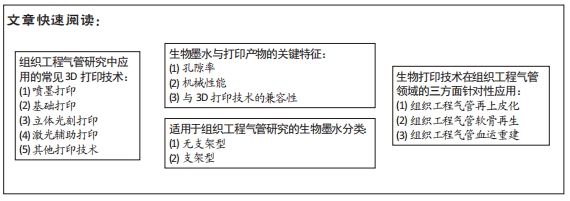
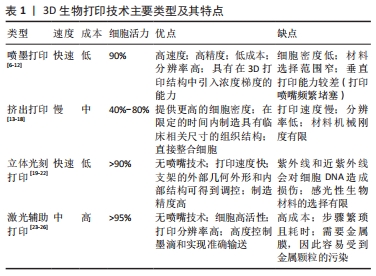
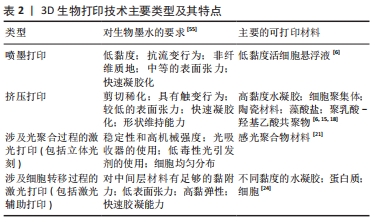
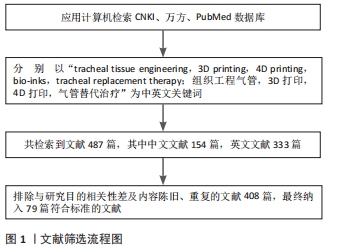
[1] SUN F, PAN S, SHI HC, et al. Structural integrity, immunogenicity and biomechanical evaluation of rabbit decelluarized tracheal matrix. J Biomed Mater Res A. 2015;103(4):1509-1519.
[2] CHIANG T, PEPPER V, BEST C, et al. Clinical Translation of Tissue Engineered Trachea Grafts. Ann Otol Rhinol Laryngol. 2016;125(11): 873-885.
[3] UDELSMAN B, MATHISEN DJ, OTT HC. A reassessment of tracheal substitutes-a systematic review. Ann Cardiothorac Surg. 2018;7(2): 175-182.
[4] MACCHIARINI P, JUNGEBLUTH P, GO T, et al. Clinical transplantation of a tissue-engineered airway. Lancet. 2008;372(9655):2023-2030.
[5] KACAREVIC ZP, RIDER PM, ALKILDANI S, et al. An Introduction to 3D Bioprinting: Possibilities, Challenges and Future Aspects. Materials (Basel). 2018;11(11):2199.
[6] CHU H, YANG W, SUN L, et al. 4D Printing: A Review on Recent Progresses. Micromachines (Basel). 2020;11(9):796.
[7] LI J, CHEN M, FAN X, et al. Recent advances in bioprinting techniques: approaches, applications and future prospects. J Transl Med. 2016;14:271.
[8] JAMMALAMADAKA U, TAPPA K. Recent Advances in Biomaterials for 3D Printing and Tissue Engineering. J Funct Biomater. 2018;9(1):22.
[9] MANDRYCKY C, WANG Z, KIM K, et al. 3D bioprinting for engineering complex tissues. Biotechnol Adv. 2016;34(4):422-434.
[10] BOLAND T, XU T, DAMON B, et al. Application of inkjet printing to tissue engineering. Biotechnol J. 2006;1(9):910-917.
[11] VEGA SL, KWON MY, BURDICK JA. Recent advances in hydrogels for cartilage tissue engineering. Eur Cell Mater. 2017;33:59-75.
[12] GRAHAM AD, OLOF SN, BURKE MJ, et al. High-Resolution Patterned Cellular Constructs by Droplet-Based 3D Printing. Sci Rep. 2017;7(1): 7004.
[13] HOCH E, HIRTH T, TOVAR GEM, et al. Chemical tailoring of gelatin to adjust its chemical and physical properties for functional bioprinting. J Mater Chem B. 2013;1(41):5675-5685.
[14] HE Y, YANG F, ZHAO H, et al. Research on the printability of hydrogels in 3D bioprinting. Sci Rep. 2016;6:29977.
[15] HöLZL K, LIN S, TYTGAT L, et al. Bioink properties before, during and after 3D bioprinting. Biofabrication. 2016;8(3):032002.
[16] CUI H, NOWICKI M, FISHER JP, et al. 3D Bioprinting for Organ Regeneration. Adv Healthc Mater. 2017;6(1):10.
[17] KUNDU J, SHIM JH, JANG J, et al. An additive manufacturing-based PCL-alginate-chondrocyte bioprinted scaffold for cartilage tissue engineering. J Tissue Eng Regen Med. 2015;9(11):1286-1297.
