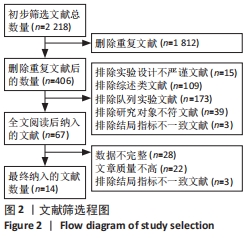
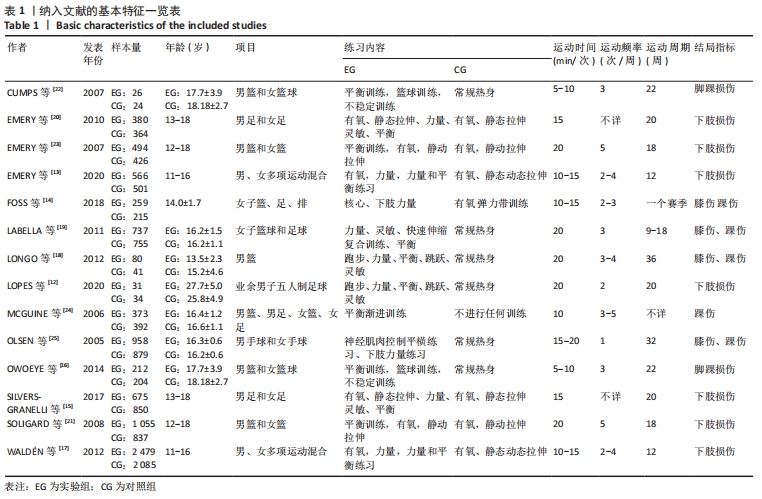
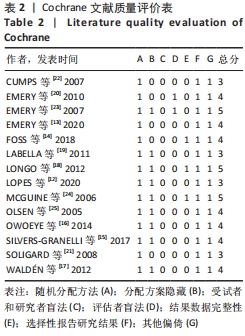
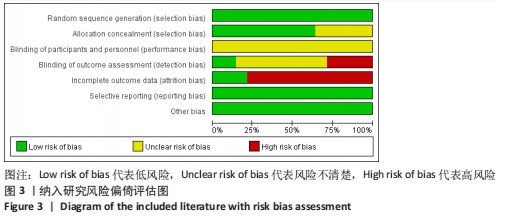
[1] ARUMUGAM A, BJÖRKLUND M, MIKKO S, et al. Effects of neuromuscular training on knee proprioception in individuals with anterior cruciate ligament injury: a systematic review and GRADE evidence synthesis. BMJ Open. 2021;11(5):e049226.
[2] 水祎舟,傅鸿浩.整合性神经肌肉训练设计对青少年女子足球运动员专项运动表现的影响[J].成都体育学院学报,2018, 44(5):84-90.
[3] 赵响,詹建国,许滨.整合性神经肌肉训练预防青少年女性运动性膝关节损伤[J].中国组织工程研究,2017,21(32): 5108-5114.
[4] TRAJKOVIĆ N, BOGATAJ Š. Effects of Neuromuscular Training on Motor Competence and Physical Performance in Young Female Volleyball Players. Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2020;17(5):1755.
[5] STEFFEN K, MYKLEBUST G, OLSEN OE, et al. Preventing injuries in female youth football - A cluster-randomized controlled trial. Scand J Med Sci Sports. 2008;18(5):605-614.
[6] SAÑUDO B, SÁNCHEZ-HERNÁNDEZ J, BERNARDO-FILHO M, et al. Integrative Neuromuscular Training in Young Athletes, Injury Prevention, and Performance Optimization: A Systematic Review. Applied Sci. 2019;9(18):3839.
[7] EMERY CA, ROY TO, WHITTAKER JL, et al. Neuromuscular training injury prevention strategies in youth sport: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Br J Sports Med. 2015;49(13):865-870.
[8] HÜBSCHER M, ZECH A, PFEIFER K, et al. Neuromuscular Training for Sports Injury Prevention: A Systematic Review. Med Sci Sports Exerc. 2010;42(3):413-421.
[9] 谷鸿秋,王杨,李卫.Cochrane偏倚风险评估工具在随机对照研究Meta分析中的应用[J].中国循环杂志,2014,29(2):147-148.
[10] 付文杰,吴君怡,许杨鹏,等.Meta分析中二分类数据效应量的选取[J].中国循证心血管医学杂志,2016,8(1):7-11+22.
[11] 何寒青,陈坤.Meta分析中的异质性检验方法[J].中国卫生统计,2006(6):486-487+ 490.
[12] LOPES M, SIMÕES D, COSTA R, et al. Effects of the FIFA 11+ on injury prevention in amateur futsal players. Scand J Med Sci Sports. 2020;30(8):1434-1441.
[13] EMERY CA, VAN DEN BERG C, RICHMOND SA, et al. Implementing a junior high school-based programme to reduce sports injuries through neuromuscular training (iSPRINT): a cluster randomised controlled trial (RCT). Br J Sports Med. 2020;54(15):913-919.
