中国组织工程研究 ›› 2020, Vol. 24 ›› Issue (6): 856-861.doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-4344.2448
• 骨科植入物 orthopedic implant • 上一篇 下一篇
关节镜Bristow-Latarjet术中打内固定骨道时CT定位肩胛上神经的应用价值
袁胜超1,谭志超1,林馥纯1,杜二珠1,郭金华2,杨 春2
- 1东莞市中医院,广东省东莞市 523000;2广东医科大学东莞校区,广东省东莞市 523808
CT localization on suprascapular nerve and clinical application value in arthroscopic Bristow-Latarjet
Yuan Shengchao1, Tan Zhichao1, Lin Fuchun1, Du Erzhu1, Guo Jinhua2, Yang Chun2
- 1Dongguan Hospital of Traditional Chinese Medicine, Dongguan 523000, Guangdong Province, China; 2Dongguan Campus of Guangdong Medical University, Dongguan 523808, Guangdong Province, China
摘要:

文题释义:
Bristow-Latarjet术:是带有联合腱的喙突骨块,穿过被横断的肩胛下肌腱后,固定于肩盂前缘,是治疗复发性肩关节前脱位的有效方法。神经损伤是该术式常见并发症。
肩胛上神经:在肩胛盂上方穿过肩胛上横韧带与肩胛切迹组成的纤维骨性通道即肩胛上孔,进入冈上窝。肩胛上神经的冈上窝段紧贴着冈上肌深面向外下走行,穿过肩胛下孔(由冈盂切迹和连于肩峰根部及肩胛骨背面的肩胛下韧带构成)并绕着冈盂切迹向内下而到冈下窝,发出分支支配冈下肌。
背景:Bristow-Latarjet术是治疗复发性肩关节前脱位的可靠方法。然而据报道,其中1.6%的患者伴有神经损伤。因此全关节镜Latarjet术式越来越受欢迎,由于外科医生不能触诊神经,神经的定位和保护变得困难。
