒和微晶须混合组成表面的生物材料能够调节免疫反应、抑制局部炎症反应,促进骨形成和增加骨强度。因此,改变生物材料的表面形貌可以调节免疫微环境,促进成骨细胞的黏附、迁移、增殖和分化,从而促进骨形成和骨再生。
骨生物材料的表面粗糙度能够调节成骨细胞和破骨细胞的生成和活性,并且可通过抛光和喷砂改善其表面粗糙度[90]。钛是骨生物材料表面常用的金属离子,在免疫反应中起调节作用,并且钛的粗糙度能够影响细胞的黏附和扩散。当钛组成的表面粗糙度增加时,巨噬细胞的扩散也会加快;此外,钛粗糙度对巨噬细胞也有显著的刺激作用,能够调节炎症细胞因子和趋化因子的产生[91]。HOTCHKISS等[92]发现,与光滑的钛底物促进M1极化相比,微粗化的钛表面促进巨噬细胞向M2表型极化、增加白细胞介素4和白细胞介素10等抗炎因子的生成,诱导骨形成。光滑表面的生物材料可以诱导巨噬细胞向M1表型的极化,增加炎症因子的释放和局部炎症反应,而粗糙表面的生物材料可以促进巨噬细胞向M2抗炎表型的转化,增加巨噬细胞诱导的成骨细胞分化,促进骨再生[79]。因此,适当提高骨生物材料表面的粗糙度能够促进有利于骨生成免疫微环境的形成,从而促进骨生成和骨再生。生物材料物理特性调节免疫微环境促进骨再生的相关研究总结,见表3。
| [1] ZHANG H, WU S, CHEN W, et al. Bone/cartilage targeted hydrogel: Strategies and applications. Bioact Mater. 2023;23:156-69. [2] LIU T, FANG W, WU G, et al. Low Dose BMP2-Doped Calcium Phosphate Graft Promotes Bone Defect Healing in a Large Animal Model. Front Cell Dev Biol. 2020;8:613891. [3] HALL DJ, TURNER TM, URBAN RM. Healing bone lesion defects using injectable CaSO4/CaPO4 -TCP bone graft substitute compared to cancellous allograft bone chips in a canine model. J Biomed Mater Res B Appl Biomater. 2019;107(2):408-414. [4] LI J, CAO F, WU B, et al. Immobilization of bioactive vascular endothelial growth factor onto Ca-deficient hydroxyapatite-coated Mg by covalent bonding using polydopamine. J Orthop Translat. 2021;30:82-92. [5] KOUSHIK TM, MILLER CM, ANTUNES E. Bone Tissue Engineering Scaffolds: Function of Multi-Material Hierarchically Structured Scaffolds. Adv Healthc Mater. 2023;12(9): e2202766. [6] ZHU Y, GOH C, SHRESTHA A. Biomaterial Properties Modulating Bone Regeneration. Macromol Biosci. 2021;21(4):e2000365. [7] FISCHER V, HAFFNER-LUNTZER M. Interaction between bone and immune cells: Implications for postmenopausal osteoporosis. Semin Cell Dev Biol. 2022;123:14-21. [8] ZHANG J, TONG D, SONG H, et al. Osteoimmunity-Regulating Biomimetically Hierarchical Scaffold for Augmented Bone Regeneration. Adv Mater. 2022;34(36): e2202044. [9] HORTON JE, RAISZ LG, SIMMONS HA, et al. Bone resorbing activity in supernatant fluid from cultured human peripheral blood leukocytes. Science. 1972;177(4051):793-795. [10] TAKAYANAGI H, OGASAWARA K, HIDA S, et al. T-cell-mediated regulation of osteoclastogenesis by signalling cross-talk between RANKL and IFN-gamma. Nature. 2000;408(6812):600-605. [11] TAKAYANAGI H. Osteoimmunology and the effects of the immune system on bone. Nat Rev Rheumatol. 2009;5(12):667-676. [12] MORRISON SJ, SCADDEN DT. The bone marrow niche for haematopoietic stem cells. Nature. 2014;505(7483):327-334. [13] QI K, LI N, ZHANG Z, et al. Tissue regeneration: The crosstalk between mesenchymal stem cells and immune response. Cell Immunol. 