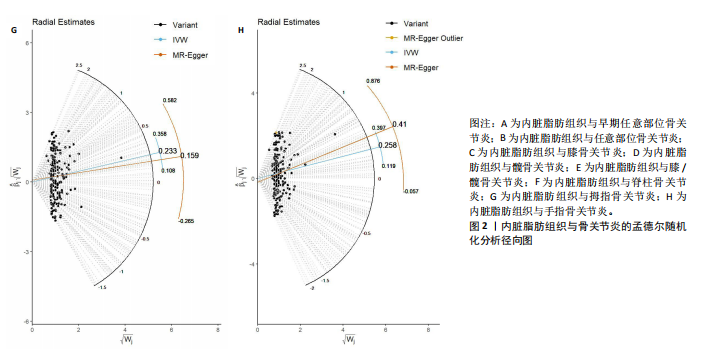
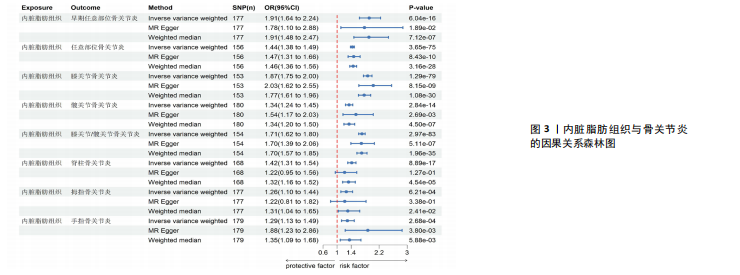
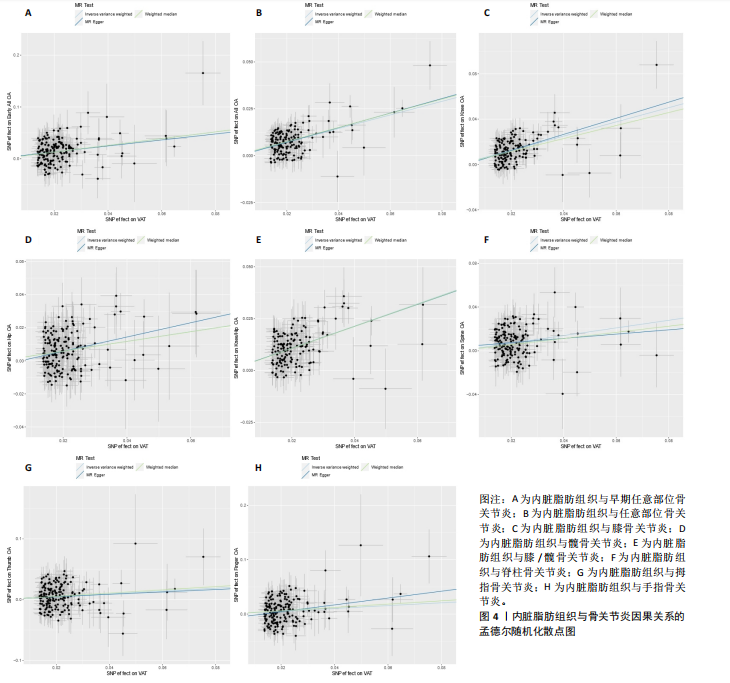
[1] KATZ JN, ARANT KR, LOESER RF. Diagnosis and Treatment of Hip and Knee Osteoarthritis: A Review. JAMA. 2021; 325(6):568-578.
[2] RAGNI E, MANGIAVINI L, VIGANÒ M, et al. Management of Osteoarthritis During the COVID‐19 Pandemic. Clin Pharmacol Ther.2020;108(4):719-729.
[3] QUICKE JG, CONAGHAN PG, CORP N, et al. Osteoarthritis year in review 2021: epidemiology & therapy. Osteoarthritis Cartilage. 2022;30(2):196-206.
[4] HUNTER DJ, MARCH L, CHEW M. Osteoarthritis in 2020 and beyond: a Lancet Commission. Lancet. 2020;396(10264): 1711-1712.
[5] PAPATHANASIOU I, ANASTASOPOULOU L, TSEZOU A. Cholesterol metabolism related genes in osteoarthritis. Bone. 2021;152: 116076.
[6] ALISSA EM, ALZUGHAIBI LS, MARZOUKI ZM.
Dietary intake of fatty acids and antioxidants in relation to radiographic knee osteoarthritis: results from a case-control study. J Hum Nutr Diet, 2020;33(3):431-438.
[7] KHANNA D, PELTZER C, KAHAR P, et al. Body Mass Index (BMI): A Screening Tool Analysis. Cureus. 2022;14(2):e22119.
[8] ARSENAULT BJ, CARPENTIER AC, POIRIER P, et al. Adiposity, type 2 diabetes and atherosclerotic cardiovascular disease risk: Use and abuse of the body mass index. Atherosclerosis. 2024;14:117546.
