[1] BAYER S, MEREDITH SJ, WILSON KW, et al. Knee Morphological Risk Factors for Anterior Cruciate Ligament Injury: A Systematic Review. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2020;102(8):703-718.
[2] GIANOTTI SM, MARSHALL SW, HUME PA, et al. Incidence of anterior cruciate ligament injury and other knee ligament injuries: A national population-based study. J Sci Med Sport. 2009;12(6):622-627.
[3] EGGER AC, PARIKH SN, WILSON PL, et al. What’s New in the Management of Pediatric Anterior Cruciate Ligament Tears and Tibial Spine Fractures. Instr Course Lect. 2021;70:399-414.
[4] LANSDOWN D, MA CB. The Influence of Tibial and Femoral Bone Morphology on Knee Kinematics in the Anterior Cruciate Ligament Injured Knee. Clin Sports Med. 2018;37(1):127-136.
[5] NAZZAL EM, ZSIDAI B, PUJOL O, et al. Considerations of the Posterior Tibial Slope in Anterior Cruciate Ligament Reconstruction: a Scoping Review. Curr Rev Musculoske. 2022;15(4):291-299.
[6] LIU Z, JIANG J, YI Q, et al. An increased posterior tibial slope is associated with a higher risk of graft failure following ACL reconstruction: a systematic review. Knee Surg Sports Traumatol Arthrosc. 2022;30(7):2377-2387.
[7] 龚恒,黄斌,付立功,等.中国汉族人与美国高加索白人膝关节几何形态的比较[J].中国组织工程研究,2020,24(33):5366-5370.
[8] BUCHER C, LAMY D, DEBATY G, et al. Validity of the lever sign test for the clinical diagnosis of anterior cruciate ligament tears: Assessments in ski resorts. Orthop Traumatol Surg Res. 2022;108(3):103254.
[9] 常丽鹏,赵敏,龚国龄,等.MRI在膝关节半月板损伤,前交叉韧带损伤诊断中的应用价值研究[J].中国CT和MRI杂志,2020,18(8):164-167.
[10] ADHIKARI V, JOSHI A, SINGH N, et al. Predictive Accuracy of Blumensaat Line Angle and Its Apex along with Anterior Cruciate Ligament Tear with Abundant Remnant. J Nepal Health Res Counc. 2021;18(4):604-609.
[11] GUNAYDIN B, SAHIN GG, SARI A, et al. A new method for diagnosis of anterior cruciate ligament tear: MRI with maximum flexion of knee in the prone position: A case control study. Int J Surg. 2019;68(2):142-147.
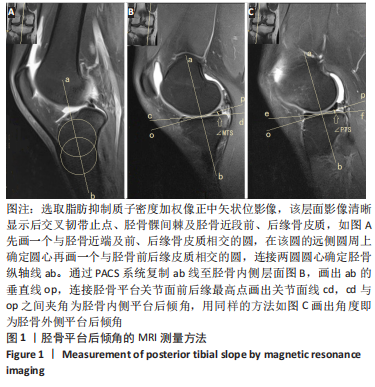
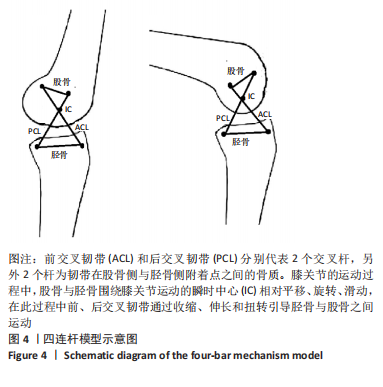
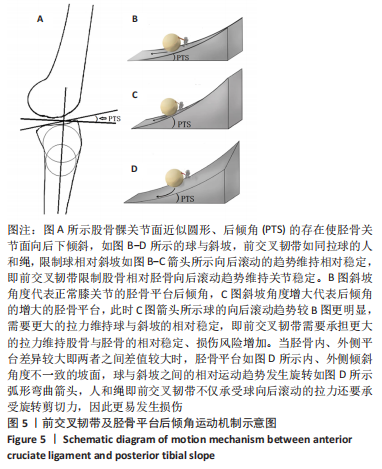
[12] 翁习生,卫小春,主译.膝关节创伤及疾病的MRI图谱[M].北京:中国协和医科大学出版社,2005:29-31.
[13] HUDEK R, FUCHS B, REGENFELDER F, et al. Is noncontact ACL injury associated with the posterior tibial and meniscal slope? Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2011;469(8): 2377-2384.
[14] 王善安,杨友刚,戚世鹏,等. 前交叉韧带损伤合并内侧胫骨平台骨性关节炎患者临床特点分析[J]. 成都医学院学报,2021,42(4):371-374.
[15] KAPLAN JT, RAMSAY JW, CAMERON SE, et al. Association Between Knee Anatomic Metrics and Biomechanics for Male Soldiers Landing With Load. Am J Sport Med. 2020;48(7):1389-1397.
[16] 敖英芳,刘宝戈,龚熹,主译.骨科运动医学原理与实践[M].北京:北京大学出版社,2005:1065-1066.
[17] BLAHA JD, MANCINELLI CA, SIMONS WH, et al. Kinematics of human knee using an open chain cadaver model. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2003;(410):25-34.
[18] ALAIA MJ, KAPLAN DJ, MANNINO BJ, et al. Tibial Sagittal Slope in Anterior Cruciate Ligament Injury and Treatment. J Am Acad Orthop Surg. 2021;29(21): e1045-e1056.