2018;326:86-93. [14] YANG N, LIU Y. The Role of the Immune Microenvironment in Bone Regeneration. Int J Med Sci. 2021;18(16):3697-707. [15] LU T, ZHANG Z, ZHANG J, et al. CD73 in small extracellular vesicles derived from HNSCC defines tumour-associated immunosuppression mediated by macrophages in the microenvironment. J Extracell Vesicles. 2022;11(5):e12218. [16] LIU T, YOU Z, SHEN F, et al. Tricarboxylic Acid Cycle Metabolite-Coordinated Biohydrogels Augment Cranial Bone Regeneration Through Neutrophil-Stimulated Mesenchymal Stem Cell Recruitment and Histone Acetylation-Mediated Osteogenesis. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces. 2024;16(5):5486-5503. [17] HERATH TDK, SAIGO L, SCHALLER B, et al. In Vivo Efficacy of Neutrophil-Mediated Bone Regeneration Using a Rabbit Calvarial Defect Model. Int J Mol Sci. 2021;22(23):13016. [18] KOVTUN A, BERGDOLT S, WIEGNER R, et al. The crucial role of neutrophil granulocytes in bone fracture healing. Eur Cell Mater. 2016;32:152-162. [19] PEISELER M, KUBES P. More friend than foe: the emerging role of neutrophils in tissue repair. J Clin Invest. 2019;129(7):2629-2639. [20] CAI B, LIN D, LI Y, et al. N2-Polarized Neutrophils Guide Bone Mesenchymal Stem Cell Recruitment and Initiate Bone Regeneration: A Missing Piece of the Bone Regeneration Puzzle. Adv Sci (Weinh). 2021; 8(19):e2100584. [21] DAS A, SINHA M, DATTA S, et al. Monocyte and macrophage plasticity in tissue repair and regeneration. Am J Pathol. 2015;185(10): 2596-2606. [22] PAPAGORAS C, CHRYSANTHOPOULOU A, MITSIOS A, et al. IL-17A expressed on neutrophil extracellular traps promotes mesenchymal stem cell differentiation toward bone-forming cells in ankylosing spondylitis. Eur J Immunol. 2021;51(4):930-942. [23] BASTIAN OW, KOENDERMAN L, ALBLAS J, et al. Neutrophils contribute to fracture healing by synthesizing fibronectin+ extracellular matrix rapidly after injury. Clin Immunol. 2016;164:78-84. [24] PARK MD, SILVIN A, GINHOUX F, et al. Macrophages in health and disease. Cell. 2022;185(23):4259-4279. [25] GOU M, WANG H, XIE H, et al. Macrophages in guided bone regeneration: potential roles and future directions. Front Immunol. 2024;15:1396759. [26] SCHLUNDT C, FISCHER H, BUCHER CH, et al. The multifaceted roles of macrophages in bone regeneration: A story of polarization, activation and time. Acta Biomater. 2021; 133:46-57. [27] GONG L, ZHAO Y, ZHANG Y, et al. The Macrophage Polarization Regulates MSC Osteoblast Differentiation in vitro. Ann Clin Lab Sci. 2016;46(1):65-71. [28] ZHANG Y, BÖSE T, UNGER RE, et al. Macrophage type modulates osteogenic differentiation of adipose tissue MSCs. Cell Tissue Res. 2017;369(2):273-286. [29] VALLÉS G, BENSIAMAR F, MAESTRO-PARAMIO L, et al. Influence of inflammatory conditions provided by macrophages on osteogenic ability of mesenchymal stem cells. Stem Cell Res Ther. 2020;11(1):57. [30] LU LY, LOI