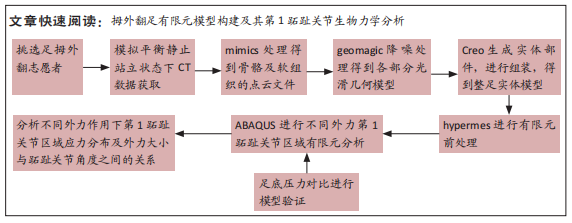
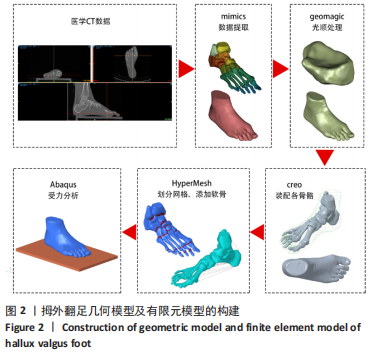
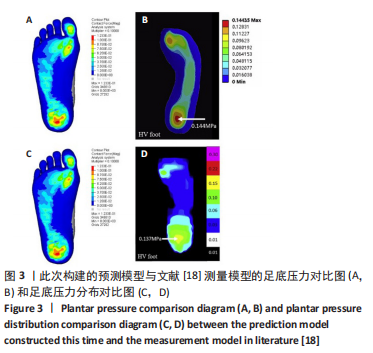
2.1 模型验证 此次预测的足底压力与文献[18]中拇外翻模型足底压力对比结果显示:两种模型的压力峰值分别为
0.123 MPa和0.144 MPa,差异无显著性意义(P > 0.05)[4]。压力分布趋势上,此次构建的模型足底外侧、大脚趾正下方的受力会更明显一些,推测与影像数据的采集为模拟平衡站立状态,而对比文献中的模型是在松弛不受力状态采集相关,但整体压力分布趋势较吻合,峰值位于足跟区域。由文献[18]中对正常足与拇外翻足底压力分布对比试验可知,拇外翻足第3跖骨的von Mises应力集中程度最高,其次是第2、第4和第1跖骨,第5跖骨最低,即应力集中现象在跖骨区域整体外移;此次试验结果也符合这一观点,由图3可以看出此次试验预测和文献[18]试验结果的压力分布与峰值的分布模式也较一致。以上证明该模型的构建及模拟是有效的。
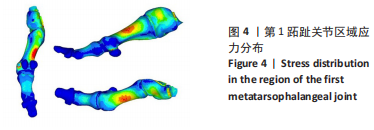
2.2 第1跖趾关节区域应力 拇外翻即第1跖趾关节拇外翻,第1跖趾关节区域的应力分布及大小与拇外翻发展有直接关系。YU 等[13]利用有限元方法,证明了在长时间穿高跟鞋站立时,第1跖趾关节外侧和背侧区域von Mises应力的增加可能诱发拇外翻畸形的发展。在模拟裸足静止站立工况下,对拇外翻足右侧第1跖趾关节区域进行有限元分析,见图4;拇趾远节趾骨受力最小,基本无应力集中,拇趾近节趾骨应力也较小,集中在骨体背侧与底侧的中心,数值在1.875-2.500 MPa之间。较大的应力集中现象出现在第1跖骨,分布趋势为由骨体内侧中部及外侧中部,逐渐向骨体背侧底侧减小,von Mises应力的最大值为8.103 MPa。与正常足第1跖趾关节区域应力分布情况相比,第1跖骨Von Mises应力值更大,且随着拇外翻角的增大,最大主应力值也会增大[13]。这表明减小第1跖趾关节区域的应力集中现象,可以改善拇外翻症状。
2.3 不同外力作用下的模拟分析
2.3.1 标准化角度测量及载荷 临床上利用X射线片诊断拇外翻时,跖趾关节角是一个重要的形态学指标[19],即跖趾关节角越大,拇外翻病症越严重。第1跖趾关节角定义为以第1跖骨的纵轴和长轴作为跖趾关节的矢状面;在矢状面上,第1跖骨长轴与第1近节指骨的夹角为跖趾关节的夹角[13]。
在有限元模拟分析时,模型不同的选取角度、测量方式、外力施加位置都会使结果出现巨大差异,导致同一模型下的数据也不具有可对比性,因此针对此次试验确定一套标准十分有必要。