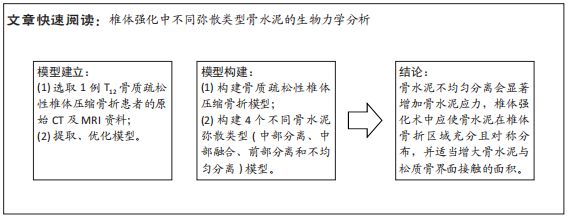
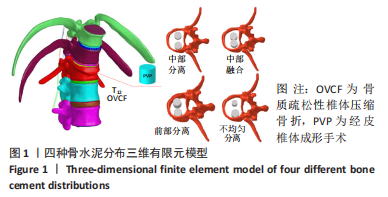
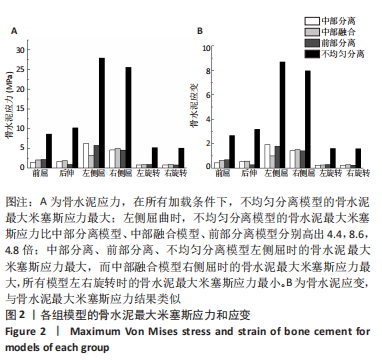
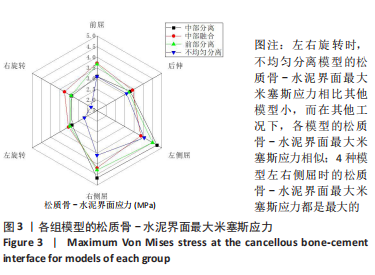
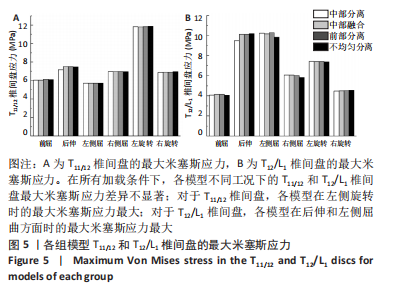
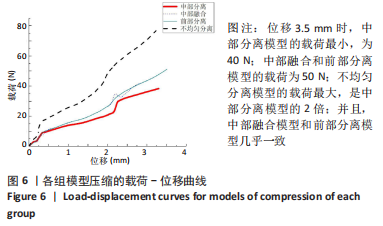
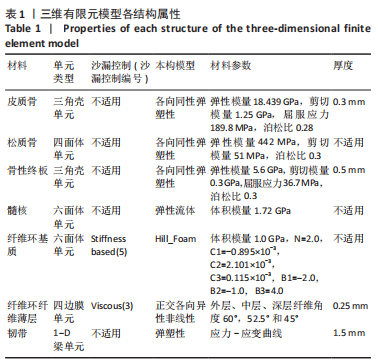
[1] KLAZEN CA, LOHLE PN, DE VRIES J, et al. Vertebroplasty versus conservative treatment in acute osteoporotic vertebral compression fractures (Vertos II): an open-label randomised trial. Lancet. 2010; 376(9746):1085-1092.
[2] LI HM, ZHANG RJ, GAO H, et al. New vertebral fractures after osteoporotic vertebral compression fracture between balloon kyphoplasty and nonsurgical treatment PRISMA. Medicine (Baltimore). 2018;97(40):e12666.
[3] KUTSAL FY, ERGIN ERGANI GO. Vertebral compression fractures: Still an unpredictable aspect of osteoporosis. Turk J Med Sci. 2021;51(2):393-399.
[4] PARK JS, PARK YS. Survival analysis and risk factors of new vertebral fracture after vertebroplasty for osteoporotic vertebral compression fracture. Spine J. 2021;21(8):1355-1361.
[5] MAO W, DONG F, HUANG G, et al. Risk factors for secondary fractures to percutaneous vertebroplasty for osteoporotic vertebral compression fractures: a systematic review. J Orthop Surg Res. 2021;16(1):644.
[6] SUZUKI N, OGIKUBO O, HANSSON T. The prognosis for pain, disability, activities of daily living and quality of life after an acute osteoporotic vertebral body fracture: its relation to fracture level, type of fracture and grade of fracture deformation. Eur Spine J. 2009;18(1):77-88.