F, NATHAN K, et al. Pro-inflammatory M1 macrophages promote Osteogenesis by mesenchymal stem cells via the COX-2-prostaglandin E2 pathway. J Orthop Res. 2017;35(11):2378-2385. [31] ADU-BERCHIE K, OBUSEH FO, MOONEY DJ. T Cell Development and Function. Rejuvenation Res. 2023;26(4):126-138. [32] UEHARA IA, SOLDI LR, SILVA MJB. Current perspectives of osteoclastogenesis through estrogen modulated immune cell cytokines. Life Sci. 2020;256:117921. [33] SCHLUNDT C, REINKE S, GEISSLER S, et al. Individual Effector/Regulator T Cell Ratios Impact Bone Regeneration. Front Immunol. 2019;10:1954. [34] BI CS, WANG J, QU HL, et al. Calcitriol suppresses lipopolysaccharide-induced alveolar bone damage in rats by regulating T helper cell subset polarization. J Periodontal Res. 2019;54(6):612-623. [35] CHEN F, WU Y, REN G, et al. Impact of T helper cells on bone metabolism in systemic lupus erythematosus. Hum Immunol. 2023;84(5-7):327-336. [36] LIU Y, WANG L, LIU S, et al. Transplantation of SHED prevents bone loss in the early phase of ovariectomy-induced osteoporosis. J Dent Res. 2014;93(11):1124-1132. [37] GRČEVIĆ D, SIRONI M, VALENTINO S, et al. The Long Pentraxin 3 Plays a Role in Bone Turnover and Repair. Front Immunol. 2018; 9:417. [38] FRASE D, LEE C, NACHIAPPAN C, et al. The Inflammatory Contribution of B-Lymphocytes and Neutrophils in Progression to Osteoporosis. Cells. 2023;12(13):1744. [39] KÖNNECKE I, SERRA A, EL KHASSAWNA T, et al. T and B cells participate in bone repair by infiltrating the fracture callus in a two-wave fashion. Bone. 2014;64:155-165. [40] SUN X, LI K, HASE M, et al. Suppression of breast cancer-associated bone loss with osteoblast proteomes via Hsp90ab1/moesin-mediated inhibition of TGFβ/FN1/CD44 signaling. Theranostics. 2022; 12(2):929-943. [41] KALLURI R, LEBLEU VS. The biology, function, and biomedical applications of exosomes. Science. 2020;367(6478): eaau6977. [42] SHAHIN HI, RADNAA E, TANTENGCO OAG, et al. Microvesicles and exosomes released by amnion epithelial cells under oxidative stress cause inflammatory changes in uterine cells. Biol Reprod. 2021;105(2):464-480. [43] GONG L, CHEN B, ZHANG J, et al. Human ESC-sEVs alleviate age-related bone loss by rejuvenating senescent bone marrow-derived mesenchymal stem cells. J Extracell Vesicles. 2020;9(1):1800971. [44] LIANG G, KOW ASF, THAM CL, et al. Ameliorative Effect of Tocotrienols on Perimenopausal-Associated Osteoporosis-A Review. Antioxidants (Basel). 2022;11(11): 2179. [45] LU T, LIU Y, HUANG X, et al. Early-Responsive Immunoregulation Therapy Improved Microenvironment for Bone Regeneration Via Engineered Extracellular Vesicles. Adv Healthc Mater. 