[18] XU N, YE X, WEI D, et al. 3D artificial bones for bone repair prepared by computed tomography-guided fused deposition modeling for bone repair. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces. 2014;6(17):14952-14963.
[19] PARK HS, PARK HJ, LEE J, et al. A 4-Axis Technique for Three-Dimensional Printing of an Artificial Trachea. Tissue Eng Regen Med. 2018;15(4): 415-425.
[20] WANG Y, GAO M, WANG D, et al. Nanoscale 3D Bioprinting for Osseous Tissue Manufacturing. Int J Nanomedicine. 2020;15:215-226.
[21] WANG Z, ANDULLA R, PARKER B, et al. A Simple and High-Resolution Stereolithography-Based 3D Bioprinting System Using Visible Light Crosslinkable Bioinks. Biofabrication. 2015;7(4):045009.
[22] LAM T, DEHNE T, KRTGER JP, et al. Photopolymerizable gelatin and hyaluronic acid for stereolithographic 3D bioprinting of tissue-engineered cartilage. J Biomed Mater Res B Appl Biomater. 2019; 107(8):2649-2657.
[23] JANA S, LERMAN A. Bioprinting a cardiac valve. Biotechnol Adv. 2015; 33(8):1503-1521.
[24] CATROS S, FRICAIN JC, GUILLOTIN B, et al. Laser-assisted bioprinting for creating on-demand patterns of human osteoprogenitor cells and nano-hydroxyapatite. Biofabrication. 2011;3(2):025001.
[25] LI Z, ZHOU W, YANG L, et al. Glass Fiber-Reinforced Phenol Formaldehyde Resin-Based Electrical Insulating Composites Fabricated by Selective Laser. Polymers (Basel). 2019;11(1):e135.
[26] HAN Y, YANG S, HUANG W, et al. A Hem-o-Lok-Induced Tracheoesophageal Fistula Cured by Temporary Airway Stenting Modified With Three-Dimensional Printing. Ann Thorac Surg. 2018; 106(4):e219-e221.
[27] TAPPA K, JAMMALAMADAKA U. Novel Biomaterials Used in Medical 3D Printing Techniques. J Funct Biomater. 2018;9(1):17.
[28] XU Y, LI D, YIN Z, et al. Tissue-engineered trachea regeneration using decellularized trachea matrix treated with laser micropore technique. Acta Biomater. 2017;58:113-121.
[29] DO AV, KHORSAND B, GEARY SM, et al. 3D Printing of Scaffolds for Tissue Regeneration Applications. Adv Healthc Mater. 2015;4(12): 1742-1762.
[30] ROSETI L, PARISI V, PETRETTA M, et al. Scaffolds for Bone Tissue Engineering: State of the art and new perspectives. Mater Sci Eng C Mater Biol Appl. 2017;78:1246-1262.
[31] GRUENE M, DEIWICK A, KOCH L, et al. Laser printing of stem cells for biofabrication of scaffold-free autologous grafts. Tissue Eng Part C Methods. 2011;17(1):79-87.
[32] ROSETI L, CAVALLO C, DESANDO G, et al. Three-Dimensional Bioprinting of Cartilage by the Use of Stem Cells: A Strategy to Improve Regeneration. Materials (Basel). 2018;11(9):1749.
[33] YOU S, LI J, ZHU W, et al. Nanoscale 3D printing of hydrogels for cellular tissue engineering. J Mater Chem B. 2018;6(15):2187-2197.
[34] GOPINATHAN J, NOH I. Recent trends in bioinks for 3D printing. Biomater Res. 2018;22:11.
[35] HOCKADAY LA, KANG KH, COLANGELO NW, et al. Rapid 3D printing of anatomically accurate and mechanically heterogeneous aortic valve hydrogel scaffolds. Biofabrication. 2012;4(3):035005.
[36] ZHU W, QU X, ZHU J, et al. Direct 3D bioprinting of prevascularized tissue constructs with complex microarchitecture. Biomaterials. 2017; 124:106-115.
[37] BAIGUERA S, JUNGEBLUTH P, BURNS A, et al. Tissue engineered human tracheas for in vivo implantation. Biomaterials. 2010;31(34):8931-8938.
[38] HAYKAL S, SOLEAS JP, SALNA M, et al. Evaluation of the structural integrity and extracellular matrix components of tracheal allografts following cyclical decellularization techniques: comparison of three protocols. Tissue Eng Part C Methods. 2012;18(8):614-23.