[9] ZENG Q, WANG L, DONG S, et al. CT-derived abdominal adiposity: Distributions and better predictive ability than BMI in a nationwide study of 59,429 adults in China. Metabolism. 2021;115:154456.
[10] DHOKTE S, CZAJA K. Visceral Adipose Tissue: The Hidden Culprit for Type 2 Diabetes. Nutrients. 2024;16(7):1015.
[11] TOUSSIROT E, MICHEL F, BEREAU M, et al. Serum adipokines, adipose tissue measurements and metabolic parameters in patients with advanced radiographic knee osteoarthritis. Clin Rheumatol. 2017; 36(11):2531-2539.
[12] LI S, SCHWARTZ AV, LAVALLEY MP, et al. Association of Visceral Adiposity With Pain but Not Structural Osteoarthritis. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2020;72(7):1103-1110.
[13] CHEN LG, TUBBS JD, LIU Z, et al. Mendelian randomization: causal inference leveraging genetic data. Psychol Med. 2024;19:1-14.
[14] GILL D, WALKER VM, MARTIN RM, et al. Comparison with randomized controlled trials as a strategy for evaluating instruments in Mendelian randomization. Int J Epidemiol. 2020;49(4):1404-1406.
[15] KARLSSON T, RASK-ANDERSEN M, PAN G, et al. Contribution of genetics to visceral adiposity and its relation to cardiovascular and metabolic disease. Nat Med. 2019; 25(9):1390-1395.
[16] BOER CG, HATZIKOTOULAS K, SOUTHAM L, et al. Deciphering osteoarthritis genetics across 826,690 individuals from 9 populations. Cell. 2021;184(24):6003-6005.
[17] BURGESS S, THOMPSON SG. Avoiding bias from weak instruments in Mendelian randomization studies. Int J Epidemiol. 2011;40(3):755-764.
[18] BURGESS S, BUTTERWORTH A, THOMPSON SG. Mendelian randomization analysis with multiple genetic variants using summarized data. Genet Epidemiol. 2013;37(7):658-665.
[19] BOWDEN J, DAVEY SG, HAYCOCK PC, et al. Consistent Estimation in Mendelian Randomization with Some Invalid Instruments Using a Weighted Median Estimator. Genet Epidemiol. 2016;40(4): 304-314.
[20] BOWDEN J, DAVEY SG, BURGESS S. Mendelian randomization with invalid instruments: effect estimation and bias detection through Egger regression. Int J Epidemiol. 2015;44(2):512-525.
[21] DAVEY SG, HEMANI G. Mendelian randomization: genetic anchors for causal inference in epidemiological studies. Hum Mol Genet. 2014;23(R1):R89-R98.
[22] BOWDEN J, SPILLER W, DEL GMF, et al. Improving the visualization, interpretation and analysis of two-sample summary data Mendelian randomization via the Radial plot and Radial regression. Int J Epidemiol. 2018;47(4):1264-1278.
[23] VERBANCK M, CHEN CY, NEALE B, et al. Detection of widespread horizontal pleiotropy in causal relationships inferred from Mendelian randomization between complex traits and diseases. Nat Genet. 2018;50(5):693-698.
[24] ZHAO Q, CHEN Y, WANG J, et al. Powerful three-sample genome-wide design and robust statistical inference in summary-data Mendelian randomization. Int J Epidemiol. 2019;48(5):1478-1492.
[25] HEMANI G, TILLING K, DAVEY SG. Orienting the causal relationship between imprecisely measured traits using GWAS summary data. PLoS Genet. 2017;13(11):e1007081.
[26] BURGESS S, BOWDEN J, FALL T, et al. Sensitivity Analyses for Robust Causal Inference from Mendelian Randomization Analyses with Multiple Genetic Variants. Epidemiology. 2017;28(1):30-42.
[27] CURTIN F, SCHULZ P. Multiple correlations and Bonferroni’s correction. Biol Psychiatry. 1998;44(8):775-777.
[28] HEMANI G, ZHENG J, ELSWORTH B, et al. The MR-Base platform supports systematic causal inference across the human phenome. Elife. 2018;7:e34408.
[29] REYES C, LEYLAND KM, PEAT G, et al. Association Between Overweight and Obesity and Risk of Clinically Diagnosed Knee, Hip, and Hand Osteoarthritis: A Population-Based Cohort Study. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2016;68(8):1869-1875.
[30] MAGNUSSON K, SLATKOWSKY-CHRISTENSEN B, VAN DER HEIJDE D, et al. Body mass index and progressive hand osteoarthritis: data from the Oslo hand osteoarthritis cohort. Scand J Rheumatol. 2015;44(4):331-336.
[31] HOVEIDAEI AH, NAKHOSTIN-ANSARI A, CHALIAN M, et al. Burden of Hand Osteoarthritis in the Middle East and North Africa (MENA): An Epidemiological Analysis From 1990 to 2019. J Hand Surg Am. 2023; 48(3):245-256.
