中国组织工程研究 ›› 2017, Vol. 21 ›› Issue (21): 3352-3357.doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-4344.2017.21.012
• 干细胞移植 stem cell transplantation • 上一篇 下一篇
丹酚酸B促进内皮祖细胞动员和黏附的作用
赵先锋1,2,徐 予1,2
- 1郑州大学人民医院心血管内科,河南省郑州市 450003;2河南省人民医院心血管内科,河南省郑州市 450003
Salveanolic acid B promotes the mobilization and adhesion of endothelial progenitor cells
Zhao Xian-feng1, 2, Xu Yu1, 2
- 1Department of Vasculocardiology, the People’s Hospital of Zhengzhou University, Zhengzhou 450003, Henan province, China; 2Department of Vasculocardiology, the People’s Hospital of Zhengzhou University, Zhengzhou 450003, Henan province, China
摘要:
文章快速阅读:
.jpg)
文题释义: 血管内皮祖细胞:是血管内皮细胞的前体细胞,在生理或病理因素刺激下,可从骨髓动员到外周血参与损伤血管的修复,近年来研究显示,内皮祖细胞在心脑血管疾病、外周血管疾病、肿瘤血管形成及创伤愈合等方面均发挥重要作用,并为缺血性疾病的研究治疗提供了新思路。 骨髓动员:骨髓中存在许多种类的成体干细胞,其中包括造血干细胞、血管内皮祖细胞以及间充质干/祖细胞等干细胞群和间充质细胞,将这些细胞从骨髓中动员到外周血中的过程称作骨髓动员。
摘要
背景:动脉粥样硬化、高血压和糖尿病等多种疾病都伴有血管内皮损伤,而体循环中的内皮祖细胞可以对受损内皮细胞进行有效的修复。
目的:研究丹酚酸B在小鼠体内对血管内皮祖细胞动员和黏附的作用。
方法:选取30只C57BL/6小鼠,随机分为手术组和假手术组,每组15只,手术组小鼠颈总动脉损伤后按照给药不同分为对照亚组、丹酚酸B亚组和血管内皮生长因子亚组,每组5只。对照亚组给予5%葡萄糖注射液,丹酚酸B亚组注射100 g/L丹酚酸B,血管内皮生长因子亚组注射10 μmol/L血管内皮生长因子,给药剂量均为10 mL/kg。假手术组并未进行颈总动脉损伤,分组和给药方式与手术组相同;连续给药7 d后,分离小鼠外周血中的血管内皮祖细胞,并通过流动腔实验检测内皮祖细胞黏附性;酶联免疫吸附法检测血清基质细胞衍生因子1和白细胞介素8水平。
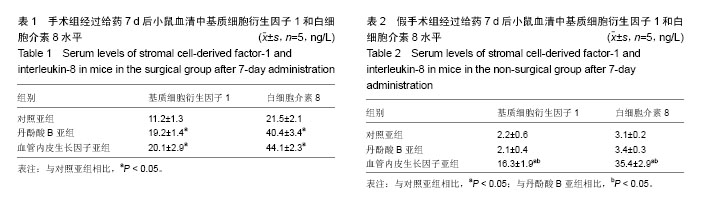
结果与结论:①手术组中内皮祖细胞占有核细胞的比例明显增加,与假手术组相比差异有显著性意义(P < 0.05);②给药7 d后,手术组中丹酚酸B亚组和血管内皮生长因子亚组内皮祖细胞占有核细胞的比例明显高于对照亚组,差异有显著性意义(P < 0.05);假手术组中血管内皮生长因子亚组内皮祖细胞占有核细胞的比例明显高于对照亚组和丹酚酸B亚组,差异有显著性意义(P < 0.05);③流动腔实验结果显示丹酚酸B组内皮祖细胞明显高于对照亚组,差异有显著性意义(P < 0.05);④在手术组中,丹酚酸B亚组与血管内皮生长因子亚组血清中基质细胞衍生因子1和白细胞介素8水平明显高于对照亚组,差异有显著性意义(P < 0.05);在假手术组中,血管内皮生长因子亚组血清中基质细胞衍生因子1和白细胞介素8水平明显高于对照亚组,差异有显著性意义(P < 0.05);⑤结果表明,丹酚酸B可以在体内增加内皮祖细胞骨髓动员的效率,帮助内皮祖细胞黏附于胶原表面,同时还可以上调基质细胞衍生因子1和白细胞介素8细胞活性因子水平。
中图分类号:

.jpg)