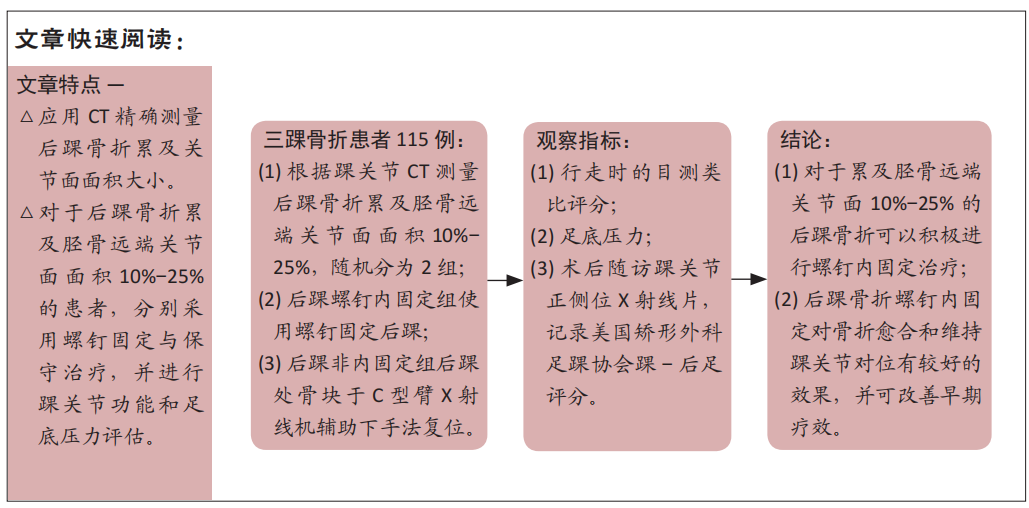
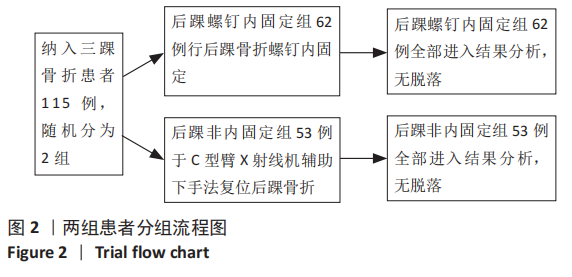
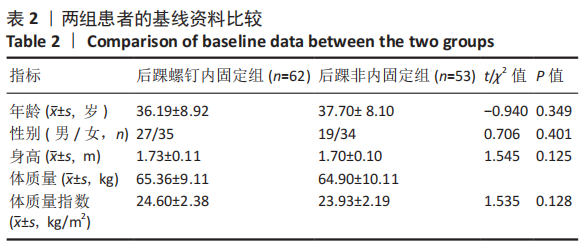
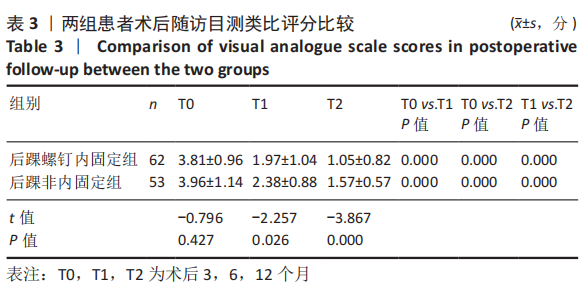
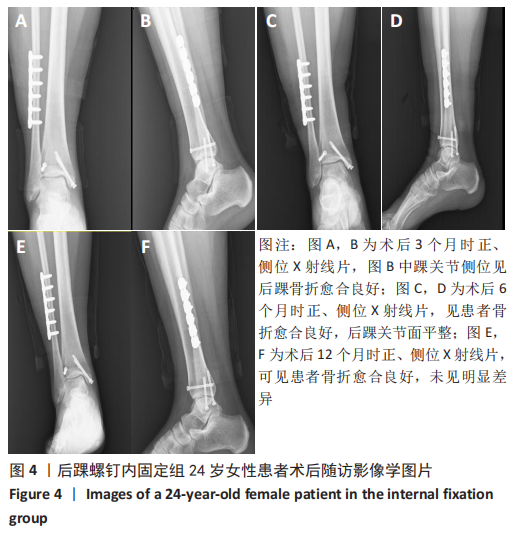
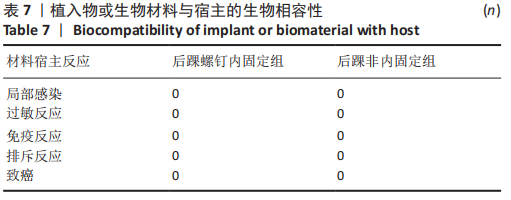
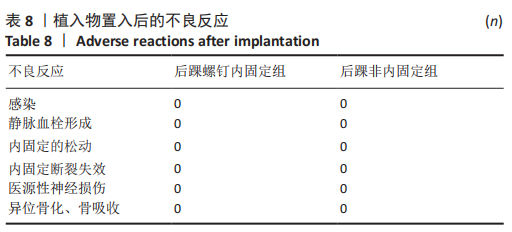
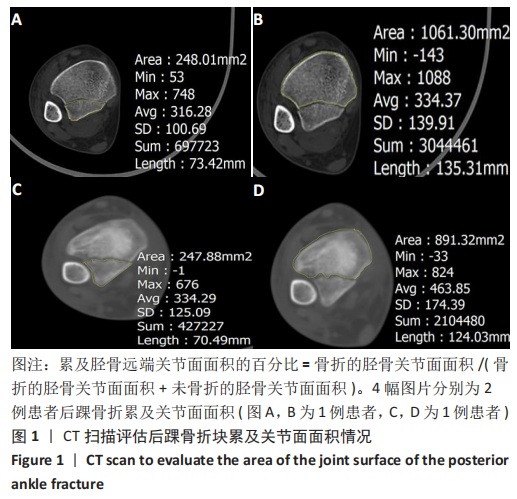
[1] KOVAL KJ, LURIE J, ZHOU W, et al. Ankle fractures in the elderly: What you get depends on where you live and who you see. J Orthop Trauma. 2005;19:635-639.
[2] JASKULKA RA, ITTNER G, SCHEDL R. Fractures of the posterior tibial mar gin: Their role in the prognosis of malleolar fractures. J Trauma. 1989;29:1565-1570.
[3] VERHAGE SM, BOOT F, SCHIPPER IB, et al. Open reduction and internal fixation of posterior malleolar fractures using the posterolateral approach. Bone Joint J. 2016;98-B(6):812-817.
[4] VAN DEN BEKEROM MP, HAVERKAMP D, KLOEN P. Biomechanical and clinical evaluation of posterior malleolar fractures. A systematic review of the literature. J Trauma. 2009;66:279-284.
[5] DRIJFHOUT VAN HOOFF CC, VERHAGE SM, HOOGENDOORN JM. Influence of fragment size and postoperative joint congruency on long-term outcome of posterior malleolar fractures. Foot Ankle Int. 2015;36; 673-678.
[6] XU HL, LI X, ZHANG DY, et al. A retrospective study of posterior malleolus fractures. Int Orthop. 2012;36:1929-1936.
[7] TOSUN B, SELEK O, GOK U, et al. Posterior Malleolus Fractures in Trimalleolar Ankle Fractures: Malleolus versus Transyndesmal Fixation. Indian J Orthop. 2018;52(3):309-314.
[8] EVERS J, BARZ L, WÄHNERT D, et al. Size matters: The influence of the posterior fragment on patient outcomes in trimalleolar ankle fractures. Injury. 2015;46 Suppl 4:S109-S113.
[9] NELSON MC, JENSEN NK. The treatment of trimalleolar fractures of the ankle. Surg Gynecol Obst. 1940;71:509-514.
[10] DRIJFHOUT VAN HOOFF CC, VERHAGE SM, et al. Influence of Fragment Size and Postoperative Joint Congruency on Long-Term Outcome of Posterior Malleolar Fractures. Foot Ankle Int. 2015;36(6):673-678.
[11] EGOL KA, TEJWANI NC, WALSH MG, et al. Predictors of short-term functional outcome following ankle fracture surgery. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2006;88(5):974-979.
