[1] BUCK DW 2ND, DUMANIAN GA. Bone biology and physiology: Part I. The fundamentals. Plast Reconstr Surg. 2012; 129(6):1314-1320.
[2] CHILIBECK PD, SALE DG, WEBBER CE. Exercise and bone mineral density. Sports Med. 1995;19(2):103-122.
[3] CHEN M, GERGES M, RAYNOR WY, et al. State of the Art Imaging of Osteoporosis. Semin Nucl Med. 2024;54(3):415-426.
[4] LIU K, LIU P, LIU R, et al. Relationship between serum leptin levels and bone mineral density: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Clin Chim Acta. 2015;444: 260-263.
[5] LEE S, KIM JH, JEON YK, et al. Effect of adipokine and ghrelin levels on BMD and fracture risk: an updated systematic review and meta-analysis. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2023;14:1044039.
[6] HARTLEY A, SANDERSON E, GRANELL R, et al. Using multivariable Mendelian randomization to estimate the causal effect of bone mineral density on osteoarthritis risk, independently of body mass index. Int J Epidemiol. 2022;51(4):1254-1267.
[7] GIELEN E, DUPONT J, DEJAEGER M, et al. Sarcopenia, osteoporosis and frailty. Metabolism. 2023;145:155638.
[8] LASKOU F, FUGGLE NR, PATEL HP, et al. Associations of osteoporosis and sarcopenia with frailty and multimorbidity among participants of the Hertfordshire Cohort Study. J Cachexia Sarcopenia Muscle. 2022; 13(1):220-229.
[9] 李明嘉,赵苗妙,杨金奎.组织蛋白酶在糖尿病及糖尿病肾病作用机制中的研究进展[J].首都医科大学学报,2023,44(3): 413-419.
[10] YADATI T, HOUBEN T, BITORINA A, et al. The Ins and Outs of Cathepsins: Physiological Function and Role in Disease Management. Cells. 2020;9(7):1679.
[11] 董飞,王玲.绝经后女性骨转换生化标志物水平与骨密度的相关性分析[J].检验医学与临床,2021,18(9):1323-1325.
[12] LEE GH, HOANG TH, LEE HY, et al. Ramie leaf Extract Alleviates Bone Loss in Ovariectomized Rats-The Involvement of ROS and Its Associated Signalings. Nutrients. 2023;15(3):745.
[13] LU J, WANG M, WANG Z, et al. Advances in the discovery of cathepsin K inhibitors on bone resorption. J Enzyme Inhib Med Chem. 2018;33(1):890-904.
[14] GAO LH, LI SS, YUE H, et al. Associations of Serum Cathepsin K and Polymorphisms in CTSK Gene With Bone Mineral Density and Bone Metabolism Markers in Postmenopausal Chinese Women. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2020;11:48.
[15] CLAYTON GL, GONÇALVES A, SOARES, et al. A framework for assessing selection and misclassification bias in mendelian randomisation studies: an illustrative example between body mass index and covid-19. BMJ. 2023;381:e072148.
[16] NAZARZADEH M, PINHO-GOMES AC, BIDEL Z, et al. Plasma lipids and risk of aortic valve stenosis: a Mendelian randomization study. Eur Heart J. 2020;41(40):3913-3920.
[17] BURGESS S, SCOTT RA, TIMPSON NJ, et al. EPIC- InterAct Consortium. Using published data in Mendelian randomization: a blueprint for efficient identification of causal risk factors. Eur J Epidemiol. 2015; 30(7):543-552.
[18] BURGESS S, DAVEY SMITH G, DAVIES NM, et al. Guidelines for performing Mendelian randomization investigations: update for summer 2023. Wellcome Open Res. 2023;4:186.
[19] SKRIVANKOVA VW, RICHMOND RC, WOOLF BAR, et al. Strengthening the Reporting of Observational Studies in Epidemiology Using Mendelian Randomization: The STROBE-MR Statement. JAMA. 2021;326(16):1614-1621.
[20] BURGESS S, THOMPSON SG. Bias in causal estimates from Mendelian randomization studies with weak instruments. Stat Med. 2011;30(11):1312-1323.