2024;13(11):e2303681. [46] LIU N, DONG J, LI L, et al. Osteoimmune Interactions and Therapeutic Potential of Macrophage-Derived Small Extracellular Vesicles in Bone-Related Diseases. Int J Nanomedicine. 2023;18:2163-2180. [47] YUAN YG, WANG JL, ZHANG YX, et al. Biogenesis, Composition and Potential Therapeutic Applications of Mesenchymal Stem Cells Derived Exosomes in Various Diseases. Int J Nanomedicine. 2023;18:3177-3210. [48] JOHNSON BL III, KUETHE JW, CALDWELL CC. Neutrophil derived microvesicles: emerging role of a key mediator to the immune response. Endocr Metab Immune Disord Drug Targets. 2014;14(3):210-217. [49] YU H, ZHANG J, LIU X, et al. microRNA-136-5p from bone marrow mesenchymal stem cell-derived exosomes facilitates fracture healing by targeting LRP4 to activate the Wnt/β-catenin pathway. Bone Joint Res. 2021; 10(12):744-758. [50] LIU K, LUO X, LV Z Y, et al. Macrophage-Derived Exosomes Promote Bone Mesenchymal Stem Cells Towards Osteoblastic Fate Through microRNA-21a-5p. Front Bioeng Biotechnol. 2021;9:801432. [51] XIONG Y, CHEN L, YAN C, et al. M2 Macrophagy-derived exosomal miRNA-5106 induces bone mesenchymal stem cells towards osteoblastic fate by targeting salt-inducible kinase 2 and 3. J Nanobiotechnology. 2020;18(1):66. [52] BIN-BIN Z, DA-WA Z X, CHAO L, et al. M2 macrophagy-derived exosomal miRNA-26a-5p induces osteogenic differentiation of bone mesenchymal stem cells. J Orthop Surg Res. 2022;17(1):137. [53] GANGADARAN P, RAJENDRAN RL, OH JM, et al. Extracellular vesicles derived from macrophage promote angiogenesis In vitro and accelerate new vasculature formation In vivo. Exp Cell Res. 2020;394(2):112146. [54] LI S, CUI Y, LIU H, et al. Application of bioactive metal ions in the treatment of bone defects. J Mater Chem B. 2022;10(45):9369-9388. [55] KANG Y, XU C, MENG L, et al. Exosome-functionalized magnesium-organic framework-based scaffolds with osteogenic, angiogenic and anti-inflammatory properties for accelerated bone regeneration. Bioact Mater. 2022;18:26-41. [56] QIN S, NIU Y, ZHANG Y, et al. Metal Ion-Containing Hydrogels: Synthesis, Properties, and Applications in Bone Tissue Engineering. Biomacromolecules. 2024;25(6):3217-3248. [57] KANG Z, WU B, ZHANG L, et al. Metabolic regulation by biomaterials in osteoblast. Front Bioeng Biotechnol. 2023;11:1184463. [58] YOU J, ZHANG Y, ZHOU Y. Strontium Functionalized in Biomaterials for Bone Tissue Engineering: A Prominent Role in Osteoimmunomodulation. Front Bioeng Biotechnol. 2022;10:928799. [59] BOSCH-RUÉ È, DÍEZ-TERCERO L, BUITRAGO J O, et al. Angiogenic and immunomodulation role of ions for initial stages of bone tissue regeneration. Acta Biomater. 2023;166:14-41. [60] FIORENTINI D, CAPPADONE C, FARRUGGIA G, et al. Magnesium: Biochemistry, Nutrition, Detection, and Social Impact of Diseases Linked to Its Deficiency. Nutrients. 