[39] BUTLER CR, HYNDS RE, CROWLEY C, et al. Vacuum-assisted decellularization: an accelerated protocol to generate tissue-engineered human tracheal scaffolds. Biomaterials. 2017;124:95-105.
[40] FISHMAN JM, WILES K, LOWDELL MW, et al. Airway tissue engineering: an update. Expert Opin Biol Ther. 2014;14(10):1477-1491.
[41] JI S, GUVENDIREN M. Recent Advances in Bioink Design for 3D Bioprinting of Tissues and Organs. Front Bioeng Biotechnol. 2017;5:23.
[42] RICHARDS D, JIA J, YOST M, et al. 3D Bioprinting for Vascularized Tissue Fabrication. Ann Biomed Eng. 2017;45(1):132-147.
[43] DIKINA AD, STROBEL HA, LAI BP, et al. Engineered cartilaginous tubes for tracheal tissue replacement via self-assembly and fusion of human mesenchymal stem cell constructs. Biomaterials. 2015;52:452-462.
[44] FAN D, STAUFER U, ACCARDO A. Engineered 3D Polymer and Hydrogel Microenvironments for Cell Culture Applications. Bioengineering (Basel). 2019;6(4):113.
[45] Ceccaldi C, Bushkalova R, Cussac D, et al. Elaboration and evaluation of alginate foam scaffolds for soft tissue engineering. Int J Pharm. 2017; 524(1-2):433-442.
[46] PAN S, ZHONG Y, SHAN Y, et al. Selection of the optimum 3D-printed pore and the surface modification techniques for tissue engineering tracheal scaffold in vivo reconstruction. J Biomed Mater Res A. 2019; 107(2):360-370.
[47] PARK JH, YOON JK, LEE JB, et al. Experimental Tracheal Replacement Using 3-dimensional Bioprinted Artificial Trachea with Autologous Epithelial Cells and Chondrocytes. Sci Rep. 2019;9(1):2103.
[48] DAS S, PATI F, CHOI YJ, et al. Bioprintable, cell-laden silk fibroin-gelatin hydrogel supporting multilineage differentiation of stem cells for fabrication of three-dimensional tissue constructs. Acta Biomater. 2015;11:233-246.
[49] KWON SK, SONG JJ, CHO CG, et al. Tracheal reconstruction with asymmetrically porous polycaprolactone/pluronic F127 membranes. Head Neck. 2014;36(5):643-651.
[50] ZHONG Y, YANG W, PAN Z, et al. In vivo transplantation of stem cells with a genipin linked scaffold for tracheal construction. J Biomater Appl. 2019;34(1):47-60.
[51] ORYAN A, KAMALI A, MOSHIRI A, et al. Chemical crosslinking of biopolymeric scaffolds: Current knowledge and future directions of crosslinked engineered bone scaffolds. Int J Biol Macromol. 2018; 107(Pt A):678-688.
[52] MUZZARElLLI RA, EL MEHTEDI M, BOTTEGONI C, et al. Genipin-Crosslinked Chitosan Gels and Scaffolds for Tissue Engineering and Regeneration of Cartilage and Bone. Mar Drugs. 2015;13(12):7314-7338.
[53] OZBOLAT IT, HOSPODIUK M. Current advances and future perspectives in extrusion-based bioprinting. Biomaterials. 2016;76:321-343.
[54] GUDAPATI H, DEY M, OZBOLAT I. A comprehensive review on droplet-based bioprinting: Past, present and future. Biomaterials. 2016;102: 20-42.
[55] HOSPODIUK M, DEY M, SOSNOSKI D, et al. The bioink: A comprehensive review on bioprintable materials. Biotechnol Adv. 2017;35(2):217-239.
[56] SUN YC, WAN Y, NAM R, et al. 4D-printed hybrids with localized shape memory behaviour: Implementation in a functionally graded structure. Sci Rep. 2019;9(1):18754.
[57] QASIM M, CHAE DS, LEE NY. Advancements and frontiers in nano-based 3D and 4D scaffolds for bone and cartilage tissue engineering. Int J Nanomedicine. 2019;14:4333-4351.
[58] TAMAY DG, USAL DT, ALAGOZ AS, et al. 3D and 4D Printing of Polymers for Tissue Engineering Applications. Front Bioeng Biotechnol. 2019;7: 164.
[59] CHU H, YANG W, SUN L, et al. 4D Printing: A Review on Recent Progresses. Micromachines (Basel). 2020;11(9):796.