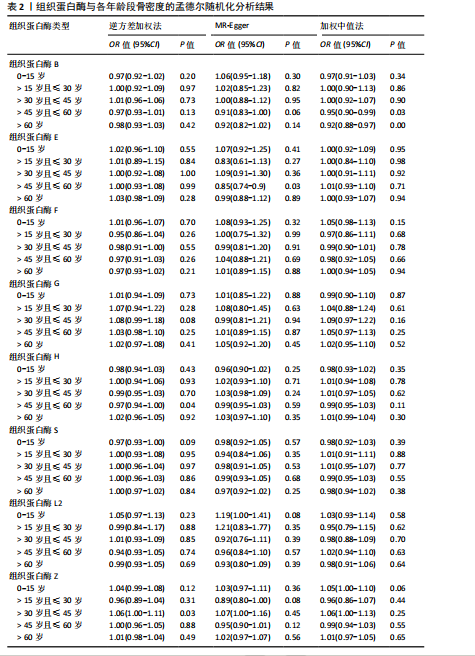
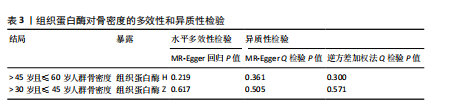
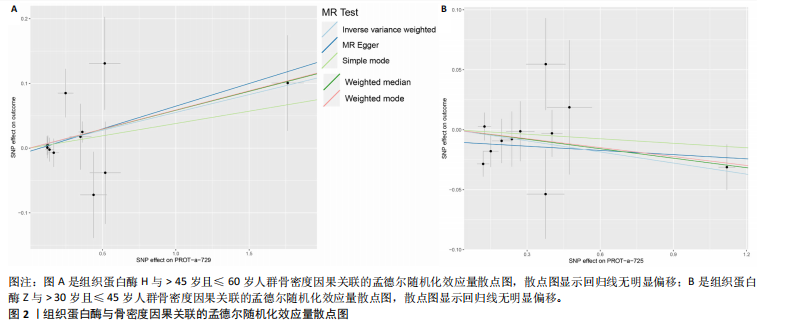
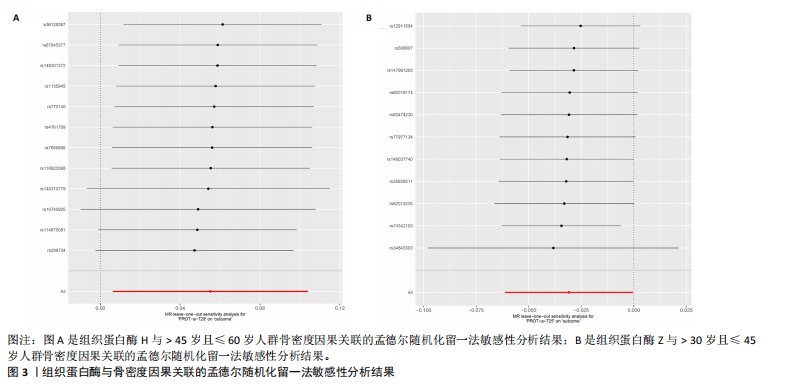
[21] 黄国鑫,陈霞丽,裴斌.孟德尔随机化探索骨密度与膝关节骨性关节炎的因果关联[J].中国骨质疏松杂志,2023,29(4): 512-517.
[22] CODD V, NELSON CP, ALBRECHT E, et al. Identification of seven loci affecting mean telomere length and their association with disease. Nat Genet. 2013;45(4):422-427.
[23] LI W, LU Q, QIAN J, et al. Assessing the causal relationship between genetically determined inflammatory biomarkers and low back pain risk: a bidirectional two-sample Mendelian randomization study. Front Immunol. 2023;14:1174656.
[24] LEVIN MG, JUDY R, GILL D, et al. Genetics of height and risk of atrial fibrillation: A Mendelian randomization study. PLoS Med. 2020;17(10):e1003288.
[25] CODD V, NELSON CP, ALBRECHT E, et al. Identification of seven loci affecting mean telomere length and their association with disease. Nat Genet. 2013;45(4): 422-427e4272.
[26] ZHAO J, WANG J, XU H, et al. Intervertebral Disk Degeneration and Bone Mineral Density: A Bidirectional Mendelian Randomization Study. Calcif Tissue Int. 2024;114(3):228-236.
[27] YUAN S, MIAO Y, RUAN X, et al. Therapeutic role of interleukin-1 receptor antagonist in pancreatic diseases: mendelian randomization study. Front Immunol. 2023;14:1240754.
[28] HAN Y, ZHANG Y, ZENG X. Assessment of causal associations between uric acid and 25-hydroxyvitamin D levels. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2022;13:1024675.
[29] BURGESS S, DUDBRIDGE F, THOMPSON SG. Combining information on multiple instrumental variables in Mendelian randomization: comparison of allele score and summarized data methods. Stat Med. 2016;35(11):1880-906.
[30] BURGESS S, BUTTERWORTH A, THOMPSON SG. Mendelian randomization analysis with multiple genetic variants using summarized data. Genet Epidemiol. 2013;37(7):658-665.
[31] LI W, LU Q, QIAN J, et al. Assessing the causal relationship between genetically determined inflammatory biomarkers and low back pain risk: a bidirectional two-sample Mendelian randomization study. Front Immunol. 2023;14:1174656.
[32] YUAN S, MIAO Y, RUAN X, et al. Therapeutic role of interleukin-1 receptor antagonist in pancreatic diseases: mendelian randomization study. Front Immunol. 2023;14:1240754.
