中国组织工程研究 ›› 2024, Vol. 28 ›› Issue (23): 3743-3750.doi: 10.12307/2024.351
• 组织构建综述 tissue construction review • 上一篇 下一篇
血流限制训练干预老年肌少症:生物学机制和应用方案建议
孔健达1,解瑛傲2,陈世娟3,朱 磊1
- 1曲阜师范大学体育科学学院,山东省曲阜市 273100;2济宁医学院附属医院,山东省济宁市 272000;3天津师范大学体育科学学院,天津市300000
-
收稿日期:2023-05-11接受日期:2023-06-15出版日期:2024-08-18发布日期:2023-09-14 -
通讯作者:朱磊,博士,教授,博士生导师,曲阜师范大学体育科学学院,山东省曲阜市 273100 -
作者简介:孔健达,男,1999年生,山东省青岛市人,汉族,曲阜师范大学体育科学学院在读硕士,主要从事慢性病的运动干预研究。 -
基金资助:山东省专业学位研究生教学案例库项目(SDYAL20103),项目负责人:朱磊
Blood flow restriction training interventions for sarcopenia in older adults: biological mechanisms and proposed application protocols
Kong Jianda1, Xie Yingao2, Chen Shijuan3, Zhu Lei1
- 1School of Sports Science, Qufu Normal University, Qufu 273100, Shandong Province, China; 2Affiliated Hospital of Jining Medical University, Jining 272000, Shandong Province, China; 3School of Sports Science, Tianjin Normal University, Tianjin 300000, China
-
Received:2023-05-11Accepted:2023-06-15Online:2024-08-18Published:2023-09-14 -
Contact:Zhu Lei, PhD, Professor, Doctoral supervisor, School of Sports Science, Qufu Normal University, Qufu 273100, Shandong Province, China -
About author:Kong Jianda, Master candidate, School of Sports Science, Qufu Normal University, Qufu 273100, Shandong Province, China -
Supported by:Shandong Province Professional Degree Graduate Teaching Case Library Project, No. SDYAL20103 (to ZL)
摘要:
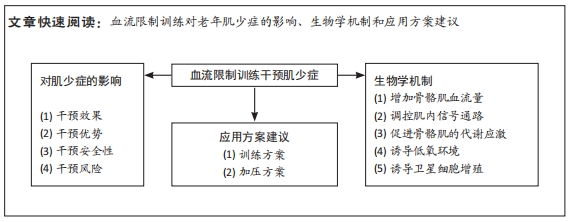
文题释义:
血流限制训练:一种通过在四肢周围加上压力带或气囊来限制血流量,从而减少氧供并提高肌肉水肿和炎症反应,促进肌肉组织恢复和肌肉生长的力量训练方式,可快速提高肌肉力量、增加肌肉体积和耐力、改善肌肉康复和预防肌肉萎缩的训练方法。肌少症:指因持续骨骼肌量流失、强度和功能下降而引起的综合征,该类患者通常站立困难、步履缓慢、容易跌倒骨折,其亦会影响器官功能,可能会引发心脏和肺部衰竭,甚至死亡。
背景:肌少症是一种慢性病,会导致力量丧失和功能下降,增加老年人虚弱、残疾、跌倒和死亡风险。血流限制训练可以有效治疗肌少症,但还缺乏对其优缺点、生物学机制和应用方案的全面回顾。
目的:通过回顾血流限制训练干预肌少症的优势、局限性和生物学机制,并基于当前已发表的证据给予应用方案建议。方法:检索各大数据库建库至2023年2月发表的文献。英文检索词:blood flow restriction training、KAATSU、elderly、sarcopenia、muscle等;中文检索词:血流限制训练、加压训练、老年人、肌少症和肌肉等。对纳入的82篇文献进行整理和分析。
结果与结论:①血流限制训练作为干预肌少症的一种方法,在外周肌群中有一定的效果,但其应用范围存在局限性,血流限制训练具备较高的可操作性和安全性,并能够提高肌肉力量和身体表现,但血流限制训练亦存在潜在风险,尤其证据报告了其对骨骼肌、心血管和内皮细胞等的不良事件,故需在科学指导下进行,并需进一步研究验证其对肌少症患者的效果。②血流限制训练干预肌少症的生物学机制可能包括:增加肌肉反应性充血导致肌肉肥大、改善肌肉蛋白合成能力、诱导代谢应激适应、促进骨骼肌生长和修复、激活血管内皮生长因子信号通路促进血管生成、促进卫星细胞增殖,但这些机制的具体作用和联合作用需要更深入的研究来确定。③血流限制训练干预肌少症主要受训练和袖带的影响,为避免出现不良事件,建议训练负荷20%-50% 1RM,重复次数20-75次,训练频率每周两三次,组间间隔30-60 s,上肢训练使用较小尺寸的袖带且加压值≤140 mmHg,下肢训练使用较大尺寸的袖带且加压值≤180 mmHg,通常选择完全闭塞动脉血流压力值的50%-80%,但老年人血流限制训练频度和组间间隔的研究还需更多探讨,同时袖带加压值的最适选择亦需要进一步研究。
https://orcid.org/0000-0003-1783-918X(孔健达)
中国组织工程研究杂志出版内容重点:组织构建;骨细胞;软骨细胞;细胞培养;成纤维细胞;血管内皮细胞;骨质疏松;组织工程
中图分类号:
引用本文
孔健达, 解瑛傲, 陈世娟, 朱 磊. 血流限制训练干预老年肌少症:生物学机制和应用方案建议[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2024, 28(23): 3743-3750.
Kong Jianda, Xie Yingao, Chen Shijuan, Zhu Lei. Blood flow restriction training interventions for sarcopenia in older adults: biological mechanisms and proposed application protocols[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(23): 3743-3750.