[32] GLOERSEN M, STEEN PP, NEOGI T, et al. Associations of Body Mass Index With Pain and the Mediating Role of Inflammatory Biomarkers in People With Hand Osteoarthritis. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2022;74(5):810-817.
[33] YUAN J, WANG D, ZHANG Y, et al. Genetically predicted obesity and risk of hip osteoarthritis. Eat Weight Disord. 2023;28(1):11.
[34] FUNCK BRENTANO T, NETHANDER M, MOVÉRARE SKRTIC S, et al. Causal Factors for Knee, Hip, and Hand Osteoarthritis: A Mendelian Randomization Study in the UK Biobank. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2019; 71(10):1634-1641.
[35] GRECO F, PICCOLO CL, D’ANDREA V, et al. Fat Matters: Exploring Cancer Risk through the Lens of Computed Tomography and Visceral Adiposity. J Clin Med. 2024;13(2): 453.
[36] BELEN E, KARAMAN O, CALISKAN G, et al. An indicator of subclinical cardiovascular disease in patients with primary osteoarthritis: epicardial fat thickness. Int J Clin Exp Med. 2015;8(6):9491-9497.
[37] VISSER AW, IOAN-FACSINAY A, DE MUTSERT R, et al. Adiposity and hand osteoarthritis: the Netherlands Epidemiology of Obesity study. Arthritis Res Ther. 2014;16(1):R19.
[38] LEVESCOT A, CHANG MH, SCHNELL J, et al. IL-1beta-driven osteoclastogenic Tregs accelerate bone erosion in arthritis. J Clin Invest. 2021;131(18):e141008.
[39] LIU S, DENG Z, CHEN K, et al. Cartilage tissue engineering: From proinflammatory and anti‑inflammatory cytokines to osteoarthritis treatments (Review). Mol Med Rep. 2022;25(3):99.
[40] LIN J, JIA S, ZHANG W, et al. Recent Advances in Small Molecule Inhibitors for the Treatment of Osteoarthritis. J Clin Med. 2023;12(5):1986.
[41] DU X, LIU ZY, TAO XX, et al. Research Progress on the Pathogenesis of Knee Osteoarthritis. Orthop Surg. 2023;15(9): 2213-2224.
[42] MOLNAR V, MATISIC V, KODVANJ I, et al. Cytokines and Chemokines Involved in Osteoarthritis Pathogenesis. Int J Mol Sci.2021;22(17):9208.
[43] WANG T, HE C. Pro-inflammatory cytokines: The link between obesity and osteoarthritis. Cytokine Growth Factor Rev. 2018;44:38-50.
[44] KOYAMA T, UCHIDA K, FUKUSHIMA K, et al. Elevated levels of TNF-α, IL-1β and IL-6 in the synovial tissue of patients with labral tear: a comparative study with hip osteoarthritis. BMC Musculoskelet Disord. 2021;22(1):33.
[45] AIT ELDJOUDI D, CORDERO BARREAL A, GONZALEZ-RODRÍGUEZ M, et al. Leptin in Osteoarthritis and Rheumatoid Arthritis: Player or Bystander? Int J Mol Sci. 2022; 23(5):2859.
[46] CASADO ME, COLLADO-PEREZ R, FRAGO LM, et al. Recent Advances in the Knowledge of the Mechanisms of Leptin Physiology and Actions in Neurological and Metabolic Pathologies. Int J Mol Sci. 2023;24(2):1422.
[47] JIANG M, HE J, SUN Y, et al. Leptin Induced TLR4 Expression via the JAK2-STAT3 Pathway in Obesity-Related Osteoarthritis. Oxid Med Cell Longev. 2021;2021:7385160.
[48] CORDERO-BARREAL A, GONZALEZ-RODRIGUEZ M, RUIZ-FERNANDEZ C, et al. An Update on the Role of Leptin in the Immuno-Metabolism of Cartilage. Int J Mol Sci. 2021;22(5):2411.
[49] FU Y, BATUSHANSKY A, KINTER M, et al. Effects of Leptin and Body Weight on Inflammation and Knee Osteoarthritis Phenotypes in Female Rats. JBMR Plus. 2023;7(7):e10754.
[50] CUZDAN CN, AY S, EVCIK FD, et al. Adiponectin: is it a biomarker for assessing the disease severity in knee osteoarthritis patients? Int J Rheum Dis. 2017;20(12):1942-1949.
[51] TANG Q, HU Z, SHEN L, et al. Association of osteoarthritis and circulating adiponectin levels: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Lipids Health Dis. 2018;17(1):189.
[52] ILIA I, NITUSCA D, MARIAN C. Adiponectin in Osteoarthritis: Pathophysiology, Relationship with Obesity and Presumptive Diagnostic Biomarker Potential. Diagnostics (Basel). 2022;12(2):455. |