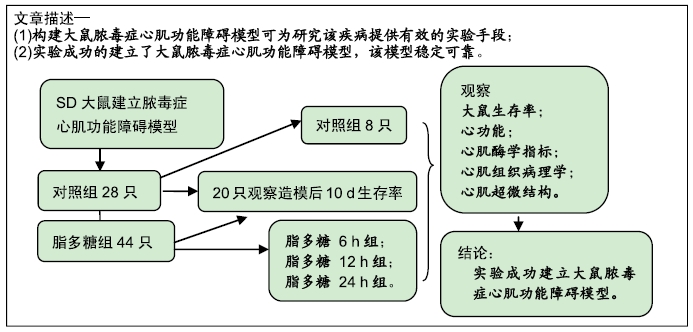
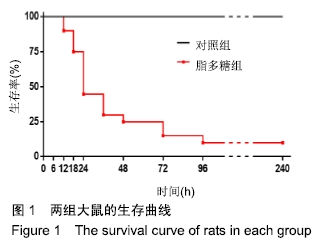
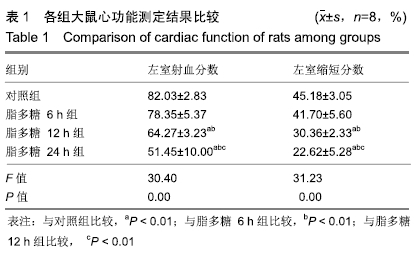
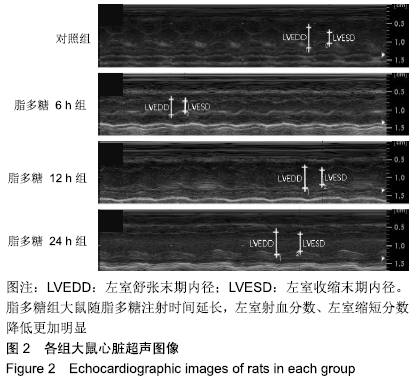
[1] ZHANG W, ZHENG Y, FENG X, et al.Systemic inflammatory response syndrome in Sepsis-3: a retrospective study. BMC Infect Dis.2019; 19(1):139-149.
[2] LIU YC, YU MM, SHOU ST, et al.Sepsis-induced cardiomyopathy: mechanisms and treatments.Front Immunol.2017;8:1021-1029.
[3] LI Y, GE S, PENG Y, et al.Inflammation and cardiac dysfunction during sepsis, muscular dystrophy, and myocarditis.Burns Trauma.2013;1(3): 109-121.
[4] PALMIERI V, INNOCENTI F, GUZZO A, et al.Left Ventricular Systolic Longitudinal Function as Predictor of Outcome in Patients With Sepsis. Circ Cardiovasc Imaging.2015; 8(11):1-7.
[5] DE BACKER D, SCOLLETTA S.Clinical management of the cardiovascular failure in sepsis.Curr Vasc Pharmacol. 2013;11(2):222-242.
[6] ANTONUCCI E, FIACCADORI E, DONADELLO K, et al. Myocardial depression in sepsis: From pathogenesis to clinical manifestations and treatment.J Crit Care.2014;29(4):500-511.
[7] STANZANI G, DUCHEN MR, SINGER M.The role of mitochondria in sepsis-induced cardiomyopathy. Biochim Biophys Acta Mol Basis Dis.2019;1;1865(4):759-773.
[8] HUBBARD WJ, CHOUDHRY M, SCHWACHA MG, et al.Cecal ligation and puncture.Shock.2005;24 Suppl 1:52-57.
[9] PREAU S, DELGUSTE F, YU Y, et al.Endotoxemia engages RhoA kinase pathway to impair cardiac function by altering cardiac cytoskeleton, mitochondrial fission and autophagy. Antioxid Redox Signal. 2015;24(10):529-542.
[10] LI L, HU BC, CHEN CQ, et al.Role of mitochondrial damage during cardiac apoptosis in septic rats. Chin Med J(Engl).2013;126(10):1860-1866.
[11] CHENG MM W, LONG Y, WANG H, et al. Role of the mTOR Signalling Pathway in Human Sepsis-Induced Myocardial Dysfunction.Can J Cardiol.2019;35(7):875-883.
[12] EHRMAN RR, SULLIVAN AN, FAVOT MJ, et al.Pathophysiology, echocardiographic evaluation, biomarker findings, and prognostic implications of septic cardiomyopathy: a review of the literature. Crit Care.2018;22(1):112-126.
[13] MAIER S, TRAEGER T, ENTLEUTNER M, et al.Cecal ligation and puncture versus colon ascendens stent peritonitis: Two distinct animal models for polymicrobial sepsis.Shock.2004;21(6):505-512.
[14] CROSS AS, OPAL SM, SADOFF JC, et al. Choice of bacteria in animal models of sepsis.Infect Immun, 1993;61(7):2741-2747.
[15] ZHAI J, GUO Y.Paeoniflorin attenuates cardiac dysfunction in endotoxemic mice via the inhibition of nuclear factor-κB.Biomed Pharmacother.2016;80:200-206.
[16] GONZALEZ AS, ELGUERO ME, FINOCCHIETTO P, et al.Abnormal mitochondrial fusion-fission balance contributes to the progression of experimental sepsis.Free Radic Res.2014;48(7):769-783.
[17] SANFILIPPO F, CORREDOR C, FLETCHER N, et al. Left ventricular systolic function evaluated by strain echocardiography and relationship with mortality in patients with severe sepsis or septic shock: a systematic review and meta-analysis.Crit Care.2018;22(1):183-195.
[18] 滕金龙,李丹,于海初,等.重组人促红细胞生成素联合骨髓间充质干细胞移植治疗脓毒症大鼠心肌损伤[J].中国组织工程研究, 2014,18(28):4530-4534.
[19] SATO R, NASU M.A review of sepsis-induced cardiomyopathy.J Intensive Care.2015;3:48.
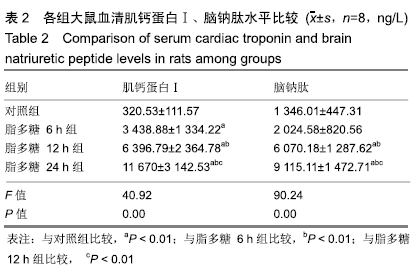
[20] MEHTA NJ, KHAN IA , GUPTA V, et al. Cardiac troponin I predicts myocardial dysfunction and adverse outcome in septic shock.Int J Cardiol.2004;95(1):13-17.
[21] KAKOULLIS L, GIANNOPOULOU E, PAPACHRISTODOULOU E, et al.The utility of brain natriuretic peptides in septic shock as markers for mortality and cardiac dysfunction: A systematic review.Int J Clin Pract.2019;73(7):e13374.
[22] LI HM, LI KY, XING Y, et al.Phenylephrine attenuated sepsis-induced cardiac inflammation and mitochondrial injury through an effect on the PI3K/Akt signaling pathway. J Cardiovasc Pharmacol. 2019; 73(3):186-194.
[23] XU W,WEITING Q,XUEFENG Q, et al. A novel role of exogenous carbon monoxide on protecting cardiac function and improving survival against sepsis via mitochondrial energetic metabolism pathway. Int J Biol Sci.2014;10(7):777-788.
|