2021;13(4):1136. [61] QIAO W, WONG K HM, SHEN J, et al. TRPM7 kinase-mediated immunomodulation in macrophage plays a central role in magnesium ion-induced bone regeneration . Nat Commun; 2021;12(1):2885. [62] ZHANG X, CHEN Q, MAO X. Magnesium Enhances Osteogenesis of BMSCs by Tuning Osteoimmunomodulation. Biomed Res Int. 2019;2019:7908205. [63] ANITUA E, TEJERO R. Provisional Matrix Formation at Implant Surfaces-The Bridging Role of Calcium Ions. Cells. 2022;11(19):3048. [64] ROMERO-GAVILÁN F, CERQUEIRA A, ANITUA E, et al. Protein adsorption/desorption dynamics on Ca-enriched titanium surfaces: biological implications. J Biol Inorg Chem. 2021;26(6): 715-726. [65] ZHANG J, WU Q, YIN C, et al. Sustained calcium ion release from bioceramics promotes CaSR-mediated M2 macrophage polarization for osteoinduction. J Leukoc Biol. 2021;110(3):485-496. [66] NARUPHONTJIRAKUL P, LI S, PINNA A, et al. Interaction of monodispersed strontium containing bioactive glass nanoparticles with macrophages. Biomater Adv. 2022;133: 112610. [67] LI T, HE H, YANG Z, et al. Strontium-doped gelatin scaffolds promote M2 macrophage switch and angiogenesis through modulating the polarization of neutrophils. Biomater Sci. 2021;9(8):2931-2946. [68] SUN Y, LI Y, ZHANG Y, et al. A polydopamine-assisted strontium-substituted apatite coating for titanium promotes osteogenesis and angiogenesis via FAK/MAPK and PI3K/AKT signaling pathways. Mater Sci Eng C Mater Biol Appl. 2021;131:112482. [69] GUO S, YU D, XIAO X, et al. A vessel subtype beneficial for osteogenesis enhanced by strontium-doped sodium titanate nanorods by modulating macrophage polarization. J Mater Chem B. 2020;8(28):6048-6058. [70] QIAO Y, ZHANG W, TIAN P, et al. Stimulation of bone growth following zinc incorporation into biomaterials. Biomaterials. 2014;35(25):6882-6897. [71] SUZUKI M, SUZUKI T, WATANABE M, et al. Role of intracellular zinc in molecular and cellular function in allergic inflammatory diseases. Allergol Int. 2021;70(2):190-200. [72] HUANG X, HUANG D, ZHU T, et al. Sustained zinc release in cooperation with CaP scaffold promoted bone regeneration via directing stem cell fate and triggering a pro-healing immune stimuli. J Nanobiotechnology. 2021;19(1):207. [73] LI J, WANG W, LI M, et al. Repair of segmental bone defect using tissue engineered heterogeneous deproteinized bone doped with lithium. Sci Rep. 2021;11(1):4819. [74] YANG C, WANG W, ZHU K, et al. Lithium chloride with immunomodulatory function for regulating titanium nanoparticle-stimulated inflammatory response and accelerating osteogenesis through suppression of MAPK signaling pathway. Int J Nanomedicine. 