[7] LI Y, FENG X, PAN J, et al. Percutaneous Vertebroplasty Versus Kyphoplasty for Thoracolumbar Osteoporotic Vertebral Compression Fractures in Patients with Distant Lumbosacral Pain. Pain Physician. 2021;24(3):E349-E356.
[8] CHANG JZ, BEI MJ, SHU DP, et al. Comparison of the clinical outcomes of percutaneous vertebroplasty vs. kyphoplasty for the treatment of osteoporotic Kümmell’s disease:a prospective cohort study. BMC Musculoskelet Disord. 2020;21(1):238.
[9] SANLI I, VAN KUIJK SMJ, DE BIE RA, et al. Percutaneous cement augmentation in the treatment of osteoporotic vertebral fractures (OVFs) in the elderly: a systematic review. Eur Spine J. 2020;29(7): 1553-1572.
[10] PAN M, GE J, LI Q, et al. Percutaneous vertebral augmentation in special Genant IV osteoporotic vertebral compression fractures. J Orthop Translat. 2019;20:94-99.
[11] ZHANG H, XU C, ZHANG T, et al. Does Percutaneous Vertebroplasty or Balloon Kyphoplasty for Osteoporotic Vertebral Compression Fractures Increase the Incidence of New Vertebral Fractures? A Meta-Analysis. Pain Physician. 2017;20(1):E13-E28.
[12] LI M, ZHANG Y, JIN P, et al. Percutaneous vertebral augmentation using drill rotation for osteoporotic vertebral compression fractures with intravertebral vacuum cleft. Skeletal Radiol. 2020;49(9):1459-1465.
[13] YU W, XU W, JIANG X, et al. Risk Factors for Recollapse of the Augmented Vertebrae After Percutaneous Vertebral Augmentation: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. World Neurosurg. 2018;111: 119-129.
[14] RABEI R, PATEL K, GINSBURG M, et al. Percutaneous Vertebral Augmentation for Vertebral Compression Fractures: National Trends in the Medicare Population (2005-2015). Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2019; 44(2):123-133.
[15] 叶林强,卢国樑,江晓兵,等.骨水泥填充位置对骨质疏松性椎体压缩骨折的生物力学特性影响:一项三维有限元分析[J].中国组织工程研究,2022,26(28):4435-4440.
[16] 蔡明,戚颖,刘肃,等.骨水泥不同分布对骨质疏松性椎体压缩性骨折的生物力学影响:三维有限元分析[J].中国医学物理学杂志, 2022,39(6):771-777.
[17] HEDAYATI Z, SHOMALI M. Maxillary anterior en masse retraction using different antero-posterior position of mini screw: a 3D finite element study. Prog Orthod. 2016;17(1):31.
[18] EL-ANWAR M, GHALI R, ABOELNAGGA M. 3D Finite Element Study on: Bar Splinted Implants Supporting Partial Denture in the Reconstructed Mandible. Open Access Maced J Med Sci. 2016;4(1):164-171.
[19] SHAMAMI DZ, KARIMI A, BEIGZADEH B, et al. A 3D finite element study for stress analysis in bone tissue around single implants with different materials and various bone qualities. J Biom Tissue Eng. 2014;4(8):
632-637.
[20] YAN J, LIAO Z, YU Y. Finite element analysis of dynamic changes in spinal mechanics of osteoporotic lumbar fracture. Eur J Med Res. 2022; 27(1):142.
[21] LU H, ZHANG Q, DING F, et al.Finite Element Analysis of Unilateral versus Bipedicular Bone-Filling Mesh Container for the Management of Osteoporotic Compression Fractures. Biomed Res Int. 2022;2022: 6850089.
[22] POLIKEIT A, NOLTE LP, FERGUSON SJ. The effect of cement augmentation on the load transfer in an osteoporotic functional spinal unit: finite-element analysis. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2003;28(10):991-996.