[14] FOSS KDB, THOMAS S, KHOURY JC, et al. A School-Based Neuromuscular Training Program and Sport-Related Injury Incidence: A Prospective Randomized Controlled Clinical Trial. J Athl Train. 2018;53(1):20-28.
[15] SILVERS-GRANELLI HJ, BIZZINI M, ARUNDALE A, et al. Does the FIFA 11+ Injury Prevention Program Reduce the Incidence of ACL Injury in Male Soccer Players? Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2017;475(10):2447-2455.
[16] OWOEYE OB, AKINBO SR, TELLA BA, et al. Efficacy of the FIFA 11+ Warm-Up Programme in Male Youth Football: A Cluster Randomised Controlled Trial. J Sports Sci Med. 2014;13(2):321-328.
[17] WALDÉN M, ATROSHI I, MAGNUSSON H, et al. Republished research: Prevention of acute knee injuries in adolescent female football players: cluster randomised controlled trial. Br J Sports Med. 2012;46(13):904.
[18] LONGO UG, LOPPINI M, BERTON A, et al. The FIFA 11+ program is effective in preventing injuries in elite male basketball players: a cluster randomized controlled trial. Am J Sports Med. 2012;40(5):996-1005.
[19] LABELLA CR, HUXFORD MR, GRISSOM J, et al. Effect of Neuromuscular Warm-up on Injuries in Female Soccer and Basketball Athletes in Urban Public High Schools: Cluster Randomized Controlled Trial. Arch Pediatr Adolesc Med. 2011;165(11):1033-1040.
[20] EMERY CA, MEEUWISSE WH. The effectiveness of a neuromuscular prevention strategy to reduce injuries in youth soccer: a cluster-randomised controlled trial. Br J Sports Med. 2010;44(8):555-562.
[21] SOLIGARD T, MYKLEBUST G, STEFFEN K, et al. Comprehensive warm-up programme to prevent injuries in young female footballers: cluster randomised controlled trial. BMJ. 2008;337:a2469.
[22] CUMPS E, VERHAGEN E, MEEUSEN R. Efficacy of a sports specific balance training programme on the incidence of ankle sprains in basketball. J Sports Sci Med. 2007;6(2):212-219.
[23] EMERY CA, ROSE MS, MCALLISTER JR, et al. A Prevention Strategy to Reduce the Incidence of Injury in High School Basketball: A Cluster Randomized Controlled Trial. Clin J Sport Med. 2007; 17(1):17-24.
[24] MCGUINE TA, KEENE JS. The Effect of a Balance Training Program on the Risk of Ankle Sprains in High School Athletes. Am J Sports Med. 2006;34(7):1103-1111.
[25] OLSEN OE, MYKLEBUST G, ENGEBRETSEN L, et al. Exercises to prevent lower limb injuries in youth sports: cluster randomised controlled trial. BMJ. 2005;330(7489):449.
[26] 彭勇.整合性神经肌肉训练改善人体运动表现和预防下肢损伤的作用与机制[J].南京体育学院学报,2020,19(8):55-68+2.
[27] HOPPER AJ, HAFF EE, JOYCE C, et al. Neuromuscular Training Improves Lower Extremity Biomechanics Associated with Knee Injury during Landing in 11-13 Year Old Female Netball Athletes: A Randomized Control Study. Front Physiol. 2017. doi: 10.3389/fphys.2017.00883.
[28] MYER GD, FORD KR, PALUMBO JP, et al. Neuromuscular training improves performance and lower-extremity biomechanics in female athletes. J Strength Cond Res. 2005;19(1):51-60.
[29] HEWETT TE, MYER GD, FORD KR, et al. Biomechanical Measures of Neuromuscular Control and Valgus Loading of the Knee Predict Anterior Cruciate Ligament Injury Risk in Female Athletes: A Prospective Study. Am J Sports Med. 2005;33(4):492-501.
[30] 何鹏飞,董范,姜自立.整合性神经肌肉训练对提高女子运动员运动表现及预防运动损伤的影响[J].体育科学,2017, 37(2):66-75.
[31] MYER GD, FORD KR, MCLEAN SG, et al. The Effects of Plyometric versus Dynamic Stabilization and Balance Training on Lower Extremity Biomechanics. Am J Sports Med. 2006;34(3):445-455.
[32] BARONI BM, RUAS CV, RIBEIRO-ALVARES JB, et al. Hamstring-to-Quadriceps Torque Ratios of Professional Male Soccer Players: A Systematic Review. J Strength Cond Res. 2020;34(1):281-293.
[33] 曹峰锐.“腘绳肌离心收缩力矩/股四头肌向心收缩力矩”在预防腘绳肌运动性拉伤和膝关节前交叉韧带损伤方面的应用[J].中国体育科技,2017,53(2):43-52+63.