2.1.1 BFR训练对骨骼肌的作用效果 当前主流的观点认为,BFR训练对骨骼肌具有一定影响,主要包括诱导生长激素分泌[9]、增加肌肉细胞肿胀和募集快肌纤维等[10-14],这说明BFR训练造成的肌肥大效应亦包括除了因产生机械应力外的其他因素。BFR训练对骨骼肌的作用已有大量证据。Meta分析表明,BFR训练能够在较低的负荷下进行,并与传统的高强度训练相比效果相同或更为明显;对于老年人,BFR训练和高强度抗阻训练相比对肌肉质量的影响相似,但对肌肉力量的影响较低[3,6-8,15-16]。对于BFR训练的作用,LIXANDR?O等[15]认为主要受袖带加压强度和宽度影响,而CENTNER等[17]和KONG等[6]认为,BFR训练在老年人中的作用类似于高强度抗阻训练,但CENTNER等[17]还认为,当前缺乏有关老年人在不同性别、加压值、训练量和训练频率下的作用的相关证据。然而,目前尚无研究直接比较低强度BFR抗阻训练和高强度抗阻训练对mTOR通路作用的差异性,但存在单次急性干预实验。FUJITA等[16]发现,BFR训练(20% 1RM)3 h后肌肉蛋白质合成显著增加,同时发现Akt磷酸化、mTOR磷酸化和p70S6K磷酸化显著增加,但该研究受试者为年轻成年人。对于老年人的研究中,FRY等[18]发现,低强度BFR抗阻训练能够增强老年男性的mTORC1信号,并促进肌肉蛋白质合成上调,这使得BFR训练改善老年人肌内信号通路有了直接证据。上述研究所得结果亦在高强度抗阻训练相关的研究中发现[19],这说明虽然尚无直接证据表明BFR训练和高强度抗阻训练对肌内信号通路作用的差异性,但可以推测二者具有相似效果。然而,BFR训练的应用范围局限于外周肌群(如四肢),无法对背部、颈部和核心等肌群产生直接作用[20]。
总的来说,BFR训练对骨骼肌具有一定影响,与高强度训练相比效果相同或更为明显,对老年人肌肉质量的影响相似,但对肌肉力量的影响较低,应用范围有限不能对背部、颈部和核心等肌群产生直接作用,见表1。

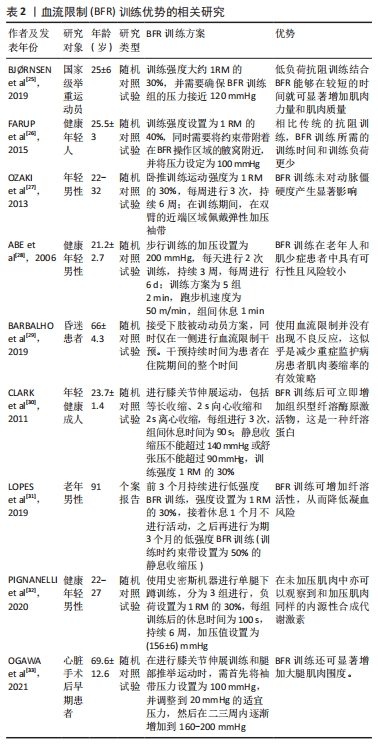
2.1.2 BFR训练的优势 AWGS达成共识,认为肌少症和基础疾病有关,往往是这些基础疾病的并发症[4]。对于老年肌少症,BFR训练干预具有较高的可操作性[21-22]。老年肌少症患者经过BFR训练联合低负荷抗阻训练干预后,未发生骨骼肌功能持续下降、骨骼肌酸痛以及骨骼肌损伤等不良反应[23-24],这说明BFR训练适用于老年肌少症患者以及其他基础疾病伴活动受限的患者,符合AWGS对肌少症共识的干预措施,具有较高的安全性。
相比传统高强度训练,BFR训练能够在低负荷下进行,并表现出相同或更优的训练效果。BJ?RNSEN等[25]发现,低负荷抗阻训练结合BFR能够在较短的时间就可显著增加肌肉力量和肌肉质量。另外,相比传统的抗阻训练,BFR训练所需的时间和负荷较少[26]。BFR训练亦能够显著增加大腿肌肉围度并改善动脉僵硬程度[21,27]。因此,BFR训练是一种更有效提高肌肉力量和身体表现的训练方法,可替代传统的抗阻训练。研究表明,肌少症与一些基础疾病有关[4],而BFR训练在肌少症患者中具有较强的可行性,且风险较小[28],故适用于肌少症患者。研究发现,肌少症患者接受低负荷BFR抗阻训练后未发现肌肉功能下降、肌肉酸痛严重或肌肉损伤增加等不良事件[14,29],这说明BFR训练适用于临床康复患者以及无法进行高强度训练的群体(如老年人),且由于BFR训练更易实施且负荷较小,可作为老年肌少症患者改善肌肉力量、质量和身体表现的干预措施。CLARK等[30]发现BFR训练后可立即增加组织型纤溶酶原激活物(一种纤溶蛋白)表达水平。与此相一致的是,LOPES等[31]一项个案报告表明,BFR训练可增加纤溶活性,可降低凝血风险。另外,BFR训练能使在未加压肌肉中观察到和加压肌肉同样的内源性合成代谢激素[32],这说明BFR训练对骨骼肌的影响具有独特性。
综上所述,BFR训练适用于老年肌少症患者和其他基础疾病伴活动受限的患者,具有较高的安全性和更有效提高肌肉力量和身体表现的训练效果,且还能增加纤溶活性和内源性合成代谢激素,见表2。
2.1.3 BFR训练的安全性 针对运动干预肌少症的有效性,EWGSOP对运动方法提出了几项基准[2],EWGSOP要求所使用的运动方法必须对老年人最适合和最有效,使老年人能够进行更多习惯性的体育活动,且为有明显身体限制的人提供传统锻炼计划的替代方案[3]。BFR训练被证明符合上述要求。
通常来说,BFR训练具有相对较高的安全性。彭通等[21]分析了BFR训练对老年人(其中纳入了肌少症患者)血压、心率、血管顺应性指标发现,BFR训练在老年人中具有较高安全性,对血管内皮功能和血管顺应性有积极作用,但由于检索不全面、纳入的文献较少、发表年份不同、文献的质量和数量等差异,使得该研究具有一定的局限性。对于老年人和年轻人[27,34],BFR训练未对动脉僵硬度产生显著影响。目前还没有直接证据能够阐述BFR训练对动脉顺应性的生理机制,但OZAKI等[27]认为,BFR训练导致的动脉顺应性下降可能与BFR训练期间收缩压增加的变化有关。因此,当年轻人和老年人接受BFR训练期间血压反应变化量时,可能会影响其动脉抗阻训练依从性。YASUDA等[35]在日本进行了一项全国性调查,被调查对象均接受了BFR训练的科学指导,其结果未发现神经压迫导致的瘫痪、肺栓塞等风险,亦未发现静脉血栓形成、横纹肌溶解、脑梗死、脑出血、肺梗死等症状。根据这项研究,可以推断BFR训练是一种较为安全的干预措施。因此,BFR训练的安全性前提条件是训练对象必须接受科学的指导,并且对健康有积极的效果。另外,BFR训练亦被报道能够改善老年人的身体功能和肌肉力量,有助于预防老年人跌倒[17]、减缓患有膝骨关节炎老年人的关节疼痛,并增加肌肉力量[36-37]。证据表明,BFR训练可改善与跌倒相关的因素,例如身体表现和肌肉力量[6]。虽然关于老年人跌倒风险的研究结果还不够充分[38],但仍有研究证实BFR训练适用于患有膝骨关节炎的老年人,可以减轻关节疼痛、增加肌肉力量,而且没有不良反应[36]。另外,BFR训练亦可以用于其他疾病的康复治疗,例如FUKUDA等[39]发现BFR训练适用于心脏康复治疗;在一些股骨内侧髁骨坏死[40]、膝关节半月板切除术等疾病康复治疗的个案报告中,BFR训练亦被应用,并且具有较高的安全性[41]。
总之,BFR训练被证明对老年人肌少症、关节疼痛等康复有积极效果,且拥有较高的安全性和相对较少的不良反应。表3总结了BFR训练的安全性报告,其中涉及到随机对照试验、定量研究以及个案报告等。
2.1.4 BFR训练的潜在风险 BFR训练对老年肌少症的干预具有潜在的优势,但其亦具有一定局限性,甚至被证明可能造成一系列不良反应。另外,BFR训练可能对加压者造成不适。ABE等[42]报告,运动期间不正确使用BFR训练可能导致心血管并发症的不良事件,如心律失常、心肌梗死、中风和心源性猝死等。而且,与传统训练相比,BFR训练后肌肉酸痛和肌肉疲劳感更佳明显[43],这说明BFR训练可能对心血管具有不利的影响。OGAWA等[33]认为,BFR训练产生的不适感可能原因是袖带对血管加压造成的。
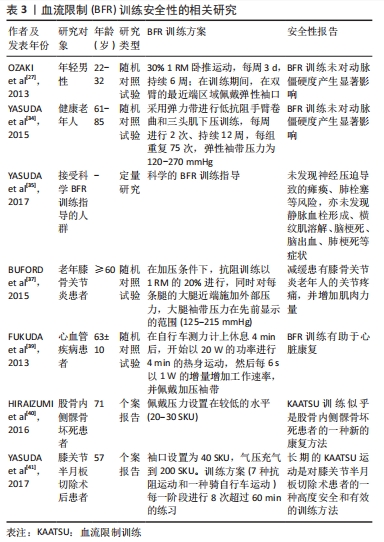
BFR训练亦可能造成微血管功能障碍,造成暂时性缺血,BFR训练结束后血流再灌注的恢复过程可能是造成微血管功能障碍的原因。在BFR训练后的血流再灌注时,骨骼肌急性释放炎症分子和反应性氧化物,进而损害微血管功能[23]。LOPES等[31]发现,老年男性进行BFR训练后,血流恢复可能降低一氧化氮的生物利用率,从而导致动脉血管舒张功能受损和纯压升高。血流的反复再灌注损伤亦能够影响内皮功能,BFR训练后肌膜通透性增加,并伴随着活性氧的产生,进而造成内皮细胞损伤[44]。另外,WILSON等[45]认为缺血后血流再灌注还能够造成神经性肌肉功能障碍,说明BFR训练可能存在神经性肌肉功能障碍的风险,但相关研究只在小鼠模型中进行,需要进一步研究验证是否在人体身上发生。BFR训练亦可能引起心脏手术后早期患者出现头晕、嗜睡、麻木、恶心、瘙痒、皮下或瘀点性出血等风险[14,33]。另外,TABATA等[46]发现过度使用BFR训练能够导致肌细胞损伤,严重可造成横纹肌溶解。由于BFR训练造成的潜在风险可能原因是由于使用方法学不同造成的[47],故BFR训练需要更加严格的标准化操作和监测,并且需要在科学指导下进行。
综上所述,BFR训练可能对人体造成潜在的风险,故在进行BFR训练时应更加注重其安全性,见表4。然而,当前相关证据较少,且是否对肌少症患者具有同样效果尚待探究。
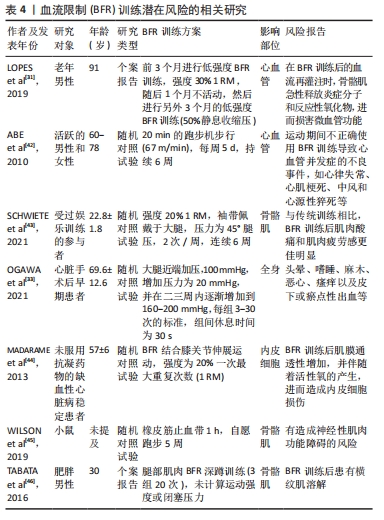
2.2 BFR训练治疗老年肌少症生物学机制 了解BFR训练干预对肌少症的优势、局限性和不良反应是不够的,亦需要进一步了解BFR训练治疗老年肌少症的生物学机制,有利于从生理学角度增强BFR训练干预对肌少症的优势、局限性和不良反应的认识。总的来说,对于治疗老年肌少症,BFR训练的机制主要包括使骨骼肌血流量增加、调控肌内信号通路、促进骨骼肌的代谢应激、诱导低氧环境和诱导卫星细胞增殖等。其中,BFR训练诱导骨骼肌血流量增加主要导致缺血反应和外周血液循环;BFR训练诱导肌内信号通路代表为mTOR通路,进而调节S6K1、S6和MnK1上调,促进AKT磷酸化以及抑制4E-BP1磷酸化;BFR训练诱导骨骼肌代谢应激进而产生机械应力、使得动脉血流减少且静脉血流量增加、并使生长激素、胰岛素样生长因子1、mTOR和热休克蛋白上调以及肌肉生长抑制素下调,促进肌纤维募集和细胞肿胀,但此机制适用于大多数运动促进肌肥大,故不能作为特有针对肌少症的机制;BFR训练亦由于短暂的缺血反应诱导低氧环境,主要体现在低氧诱导因子1α和血管内皮生长因子(vascular endothelial growth factor,VEGF)上调,激活VEGF-Pi3k-Akt-eNOS通路;另外,BFR训练诱导卫星细胞增殖的具体机制由于证据较少尚不清楚。下面将对这些机制进行展开描述,见图3。
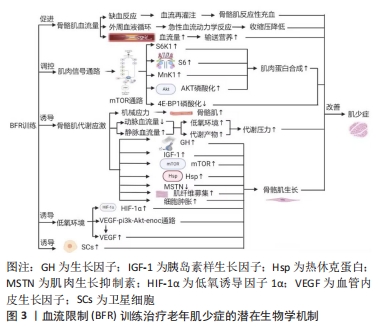
2.2.1 BFR训练使骨骼肌血流量增加 CLARK等[48]认为,肌少症在发病过程中通常伴随着骨骼肌血流量的减少,而BFR训练能够使骨骼肌血管中血流受到限制,产生短暂的缺血反应,进而增加骨骼肌血流量。进行BFR训练后解开袖带,使得骨骼肌中的血流量增加,血液再灌注后血流高于袖带限制血流前的水平。因此,BFR训练后血流量增加使骨骼肌反应性充血导致肌肥大。BFR抗阻训练改善了健康老年人骨骼肌外周的血液循环[49]。ZHANG等[50]对低负荷BFR训练对老年人血液动力学反应和血管功能的影响进行Meta分析发现,BFR训练能够引起老年人的急性血流动力学反应,训练后30 min方可恢复正常水平,且收缩压显著降低。然而,GUNDERMANN等[51]认为,BFR训练能够导致训练后的血流量短暂升高,进而输送大量营养到骨骼肌中,但其亦认为这不是BFR训练改善肌肉力量和肥大的主要机制,这说明BFR训练后的对骨骼肌改善的效果可能涉及到其他潜在的信号通路作用。
总之,BFR训练可通过短暂限制骨骼肌血流引起缺血反应,增加骨骼肌血流量并导致肌肉反应性充血,改善老年人骨骼肌外周的血液循环,但其作用机制可能涉及其他信号通路。
2.2.2 BFR训练调控肌内信号通路 证据表明,肌少症患者的肌肉蛋白合成能力较低,这和肌内信号通路的失调有关。高负荷的抗阻训练因受到肌肥大特定信号通路的抑制作用,不利于老年人的合成代谢能力,老年人肌肉蛋白合成的合成代谢反应受损与S6K1调节失调有关[52],而且老年人的基础mTORC1信号通路过度磷酸化可能不利于胰岛素合成,亦对骨骼肌蛋白代谢对营养和运动年龄相关合成代谢能力具有不利影响[53]。FRY等[18]认为,老年人进行BFR训练后3 h后,mTOR通路诱导的S6K1、S6、丝裂活化蛋白激酶相互作用激酶1(MnK1)和AKT的磷酸化达到峰值,并且此时肌肉蛋白合成显著增加。另外,4E-BP1蛋白的磷酸化亦和mTORC1信号通路显著相关[54]。FRY等[18]认为,BFR训练能够使骨骼肌的4E-BP1磷酸化,但仅限在年轻人的研究中发现这一点机制,而在老年人的研究中未有相同结果发现,这说明BFR训练在老年人和年轻人促进肌肥大中的机制有一定区别,进一步说明BFR训练改善老年肌少症的一种可能原因是4E-BP1表达能力受到抑制。LE BACQUER等[55]发现,敲除4E-BP1基因后,小鼠中肌肉蛋白的合成能力增强,且小鼠骨骼肌质量和力量得到显著提升,这说明4E-BP1磷酸化可能是治疗肌少症的靶点,而BFR训练能够抑制4E-BP1磷酸化,进而对肌少症的改善起到一定的积极作用。然而,目前来说虽然BFR训练后肌肥大反应的生物学机制已经提出很多,但具体机制尚不完善。
2.2.3 BFR训练促进骨骼肌的代谢应激 NASCIMENTO等[56]认为,肌少症和代谢应激相关激素和蛋白显著相关,包括生长激素和胰岛素样生长因子等激素水平升高,mTOR、热休克蛋白、肌肉生长抑制素、肾上腺素和去甲肾上腺素等。肌少症往往伴随骨骼肌质量降低,故诱导代谢应激相关蛋白往往能够促进骨骼肌生长修复和重建,进而防治肌少症。BFR训练能够对骨骼肌提供一定机械张力并诱导代谢应激[57],进而促进骨骼肌生长[9]。BFR训练能够使动脉血流量减少,静脉血液聚集,形成低氧环境,造成乳酸等代谢产物堆积,最终引起代谢压力水平增加;生长激素和胰岛素样生长因子1等激素水平升高,mTOR和热休克蛋白等合成表达增加,肌肉生长抑制素降低,肌纤维募集增多,以及细胞肿胀等过程,进而导致骨骼肌生长[9]。另外,GOTO等[58]发现,运动引起的代谢应激与抗阻训练后的急性生长激素、肾上腺素和去甲肾上腺素反应以及慢性肌肉适应有关,这表明代谢应激和肌肥大之间存在一定相关性,亦可适用于改善肌少症。然而,代谢应激适用于大多数运动促进肌肥大的机制解释[59],但无法作为BFR训练改善肌少症的特有机制。
2.2.4 BFR训练诱导低氧环境 在低氧环境下,低氧诱导因子1α激活血管内皮生长因子的转录和释放,促进血管生成和组织氧供。肌少症随着年龄的增长而加剧,导致肌肉功能衰退和身体能力下降。研究发现,低氧和血管生成亦与肌少症密切相关,表明血管内皮生长因子和低氧诱导因子1α可能参与肌少症的发病机制中。低氧诱导因子1α/血管内皮生长因子信号通路在老年肌肉缺血性损伤修复中起到关键作用,其缺失可导致老年鼠的肌肉萎缩加剧[60];另外,血管内皮生长因子基因多态性可能与骨骼肌质量和动力学功能的损失相关[61],这表明低氧诱导因子1α/血管内皮生长因子信号通路可能在肌少症的发展中发挥重要作用。BFR训练能够诱导低氧环境,有助于增强运动后的代谢应激[62]。
RAMOS-CAMPO等[63]认为,BFR干预下的低氧抗阻训练相比于常氧抗阻训练更有利于骨骼肌质量和力量的增加。BARJASTE等[64]发现,BFR训练能够增加低氧诱导因子1α表达上调,同时增加肌肥大,这说明低氧诱导因子1α可能对诱导骨骼肌肥大起到积极作用。BFR训练亦能够刺激血管内皮生长因子释放。TAN等[65]发现,BFR训练可激活VEGF-Pi3k-Akt-eNOS通路,上调血液中血管内皮生长因子的表达,改善微血管稀疏,促进心肌微血管循环,从而改善心功能,降低血压,达到早期高血压的预防作用。HUEY[66]发现,成年小鼠骨骼肌中血管内皮生长因子缺失不利于骨骼肌收缩和肌肥大适应,这说明BFR训练能够诱导低氧环境的表达产物血管内皮生长因子表达升高,并在肌肥大中起着重要作用。
然而,上述研究仅在年轻小鼠模型中进行,仅有TAN等[65]的研究是在老年高血压小鼠模型中进行的。因此,需要更多的研究来确定BFR训练改善老年肌少症的具体生物学机制,以确定低氧诱导因子1α和血管内皮生长因子等低氧环境调控因子在BFR训练干预肌少症中的作用。
2.2.5 BFR训练诱导卫星细胞增殖 肌少症和衰老显著相关[1],而衰老过程中骨骼肌卫星细胞数目显著降低[66]。卫星细胞的增殖对骨骼肌生长起到至关重要的作用[67]。BJ?RNSEN等[68]发现,随着BFR训练结束后,骨骼肌中的卫星细胞数量增加,这说明BFR训练可能促进卫星细胞的增殖,进而可能对骨骼肌生长产生作用。然而,WERNBOM等[69]使用7名受试者以30% 1RM进行单侧膝关节伸展,并结合有无使用BFR进行比较,发现有无BFR结合的训练均有卫星细胞数目的显著升高,这说明即使BFR训练能够促进卫星细胞的增殖,但尚无法作为特有的对肌少症有效的机制看待。另外,由于尚无足够的证据证明BFR训练和卫星细胞增殖的潜在关系,故BFR训练诱导卫星细胞增殖仅能作为改善肌少症作用的一个可能机制,不具备独特性。另外,当前证据仅证实了BFR训练对卫星细胞增殖的作用,尚不清楚BFR训练诱导卫星细胞分化的作用以及具体机制,尤其要观察卫星细胞相关的调控蛋白,以及BFR训练是否对肌少症患者卫星细胞的肌源性分化产生作用。
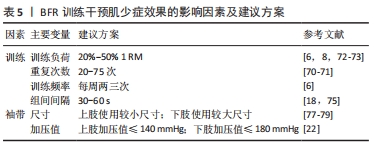
2.3 针对肌少症BFR训练的应用方案 除了BFR训练对肌少症的优势、局限性和生物学机制外,亦需获取BFR训练应用方案作为针对肌少症的运动处方。BFR训练干预肌少症的效果受多方面因素的影响,主要包括训练和袖带2个方面,其中训练负荷、训练强度、训练频率、训练的组间间隔、袖带尺寸和袖带加压值是主要运动变量[70-79]。对此,此次综述基于已有证据提出了BFR训练干预肌少症效果的影响因素及建议方案,见表5。
2.3.1 训练
(1)训练负荷和强度:训练负荷和强度是BFR训练干预肌少症的一项重要的考虑因素。YUSUDA等[70]认为,BFR训练的负荷和强度与训练重复次数呈负相关性,每组BFR训练的重复次数高于高负荷抗阻训练,在BFR结合低负荷抗阻训练的研究中,每次训练的重复次数多为45-75次,但YASUDA等[70]认为该种BFR训练负荷和强度能够显著增加上臂和胸部肌肉的肌肉尺寸以及1RM力量,该研究给BFR训练的训练负荷和强度的选择提供了一个参考值的安全范围,但其研究对象仅为年轻人,故对老年人参考价值有限。对于老年人,SHIMIZU等[71]使用20% 1RM的负荷进行BFR训练的效果较为显著,且每组重复次数为20次,且未发现不良反应。然而,LIXANDR?O等[72]认为,在进行BFR训练时并非重复次数多使得效果越好,过度延长训练时间或增加重复的次数都会导致过度训练,其认为理想负荷为20%-50% 1RM。LIXANDR?O等首次提出了BFR训练对老年人的最佳负荷的范围,BFR训练的负荷选择提供了参考价值。COOK等[73]使用了30%-50% 1RM负荷的BFR训练,亦得到了显著的效果。另外,30% 1RM的BFR训练能够诱导老年人生长激素水平的升高[73]。然而,关于BFR训练干预老年人骨骼肌力量和质量的中文研究较少,仅可知30% 1RM负荷的BFR训练比单独低负荷下的力量训练更能显著提高老年人下肢骨骼肌肌力[74]。KONG等[6]和潘玮敏等[8]分别对BFR训练对老年人肌肉力量和质量影响进行了系统评价和Meta分析,其纳入的研究中选择的负荷均为20%-50% 1RM,且均未出现不良事件。总的来说,肌少症和年龄有关,故患者均为老年人,针对该类人群BFR训练负荷和强度的最佳选择可能为20%-50% 1RM,在此范围内尚未发现有不良事件的发生。
(2)训练频率和组间间隔:对于老年肌少症患者的BFR训练,训练频率和组间间隔时长亦尤为重要。对于BFR训练的训练频率亦较低,KONG等[6]Meta分析纳入的研究中使用BFR训练的频率均为每周两三次,且未发现不良事件,这说明BFR训练干预肌少症患者时使用每周两三次的训练频率具有较高的安全性,且在这个频率下对骨骼肌力量和质量的改善具有良好的作用。
通常来说,BFR训练的组间间隔时间为30-60 s[18]。LOENNEKE等[74]认为,BFR训练的组间间隔时间较短能够促进多种骨骼肌生长的机制发生。然而,BFR训练的组间间隔应对肢体末端持续施压,此时肢体静脉血流将受阻,可增强参与BFR训练的老年人的代谢[75];另外,在较短时间内BFR训练的组间间隔加压能够使静脉阻塞,增加心肌细胞的肿胀,进而对肌少症患者的干预产生积极影响[10]。然而,值得注意的是,虽然对于BFR训练的研究热点主要内容包括不训练方法学影响变量,但关于BFR训练对老年人尤其肌少症人群的训练频率和组间间隔的研究相对较少[76],故目前尚不能确定BFR训练干预肌少症的最佳训练频率和组建间隔。
2.3.2 袖带
(1)袖带尺寸:袖带尺寸是BFR训练在肌少症患者中一个重要影响因素。FITZGIBBONS等[77]对袖带尺寸使用的指南进行了综述,旨在推广标准实践的证据并提供关于上肢和下肢安全使用袖带的现有建议,这说明袖带尺寸是BFR训练影响肌少症的限制因素之一。ROSSOW等[78]发现,使用宽的袖带会限制BFR训练的运动能力,进而使得训练体验较差,并可能导致疼痛和疲劳等不良反应。然而,较大尺寸的袖带适用于下肢加压能够更容易地达到BFR训练要求且减少血流动力学应力;较小尺寸的袖带更适用于上肢[77]。WERNBOM等[79]发现,四肢周长和所需压力值呈正相关性,通常下肢BFR训练使用较大尺寸的袖带。因此,如果袖带袖口尺寸较大,需要使用较小的压力,反之,较小尺寸的袖口应使用较大的压力。
(2)袖带加压值:袖带加压值亦是BFR训练中的一个重要因素。袖带宽度、肢体周长、踝臂指数、脂肪和肌肉厚度、动脉僵硬度、内皮功能和血压都影响BFR训练的压力值[80]。通常情况下,BFR训练的压力值较高时能够使静脉血流闭塞,较低时能够维持动脉血流量流向肌肉,故需要合适的压力值来确保其最大的效果[79]。然而,BFR训练的最佳压力值因人而异,在同一个体中亦因上肢和下肢而异。陆锦华[80]通过综述建议BFR训练需要确保使用的袖带宽度以及压力值适宜,通常选择完全闭塞动脉血流压力值的50%-80%,这和ROSSOW等[78]认为的一致。然而,对于加压值尚无统一标准,少数证据表明,上肢压力值不应超过140 mmHg,且BFR训练开始时,下肢压力值不应超过180 mmHg,这可以确保获得较好BFR训练结果,进而减少运动过程中的疼痛和损伤[81-82]。然而,由于对BFR训练干预老年人所使用袖带加压值的研究较少,故尚无法得出针对老年人BFR训练的最适袖带加压值。

| [1] CRUZ-JENTOFT AJ, SAYER AA. Sarcopenia. Lancet. 2019;393(10191):2636-2646. [2] CRUZ-JENTOFT AJ, BAHAT G, BAUER J, et al. Sarcopenia: revised European consensus on definition and diagnosis. Age Ageing. 2019;48(4):601. [3] PETERMANN-ROCHA F, BALNTZI V, GRAY SR, et al. Global prevalence of sarcopenia and severe sarcopenia: a systematic review and meta-analysis.J Cachexia Sarcopenia Muscle. 2022;13(1):86-99. [4] CHEN LK, WOO J, ASSANTACHAI P, et al. Asian Working Group for Sarcopenia: 2019 Consensus Update on Sarcopenia Diagnosis and Treatment. J Am Med Dir Assoc. 2020;21(3):300-307.e2. [5] SATO Y. The history and future of KAATSU training. Int J KAATSU Train Res. 2005;1(1):1-5. [6] KONG J, LI Z, ZHU L, et al. Comparison of blood flow restriction training and conventional resistance training for the improvement of sarcopenia in the older adults: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Sports Medicine and Health Science. 2022. doi.org/10.1016/j.smhs.2022.12.002 [7] RODRIGO-MALLORCA D, LOAIZA-BETANCUR AF, MONTEAGUDO P, et al. Resistance Training with Blood Flow Restriction Compared to Traditional Resistance Training on Strength and Muscle Mass in Non-Active Older Adults: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2021;18(21):11441. [8] 潘玮敏,王兵,韩亚兵,等.血流限制训练对老年人肌肉力量、质量和躯体能力改变影响的Meta分析[J].中国组织工程研究,2023,27(5):805-812. [9] POWERS SK, DEMINICE R, OZDEMIR M, et al. Exercise-induced oxidative stress: Friend or foe? J Sport Health Sci. 2020;9(5):415-425. [10] NAYLOR LH, WEISBROD CJ, O’DRISCOLL G, et al. Measuring peripheral resistance and conduit arterial structure in humans using Doppler ultrasound. J Appl Physiol (1985). 2005;98(6):2311-2315. [11] YASUDA T, LOENNEKE JP, THIEBAUD RS, et al. Effects of blood flow restricted low-intensity concentric or eccentric training on muscle size and strength. PLoS One. 2012;7(12):e52843. [12] LOENNEKE JP, FAHS CA, ROSSOW LM, et al. The anabolic benefits of venous blood flow restriction training may be induced by muscle cell swelling. Med Hypotheses. 2012;78(1):151-154. [13] YASUDA T, BRECHUE WF, FUJITA T, et al. Muscle activation during low-intensity muscle contractions with restricted blood flow. J Sports Sci. 2009; 27(5):479-489. [14] YASUDA T, BRECHUE WF, FUJITA T, et al. Muscle activation during low-intensity muscle contractions with varying levels of external limb compression. J Sports Sci Med. 2008;7(4):467-474. [15] LIXANDRÃO ME, UGRINOWITSCH C, BERTON R, et al. Magnitude of Muscle Strength and Mass Adaptations Between High-Load Resistance Training Versus Low-Load Resistance Training Associated with Blood-Flow Restriction: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Sports Med. 2018;48(2):361-378. [16] FUJITA S, ABE T, DRUMMOND MJ, et al. Blood flow restriction during low-intensity resistance exercise increases S6K1 phosphorylation and muscle protein synthesis.J Appl Physiol (1985). 2007;103(3):903-910. [17] CENTNER C, WIEGEL P, GOLLHOFER A, et al. Effects of blood flow restriction training on muscular strength and hypertrophy in older individuals: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Sports Med.2019;49:95-108. [18] FRY CS, GLYNN EL, DRUMMOND MJ, et al. Blood flow restriction exercise stimulates mTORC1 signaling and muscle protein synthesis in older men. J Appl Physiol (1985). 2010;108(5):1199-1209. [19] DREYER HC, FUJITA S, CADENAS JG, et al. Resistance exercise increases AMPK activity and reduces 4E-BP1 phosphorylation and protein synthesis in human skeletal muscle. J Physiol. 2006;576(Pt 2):613-624. [20] ZHANG XZ, XIE WQ, CHEN L, et al. Blood Flow Restriction Training for the Intervention of Sarcopenia: Current Stage and Future Perspective. Front Med (Lausanne). 2022;9:894996. [21] 彭通,赵大业,丁淑平,等.血流限制训练在老年人群中应用的安全性系统评价[J].护理研究,2022,36(22):3994-4001. [22] HEITKAMP HC. Training with blood flow restriction. Mechanisms, gain in strength and safety. J Sports Med Phys Fitness. 2015;55(5):446-456. [23] HUGHES L, PATON B, ROSENBLATT B, et al. Blood flow restriction training in clinical musculoskeletal rehabilitation: a systematic review and meta-analysis.Br J Sports Med. 2017;51(13):1003-1011. [24] 陈蓉,曾庆,巩泽,等.不同模式下血流限制治疗老年性肌肉减少症的效果与安全因素[J].中国组织工程研究,2021,25(32):5215-5221. [25] BJØRNSEN T, WERNBOM M, KIRKETEIG A, et al. Type 1 Muscle Fiber Hypertrophy after Blood Flow-restricted Training in Powerlifters. Med Sci Sports Exerc. 2019;51(2):288-298. [26] FARUP J, DE PAOLI F, BJERG K,et al. Blood flow restricted and traditional resistance training performed to fatigue produce equal muscle hypertrophy. Scand J Med Sci Sports. 2015;5(6):754-763. [27] OZAKI H, YASUDA T, OGASAWARA R, et al. Effects of high-intensity and blood flow-restricted low-intensity resistance training on carotid arterial compliance: role of blood pressure during training sessions. Eur J Appl Physiol. 2013;113(1):167-174. [28] ABE T, KEARNS CF, SATO Y. Muscle size and strength are increased following walk training with restricted venous blood flow from the leg muscle, Kaatsu-walk training. J Appl Physiol (1985). 2006;100(5):1460-1466. [29] BARBALHO M, ROCHA AC, SEUS TL,et al. Addition of blood flow restriction to passive mobilization reduces the rate of muscle wasting in elderly patients in the intensive care unit: a within-patient randomized trial. Clin Rehabil. 2019; 33(2):233-240. [30] CLARK BC, MANINI TM, HOFFMAN RL, et al. Relative safety of 4 weeks of blood flow-restricted resistance exercise in young, healthy adults. Scand J Med Sci Sports. 2011;21(5):653-662. [31] LOPES KG, BOTTINO DA, FARINATTI P, et al. Strength training with blood flow restriction - a novel therapeutic approach for older adults with sarcopenia? A case report. Clin Interv Aging. 2019;14:1461-1469. [32] PIGNANELLI C, PETRICK HL, KEYVANI F, et al. Low-load resistance training to task failure with and without blood flow restriction: muscular functional and structural adaptations. Am J Physiol Regul Integr Comp Physiol. 2020; 318(2):R284-R295. [33] OGAWA H, NAKAJIMA T, SHIBASAKI I, et al. Low-Intensity Resistance Training with Moderate Blood Flow Restriction Appears Safe and Increases Skeletal Muscle Strength and Size in Cardiovascular Surgery Patients: A Pilot Study. J Clin Med. 2021;10(3):547. [34] YASUDA T, FUKUMURA K, UCHIDA Y, et al. Effects of Low-Load, Elastic Band Resistance Training Combined With Blood Flow Restriction on Muscle Size and Arterial Stiffness in Older Adults. J Gerontol A Biol Sci Med Sci. 2015;70(8):950-958. [35] YASUDA T, MEGURO M, SATO Y, et al. Use and safety of KAATSU training: results of a national survey in 2016. Int J KAATSU Train Res. 2017;13(1):1-9. [36] PITSILLIDES A, STASINOPOULOS D, MAMAIS I. Blood flow restriction training in patients with knee osteoarthritis: Systematic review of randomized controlled trials. J Bodyw Mov Ther. 2021;27:477-486. [37] BUFORD TW, FILLINGIM RB, MANINI TM, et al. Kaatsu training to enhance physical function of older adults with knee osteoarthritis: Design of a randomized controlled trial. Contemp Clin Trials. 2015;43:217-222. [38] GRONLUND C, CHRISTOFFERSEN KS, THOMSEN K, et al. Effect of blood-flow restriction exercise on falls and fall related risk factors in older adults 60 years or above: a systematic review. J Musculoskelet Neuronal Interact. 2020;20(4): 513-525. [39] FUKUDA T, KURANO M, FUKUMURA K, et al. Cardiac rehabilitation increases exercise capacity with a reduction of oxidative stress. Korean Circ J. 2013; 43(7):481-487. [40] HIRAIZUMI Y, NAKAJIMA T, SATO Y, et al. KAATSU training as a new effective exercise therapy in a case of femoral medial condyle osteonecrosis. Int J KAATSU Train Res. 2016;12(1):1-4. [41] YASUDA T, OOSUMI S, SUGIMOTO S, et al. Effect of KAATSU training on thigh muscle size and safety for a patient with knee meniscectomy over 3 years. Int J KAATSU Train Res. 2017;13(1):11-14. [42] ABE T, SAKAMAKI M, FUJITA S, et al. Effects of low-intensity walk training with restricted leg blood flow on muscle strength and aerobic capacity in older adults. J Geriatr Phys Ther. 2010;33(1):34-40. [43] SCHWIETE C, FRANZ A, ROTH C, et al. Effects of Resting vs. Continuous Blood-Flow Restriction-Training on Strength, Fatigue Resistance, Muscle Thickness, and Perceived Discomfort. Front Physiol. 2021;12:663665. [44] MADARAME H, KURANO M, FUKUMURA K, et al. Haemostatic and inflammatory responses to blood flow-restricted exercise in patients with ischaemic heart disease: a pilot study. Clin Physiol Funct Imaging. 2013; 33(1):11-17. [45] WILSON RJ, DRAKE JC, CUI D, et al. Voluntary running protects against neuromuscular dysfunction following hindlimb ischemia-reperfusion in mice. J Appl Physiol (1985). 2019;126(1):193-201. [46] TABATA S, SUZUKI Y, AZUMA K, et al. Rhabdomyolysis After Performing Blood Flow Restriction Training: A Case Report. J Strength Cond Res. 2016; 30(7):2064-2068. [47] 魏佳,李博,冯连世,等.血流限制训练的方法学因素及潜在安全性问题[J].中国体育科技,2019,55(3):3-12. [48] CLARK BC, MANINI TM. Functional consequences of sarcopenia and dynapenia in the elderly. Curr Opin Clin Nutr Metab Care. 2010;13(3):271-276. [49] WACKERHAGE H, SCHOENFELD BJ, HAMILTON DL, et al. Stimuli and sensors that initiate skeletal muscle hypertrophy following resistance exercise. J Appl Physiol (1985). 2019;126(1):30-43. [50] ZHANG T, TIAN G, WANG X. Effects of Low-Load Blood Flow Restriction Training on Hemodynamic Responses and Vascular Function in Older Adults: A Meta-Analysis. Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2022;19(11):6750. [51] GUNDERMANN DM, FRY CS, DICKINSON JM, et al. Reactive hyperemia is not responsible for stimulating muscle protein synthesis following blood flow restriction exercise. J Appl Physiol (1985). 2012;112(9):1520-1528. [52] GUILLET C, PROD’HOMME M, BALAGE M, et al. Impaired anabolic response of muscle protein synthesis is associated with S6K1 dysregulation in elderly humans. FASEB J. 2004;18(13):1586-1587. [53] MARKOFSKI MM, DICKINSON JM, DRUMMOND MJ, et al. Effect of age on basal muscle protein synthesis and mTORC1 signaling in a large cohort of young and older men and women. Exp Gerontol. 2015;65:1-7. [54] BÖHM R, IMSENG S, JAKOB RP, et al.The dynamic mechanism of 4E-BP1 recognition and phosphorylation by mTORC1. Mol Cell. 2021;81(11):2403-2416.e5. [55] LE BACQUER O, COMBE K, PATRAC V, et al. 4E-BP1 and 4E-BP2 double knockout mice are protected from aging-associated sarcopenia. J Cachexia Sarcopenia Muscle. 2019; 10(3):696-709. [56] NASCIMENTO C M, INGLES M, SALVADOR-PASCUAL A, et al. Sarcopenia, frailty and their prevention by exercise. Free Radic Biol Med. 2019;132:42-49. [57] 余尾,宋刚,刘译文.血流限制介入低强度阻力训练对肌肉适能的效益及生理机制[J].中国组织工程研究,2022,26(17):2768-2774. [58] GOTO K, ISHII N, KIZUKA T, et al. The impact of metabolic stress on hormonal responses and muscular adaptations. Med Sci Sports Exerc. 2005; 37(6):955-963. [59] EL ASSAR M, ÁLVAREZ-BUSTOS A, SOSA P, et al. Effect of Physical Activity/Exercise on Oxidative Stress and Inflammation in Muscle and Vascular Aging. Int J Mol Sci. 2022;23(15):8713. [60] PAULY M, DAUSSIN F, BURELLE Y, et al. AMPK activation stimulates autophagy and ameliorates muscular dystrophy in the mdx mouse diaphragm. Am J Pathol. 2012;181(2):583-592. [61] AHMETOV II, VINOGRADOVA OL, WILLIAMS AG. Gene polymorphisms and fiber-type composition of human skeletal muscle. Int J Sport Nutr Exerc Metab. 2012;22(4):292-303. [62] 成琳,汪皓男,王丽娜,等.血流限制训练在前交叉韧带重建术后康复中的应用研究进展[J].中国运动医学杂志,2021,40(8):663-670. [63] RAMOS-CAMPO DJ, SCOTT BR, ALCARAZ PE, et al. The efficacy of resistance training in hypoxia to enhance strength and muscle growth: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Eur J Sport Sci. 2018;18(1):92-103. [64] BARJASTE A, MIRZAEI B, RAHMANI-NIA F, et al. Concomitant aerobic-and hypertrophy-related skeletal muscle cell signaling following blood flow-restricted walking. Science & Sports. 2021;36(2):e51-e58. [65] TAN Z, ZHAO Y, ZHENG Y, et al. The Effect of Blood Flow-Restricted Low Resistance Training on Microvascular Circulation of Myocardium in Spontaneously Hypertensive Rats. Front Physiol. 2022;13:829718. [66] HUEY KA. Potential Roles of Vascular Endothelial Growth Factor During Skeletal Muscle Hypertrophy. Exerc Sport Sci Rev. 2018;46(3):195-202. [67] 孔健达,穆玉晶,朱磊,等.骨骼肌再生过程中卫星细胞调控机制及其生态位信号的作用[J].中国组织工程研究,2024,28(7):1105-1111. [68] BJØRNSEN T, WERNBOM M, LØVSTAD A, et al. Delayed myonuclear addition, myofiber hypertrophy, and increases in strength with high-frequency low-load blood flow restricted training to volitional failure. J Appl Physiol (1985). 2019;126(3):578-592. [69] WERNBOM M, APRO W, PAULSEN G, et al. Acute low-load resistance exercise with and without blood flow restriction increased protein signalling and number of satellite cells in human skeletal muscle. Eur J Appl Physiol. 2013;113(12):2953-2965. [70] YASUDA T, FUJITA S, OGASAWARA R, et al. Effects of low-intensity bench press training with restricted arm muscle blood flow on chest muscle hypertrophy: a pilot study. Clin Physiol Funct Imaging. 2010;30(5):338-343. [71] SHIMIZU R, HOTTA K, YAMAMOTO S, et al. Low-intensity resistance training with blood flow restriction improves vascular endothelial function and peripheral blood circulation in healthy elderly people. Eur J Appl Physiol. 2016;116(4):749-757. [72] LIXANDRÃO ME, UGRINOWITSCH C, LAURENTINO G, et al. Effects of exercise intensity and occlusion pressure after 12 weeks of resistance training with blood-flow restriction. Eur J Appl Physiol. 2015;115(12):2471-2480. [73] COOK SB, CLEARY CJ. Progression of Blood Flow Restricted Resistance Training in Older Adults at Risk of Mobility Limitations. Front Physiol. 2019; 10:738. [74] LOENNEKE JP, KIM D, FAHS CA, et al. Effects of exercise with and without different degrees of blood flow restriction on torque and muscle activation. Muscle Nerve. 2015;51(5):713-721. [75] 姜艳菊,冯武仪,叶汪泉,等.血流限制性训练对老年人下肢肌力和平衡步态的疗效观察[J].按摩与康复医学,2021,12(11):21-23+27. [76] LOENNEKE JP, WILSON GJ, WILSON JM. A mechanistic approach to blood flow occlusion. Int J Sports Med. 2010;31(1):1-4. [77] FITZGIBBONS PG, DIGIOVANNI C, HARES S, et al. Safe tourniquet use: a review of the evidence. J Am Acad Orthop Surg. 2012;20(5):310-319. [78] ROSSOW LM, FAHS CA, LOENNEKE JP, et al. Cardiovascular and perceptual responses to blood-flow-restricted resistance exercise with differing restrictive cuffs. Clin Physiol Funct Imaging. 2012;32(5):331-337. [79] WERNBOM M, JÄRREBRING R, ANDREASSON MA, et al. Acute effects of blood flow restriction on muscle activity and endurance during fatiguing dynamic knee extensions at low load. J Strength Cond Res. 2009;23(8): 2389-2395. [80] 陆锦华.血流限制训练的效果、作用机制与实践策略[J].河北体育学院学报,2020,34(3):77-84. [81] CERQUEIRA MS, COSTA EC, SANTOS OLIVEIRA R, et al. Blood Flow Restriction Training: To Adjust or Not Adjust the Cuff Pressure Over an Intervention Period? Front Physiol. 2021;12:678407. [82] FREITAS EDS, KARABULUT M, BEMBEN MG. The Evolution of Blood Flow Restricted Exercise. Front Physiol. 2021;12:747759. |
| [1] | 魏 娟, 李 婷, 郇梦婷, 谢 颖, 谢舟煜, 韦庆波, 吴云川. 静力性训练改善2型糖尿病骨骼肌胰岛素抵抗的机制[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2024, 28(8): 1271-1276. |
