[1] SHAFFER F, MEEHAN Z M. A practical guide to resonance frequency assessment for heart rate variability biofeedback. Front Neurosci. 2020;14:570400.
[2] KAUR D, TIWANA H, STINO A, et al. Autonomic neuropathies. Muscle Nerve. 2021;63(1):10-21.
[3] LECHNER K, VON SCHACKY C, MCKENZIE AL, et al. Lifestyle factors and high-risk atherosclerosis:pathways and mechanisms beyond traditional risk factors. Eur J Prev Cardiol. 2020;27(4):394-406.
[4] ZALEWSKI P, SLOMKO J, ZAWADKA-KUNIKOWSKA M. Autonomic dysfunction and chronic disease. Br Med Bull. 2018;128(1):61-74.
[5] MANCIA G, GRASSI G. The autonomic nervous system and hypertension. Circ Res. 2014;114(11):1804-1814.
[6] SHEN MJ, ZIPES DP. Role of the autonomic nervous system in modulating cardiac arrhythmias. Circ Res. 2014;114(6):1004-1021.
[7] LEHRER PM, VASCHILLO E, VASCHILLO B. Resonant frequency biofeedback training to increase cardiac variability:rationale and manual for training. Appl Psychophysiol Biofeedback. 2000;25(3):177-191.
[8] FELDMAN G, GREESON J, SENVILLE J. Differential effects of mindful breathing, progressive muscle relaxation, and loving-kindness meditation on decentering and negative reactions to repetitive thoughts. Behav Res Ther. 2010;48(10):1002-1011.
[9] GUO C, WANG Y, WANG S, et al. Effect and mechanism of traditional chinese medicine exercise therapy on stroke recovery. Evid Based Complement Alternat Med. 2023;2023:5507186.
[10] LITSCHER G, WENZEL G, NIEDERWIESER G, et al. Effects of QiGong on brain function. Neurol Res. 2001;23(5):501-505.
[11] CHRISTA E, SRIVASTAVA P, CHANDRAN DS, et al. Effect of yoga based cardiac rehabilitation on blood pressure variability and baroreflex sensitivity: RCT in patients post MI. Appl Psychophysiol Biofeedback. 2023;48(1):1-15.
[12] SCHWERDTFEGER AR, SCHWARZ G, PFURTSCHELLER K, et al. Heart rate variability (HRV): from brain death to resonance breathing at 6 breaths per minute. Clin Neurophysiol. 2020;131(3):676-693.
[13] MASON OJ, BRADY F. The psychotomimetic effects of short-term sensory deprivation. J Nerv Ment Dis. 2009;197(10):783-785.
[14] JUSTER RP, MCEWEN BS, LUPIEN SJ. Allostatic load biomarkers of chronic stress and impact on health and cognition. Neurosci Biobehav Rev. 2010;35(1):2-16.
[15] WIESENFELD K, MOSS F. Stochastic resonance and the benefits of noise:from ice ages to crayfish and SQUIDs. Nature. 1995;373(6509):33-36.
[16] KAUFMANN H, NORCLIFFE-KAUFMANN L, PALMA JA. Baroreflex dysfunction. N Engl J Med. 2020;382(2):163-178.
[17] VASCHILLO E, LEHRER P, RISHE N, et al. Heart rate variability biofeedback as a method for assessing baroreflex function: a preliminary study of resonance in the cardiovascular system. Appl Psychophysiol Biofeedback. 2002;27(1):1-27.
[18] VASCHILLO E, VASCHILLO B, LEHRER P. Heartbeat synchronizes with respiratory rhythm only under specific circumstances. Chest. 2004;126(4):1385-1386.
[19] VAN DE VOOREN H, GADEMAN MG, SWENNE CA, et al. Baroreflex sensitivity, blood pressure buffering, and resonance: what are the links? Computer simulation of healthy subjects and heart failure patients. J Appl Physiol (1985). 2007;102(4):1348-1356.
[20] CHRISTOU DD, JONES PP, SEALS DR. Baroreflex buffering in sedentary and endurance exercise-trained healthy men. Hypertension. 2003;41(6):1219-1222.
[21] JUST A, WITTMANN U, NAFZ B, et al. The blood pressure buffering capacity of nitric oxide by comparison to the baroreceptor reflex. Am J Physiol. 1994;267(2 Pt 2):H521-H527.