[12] KEENE DJ, COSTA ML, TUTTON E, et al. Progressive functional exercise versus best practice advice for adults aged 50 years or over after ankle fracture: protocol for a pilot randomised controlled trial in the UK - the Ankle Fracture Treatment: Enhancing Rehabilitation (AFTER) study. BMJ Open. 2019;9(11):e030877.
[13] BECKER HP, ROSENBAUM D, KRIESE T, et al. Gait asymmetry following successful surgical treatment of ankle fractures in young adults. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 1995;(311):262-269.
[14] MASON LW, KAYE A, WIDNALL J, et al. Posterior Malleolar Ankle Fractures: An Effort at Improving Outcomes. JB JS Open Access. 2019;4(2):e0058.
[15] MANGNUS L, MEIJER DT, STUFKENS SA, et al. Posterior malleolar fracture patterns. J Orthop Trauma. 2015;29(9):428-435.
[16] GARDNER MJ, BRODSKY A, BRIGGS SM, et al. Fixation of posterior malleolar fractures provides greater syndesmotic stability. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2006;447:165-171.
[17] VAN DEN BEKEROM MP, HAVERKAMP D, KLOEN P. Biomechanical and clinical evaluation of posterior malleolar fractures. A systematic review of the literature. J Trauma. 2009;66(1):279-284.
[18] LANGENHUIJSEN JF, HEETVELD MJ, ULTEE JM, et al. Results of ankle fractures with involvement of the posterior tibial margin. J Trauma. 2002;53:55-60.
[19] MINGO-ROBINET J, LOPEZ-DURAN L, GALEOTE JE, et al. Ankle fractures with posterior malleolar fragment: management and results. J Foot Ankle Surg. 2011;50:141-145.
[20] GONZALEZ TA, WATKINS C, DRUMMOND R, et al. Transfibular Approach to Posterior Malleolus Fracture Fixation: Technique Tip. Foot Ankle Int. 2016;37(4):440-445.
[21] CHOI JY, KIM JH, KO HT, et al. Single Oblique Posterolateral Approach for Open Reduction and Internal Fixation of Posterior Malleolar Fractures With an Associated Lateral Malleolar Fracture. J Foot Ankle Surg. 2015; 54(4):559-564.
[22] 万全会.后踝关节骨折不同内固定方式的生物力学性能对比[J].中国组织工程研究,2015,19(48):7806-7810.
[23] KANG C, HWANG DS, LEE JK, et al. Screw Fixation of the Posterior Malleolus Fragment in Ankle Fracture. Foot Ankle Int. 2019;40(11): 1288-1294.
[24] MARTIN KD. Posterior Arthroscopic Reduction and Internal Fixation for Treatment of Posterior Malleolus Fractures. Foot Ankle Int. 2020; 41(1):115-120.
[25] VIDOVIĆ D, ELABJER E, MUŠKARDIN IVA, et al. Posterior fragment in ankle fractures: anteroposterior vs posteroanterior fixation. Injury. 2017;48 Suppl 5:S65-S69.
[26] HOEKSTRA H, ROSSEELS W, RAMMELT S, et al. Direct fixation of fractures of the posterior pilon via a posteromedial approach. Injury. 2017;48(6):1269-1274.
[27] KARIM A, SO E, TAYLOR BC, et al. Ankle Fracture Fixation: Medial or Lateral First? J Foot Ankle Surg. 2019;58(1):75-79.
[28] OʼCONNOR TJ, MUELLER B, LY TV, et al. “A to p” screw versus posterolateral plate for posterior malleolus fixation in trimalleolar ankle fractures. J Orthop Trauma. 2015;29(4):e151-156.
[29] PALMANOVICH E, OHANA N, YAACOBI E, et al. Preoperative planning and surgical technique for optimizing internal fixation of posterior malleolar fractures: CT versus standard radiographs. J Orthop Surg Res. 2020;15(1):119.
[30] ERDEM MN, ERKEN HY, BURC H, et al. Comparison of lag screw versus buttress plate fixation of posterior malleolar fractures. Foot Ankle Int. 2014;35(10):1022-1030.
|