[23] BAROUD G, NEMES J, HEINI P, et al. Load shift of the intervertebral disc after a vertebroplasty: a finite-element study. Eur Spine J. 2003; 12(4):421-426.
[24] YU W, XU W, JIANG X, et al. Risk Factors for Recollapse of the Augmented Vertebrae After Percutaneous Vertebral Augmentation:
A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. World Neurosurg. 2018;111: 119-129.
[25] HE D, LOU C, YU W, et al. Cement Distribution Patterns Are Associated with Recompression in Cemented Vertebrae After Percutaneous Vertebroplasty: A Retrospective Study. World Neurosurg. 2018;120:e1-e7.
[26] WANG D, LI Y, YIN H, et al. Three-dimensional finite element analysis of optimal distribution model of vertebroplasty. Ann Palliat Med. 2020; 9(3):1062-1072.
[27] JANSSEN D, MANN KA, VERDONSCHOT N. Micro-mechanical modeling of the cement-bone interface: the effect of friction, morphology and material properties on the micromechanical response. J Biomech. 2008;41(15):3158-3163.
[28] LI YX, GUO DQ, ZHANG SC, et al. Risk factor analysis for re-collapse of cemented vertebrae after percutaneous vertebroplasty (PVP) or percutaneous kyphoplasty (PKP). Int Orthop. 2018;42(9):2131-2139.
[29] LIANG D, YE LQ, JIANG XB, et al. Biomechanical effects of cement distribution in the fractured area on osteoporotic vertebral compression fractures: a three-dimensional finite element analysis. J Surg Res. 2015;195(1):246-256.
[30] LIU H, ZHANG J, LIANG X, et al. Distribution Pattern Making Sense: Patients Achieve Rapider Pain Relief with Confluent Rather Than Separated Bilateral Cement in Percutaneous Kyphoplasty for Osteoporotic Vertebral Compression Fractures. World Neurosurg. 2019;126:e1190-e1196.
[31] 张大鹏,毛克亚,强晓军,等.椎体增强术后骨水泥分布形态分型及其临床意义[J].中华创伤杂志,2018,34(2):130-137.
[32] HE S, ZHANG Y, LV N, et al. The effect of bone cement distribution on clinical efficacy after percutaneous kyphoplasty for osteoporotic vertebral compression fractures. Medicine (Baltimore). 2019;98(50): e18217.
[33] 任学平,杨松涛.基于LS-DYNA和HyperMesh的转炉倾动机构减速器不同步启动仿真[J].机械传动,2015,39(6):88-92.
[34] 钟尖,刘唐志,陈柳晓.基于Hypermesh/Ls-Dyna的油桶拦挡安全性能与适用条件研究[J].武汉理工大学学报,2015,37(10):51-56.
[35] CHEN LH, HSIEH MK, LIAO JC, et al. Repeated percutaneous vertebroplasty for refracture of cemented vertebrae. Arch Orthop Trauma Surg. 2011;131(7):927-933.
[36] ZHAO WT, QIN DP, ZHANG XG, et al. Biomechanical effects of different vertebral heights after augmentation of osteoporotic vertebral compression fracture: a three-dimensional finite element analysis. J Orthop Surg Res. 2018;13(1):32.
[37] PENG Y, DU X, HUANG L, et al. Optimizing bone cement stiffness for vertebroplasty through biomechanical effects analysis based on patient-specific three-dimensional finite element modeling. Med Biol Eng Comput. 2018;56(11):2137-2150.
[38] ZHOU F, YANG S, LIU J, et al. Finite element analysis comparing short-segment instrumentation with conventional pedicle screws and the Schanz pedicle screw in lumbar 1 fractures. Neurosurg Rev. 2020;43(1):301-312.
[39] KIM JM, SHIN DA, BYUN DH, et al. Effect of bone cement volume and stiffness on occurrences of adjacent vertebral fractures after vertebroplasty. J Korean Neurosurg Soc. 2012;52(5):435-440.
[40] HE SC, TENG GJ, DENG G, et al. Repeat vertebroplasty for unrelieved pain at previously treated vertebral levels with osteoporotic vertebral compression fractures. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2008;33(6):640-647. |