[22] EPSTEIN M, DUPREZ DA. Resistant hypertension and the pivotal role for mineralocorticoid receptor antagonists: a clinical update 2016. Am J Med. 2016; 129(7):661-666.
[23] STEVENS SL, WOOD S, KOSHIARIS C, et al. Blood pressure variability and cardiovascular disease: systematic review and meta-analysis. BMJ. 2016;354: i4098.
[24] YASUMA F, HAYANO J. Respiratory sinus arrhythmia: why does the heartbeat synchronize with respiratory rhythm? Chest. 2004;125(2):683-690.
[25] KOLLAI M, MIZSEI G. Respiratory sinus arrhythmia is a limited measure of cardiac parasympathetic control in man. J Physiol. 1990;424:329-342.
[26] DEMPSEY JA. “Respiratory-related heart rate variability persists during central apnea in dogs: mechanisms and implications”. J Appl Physiol (1985). 1995;78(6): 2001-2002.
[27] HELLMAN JB, STACY RW. Variation of respiratory sinus arrhythmia with age. J Appl Physiol. 1976;41(5 Pt 1):734-738.
[28] DE MEERSMAN RE. Respiratory sinus arrhythmia alteration following training in endurance athletes. Eur J Appl Physiol Occup Physiol. 1992;64(5):434-436.
[29] HIRSCH JA, BISHOP B. Respiratory sinus arrhythmia in humans:how breathing pattern modulates heart rate. Am J Physiol. 1981;241(4):H620-H629.
[30] LEHRER PM, GEVIRTZ R. Heart rate variability biofeedback: how and why does it work? Front Psychol. 2014;5:756.
[31] LEHRER PM, VASCHILLO EG, VIDALI V. Heart rate and breathing are not always in phase during resonance frequency breathing. Appl Psychophysiol Biofeedback. 2020;45(3):145-152.
[32] LEHRER P, EDDIE D. Dynamic processes in regulation and some implications for biofeedback and biobehavioral interventions. Appl Psychophysiol Biofeedback. 2013;38(2):143-155.
[33] GENTILE F, PASSINO C, EMDIN M, et al. Baroreflex activation therapy in heart failure: targeting the right patient. Eur J Heart Fail. 2022;24(9):1674-1676.
[34] HAMMER PE, SAUL JP. Resonance in a mathematical model of baroreflex control: arterial blood pressure waves accompanying postural stress. Am J Physiol Regul Integr Comp Physiol. 2005;288(6):R1637-R1648.
[35] DEBOER RW, KAREMAKER JM, STRACKEE J. Hemodynamic fluctuations and baroreflex sensitivity in humans: a beat-to-beat model. Am J Physiol. 1987;253(3 Pt 2):H680-H689.
[36] JANSSEN BJ, MALPAS SC, BURKE SL, et al. Frequency-dependent modulation of renal blood flow by renal nerve activity in conscious rabbits. Am J Physiol. 1997;273(2 Pt 2):R597-R608.
[37] BERTRAM D, BARRES C, CUISINAUD G, et al. The arterial baroreceptor reflex of the rat exhibits positive feedback properties at the frequency of mayer waves. J Physiol. 1998;513(Pt 1):251-261.
[38] LEHRER PM, VASCHILLO E, VASCHILLO B, et al. Heart rate variability biofeedback increases baroreflex gain and peak expiratory flow. Psychosom Med. 2003;65(5): 796-805.
[39] KEMP AH, QUINTANA DS, GRAY MA, et al. Impact of depression and antidepressant treatment on heart rate variability: a review and meta-analysis. Biol Psychiatry. 2010;67(11):1067-1074.
[40] KEMP AH, QUINTANA DS, FELMINGHAM KL, et al. Depression, comorbid anxiety disorders, and heart rate variability in physically healthy, unmedicated patients:implications for cardiovascular risk. PloS one. 2012;7(2):e30777.
[41] BASSETT D. A literature review of heart rate variability in depressive and bipolar disorders. Aust N Z J Psychiatry. 2016;50(6):511-519.
[42] LEHRER PM, VASCHILLO E, VASCHILLO B, et al. Biofeedback treatment for asthma. Chest. 2004;126(2):352-361.
[43] LEHRER PM, IRVIN CG, LU SE, et al. Heart rate variability biofeedback does not substitute for asthma steroid controller medication. Appl Psychophysiol Biofeedback. 2018;43(1):57-73.