[33] LU Y, WANG Z, ZHENG L. Association of smoking with coronary artery disease and myocardial infarction: A Mendelian randomization study. Eur J Prev Cardiol. 2021;28(12):e11-e12.
[34] BOWDEN J, DAVEY SMITH G, HAYCOCK PC, et al. Consistent Estimation in Mendelian Randomization with Some Invalid Instruments Using a Weighted Median Estimator. Genet Epidemiol. 2016; 40(4):304-314.
[35] BOWDEN J, DEL GRECO MF, MINELLI C,
et al. Assessing the suitability of summary data for two-sample Mendelian randomization analyses using MR-Egger regression: the role of the I2 statistic. Int J Epidemiol. 2016;45(6):1961-1974.
[36] BOWDEN J, DEL GRECO MF, MINELLI C,
et al. Improving the accuracy of two-sample summary-data Mendelian randomization: moving beyond the NOME assumption. Int J Epidemiol. 2019;48(3):728-742.
[37] MATSUZAKI M, PANT R, KULKARNI B, et al. Comparison of Bone Mineral Density between Urban and Rural Areas: Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. PLoS One. 2015; 10(7):e0132239.
[38] YUAN J, JIA P, ZHOU JB. Comparison of Bone Mineral Density in US Adults With Diabetes, Prediabetes and Normoglycemia From 2005 to 2018. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2022;13:890053.
[39] PLUSKIEWICZ W, ADAMCZYK P, DROZDZOWSKA B. Glucocorticoids Increase Fracture Risk and Fracture Prevalence Independently from Bone Mineral Density and Clinical Risk Factors: Results from the Gliwice Osteoporosis (GO) Study. Horm Metab Res. 2022;54(1):20-24.
[40] BLAIR HC, KAHN AJ, CROUCH EC, et al. Isolated osteoclasts resorb the organic and inorganic components of bone. J Cell Biol. 1986;102(4):1164-1172.
[41] BILLINGTON EO, MAHAJAN A, BENHAM JL, et al. Effects of probiotics on bone mineral density and bone turnover: A systematic review. Crit Rev Food Sci Nutr. 2023;63(19):4141-4152.
[42] SHOREY S, HEERSCHE JN, MANOLSON MF. The relative contribution of cysteine proteinases and matrix metalloproteinases to the resorption process in osteoclasts derived from long bone and scapula. Bone. 2004;35(4):909-917.
[43] STRÅLBERG F, KASSEM A, KASPRZYKOWSKI F, et al. Inhibition of lipopolysaccharide-induced osteoclast formation and bone resorption in vitro and in vivo by cysteine proteinase inhibitors. J Leukoc Biol. 2017; 101(5):1233-1243.
[44] HOLZER G, NOSKE H, LANG T, et al. Soluble cathepsin K: a novel marker for the prediction of nontraumatic fractures? J Lab Clin Med. 2005;146(1):13-17.
[45] LANG TH, WILLINGER U, HOLZER G. Soluble cathepsin-L: a marker of bone resorption and bone density? J Lab Clin Med. 2004;144(3):163-166.
[46] WILSON TJ, NANNURU KC, SINGH RK. Cathepsin G-mediated activation of pro-matrix metalloproteinase 9 at the tumor-bone interface promotes transforming growth factor-beta signaling and bone destruction. Mol Cancer Res. 2009;7(8): 1224-1233.
[47] JEVNIKAR Z, OBERMAJER N, BOGYO M, et al. The role of cathepsin X in the migration and invasiveness of T lymphocytes. J Cell Sci. 2008;121(Pt 16):2652-2661.
[48] CAI X, GAO C, SONG H, et al. Characterization, expression profiling and functional characterization of cathepsin Z (CTSZ) in turbot (Scophthalmus maximus L.). Fish Shellfish Immunol. 2019;84:599-608.
[49] UDAGAWA N, TAKAHASHI N, AKATSU T, et al. Origin of osteoclasts: mature monocytes and macrophages are capable of differentiating into osteoclasts under a suitable microenvironment prepared by bone marrow-derived stromal cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990;87(18):7260-7264.
[50] TROEN BR. The role of cathepsin K in normal bone resorption. Drug News Perspect. 2004;17(1):19-28.
[51] STAUDT ND, AICHER WK, KALBACHER H, et al. Cathepsin X is secreted by human osteoblasts, digests CXCL-12 and impairs adhesion of hematopoietic stem and progenitor cells to osteoblasts. Haematologica. 2010;95(9):1452-1460.
[52] LIU M, GOSS PE, INGLE JN, et al. Aromatase inhibitor-associated bone fractures: a case-cohort GWAS and functional genomics. Mol Endocrinol. 2014;28(10):1740-1751.
[53] DERA AA, RANGANATH L, BARRACLOUGH R, et al. Cathepsin Z as a novel potential biomarker for osteoporosis. Sci Rep. 2019; 9(1):9752.
|