2019; 14:7475-7488. [75] YANG B, YAO H, YANG J, et al. In Situ Synthesis of Natural Antioxidase Mimics for Catalytic Anti-Inflammatory Treatments: Rheumatoid Arthritis as an Example. J Am Chem Soc. 2022; 144(1):314-330. [76] HUO S, LIU S, LIU Q, et al. Copper-Zinc-Doped Bilayer Bioactive Glasses Loaded Hydrogel with Spatiotemporal Immunomodulation Supports MRSA-Infected Wound Healing. Adv Sci (Weinh). 2024;11(5):e2302674. [77] XU D, QIAN J, GUAN X, et al. Copper-Containing Alloy as Immunoregulatory Material in Bone Regeneration via Mitochondrial Oxidative Stress. Front Bioeng Biotechnol. 2020;8: 620629. [78] LI N, XU Z, ZHENG S, et al. Superamphiphilic TiO(2) Composite Surface for Protein Antifouling. Adv Mater. 2021;33(25):e2003559. [79] ABARICIA JO, SHAH AH, MUSSELMAN RM, et al. Hydrophilic titanium surfaces reduce neutrophil inflammatory response and NETosis. Biomater Sci. 2020;8(8):2289-2299. [80] LI Q, SHEN A, WANG Z. Enhanced osteogenic differentiation of BMSCs and M2-phenotype polarization of macrophages on a titanium surface modified with graphene oxide for potential implant applications. RSC Adv. 2020; 10(28):16537-16550. [81] ZHAO S, ZHOU X, DANG J, et al. Construction of a layer-by-layer self-assembled rosemarinic acid delivery system on the surface of CFRPEEK implants for enhanced anti-inflammatory and osseointegration activities. J Mater Chem B. 2024;12(12):3031-3046. [82] YANG X, GAO J, YANG S, et al. Pore size-mediated macrophage M1 to M2 transition affects osseointegration of 3D-printed PEEK scaffolds. Int J Bioprint. 2023;9(5):755. [83] SHIBAHARA K, HAYASHI K, NAKASHIMA Y, et al. Controlling the pore size of carbonate apatite honeycomb scaffolds enhances orientation and strength of regenerated bone. Biomater Adv. 2025;166:214026. [84] CHEN Z, NI S, HAN S, et al. Nanoporous microstructures mediate osteogenesis by modulating the osteo-immune response of macrophages. Nanoscale. 2017;9(2):706-718. [85] HAN Q, WANG C, CHEN H, et al. Porous Tantalum and Titanium in Orthopedics: A Review. ACS Biomater Sci Eng. 2019;5(11): 5798-5824. [86] SADOWSKA JM, WEI F, GUO J, et al. Effect of nano-structural properties of biomimetic hydroxyapatite on osteoimmunomodulation. Biomaterials. 2018;181:318-332. [87] LI M, GUO X, QI W, et al. Macrophage polarization plays roles in bone formation instructed by calcium phosphate ceramics. J Mater Chem B. 2020;8(9):1863-1877. [88] POSADA VM, RAMíREZ J, CIVANTOS A, et al. Ion-bombardment-driven surface modification of porous magnesium scaffolds: Enhancing biocompatibility and osteoimmunomodulation. Colloids Surf B Biointerfaces. 2024;234:113717. [89] ZHU Y, ZHANG K, ZHAO R, et al. Bone regeneration with micro/nano hybrid-structured biphasic calcium phosphate bioceramics at segmental bone defect and the induced immunoregulation of MSCs. Biomaterials. 