[44] HALLMAN DM, OLSSON EM, VON SCHéELE B, et al. Effects of heart rate variability biofeedback in subjects with stress-related chronic neck pain: a pilot study. Appl Psychophysiol Biofeedback. 2011;36(2):71-80.
[45] RENEAU M. Heart rate variability biofeedback to treat fibromyalgia: an integrative literature review. Pain Manag Nurs. 2020;21(3):225-232.
[46] SEVRE K, LEFRANDT JD, NORDBY G, et al. Autonomic function in hypertensive and normotensive subjects: the importance of gender. Hypertension. 2001; 37(6):1351-1356.
[47] JOSEPH CN, PORTA C, CASUCCI G, et al. Slow breathing improves arterial baroreflex sensitivity and decreases blood pressure in essential hypertension. Hypertension. 2005;46(4):714-718.
[48] JONES CU, SANGTHONG B, PACHIRAT O. An inspiratory load enhances the antihypertensive effects of home-based training with slow deep breathing: a randomised trial. J Physiother. 2010;56(3):179-186.
[49] JONES CU, SANGTHONG B, PACHIRAT O, et al. Slow breathing training reduces resting blood pressure and the pressure responses to exercise. Physiol Res. 2015;64(5):673-682.
[50] LIN G, XIANG Q, FU X, et al. Heart rate variability biofeedback decreases blood pressure in prehypertensive subjects by improving autonomic function and baroreflex. J Altern Complement Med. 2012;18(2):143-152.
[51] 陈思娟,汪胜,林桂平,等.心率变异性生物反馈对高血压前期患者应激反应的干预效果[J]. 热带医学杂志,2012,12(5):562-565.
[52] CARNEY RM, FREEDLAND KE, STEIN PK, et al. Change in heart rate and heart rate variability during treatment for depression in patients with coronary heart disease. Psychosom Med. 2000;62(5):639-647.
[53] YU LC, LIN IM, FAN SY, et al. One-year cardiovascular prognosis of the randomized, controlled, short-term heart rate variability biofeedback among patients with coronary artery disease. Int J Behav Med. 2018;25(3):271-282.
[54] ZUCKER TL, SAMUELSON KW, MUENCH F, et al. The effects of respiratory sinus arrhythmia biofeedback on heart rate variability and posttraumatic stress disorder symptoms: a pilot study. Appl Psychophysiol Biofeedback. 2009;34(2):135-143.
[55] TAN G, DAO TK, FARMER L, et al. Heart rate variability (HRV) and posttraumatic stress disorder (PTSD): a pilot study. Appl Psychophysiol Biofeedback. 2011;36(1):27-35.
[56] SUTARTO AP, WAHAB MN, ZIN NM. Resonant breathing biofeedback training for stress reduction among manufacturing operators. Int J Occup Saf Ergon. 2012; 18(4):549-561.
[57] RATANASIRIPONG P, RATANASIRIPONG N, KATHALAE D. Biofeedback intervention for stress and anxiety among nursing students: a randomized controlled trial. ISRN Nurs. 2012;2012:827972.
[58] DZIEMBOWSKA I, IZDEBSKI P, RASMUS A, et al. Effects of heart rate variability biofeedback on eeg alpha asymmetry and anxiety symptoms in male athletes: a pilot study. Appl Psychophysiol Biofeedback. 2016;41(2):141-150.
[59] PENZLIN A I, SIEPMANN T, ILLIGENS BM, et al. Heart rate variability biofeedback in patients with alcohol dependence: a randomized controlled study. Neuropsychiatr Dis Treat. 2015;11:2619-2627.
[60] LIN IM, FAN SY, YEN CF, et al. Heart rate variability biofeedback increased autonomic activation and improved symptoms of depression and insomnia among patients with major depression disorder. Clin Psychopharmacol Neurosci. 2019;17(2):222-232.
[61] PARK SM, JUNG HY. Respiratory sinus arrhythmia biofeedback alters heart rate variability and default mode network connectivity in major depressive disorder: a preliminary study. Int J Psychophysiol. 2020;158:225-237.
[62] YEN CF, KO CH, HSU CY, et al. A pilot randomized control study on effect brief heart rate variability biofeedback as a complementary treatment in men with methamphetamine use disorder. Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2022;19(9):5230.