目的:研究肩胛上神经在肩胛颈后上方的CT定位,提高对Bristow-Latarjet术临床操作安全范围的认知。
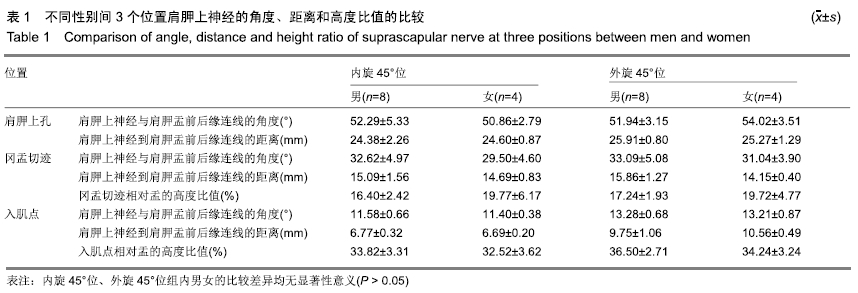
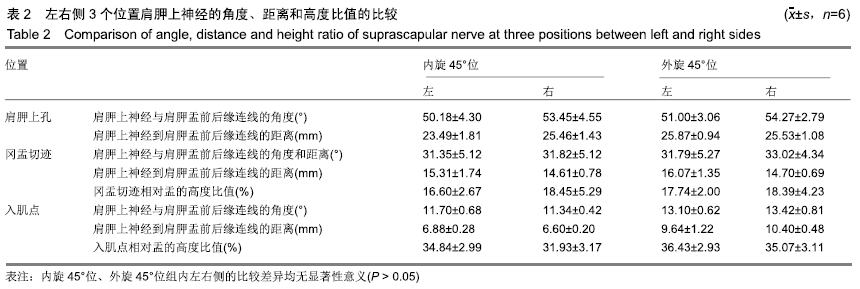
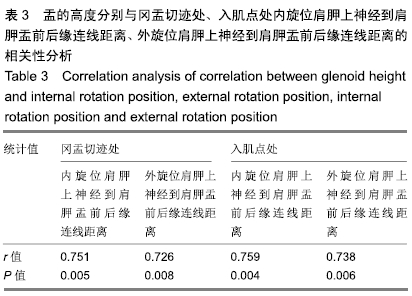
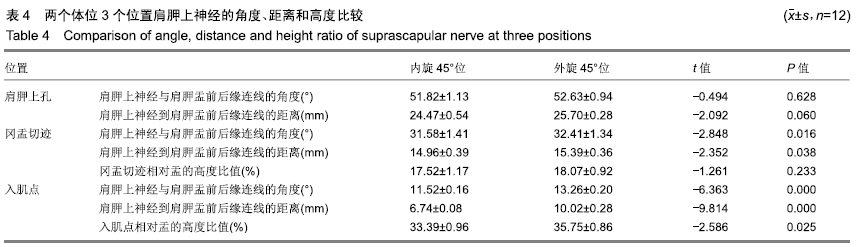
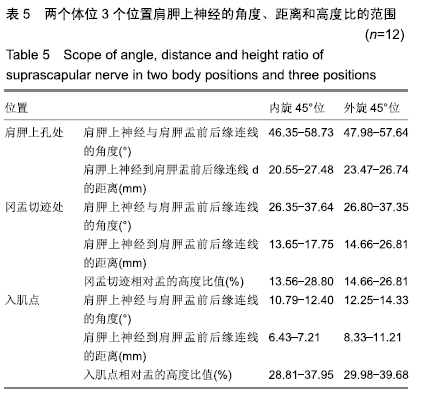
方法:选用经甲醛常规固定的成年尸体上肢标本12侧,男8侧,女4侧,实验方案符合东莞市中医院对研究的相关伦理要求。解剖并使用显影线标记12侧标本肩胛上神经的主干和分支,CT水平位上测量肩胛上孔、冈盂切迹、最外侧神经分支入肌点3个位置在肩关节内旋45°和外旋45°体位时到肩胛盂前后缘连线的距离、成角以及与肩胛盂的高度比,所得数据进行统计学处理。
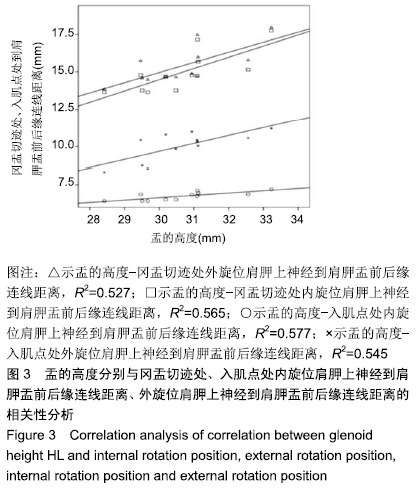
结果与结论:①Pearson 相关性分析:盂的高度分别与冈盂切迹、入肌点到关节面的距离呈正相关;②内旋45°与外旋45°两个体位比较:肩胛上孔处的距离和成角度数差异无显著性(P均> 0.05);冈盂切迹处的距离和成角差异有显著性意义(P均< 0.01),高度比差异无显著性意义(P > 0.05);入肌点处的距离、成角和高度比差异均有显著性意义(P均< 0.01),表明与内旋位相比,外旋位具有更大的角度和距离的安全范围;③内外旋45°位时,冈盂切迹处与入肌点处的角度、距离、高度比差异均有显著性意义(P均< 0.01),表明相比冈盂切迹,入肌点与关节面的角度更小、距离更短,相对盂的高度比更大;④提示关节镜下Bristow-Laterjet术打内固定骨道时建议外旋位操作,以减少神经损伤的发生概率。ORCID: 0000-0002-6828-042X(袁胜超)
中国组织工程研究杂志出版内容重点:人工关节;骨植入物;脊柱;骨折;内固定;数字化骨科;组织工程
中图分类号: