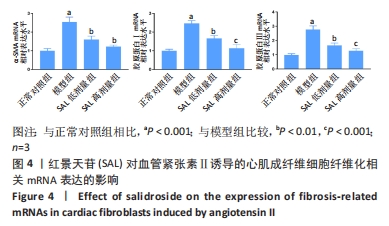
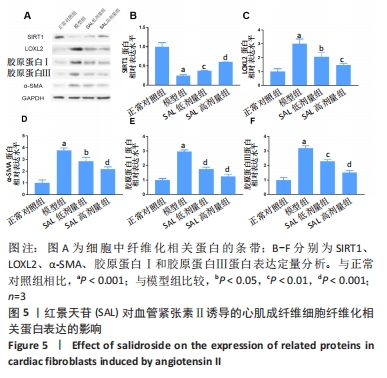
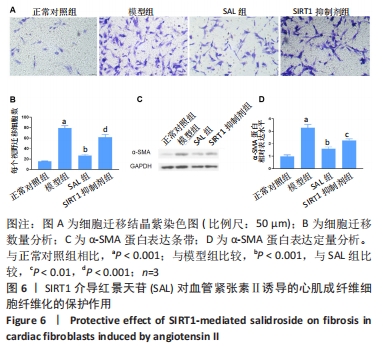
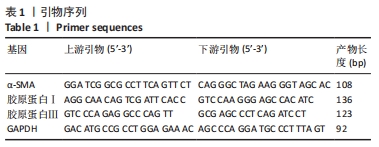
[1] ROTH GA, MENSAH GA, JOHNSON CO, et al. Global Burden of Cardiovascular Diseases and Risk Factors, 1990-2019: Update From the GBD 2019 Study. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2020; 76(25):2982-3021.
[2] ROTH GA, MENSAH GA, FUSTER V. The Global Burden of Cardiovascular Diseases and Risks: A Compass for Global Action. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2020;76(25):2980-2981.
[3] GONZALEZ A, SCHELBERT EB, DIEZ J, et al. Myocardial Interstitial Fibrosis in Heart Failure: Biological and Translational Perspectives. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2018;71(15):1696-1706.
[4] QIN W, CAO L, MASSEY I Y. Role of PI3K/Akt signaling pathway in cardiac fibrosis. Mol Cell Biochem. 2021;476(11):4045-4059.
[5] GARBERN JC, LEE RT. Heart regeneration: 20 years of progress and renewed optimism. Dev Cell. 2022;57(4):424-439.
[6] REN C, ZHAO X, LIU K, et al. Research progress of natural medicine Astragalus mongholicus Bunge in treatment of myocardial fibrosis. J Ethnopharmacol. 2023;305: 116128.
[7] LIU ZH, ZHANG Y, WANG X, et al. SIRT1 activation attenuates cardiac fibrosis by endothelial-to-mesenchymal transition. Biomed Pharmacother. 2019;118:109227.
[8] ERASMUS M, SAMODIEN E, LECOUR S, et al. Linking LOXL2 to Cardiac Interstitial Fibrosis. Int J Mol Sci. 2020;21(16):5913.
[9] AMES MK, ATKINS CE, PITT B. The renin-angiotensin-aldosterone system and its suppression. J Vet Intern Med. 2019;33(2):363-382.
[10] MA ZG, YUAN YP, WU HM, et al. Cardiac fibrosis: new insights into the pathogenesis. Int J Biol Sci. 2018;14(12):1645-1657.
[11] CONTESSOTTO P, PANDIT A. Therapies to prevent post-infarction remodelling: From repair to regeneration. Biomaterials. 2021;275:120906.
[12] NI J, LI Y, XU Y, et al. Salidroside protects against cardiomyocyte apoptosis and ventricular remodeling by AKT/HO-1 signaling pathways in a diabetic cardiomyopathy mouse model. Phytomedicine. 2021;82:153406.
[13] GAO H, LIU X, TIAN K, et al. Insight into the Protective Effect of Salidroside against H(2)O(2)-Induced Injury in H9C2 Cells. Oxid Med Cell Longev. 2021;2021:1060271.
[14] LIEBEN LOUIS X, MEIKLE Z, CHAN L, et al. Divergent Effects of Resveratrol on Rat Cardiac Fibroblasts and Cardiomyocytes. Molecules. 2019;24(14):2604.
[15] TARBIT E, SINGH I, PEART JN, et al. Increased release of serotonin from rat primary isolated adult cardiac myofibroblasts. Sci Rep.2021;11(1): 20376.
[16] KUROSE H. Cardiac Fibrosis and Fibroblasts. Cells. 2021;10(7):1716.
[17] MUHL L, GENOVE G, LEPTIDIS S, et al. Single-cell analysis uncovers fibroblast heterogeneity and criteria for fibroblast and mural cell identification and discrimination. Nat Commun. 2020;11(1):3953.
[18] TARBIT E, SINGH I, PEART JN, et al. Biomarkers for the identification of cardiac fibroblast and myofibroblast cells. Heart Fail Rev. 2019;24(1):1-15.
[19] CUI S, LIU Z, TAO B, et al. miR-145 attenuates cardiac fibrosis through the AKT/GSK-3beta/beta-catenin signaling pathway by directly targeting SOX9 in fibroblasts. J Cell Biochem. 2021;122(2):209-221.
[20] HUANG C, WANG R, LU J, et al. MicroRNA-338-3p as a therapeutic target in cardiac fibrosis through FGFR2 suppression. J Clin Lab Anal. 2022;36(8):e24584.
[21] KIM H, XUE X. Detection of Total Reactive Oxygen Species in Adherent Cells by 2’,7’-Dichlorodihydrofluorescein Diacetate Staining. J Vis Exp. 2020;(160): 10.3791/60682.
[22] WEYDERT CJ, CULLEN JJ. Measurement of superoxide dismutase, catalase and glutathione peroxidase in cultured cells and tissue. Nat Protoc. 2010;5(1):51-66.
[23] VINCENT A, THAUVIN M, QUEVRAIN E, et al. Evaluation of the compounds commonly known as superoxide dismutase and catalase mimics in cellular models. J Inorg Biochem. 2021;219:111431.
[24] MIA MM, CIBI DM, GHANI S, et al. Loss of Yap/Taz in cardiac fibroblasts attenuates adverse remodelling and improves cardiac function. Cardiovasc Res. 2022;118(7):1785-1804.
[25] KONG P, CHRISTIA P, FRANGOGIANNIS NG. The pathogenesis of cardiac fibrosis. Cell Mol Life Sci. 2014;71(4):549-574.
[26] PAUKLIN P, ZILMER M, EHA J, et al. Markers of Inflammation, Oxidative Stress, and Fibrosis in Patients with Atrial Fibrillation. Oxid Med Cell Longev. 2022;2022:4556671.
[27] REN C, LIU K, ZHAO X, et al. Research Progress of Traditional Chinese Medicine in Treatment of Myocardial fibrosis. Front Pharmacol. 2022;13:853289.
[28] MAGANI SKJ, MUPPARTHI SD, GOLLAPALLI BP, et al. Salidroside - Can it be a Multifunctional Drug? . Curr Drug Metab.2020;21(7):512-524.
[29] YANG S, PEI T, WANG L, et al. Salidroside Alleviates Renal Fibrosis in SAMP8 Mice by Inhibiting Ferroptosis. Molecules. 2022;27(22):8039.
[30] QU B, LIU X, LIANG Y, et al. Salidroside in the Treatment of NAFLD/NASH. Chem Biodivers. 2022;19(12):e202200401.
[31] MORLEY M E, RICHES K, PEERS C, et al. Hypoxic inhibition of human cardiac fibroblast invasion and MMP-2 activation may impair adaptive myocardial remodelling. Biochem Soc Trans. 2007;35(Pt 5):905-907.
[32] FRANGOGIANNIS NG. Cardiac fibrosis. Cardiovasc Res. 2021;117(6):1450-1488.
[33] LI X, MO N, LI Z. Ginsenosides: potential therapeutic source for fibrosis-associated human diseases. J Ginseng Res. 2020;44(3):386-398.
[34] STONE RC, CHEN V, BURGESS J, et al. Genomics of Human Fibrotic Diseases: Disordered Wound Healing Response. Int J Mol Sci. 2020;21(22):8590.
[35] CROSAS-MOLIST E, FABREGAT I. Role of NADPH oxidases in the redox biology of liver fibrosis. Redox Biol. 2015;6:106-111.
[36] ZOROV DB, JUHASZOVA M, SOLLOTT SJ. Mitochondrial reactive oxygen species (ROS) and ROS-induced ROS release. Physiol Rev. 2014;94(3):909-950.
[37] RAMACHANDRA CJA, CONG S, CHAN X, et al. Oxidative stress in cardiac hypertrophy: From molecular mechanisms to novel therapeutic targets. Free Radic Biol Med. 2021; 166:297-312.
[38] HAO S, SUI X, WANG J, et al. Secretory products from epicardial adipose tissue induce adverse myocardial remodeling after myocardial infarction by promoting reactive oxygen species accumulation. Cell Death Dis. 2021;12(9):848.
[39] WANG CY, SUN ZN, WANG MX, et al. SIRT1 mediates salidroside-elicited protective effects against MPP(+) -induced apoptosis and oxidative stress in SH-SY5Y cells: involvement in suppressing MAPK pathways. Cell Biol Int. 2018;42(1):84-94.
[40] HAN X, DING C, SANG X, et al. Targeting Sirtuin1 to treat aging-related tissue fibrosis: From prevention to therapy. Pharmacol Ther. 2022;229:107983.
[41] BUGYEI-TWUM A, FORD C, CIVITARESE R, et al. Sirtuin 1 activation attenuates cardiac fibrosis in a rodent pressure overload model by modifying Smad2/3 transactivation. Cardiovasc Res. 2018;114(12):1629-1641.
[42] ZHAO D, SUN X, LV S, et al. Salidroside attenuates oxidized lowdensity lipoproteininduced endothelial cell injury via promotion of the AMPK/SIRT1 pathway. Int J Mol Med. 2019;43(6):2279-2290.
[43] ZEISBERG EM, TARNAVSKI O, ZEISBERG M, et al. Endothelial-to-mesenchymal transition contributes to cardiac fibrosis. Nat Med. 2007;13(8):952-961.
[44] PARDALI E, SANCHEZ-DUFFHUES G, GOMEZ-PUERTO MC, et al. TGF-beta-Induced Endothelial-Mesenchymal Transition in Fibrotic Diseases. Int J Mol Sci. 2017;18(10):2157.
[45] LI N, ZHOU H, MA ZG, et al. Geniposide Alleviates Isoproterenol-Induced Cardiac Fibrosis Partially via SIRT1 Activation in vivo and in vitro. Front Pharmacol. 2018;9:854.
[46] ZERR P, PALUMBO-ZERR K, HUANG J, et al. Sirt1 regulates canonical TGF-beta signalling to control fibroblast activation and tissue fibrosis. Ann Rheum Dis. 2016;75(1):226-233.
[47] LI S, ZHU Z, XUE M, et al. Fibroblast growth factor 21 protects the heart from angiotensin II-induced cardiac hypertrophy and dysfunction via SIRT1. Biochim Biophys Acta Mol Basis Dis. 2019;1865(6):1241-1252.
[48] YANG J, SAVVATIS K, KANG JS, et al. Targeting LOXL2 for cardiac interstitial fibrosis and heart failure treatment. Nat Commun. 2016;7:13710.
|