[19] MAROUANE H, SHIRAZI-ADL A, HASHEMI J. Quantification of the role of tibial posterior slope in knee joint mechanics and ACL force in simulated gait. J Biomech. 2015;10(48): 1899-1905.
[20] MEIER M, JANSSEN D, KOECK FX, et al. Variations in medial and lateral slope and medial proximal tibial angle. Knee Surg Sports Traumatol Arthrosc. 2021;29(3): 939-946.
[21] ALJUHANI WS, QASIM SS, ALRASHEED A, et al. The effect of gender, age, and body mass index on the medial anda lateral posterior tibial slopes: a magnetic resonance imaging study. Knee Surg Relat Res. 2021;33(1):12-30.
[22] 佟志忠,蒋雯,程晓光,等.利用EOS X线影像系统评估前交叉韧带损伤患者的胫骨平台后倾角[J].骨科临床与研究杂志,2020,5(5):268-271.
[23] KACMAZ IE, TOPKAYA Y, BASA CD, et al. Posterior tibial slope of the knee measured on X-rays in a Turkish population. Surg Radiol Anat. 2020;42(6):673-679.
[24] BERNHARDSON AS, AMAN ZS, DORNAN GJ, et al. Tibial Slope and Its Effect on Force in Anterior Cruciate Ligament Grafts: Anterior Cruciate Ligament Force Increases Linearly as Posterior Tibial Slope Increases. Am J Sport Med. 2019; 47(2):296-302.
[25] NUNLEY RM, NAM D, JOHNSON SR, et al. Extreme Variability in Posterior Slope of the Proximal Tibia: Measurements on 2395 CT Scans of Patients Undergoing UKA? J Arthroplasty. 2014;29(8):1677-1680.
[26] RAJA B, MARATHE N, DESAI J, et al. Evaluation of anatomic risk factors using magnetic resonance imaging in non-contact anterior cruciate ligament injury. J Clin Orthop Trauma. 2019;10(4):710-715.
[27] KUMAR PANIGRAHI T, DAS A, MOHANTY T, et al. Study of relationship of posterior tibial slope in anterior cruciate ligament injury. J Orthop. 2020;21:487-490.
[28] HOHMANN E, TETSWORTH K, GLATT V, et al. Medial and Lateral Posterior Tibial Slope Are Independent Risk Factors for Noncontact ACL Injury in Both Men and Women. Orthop J Sports Med. 2021;9(8):227-239.
[29] GOLDSTEIN SA, WILSON DL, SONGTEGARD DA, et al. The mechanical properties of human tibial trabecular bone as a function of metaphyseal location. J Biomech. 1983;16(12):965-969.
[30] 郑亮亮,周志鹏.非接触性前交叉韧带损伤风险因素的循证研究进展[J].中国运动医学杂志,2014,33(6):596-604.
[31] TODD MS, LALLISS S, GARCIA E, et al. The relationship between posterior tibial slope and anterior cruciate ligament injuries. Am J Sport Med. 2010;38(1):63-67.
[32] VYAS S, VAN ECK CF, VYAS N, et al. Increased medial tibial slope in teenage pediatric population with open physes and anterior cruciate ligament injuries. Knee Surg Sports Traumatol Arthrosc. 2010;19(3):372-377.
[33] OKAZAKI Y, FURUMATSU T, HIRANAKA T, et al. Steep posterior slope of the medial tibial plateau is associated with ramp lesions of the medial meniscus and a concomitant anterior cruciate ligament injury. Asia Pac J Sports Med Arthrosc Rehabil Technol. 2021;24(3):23-28.
[34] WILLINGER L, BALENDRA G, PAI V, et al. Medial meniscal ramp lesions in ACL-injured elite athletes are strongly associated with medial collateral ligament injuries and medial tibial bone bruising on MRI. Knee Surg Sports Traumatol Arthrosc. 2022;30(5):1502-1510.
[35] SALMON LJ, HEATH E, AKRAWI H, et al. 20 year outcomes of ACL reconstruction with hamstring tendon autograft. The catastrophic effect of age and posterior tibial slope. Am J Sport Med. 2018;46(3):531-543.
[36] LIU C, GE J, HUANG C, et al. A radiographic model predicting the status of the anterior cruciate ligament in varus knee with osteoarthritis. Bmc Musculoskelet Disord. 2022;23(1):603-612.
[37] ZEE MJM, KEIZER MNJ, DIJKERMAN L, et al. The correlation between posterior tibial slope and dynamic anterior tibial translation and dynamic range of tibial rotation. J Exp Orthop. 2021;8(1):71-78.
[38] HOHMANN E, TETSWORTH K, GLATT V, et al. The posterior horn of the medial and lateral meniscus both reduce the effective posterior tibial slope: a radiographic MRI study. Surg Radiol Anat. 2021;43(7):1123-1130.
[39] JIANG J, LIU Z, WANG X, et al. Increased Posterior Tibial Slope and Meniscal Slope Could Be Risk Factors for Meniscal Injuries: A Systematic Review. Arthroscopy. 2022;38(7):2331-2341.
[40] SMEETS A, WILLEMS M, GILSON L, et al. Neuromuscular and biomechanical landing alterations persist in athletes returning to sport after anterior cruciate ligament reconstruction. Knee. 2021;33:305-317.
[41] HUANG M, LI Y, LI H, et al. Correlation between knee anatomical angles and anterior cruciate ligament injury in males. Radiol Med. 2021;(10):1201-1206.
|