[34] RODRÍGUEZ C, ECHEGOYEN S, AOYAMA T. The effects of “Prevent Injury and Enhance Performance Program” in a female soccer team. J Sports Med Phys Fitness. 2018; 58(5):659-663
[35] SABET S, LETAFATKAR A, EFTEKHARI F, et al. Trunk and hip control neuromuscular training to target inter limb asymmetry deficits associated with anterior cruciate ligament injury. Phys Ther Sport. 2019. doi: 10.1016/j.ptsp.2019.04.014.
[36] Correia P, Santos P, Mil-Homens P, et al. Rapid hamstrings to quadriceps ratio at long muscle lengths in professional football players with previous hamstring strain injury. Eur J Sport Sci. 2020;20(10):1405-1413.
[37] DE BLAISER C, ROOSEN P, WILLEMS T, et al. Is core stability a risk factor for lower extremity injuries in an athletic population? A systematic review. Phys Ther Sport. 2018;30(1):48-56.
[38] MYER GD, BRENT JL, FORD KR, et al. A pilot study to determine the effect of trunk and hip focused neuromuscular training on hip and knee isokinetic strength. Br J Sports Med. 2008;42(7):614-619.
[39] DE RIDDER R, WITVROUW E, DOLPHENS M, et al. Hip Strength as an Intrinsic Risk Factor for Lateral Ankle Sprains in Youth Soccer Players: A 3-Season Prospective Study. Am J Sports Med. 2017;45(2):410-416.
[40] 孙孟凡,扈盛.本体感觉神经促进技术联合核心稳定性训练对功能性踝关节不稳患者下肢功能康复的影响[J].中华物理医学与康复杂志,2017,39(11):834-838.
[41] 章琴,罗志增.视觉和本体感觉对人体静态平衡稳定性的影响[J].华中科技大学学报(自然科学版),2015,43(S1):396-400.
[42] KOWALCZYK M, TOMASZEWSKI P, BARTOSZEK N, et al. Three-Week Intensive Neuromuscular Training Improves Postural Control in Professional Male Soccer Players. Polish J Sport Tourism. 2019;26(2):14.
[43] ANGUISH B, SANDREY MA. Two 4-Week Balance-Training Programs for Chronic Ankle Instability. J Athl Train. 2018,53(7): 662-671.
[44] EILS E, SCHRÖTER R, SCHRÖDER M, et al. Multistation Proprioceptive Exercise Program Prevents Ankle Injuries in Basketball. Med Sci Sports Exerc. 2010, 42(11):2098-2105.
[45] STEIB S, RAHLF AL, PFEIFER K, et al. Dose-Response Relationship of Neuromuscular Training for Injury Prevention in Youth Athletes: A Meta-Analysis. Front Physiol. 2017. doi:10.3389/fphys.2017.00920.
[46] MYER GD, SUGIMOTO D, THOMAS S, et al. The influence of age on the effectiveness of neuromuscular training to reduce anterior cruciate ligament injury in female athletes: a meta-analysis. Am J Sports Med. 2013;41(1):203-215.
[47] SUGIMOTO D, MYER GD, FOSs KD, et al. Dosage Effects of Neuromuscular Training Intervention to Reduce Anterior Cruciate Ligament Injuries in Female Athletes: Meta- and Sub-Group Analyses. Sports Med. 2014; 44(4):551-562.
[48] LESINSKI M, HORTOBÁGYI T, MUEHLBAUER T, et al. Dose-response relationships of balance training in healthy young adults: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Sports Med. 2015;45(4):557-576.
[49] ZECH A, KLAHN P, HOEFT J, et al. Time course and dimensions of postural control changes following neuromuscular training in youth field hockey athletes. Eur J Appl Physiol. 2014;114(2):395.
[50] STEFFEN K, EMERY CA, ROMITI M, et al. High adherence to a neuromuscular injury prevention programme (FIFA 11+) improves functional balance and reduces injury risk in Canadian youth female football players: a cluster randomised trial. Br J Sports Med. 2013;47(12):794-802.
[51] RÖSSLER R, DONATH L, VERHAGEN E, et al. Exercise-Based Injury Prevention in Child and Adolescent Sport: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Sports Med. 2014;44(12):1733-1748.
[52] STEVENSON JH, BEATTIE CS, SCHWARTZ JB, et al. Assessing the effectiveness of neuromuscular training programs in reducing the incidence of anterior cruciate ligament injuries in female athletes: a systematic review. Am J Sports Med. 2015; 43(2):1733-1748.
[53] MICHAELIDIS M, KOUMANTAKIS GA. Effects of knee injury primary prevention programs on anterior cruciate ligament injury rates in female athletes in different sports: A systematic review. Phys Ther Sport. 2014; 15(3):200-210.
|