[63] DEMIN D, POSKOTINOVA L. Neurophysiologic reactions during heart rate variability biofeedback session in adolescents with different risk of internet addiction. Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2022;19(5):2759.
[64] HASSETT AL, RADVANSKI DC, VASCHILLO EG, et al. A pilot study of the efficacy of heart rate variability (HRV) biofeedback in patients with fibromyalgia. Appl Psychophysiol Biofeedback. 2007;32(1):1-10.
[65] SWANSON KS, GEVIRTZ RN, BROWN M, et al. The effect of biofeedback on function in patients with heart failure. Appl Psychophysiol Biofeedback. 2009; 34(2):71-91.
[66] NOLAN RP, FLORAS JS, HARVEY PJ, et al. Behavioral neurocardiac training in hypertension: a randomized, controlled trial. Hypertension. 2010;55(4):1033-1039.
[67] SOER R, VOS D, HOFSTRA B, et al. Heart coherence training combined with back school in patients with chronic non-specific low back pain: first pragmatic clinical results. Appl Psychophysiol Biofeedback. 2014;39(3-4):259-267.
[68] PAUL M, GARG K, SINGH SANDHU J. Role of biofeedback in optimizing psychomotor performance in sports. Asian J Sports Med. 2012;3(1):29-40.
[69] TOLIN D F, LEE E, LEVY H C, et al. Psychophysiological assessment of stress reactivity and recovery in anxiety disorders. J Anxiety Disord. 2021;82:102426.
[70] RIJKEN N H, SOER R, DE MAAR E, et al. Increasing performance of professional soccer players and elite track and field athletes with peak performance training and biofeedback: a pilot study. Appl Psychophysiol Biofeedback. 2016;41(4):421-430.
[71] 安燕,郑樊慧,陆姣姣.共振呼吸反馈训练对射击运动员心率变异性及压力应对和情绪调节的影响[J].中国运动医学杂志,2018,37(9):725-731.
[72] 安燕,郑樊慧,陆姣姣.共振呼吸反馈训练对运动员心率变异性和选择反应时的影响[J].中国应用生理学杂志,2020,36(5):477-480.
[73] LI Q, STEWARD CJ, CULLEN T, et al. Presleep heart-rate variability biofeedback improves mood and sleep quality in chinese winter olympic bobsleigh athletes. Int J Sports Physiol Perform. 2022;17(10):1516-1526.