[60] MIAO S, CASTRO N, NOWICKI M, et al. 4D printing of polymeric materials for tissue and organ regeneration. Mater Today (Kidlington). 2017;20(10):577-591.
[61] ZAREK M, MANSOUR N, SHAPIRA S, et al. 4D Printing of Shape Memory-Based Personalized Endoluminal Medical Devices. Macromol Rapid Commu. 2017;38(2). doi: 10.1002/marc.201600628.
[62] BOGAN SL, TEOH GZ, BIRCHALL MA. Tissue Engineered Airways: A Prospects Article. J Cell Biochem. 2016;117(7):1497-1505.
[63] FAN D, LI Y, WANG X, et al. Progressive 3D Printing Technology and Its Application in Medical Materials. Front Pharmacol. 2020;11:122.
[64] MORRISON RJ, HOLLISTER SJ, NIEDNER MF, et al. Mitigation of tracheobronchomalacia with 3D-printed personalized medical devices in pediatric patients. Sci Transl Med. 2015;7(285):285ra64.
[65] MAUGHAN EF, HYNDS RE, PROCTOR TJ, et al. Autologous Cell Seeding in Tracheal Tissue Engineering. Curr Stem Cell Rep. 2017;3(4):279-289.
[66] CROWLEY C, BIRCHALL M, SEIFALIAN AM. Trachea transplantation: from laboratory to patient. J Tissue Eng Regen Med. 2015;9(4):357-367.
[67] PEPPER V, BEST CA, BUCKLEY K, et al. Factors Influencing Poor Outcomes in Synthetic Tissue-Engineered Tracheal Replacement. Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg. 2019;161(3):458-467.
[68] GO T, JUNGEBLUTH P, BAIGUERO S, et al. Both epithelial cells and mesenchymal stem cell-derived chondrocytes contribute to the survival of tissue-engineered airway transplants in pigs. J Thorac Cardiovasc Surg. 2010;139(2):437-443.
[69] SAKSENA R, GAO C, WICOX M, et al. Tubular organ epithelialisation. J Tissue Eng. 2016;7:2041731416683950.
[70] CHANG JW, PARK SA, PARK JK, et al. Tissue-engineered tracheal reconstruction using three-dimensionally printed artificial tracheal graft: preliminary report. Artif Organs. 2014;38(6):E95-E105.
[71] REHMANI SS, AL-AYOUBI AM, AYUB A, et al. Three-Dimensional-Printed Bioengineered Tracheal Grafts: Preclinical Results and Potential for Human Use. Ann Thorac Surg. 2017;104(3):998-1004.
[72] RAGHUNATH J, ROLLO J, SALES KM, et al. Biomaterials and scaffold design: key to tissue-engineering cartilage. Biotechnol Appl Biochem. 2007;46(Pt 2):73-84.
[73] GHORBANI F, MORADI L, SHADMEHR MB, et al. In-vivo characterization of a 3D hybrid scaffold based on PCL/decellularized aorta for tracheal tissue engineering. Mater Sci Eng C Mater Biol Appl. 2017;81:74-83.
[74] PARK JH, HONG JM, JU YM, et al. A novel tissue-engineered trachea with a mechanical behavior similar to native trachea. Biomaterials. 2015;62:106-115.
[75] HAMILTON N, BULLOCK AJ, MACNEIL S, et al. Tissue engineering airway mucosa: a systematic review. Laryngoscope. 2014;124(4):961-968.
[76] WU T , ZHENG H , CHEN J , et al. Application of a bilayer tubular scaffold based on electrospun poly(l-lactide-co-caprolactone)/collagen fibers and yarns for tracheal tissue engineering. J Mater Chem B. 2017; 5(1):139-150.
[77] LI S, YU D, JI H, et al. In vivo degradation and neovascularization of silk fibroin implants monitored by multiple modes ultrasound for surgical applications. Biomed Eng Online. 2018;17(1):87.
[78] WANG K, CHEN X, PAN Y, et al. Enhanced vascularization in hybrid PCL/gelatin fibrous scaffolds with sustained release of VEGF. Biomed Res Int. 2015;2015:865076.
[79] LIU Q, HUANG Y, LAN Y, et al. Acceleration of skin regeneration in full-thickness burns by incorporation of bFGF-loaded alginate microspheres into a CMCS-PVA hydrogel. J Tissue Eng Regen Med. 2017;11(5):1562-1573.
|