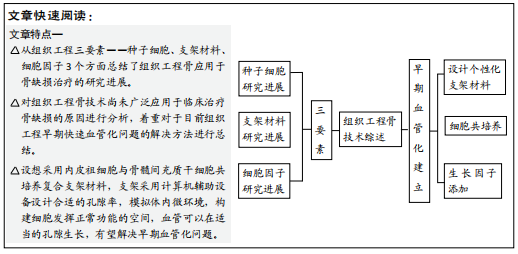
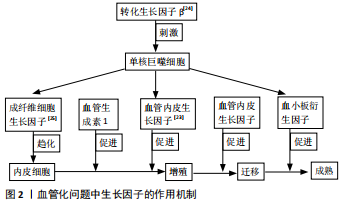
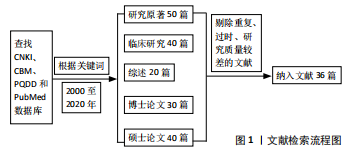
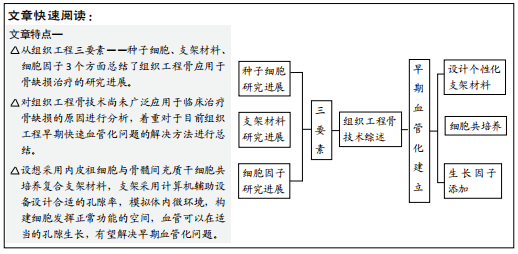
[1] 秦宇星,任前贵,沈佩锋.组织工程骨技术治疗骨缺损的优越性[J].中国组织工程研究,2020,24(24):3877-3882.
[2] 刘杰,吴雪晖,罗飞,等.自体间充质干细胞构建组织工程骨修复人长骨缺损的临床观察[J].第三军医大学学报,2008,30(9):851-854.
[3] 耿海霞,封伟,钱君荣,等.羟基磷灰石-凝胶支架复合成骨细胞修复兔颅骨缺损的组织学评价[J].临床口腔医学杂志,2014,30(9): 519-521
[4] LI X, PENG B, PAN Y, et al. Icariin stimulates osteogenicdifferentiation and suppresses adipogenic differentiation ofrBMSCs via estrogen receptor signaling. Mol Med Rep. 2018;18(3):3483-3489.
[5] KFOURY Y , SCADDEN DT. Mesenchymal cell contributions to the stem cell niche. Cell Stem Cell. 2015;16(3):239-253.
[6] MOON KM, PARK YH, LEE JS, et al. The effect of secretory factors of adipose-derived stem cells on human keratinocytes. Int J Mol Sci. 2012; 13(1):1239-1257.
[7] SIEGEL KR, CLEVENGER TN, CLEGG DO, et al. Adipose Stem Cells Incorporated in Fibrin Clot Modulate Expression of Growth Factors.Arthroscopy. 2018;34(2):581-591.
[8] BANFI A, MURAGLIA A, DOZIN B, et al.Proliferation kinetics and differentiation potential of ex vivo expanded human bone marrow stromal cells:Implications for their use in cell therapy. Exp Hematol. 2001;28(6):707-715.
[9] 唐文胜,蒋电明.羟基磷灰石及其复合材料在骨修复中的作用及研究进展[J].中华创伤骨科杂志,2003,5(4):370-373.
[10] Wahajuddin,Arora S. Superparamagnetic iron oxide nanoparticles: magneticnanoplatforms as drug carriers. Int J Nanomedicine. 2012;7: 3445-3471.
[11] 周静,冯卓卓,罗洁,等.纳米支架材料在骨组织工程应用中的优势[J].临床口腔医学杂志,2018,34(10):633-635.
[12] 夏德萌,冯拥璞,夏琰,等.纳米结构羟基磷灰石负载万古霉素对大鼠股骨慢性骨髓炎的治疗作用[J].中国骨与关节损伤杂志,2019, 34(9):936-940.
[13] BAI L, DU Z, DU J,et al. A multifaceted coating on titanium dictates osteoimmunomodulation and osteo/angio-genesis towards ameliorative osseointegration. Biomaterials. 2018;162:154-169.
[14] LI D, SUNH, JIANGL, et al. Enhanced biocompatibility of PLGAnanofibers with gelatin/nano-hydroxyapatite bone biomimetics incorporation.ACS Appl Mater Interfaces. 2014;6(12):9402-9410.