| [2] | 王 继, 张 敏, 李文博, 杨中亚, 张 龙. 有氧运动对2型糖尿病大鼠糖脂代谢、骨骼肌炎症和自噬的影响[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2024, 28(8): 1200-1205. |
| [3] | 孔健达, 穆玉晶, 朱 磊, 李志林, 陈世娟. 骨骼肌再生过程中卫星细胞调控机制及其生态位信号的作用[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2024, 28(7): 1105-1111. |
| [4] | 杨毅峰, 黄 健, 叶 楠, 王 琳. 全膝关节置换中的缺血再灌注损伤[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2024, 28(6): 955-960. |
| [5] | 刘志杨, 傅泽铤, 夏 雨, 丁海丽. 运动性骨骼肌损伤中时钟基因BMAL1与MyoD的作用[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2024, 28(4): 510-515. |
| [6] | 姬卫秀, 白 毅, 王 硕, 赵云罡. 3-硝基-N-甲基水杨酰胺对肢体缺血再灌注损伤大鼠骨骼肌的保护作用及机制[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2024, 28(20): 3164-3169. |
| [7] | 谢恩礼, 陶慧敏. 血流限制训练在临床康复医学中的应用趋势[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2024, 28(2): 258-262. |
| [8] | 谢 鹏, 张 江, 邓小磊, 魏 波, 侯德才. 肌少症小鼠模型构建的系统回顾[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2024, 28(2): 263-266. |
| [9] | 王京峰, 文登台, 王士杰, 高颖晖. Atg介导的自噬、运动和骨骼肌衰老[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2024, 28(2): 295-301. |
| [10] | 龙 宜, 杨佳明, 叶 花, 钟燕彪, 王茂源. 细胞外囊泡在少肌性肥胖中的作用及机制[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2024, 28(2): 315-320. |
| [11] | 赵莎莎, 贺 庆, 李 佳, 吴 迎. 补充重组人源胶原蛋白对离心运动后小鼠骨骼肌细胞外基质重塑的影响[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2024, 28(16): 2542-2549. |
| [12] | 王 继, 胡 立, 杨中亚, 韩 鹏. 云贵高原部分地区老年肌少症患病率及危险因素的横断面调查[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2024, 28(14): 2197-2201. |
| [13] | 张 玥, 郭英杰, 程 杨, 杨婷婷. 血流限制训练对上肢肌肉适能效益的影响[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2024, 28(14): 2248-2253. |
| [14] | 左会武, 耿治中, 陈 鹏, 林熙凯, 陈 建. 血流限制训练对前交叉韧带重建患者膝关节功能恢复的Meta分析[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2024, 28(12): 1962-1968. |
| [15] | 白峥嵘, 孙 羽, 张振显, 潘诗农. 延迟性肌肉酸痛与运动性骨骼肌记忆[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2024, 28(11): 1762-1766. |
血流限制(blood flow retriction,BFR)训练(又称KAATSU训练)作为一种新兴的运动干预方法,近年来备受关注。该训练方法通过限制肌肉血流量,刺激肌肉对于低强度运动的适应性反应,从而提高肌肉力量和质量[5]。循证研究表明,BFR训练相比传统抗阻训练对老年人肌肉力量和质量的改善作用更佳,甚至可以替代传统训练方法[6-8]。然而,BFR训练亦存在一些潜在的局限性和不良反应,例如可能引发血管疾病、肌肉损伤等,这使得BFR训练的优势、安全性和风险需要深入探讨;另外,针对老年肌少症的BFR训练的生物学机制和应用方案亦有待进一步深入的探讨。
因此,文章旨在详细回顾BFR训练在干预老年肌少症方面的影响(尤其是优势、安全性和风险)及其生物学机制和应用方案,探讨该训练方法的潜在风险和适用范围,进而为制定针对老年肌少症的运动处方提供理论基础。 中国组织工程研究杂志出版内容重点:组织构建;骨细胞;软骨细胞;细胞培养;成纤维细胞;血管内皮细胞;骨质疏松;组织工程
1.1.1 检索人 孔健达,陈世娟。
1.1.2 检索文献时限 各数据库建库至2023年2月。
1.1.3 检索数据库 英文数据库:Web of Science和PubMed等;中文数据库:中国知网(CNKI)、万方、维普等。
1.1.4 检索词 英文检索词:blood flow restriction training、KAATSU、elderly、sarcopenia、muscle和Skeletal muscle等;中文检索词:血流限制训练、加压训练、老年人、肌少症和肌肉等。
1.1.5 检索文献类型 随机对照试验、单因素实验、综述、案例研究和非随机性历史对照试验等。
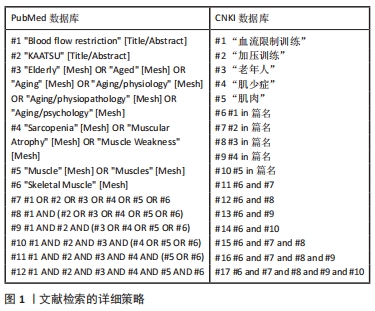
1.1.6 文献检索策略 运用布尔逻辑运算符“or”和“and”分别将检索词连接进行检索。以PubMed和CNKI数据库为例,文献检索的详细策略见图1。
1.2 纳入和排除标准
1.2.1 纳入标准 ①与BFR训练干预对肌少症影响的相关文献;②与BFR训练治疗老年肌少症生物学机制相关的文献;③与肌少症BFR训练方案相关的文献;④经同行专家评审认可并发表的文献;⑤研究内容和此次综述选题相关的文献。
1.2.2 排除标准 ①所在期刊无同行评审环节的文献;②各数据库中重复的文献;③无法获取全文的文献。
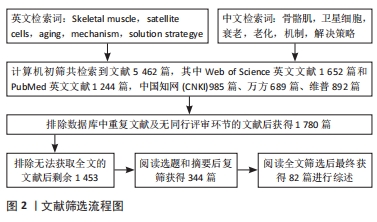
1.3 文献质量评价 数据库共检索到文献5 462篇,严格按照纳入和排除标准进行筛选,最终纳入文献82篇。文献筛选流程图见图2。
180 mmHg,通常选择完全闭塞动脉血流压力值的50%-80%。老年人BFR训练频度和组间间隔的研究还需探讨,袖带加压值的最适选择亦需要进一步研究。这些观点均基于和BFR训练干预肌少症相关的文献资料,有助于深入理解BFR训练干预肌少症的效果、优势、安全性和风险,以及BFR训练干预肌少症的生物学机制和应用方案。
此次综述也提出了未来的研究方向:①使用肌少症小鼠模型研究BFR训练对低氧环境的影响,尤其观察BFR训练对低氧诱导因子1α和血管内皮生长因子等低氧环境调控因子的作用;②使用BFR训练干预肌少症患者或相关小鼠模型,观察BFR训练诱导卫星细胞增殖的作用以及具体机制,尤其观察卫星细胞相关的调控蛋白,以及BFR训练是否对肌少症患者卫星细胞的肌源性分化产生作用;③使用特定加压值进行更大样本的调查研究或进行系统评价和Meta分析纳入相关研究,尤其以地区、人种和健康状况等为基准作亚组分析,以评估BFR训练在这些因素下所使用的安全范围,并根据亚组分析结果探究影响BFR训练安全性的其他因素。这些研究方向有助于进一步确定BFR训练干预肌少症的潜在机制,为BFR训练干预肌少症的临床应用中进一步提供理论参考,有助于BFR训练应用推广,并根据这些影响因素为BFR训练的应用方案提供新的思路作为参考。 中国组织工程研究杂志出版内容重点:组织构建;骨细胞;软骨细胞;细胞培养;成纤维细胞;血管内皮细胞;骨质疏松;组织工程
 #br#
#br#
文题释义:
血流限制训练:一种通过在四肢周围加上压力带或气囊来限制血流量,从而减少氧供并提高肌肉水肿和炎症反应,促进肌肉组织恢复和肌肉生长的力量训练方式,可快速提高肌肉力量、增加肌肉体积和耐力、改善肌肉康复和预防肌肉萎缩的训练方法。肌少症:指因持续骨骼肌量流失、强度和功能下降而引起的综合征,该类患者通常站立困难、步履缓慢、容易跌倒骨折,其亦会影响器官功能,可能会引发心脏和肺部衰竭,甚至死亡。
此次综述重点回顾了血流限制(blood flow restriction,BFR)训练对肌少症的干预,包括其影响、生物学机制和应用方案建议。在影响方面,BFR训练被证明能够有效改善肌弱、肌肉萎缩等肌少症状,具有优势,但亦存在安全性和风险问题。从生物学机制角度来看,BFR训练可以增加骨骼肌血流量,调控肌内信号通路,促进骨骼肌的代谢应激,诱导低氧环境和诱导卫星细胞增殖等。在应用方案建议方面,从训练负荷、重复次数、训练频、组间间隔以及袖带尺寸和加压值的角度方面进行了综述,提出了相应的建议。总之,BFR训练有望成为一种有效的干预肌少症的新方法,但在实践中应该谨慎操作,注意安全性和风险问题。
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||