在跖趾关节角测量方面,首先将整足模型体坐标标准化,之后使用COUGHLIN等[20]出版在美国足与踝关节协会(The American Orthopaedic Foot & Ankle Society,AOFAS)角度测量专门委员会报告上的第1跖骨、第2跖骨和拇趾近节趾骨轴线参考点的确定方法,见图5;取顶视图,无透视,测量得初始第1跖趾关节角=(27.67±0.10)°,第1-2跖骨间角(Intermetatarsal Angle,IMA1-2)=(12.34±0.10)°。该组数据与此次试验医生通过临床方法给出的诊断数值(跖趾关节角)=26°、(IMA1-2)=13°差值< 2°,证明了由上述测量方法所得数据是有效的。

在外力施加位置方面,参考文献[21]提出的拇外翻矫形力学原理,确定3个施加外力点,分别为第1拇趾远节趾骨外侧中部、跖趾关节内侧囊处及跖骨近端内侧面,见图6。力的大小通过假设一组初始定值来试验。

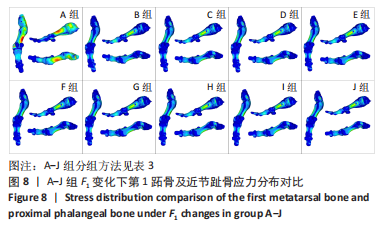
2.3.2 矫正力与跖趾关节角 通常当15° <第1跖趾关节角< 20°,和(或 )9° < (IMA1-2) < 11°时,被认为是轻度拇外翻足;20° <第1跖趾关节角< 40°,11°< (IMA1-2) < 16°为中度;第1跖趾关节角> 40°,(IMA1-2) > 16°为重度拇外翻足[22]。初始工况下,对足第1拇趾远节趾骨外侧中部区域施加向足内侧水平力F1、对足跖趾关节内侧囊处区域施加向足外侧水平力F2、对跖骨近端内侧面施加向足外侧的水平力F3。力的大小通过估测一组定值并控制变量来完成试验,结合试验多组力下第1跖趾关节区域骨头形变及应力分布,并考虑实际骨可承受的外力,将初始一组数据选取原则定为该组值可使第1跖趾关节角< 27°,即第1跖骨长轴与第1近节指骨长轴间的夹角减小,且(IMA1-2) < 12°,通过试验,选取的值分别为F1=50 N,F2=30 N,F3=30 N。第1次试验保持F2与F3的大小不变,等量增加F1的值,设定10组(A-J组),通过上述第1跖趾关节角和IMA1-2测量方式记录不同外力作用下对应跖趾关节角值、IMA1-2值及第1跖趾关节区域最大应力值,所得数据见表3与图7。
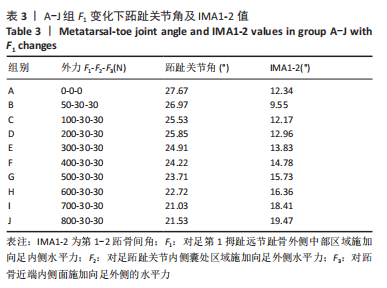
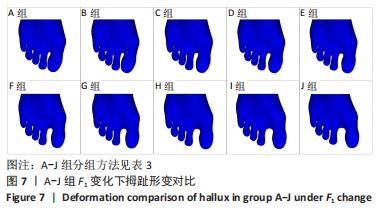
由所得数据表3可知,随着F1的增加跖趾关节角减小,但持续增加F1值,见第J组数据,并不能使跖趾关节角继续减小,反而会增加;IMA1-2只有起初B组数据有明显的减小,随后F1增加,IMA1-2的值逐步增大。图7为A-J组外力作用下拇外翻足拇趾形变模拟图,可以看到B-G组有直观明显的矫正效果,而H-J组由于外力过大而产生了畸变,结合表3数据,认为G组F1数据已经达到矫正效果,H-J组的数据不具有参考性。
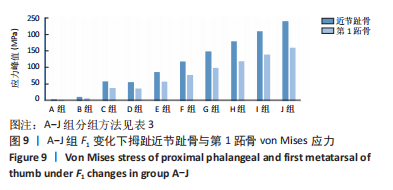
图8为10组外力作用下第1跖趾关节区域应力分布情况,观察可知B-J组与A组相比,拇趾近节趾骨上的应力集中现象由上下侧分布变为内外两侧分布;且由图9可知,随着F1的增加,von Mises应力最大值增大;第1跖骨内外两侧的应力也随F1的增大而增大。