[15] HE X, FAN X, FENG W, et al. Incorporation of microfibrillated cellulose into collagen-hydroxyapatite scaffold for bone tissue engineering. Int J Biol Macromol. 2018;115(6):385-392.
[16] FAN J, BI L, WU T, et al. A combined chitosan/nano-size hydroxyapatite system for the controlled release of icariin. J Mater Sci Mater Med. 2012;23(2):399-407.
[17] 梁卫寰,谭竹钧,区硕俊,等.羟基磷灰石/壳聚糖-柚皮苷缓释材料的制备及性能初探[J].功能材料,2015(19):19131-19135.
[18] 丁焕文,涂强,王迎军,等.数字化骨科手术新方法的建立及其临床广泛应用[J].中国骨科临床与基础研究杂志,2010,2(2):92-97.
[19] ASAHARA T, MUROHARA T, SULLIVAN A, et al. Isolation of putative progenitor endothelial cells for angiogenesis. Science. 1997;275(5302): 964-967.
[20] 徐荣胜,何芸,李彪,等.血管内皮生长因子165转染脐静脉内皮细胞与骨髓间充质干细胞共培养在血管形成中的作用[J].中国组织工程研究,2017,21(33):5268-5273.
[21] 徐荣胜.BMSCs和HUVECs复合HA-TCP支架共培养对大鼠颅骨缺损修复的成骨能力影响[D].泸州:西南医科大学,2018.
[22] 韦惠平. 大鼠BMSCs/EPCs联合培养与聚乳酸支架构建组织工程骨的实验研究[D].南宁:广西医科大学,2011.
[23] HARRIS GM, RUTLEDGE K, CHENG Q, et al. Strategies to Direct Angiogenesis within Scaffolds for Bone Tissue Engineering. Curr Pharm Des. 2013;19(19):3456-3465.
[24] DONG QS, LIN C, SHANG HT, et al. Modified approach to construct a vascularized coral bone in rabbit using an arteriovenous loop. J Reconstr Microsurg.2010,26(2):95-102.
[25] 陈凯,张超,王路,等.骨组织工程中促进血管化策略的研究进展[J].中国骨伤,2015,28(4):383-388.
[26] 张丽丽. 浓缩生长因子对兔骨膜来源细胞增殖、成骨分化及成血管潜能的研究[D].沈阳:中国医科大学,2019.
[27] STONE OA, CARTER JG, LIN PC, et al. Differential regulation of blood flow‐induced neovascularization and mural cell recruitment by vascular endothelial growth factor and angiopoietin signalling. J Physiol. 2017; 595(5):1575-1591.
[28] HUANG YC, KAIGLER D, RICE KG, et al. Combined angiogenic and osteogenic factor delivery enhances bone marrow stromal cell-driven bone regeneration. J Bone Miner Res. 2005;20(5):848-857.
[29] 刘双阳,田雅光,王洪一,等.富血小板血浆促进骨髓间充质干细胞对大鼠骨缺损的修复作用[J].中国美容整形外科杂志,2019,30(4): 210-213.
[30] 任前贵,王瞾,张坤.仿生控释BMP-2和VEGF的PELA微球支架对骨髓间充质干细胞向成骨细胞分化的Wnt/β-catenin通路的影响[J].中国生物制品学杂志,2018,31(10):1118-1121+1125.
[31] ROBERTS JJ, FARRUGIA BL, GREEN RA, et al. In situ formation of poly(vinyl alcohol)–heparin hydrogels for mild encapsulation and prolonged release of basic fibroblast growth factor and vascular endothelial growth factor. J Tissue Eng. 2016;7:153-170.
[32] GOLUB JS, KIM YT, DUVALL CL, et al. Sustained VEGF delivery via PLGA nanoparticles promotes vascular growth. Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol. 2010;298(6):1959-1965.
[33] 兰红波,李涤尘,卢秉恒.微纳尺度3D打印[J].中国科学:技术科学,2015,45(9):919-940.
[34] 易灿. 计算机辅助临床大段骨缺损的精确修复[D].广州:广州中医药大学,2011:27-38.
[35] 胡超然,邱冰. 3D生物打印技术在骨组织工程中的应用[J]. 中国组织工程研究,2018,22(2):316-322.
[36] FERLIN KM, PRENDERGAST ME, MILLER ML, et al. Influence of 3D printed porous architecture on mesenchymal stem cell enrichment and differentiation. Acta Biomaterialia. 2016;32:161-169.
(责任编辑:GD,ZN,DL)
|