2017;147:133-144. [90] MATOS GRM. Surface Roughness of Dental Implant and Osseointegration. J Maxillofac Oral Surg. 2021;20(1):1-4. [91] PITCHAI M, IPE D, TADAKAMADLA S, et al. Titanium Implant Surface Effects on Adherent Macrophage Phenotype: A Systematic Review. Materials (Basel). 2022;15(20):7314. [92] HOTCHKISS KM, REDDY GB, HYZY SL, et al. Titanium surface characteristics, including topography and wettability, alter macrophage activation. Acta Biomater. 2016;31:425-434. |
| [1] | 傅振燚, 李俊豪, 张雅婷, 何昀锴, 刘俊妤, 魏云昊, 刘佳鑫. 施万细胞促进外周神经再生:回顾与展望[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2026, 30(5): 1236-1246. |
| [2] | 刘新月, 李春年, 李一卓, 徐世芳. 口腔牙槽骨缺损的再生修复[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2026, 30(5): 1247-1259. |
| [3] | 曹文琪, 冯秀芝, 赵 奕, 王智民, 陈怡然, 杨 潇, 任艳玲. 巨噬细胞极化对2型糖尿病性骨质疏松症成骨-成血管偶联的影响[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2026, 30(4): 917-925. |
| [4] | 余诗宇, 俞苏桐, 徐 杨, 镇祥燕, 韩凤选. 组织工程治疗策略在口腔黏膜下纤维化中的研究与应用进展[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2026, 30(4): 936-948. |
| [5] | 顾健美, 袁坤山, 周 强, 张海军, . 激光微孔化脱细胞支架在组织再生中的应用[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2026, 30(2): 499-507. |
| [6] | 杨凤丽, 周 朝, 熊 伟, 周宇翔, 李登顺, 王 鑫, 李展振. 3D打印聚乳酸骨支架修复骨缺损[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2026, 30(2): 507-515. |
| [7] | 许文和, 李小兵, 刘 芳. 功能化仿生矿化胶原修饰的骨科植入物[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2026, 30(2): 516-527. |
| [8] | 姜 侃, 阿力木江·阿不都肉苏力, 沙拉依丁·艾尔西丁, 艾克拜尔江·艾赛提, 库提鲁克·守克尔, 艾克热木江·木合热木. 生物材料与骨再生:研究热点及有影响力的500篇文献分析[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2026, 30(2): 528-536. |
| [9] | 张其娅, 童伊翔, 杨世姣, 张宇梦, 邓 凌, 吴 玮, 解 瑶, 廖 健, 毛 岭. 梯度玻璃分级超透氧化锆的体外生物相容性[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2026, 30(2): 443-450. |
| [10] | 王 卓, 孙盼盼, 程焕芝, 曹婷婷. 壳聚糖在口腔软硬组织修复与再生中的应用[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2026, 30(2): 459-468. |
| [11] | 王 域, 范民杰, 郑朋飞. 多重刺激响应性水凝胶在骨损伤修复中的应用:特殊响应能力及多样性功能[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2026, 30(2): 469-479. |
| [12] | 谢培森, 关振鹏, 魏贤杰, 张克石, 康清源, 肖文韬, 郭晓帅. 二氧化铈纳米粒调控M1巨噬细胞影响成纤维细胞共培养体系的炎症因子表达[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2026, 30(2): 375-383. |
| [13] | 闫启全, 杨立斌, 李梦君, 倪亚卓, 陈科颖, 许 博, 李耀扬, 马士卿, 李 睿, 李建文. 负载抗菌肽KR-12-a5猪小肠黏膜下层复合纳米羟基磷灰石生物支架的制备及抗菌性能[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2026, 30(2): 384-394. |
| [14] | 赵 铮. 具有抗凝和释药双重功能的双硒聚氨酯涂层[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2026, 30(2): 414-423. |
| [15] | 袁 茜, 张 昊, 庞 杰. 负载柚皮苷壳聚糖/β-磷酸三钙支架的表征及生物学性能[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2026, 30(2): 424-432. |
骨组织工程是一种治疗骨缺损和严重骨折的潜在替代方法,它使用生物材料、细胞和生长因子来诱导骨再生[5]。生物材料为细胞增殖、黏附和分化提供空间,而生长因子可以通过自分泌和旁分泌调节细胞分化、分裂和基质合成。生物材料和生长因子的出现促进了骨科疾病治疗新方法的发展。研究发现,将基于蛋白质的生长因子与特定的支架生物材料相结合,可以显著改善骨组织的再生过程[6]。随着对“骨免疫学”的深入了解和组织工程的不断发展,免疫微环境和骨再生之间的相互作用受到了更多的关注。骨细胞和免疫细胞不仅共存于骨髓腔内,而且具有共同的祖细胞,共享多种调节分子[7],因此,骨细胞可影响免疫反应,相反,免疫细胞能够调节骨细胞的增殖和分化。免疫微环境在骨组织的愈合、修复和再生中起着至关重要的作用,它决定了骨组织再生的能力[8]。该文重点介绍免疫细胞调节免疫微环境促进骨再生的机制、小细胞外囊泡介导的免疫调节促进骨再生以及骨生物材料调节免疫微环境在骨再生中发挥的积极影响。