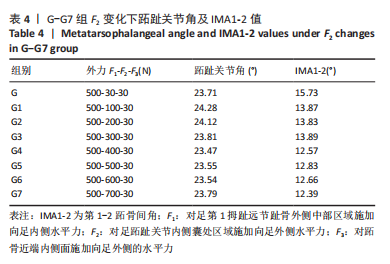
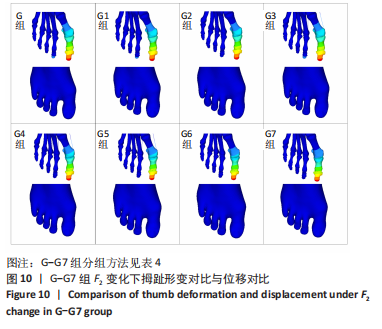
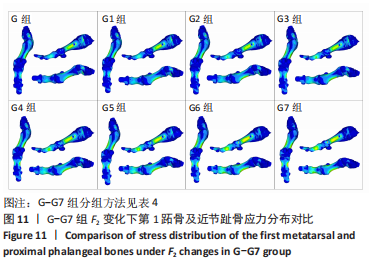
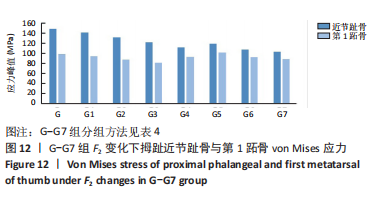
选取上述G组数据,保持作用在第1拇趾远节趾骨外侧中部区域水平力F1、作用在跖骨近端内侧面水平力F3不变,改变作用于足跖趾关节内侧囊处区域F2的大小,分为8组(G-G7组),观察跖趾关节角及IMA1-2的变化,见表4。对于跖趾关节角,随着F2的增加,其数值先增加后减小再增加,在G5后随F2的增加跖趾关节角不能继续减小。图10为拇趾形变及骨骼位移对比图,可以证明F2的变化对第1跖趾关节角度影响不大;IMA1-2的值随着F2的增加,持续减小,G7组与G组下IMA1-2差值为-3.34,说明对其影响较明显。图11,12分别为8组力作用下第1跖骨及近节趾骨应力分布及数值变化,可以看出F2对第1跖骨应力分布及大小影响较小,但可一定程度上减小近节趾骨上的应力集中现象。
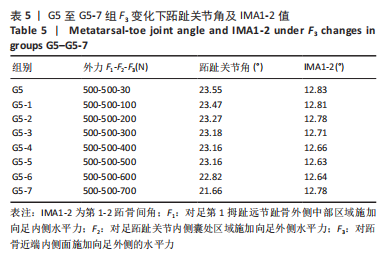
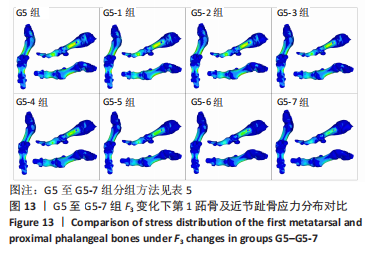
综上选取G5组数据完成下面的研究,保持作用在第1拇趾远节趾骨外侧中部区域水平力F1、作用在足跖趾关节内侧囊处区域F2不变,改变作用在跖骨近端内侧面水平力F3的大小,分为8组(G5至G5-7组),观察跖趾关节角及IMA1-2的变化。观察表5可知,随着F3的增加,G5到G5-4组跖趾关节角的值减小,但最大差值只有-0.39,而F3由500 N继续增加,跖趾关节角开始增大,见G5-5、G5-6、G5-7组数据;对于IMA1-2值,同样在G5到G5-5组,随F3的增加而减小,F3由500 N继续增加使得IMA1-2值开始增大,从图13,14也可看出,在G5-5组数据后第1跖骨及近节趾骨von Mises应力出现增加及波动。观察图15骨骼位移变化及拇趾的形变情况可知F3的变化对于第1跖趾关节区域的影响较小。
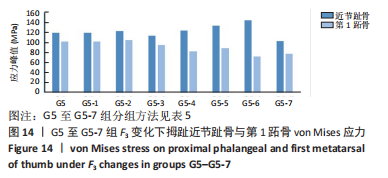
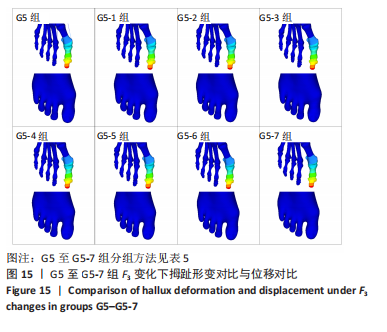
由以上3组试验,通过对第1跖趾关节角度、IMA1-2度的变化,第1跖骨、近节趾骨应力分布与大小变化以及足在外力作用下形变情况的综合分析,认为在此次试验中F1、F2、F3分别为500 N时,即第G5-5组数据下,可达到最好的矫形效果。同时可知作用在第1拇趾远节趾骨外侧中部区域水平力F1对于跖趾关节角的数值改变有直接影响,但并非线性影响;作用于足跖趾关节内侧囊处区域F2主要影响IMA1-2的大小,在同F1作用下,施加一定的F2可以减小IMA1-2;作用在跖骨近端内侧面水平力F3对跖趾关节角、IMA1-2的影响都不大。