[74] HAYANO J, YUDA E. Pitfalls of assessment of autonomic function by heart rate variability. J Physiol Anthropol. 2019;38(1):3.
[75] KUSAYAMA T, WONG J, LIU X, et al. Simultaneous noninvasive recording of electrocardiogram and skin sympathetic nerve activity (neuECG). Nat Protoc. 2020;15(5):1853-1877. |
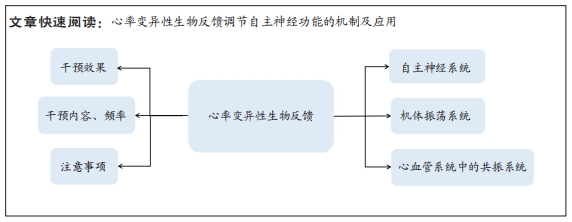


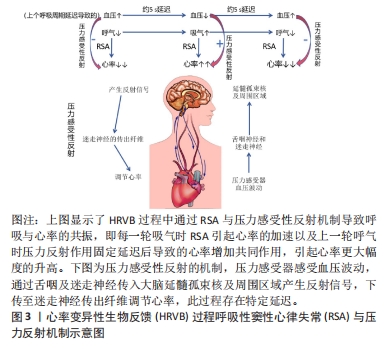
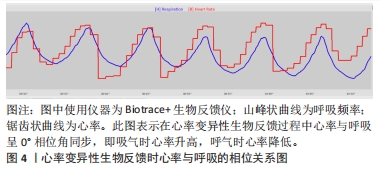

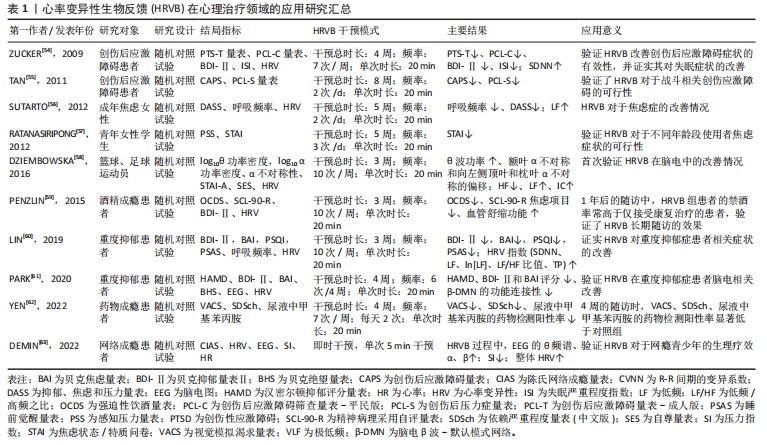

 目前的研究仍面临一个主要问题,即心率变异性生物反馈的机制尚未完全清楚。虽然一些研究已经表明心率变异性生物反馈可以提高心率变异性、调节自主神经功能并改善情绪,但其具体的作用机制仍不明确,这可能与HRV在评估自主神经功能方面存在较大局限性有关。近年来,随着研究的进一步发展,许多学者认为HRV在评估自主神经功能方面存在较大的局限性[74]。例如,HRV很大程度上受各种生理和非生理因素的影响,如年龄、性别、体位、呼吸频率、体力活动水平、睡眠及压力等,以及肌肉和电极运动的伪影等各种噪声源。此外,目前还未有研究关于心率变异性生物反馈对压力反射敏感性的直接影响,多以心率变异性的低频LF代表压力反射敏感性是以往研究的缺陷。因此,HRV最好与其他自主神经功能测量方法结合使用,或者开发更可靠和准确的方法来评估自主神经功能。例如,KUSAYAMA等[75]报道的神经心电图技术,可以同步且连续无创地准确记录人类的皮肤交感神经电位(SKNA),或许可以弥补此方面的不足。此外,现有研究大多仅限于短期的干预,很少有长期随访,无法确定心率变异性生物反馈的长期效果和稳定性。同时,尚未发现关于心率变异性生物反馈在不同性别和年龄群体中功效是否存在差异的研究。课题组团队前期的应用研究发现,约10岁青少年的共振频率要低于成年人,大约7.5次/min,这可能与青少年的血容量低于成年人有关。然而,目前关于不同人群共振频率的研究尚未见到相关文献。最重要的一点,当前研究心血管系统共振仅涉及心率-压力反射通路,在血管张力-压力反射通路是否能产生心血管共振效应以及是否与心率变异性生物反馈存在功效的差异尚不明确,是未来值得深入探究的角度。
目前的研究仍面临一个主要问题,即心率变异性生物反馈的机制尚未完全清楚。虽然一些研究已经表明心率变异性生物反馈可以提高心率变异性、调节自主神经功能并改善情绪,但其具体的作用机制仍不明确,这可能与HRV在评估自主神经功能方面存在较大局限性有关。近年来,随着研究的进一步发展,许多学者认为HRV在评估自主神经功能方面存在较大的局限性[74]。例如,HRV很大程度上受各种生理和非生理因素的影响,如年龄、性别、体位、呼吸频率、体力活动水平、睡眠及压力等,以及肌肉和电极运动的伪影等各种噪声源。此外,目前还未有研究关于心率变异性生物反馈对压力反射敏感性的直接影响,多以心率变异性的低频LF代表压力反射敏感性是以往研究的缺陷。因此,HRV最好与其他自主神经功能测量方法结合使用,或者开发更可靠和准确的方法来评估自主神经功能。例如,KUSAYAMA等[75]报道的神经心电图技术,可以同步且连续无创地准确记录人类的皮肤交感神经电位(SKNA),或许可以弥补此方面的不足。此外,现有研究大多仅限于短期的干预,很少有长期随访,无法确定心率变异性生物反馈的长期效果和稳定性。同时,尚未发现关于心率变异性生物反馈在不同性别和年龄群体中功效是否存在差异的研究。课题组团队前期的应用研究发现,约10岁青少年的共振频率要低于成年人,大约7.5次/min,这可能与青少年的血容量低于成年人有关。然而,目前关于不同人群共振频率的研究尚未见到相关文献。最重要的一点,当前研究心血管系统共振仅涉及心率-压力反射通路,在血管张力-压力反射通路是否能产生心血管共振效应以及是否与心率变异性生物反馈存在功效的差异尚不明确,是未来值得深入探究的角度。