中国组织工程研究杂志出版内容重点:人工关节;骨植入物;脊柱;骨折;内固定;数字化骨科;组织工程
1.1.1 检索人及检索时间 由第一作者在2024年11月完成文献检索。
1.1.2 文献检索时限 各数据库建库至2024年11月。
1.1.3 检索数据库 PubMed数据库、中国知网、万方数据库及维普数据库。
1.1.4 检索词 以“骨免疫学,免疫微环境,小细胞外囊泡,骨再生,骨组织修复,生物材料,组织工程”为中文检索词,以“Osteoimmunology,Immune Microenvironment,Small Extracellular Vesicles,Bone Regeneration,Bone Tissue Repair,Biomaterials,Tissue Engineering”为英文检索词。
1.1.5 检索文献类型 研究原著、学位论文和综述。
1.1.6 手工检索情况 对文献中具有高价值和重要意义的参考文献,进行手动检索并考虑是否采纳。
1.1.7 检索策略 以中国知网与PubMed数据库检索策略为例,见图1。
1.2 入组标准
纳入标准:①研究内容为免疫微环境影响骨再生或骨组织修复相关的文献;②与小细胞外囊泡调节局部微环境影响骨再生相关的文献;③与生物材料、金属离子、骨组织工程调节骨形成相关的文献;④优先选择最近10年内发表的文献。
排除标准:①研究内容与文章主题无关的文献;②观点陈旧或存在争议的文献;③缺乏创新性、可读性较低的文献。
1.3 文献质量评价和筛选 共检索到2 463篇文献,初筛剔除重复文献后,通过泛读对剩余文献的标题、摘要进行筛选,无法判别时精读全文,选取与主题更为相符的文献,最终纳入符合要求的文献92篇,全部为英文文献。文献筛选流程详见图2。
3.2 该综述区别于他人他篇的特点 该文从免疫细胞调节免疫微环境促进骨再生为切入点,详细描述了常见免疫细胞调节免疫微环境促进骨再生的机制。免疫细胞与骨细胞共同组成免疫微环境,免疫细胞可以直接或间接调控骨细胞的分化、增殖和迁移,在骨再生过程中的不同阶段发挥重要作用。小细胞外囊泡是一种新型细胞间信息传导的介质,通过旁分泌方式调节免疫微环境。该文阐述了不同细胞衍生的小型细胞外囊泡在骨再生中的作用,重点介绍骨髓间充质干细胞和巨噬细胞来源的小型细胞外囊泡通过调节免疫微环境促进成骨细胞分化、骨血管生成和成骨。该文归纳总结了生物材料表面金属离子、表面亲水性、孔隙度、孔径、表面形态和表面粗糙度均能直接调节免疫微环境,具有降低局部炎症反应、促进成骨细胞生成和血管生成的作用,从而促进骨组织再生。
3.3 该综述的局限性 限于文献检索和阅读量不足,骨免疫学的研究不够深入,该文只描述了免疫细胞调节免疫微环境影响骨再生的机制,对免疫因子等其他因素的阐述较少。目前关于小型细胞外囊泡调节免疫微环境促进骨再生的研究仍处于起步阶段,相关文献报道较少,该文重点阐述了携带miRNA的小细胞外囊泡在调节免疫微环境影响骨再生中的作用。骨再生的主要机制是促进成骨细胞的骨形成和抑制破骨细胞的骨吸收,该文重点阐述了小型细胞外囊泡调节免疫微环境促进成骨细胞的骨形成,忽略了小型细胞外囊泡对破骨细的影响。生物材料的化学特性包含表面涂层、表面化学改性、生物活性离子、表面电荷、表面官能团等,该文重点描述了化学金属离子调节免疫微环境促进骨再生。
3.4 该综述的重要意义 该文通过系统梳理和阐述免疫细胞调节免疫微环境在骨再生中的机制,有助于人们对骨再生这一复杂生理过程的深入理解。该文揭示了免疫细胞与骨细胞之间的相互作用,为理解骨再生的机制提供了新的视角。该文系统描述了小型细胞外囊泡调节免疫微环境促进骨再生的机制和潜在治疗策略,为骨再生的研究发现新的视角和切入点,可能成为骨再生研究的下一个热点。该文归纳了生物材料表面的金属离子和物理特性对免疫微环境和骨再生的积极影响,这不仅为骨科医生治疗骨缺损和严重骨折等骨骼疾病提供了新的思路和方法,也为新型生物材料的研究提供理论支持。
3.5 课题专家组对未来的建议 生物材料与免疫调节疗法的结合对组织工程和再生医学领域的发展具有重要的意义。尽管已经开发出许多增强组织再生和介导免疫调节的生物材料,但大多数研究尚未转化为临床,为了使生物材料的临床应用,应选择具有高生物安全性的材料。另外,还需要关注生物材料的精确瞄准和控制释放问题,这两方面的优化能使生物材料实现对免疫微环境的精准调控,促进其临床转化。许多关于骨生物材料调节免疫微环境的研究都集中在巨噬细胞,而其他免疫细胞(包括T细胞、B细胞和中性粒细胞)影响骨生物材料性能和功能的研究仍然缺乏,建议今后应将更多的研究重点放在全面探索免疫细胞与新型骨生物材料的关系上,并且骨生物材料的开发必须考虑免疫系统调节局部微环境和促进骨再生的能力。
中国组织工程研究杂志出版内容重点:人工关节;骨植入物;脊柱;骨折;内固定;数字化骨科;组织工程
文题释义:
免疫微环境:由骨髓间充质干细胞、成骨细胞、破骨细胞、各种免疫细胞、造血细胞和分泌的细胞因子共同组成的微环境,在骨再生过程中发挥着重要的调节作用。骨再生:是一个复杂的、精心策划的骨形成生理过程,涉及多种细胞类型以及细胞内和细胞外分子信号传导途径,以促进骨骼修复和恢复骨骼功能,最常见的骨再生形式是骨折愈合。
生物材料与免疫调节疗法的结合对组织工程和再生医学领域的发展具有重要的意义。尽管已经开发出许多增强组织再生和介导免疫调节的生物材料,但大多数研究尚未转化为临床。为了使生物材料的临床应用,应选择具有高生物安全性的材料。另外,还需要关注生物材料的精确瞄准和控制释放问题,这两方面的优化能使生物材料实现对免疫微环境的精准调控,促进其临床转化。此外,许多关于骨生物材料调节免疫微环境的研究都集中在巨噬细胞,而其他免疫细胞(包括T细胞、B细胞和中性粒细胞)在影响骨生物材料性能和功能的研究仍然缺乏。建议今后应将更多的研究重点放在全面探索免疫细胞与新型骨生物材料的关系上,并且骨生物材料的开发必须考虑免疫系统调节局部微环境和促进骨再生的能力。
#br#
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||