| [1] 汤宇,李博,杨兴海,等.非小细胞肺癌脊柱转移治疗现状及进展[J].脊柱外科杂志,2013,11(3):186-190.[2] Jemal A, Bray F, Center MM, et al. Global cancer statistics.CA Cancer J Clin. 2011;61(2):69-90.[3] Bareschino MA, Schettino C, Rossi A, et al. Treatment of advanced non small cell lung cancer. J Thorac Dis. 2011; 3(2):122-133.[4] 刘杨,李玉芬,崔玲,等.肺癌术后营养支持对免疫功能的影响[J]. 海南医学院学报, 2014, 20(12): 1705-1706.[5] Pisters KM, Ginsberg RJ, Giroux DJ, et al. Induction chemotherapy before surgery for early-stage lung cancer: A novel approach. Bimodality Lung Oncology Team.J Thorac Cardiovasc Surg. 2000;119(3):429-439.[6] Shiozawa Y, Nie B, Pienta KJ, et al. Cancer stem cells and their role in metastasis. Pharmacol Ther. 2013;138(2):285- 293.[7] Memmi EM, Sanarico AG, Giacobbe A, et al. p63 Sustains self-renewal of mammary cancer stem cells through regulation of Sonic Hedgehog signaling. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2015;112(11):3499-3504.[8] Osei-Sarfo K, Gudas LJ. Retinoic acid suppresses the canonical Wnt signaling pathway in embryonic stem cells and activates the noncanonical Wnt signaling pathway. Stem Cells. 2014;32(8):2061-2071.[9] Sturgeon CM, Ditadi A, Awong G, et al. Wnt signaling controls the specification of definitive and primitive hematopoiesis from human pluripotent stem cells. Nat Biotechnol. 2014; 32(6):554-561.[10] Mo JS, Park HW, Guan KL. The Hippo signaling pathway in stem cell biology and cancer. EMBO Rep. 2014;15(6): 642-656.[11] Oskarsson T, Batlle E, Massagué J. Metastatic stem cells: sources, niches, and vital pathways. Cell Stem Cell. 2014; 14(3):306-321.[12] Stewart DJ. Wnt signaling pathway in non-small cell lung cancer. J Natl Cancer Inst. 2014;106(1):djt356.[13] Stewart DJ, Chang DW, Ye Y, et al. Wnt signaling pathway pharmacogenetics in non-small cell lung cancer. Pharmacogenomics J. 2014;14(6):509-522.[14] Coscio A, Chang DW, Roth JA, et al. Genetic variants of the Wnt signaling pathway as predictors of recurrence and survival in early-stage non-small cell lung cancer patients. Carcinogenesis. 2014;35(6):1284-1291.[15] Kugler MC, Joyner AL, Loomis CA, et al. Sonic hedgehog signaling in the lung. From development to disease. Am J Respir Cell Mol Biol. 2015;52(1):1-13.[16] Xiong D, Ye Y, Fu Y, et al. Bmi-1 expression modulates non-small cell lung cancer progression. Cancer Biol Ther. 2015;16(5):756-763.[17] Lee JJ, Perera RM, Wang H, et al. Stromal response to Hedgehog signaling restrains pancreatic cancer progression. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2014;111(30):E3091-100.[18] Matsushita S, Onishi H, Nakano K, et al. Hedgehog signaling pathway is a potential therapeutic target for gallbladder cancer. Cancer Sci. 2014;105(3):272-280.[19] Heiden KB, Williamson AJ, Doscas ME, et al. The sonic hedgehog signaling pathway maintains the cancer stem cell self-renewal of anaplastic thyroid cancer by inducing snail expression. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2014;99(11):E2178- 2187.[20] Raz G, Allen KE, Kingsley C, et al. Hedgehog signaling pathway molecules and ALDH1A1 expression in early-stage non-small cell lung cancer. Lung Cancer. 2012;76(2):191-196.[21] 钟祥,李应东.小檗碱药理作用研究进展[J].亚太传统医药, 2012, 8(3):185-186.[22] Refaat A, Abdelhamed S, Yagita H, et al. Berberine enhances tumor necrosis factor-related apoptosis-inducing ligand-mediated apoptosis in breast cancer. Oncol Lett. 2013;6(3):840-844.[23] Zhang EB, Kong R, Yin DD, et al. Long noncoding RNA ANRIL indicates a poor prognosis of gastric cancer and promotes tumor growth by epigenetically silencing of miR-99a/miR-449a. Oncotarget. 2014;5(8):2276-2292.[24] Chidambara Murthy KN, Jayaprakasha GK, Patil BS. The natural alkaloid berberine targets multiple pathways to induce cell death in cultured human colon cancer cells. Eur J Pharmacol. 2012;688(1-3):14-21.[25] Ma X, Zhou J, Zhang CX, et al. Modulation of drug-resistant membrane and apoptosis proteins of breast cancer stem cells by targeting berberine liposomes. Biomaterials. 2013;34(18): 4452-4465.[26] 吴澄,钟丰文,罗列. A549肺癌细胞株干细胞表面标志的初步研究[J].赣南医学院学报, 2015, 35(4): 529-531.[27] Ferlay J, Shin HR, Bray F, et al. Estimates of worldwide burden of cancer in 2008: GLOBOCAN 2008. Int J Cancer. 2010;127(12):2893-2917.[28] 谭宇蕙,陈冠林,郭淑杰,等.小檗碱对人胃癌MGC-803细胞生长抑制及诱导凋亡的作用[J].中国药理学通报, 2001,17(1): 40-43.[29] Kuo CL, Chou CC, Yung BY. Berberine complexes with DNA in the berberine-induced apoptosis in human leukemic HL-60 cells. Cancer Lett. 1995;93(2):193-200.[30] Kim HS, Kim MJ, Kim EJ, et al. Berberine-induced AMPK activation inhibits the metastatic potential of melanoma cells via reduction of ERK activity and COX-2 protein expression. Biochem Pharmacol. 2012;83(3):385-394.[31] Wang L, Cao H, Lu N, et al. Berberine inhibits proliferation and down-regulates epidermal growth factor receptor through activation of Cbl in colon tumor cells. PLoS One. 2013;8(2): e56666.[32] 蒋艳,王毅,郝钰,等.小檗碱对人高转移肺癌系(PG)细胞增殖的影响及机制研究[J].中国病理生理杂志, 2005, 21(11): 2170-2173.[33] Park SH, Sung JH, Chung N. Berberine diminishes side population and down-regulates stem cell-associated genes in the pancreatic cancer cell lines PANC-1 and MIA PaCa-2. Mol Cell Biochem. 2014;394(1-2):209-215.[34] 邹宇辉,王琼,王伟民.小檗碱对U251胶质瘤干细胞的诱导分化作用[J].中国微侵袭神经外科杂志, 2016,21(12):559-562.[35] 顾红兵,李继坤.Hedgehog 信号通路与肿瘤的关系研究进展[J]. 现代肿瘤医学, 2011,19(4): 808-811.[36] 李悦,张宇,曹良启,等. Hedgehog信号通路转录因子Gli2表达对肝癌进展和生存预后的影响[J].中华普通外科学文献:电子版, 2016,10(3):174-178.[37] 黄少良,赵丽,郭青龙,等.Hedgehog信号通路参与肿瘤耐药机制研究的最新进展[J].中国药科大学学报,2016,47(3):259-266.[38] 邵欣宇,顾遷,丁希伟,等.Hedgehog信号通路与胰腺癌吉西他滨固有耐药的相关性研究[J].胃肠病学,2016,21(11):656-661.[39] 师海英,黄明莉,张广美,等. Hedgehog信号通路在卵巢癌中作用研究进展[J].中华实用诊断与治疗杂志,2016,30(7):632-634.[40] 沈冰,刘陶文.Hedgehog信号通路Gli家族成员及其在恶性肿瘤中的作用研究进展[J].广西医学,2016,38(2):237-239.[41] Park KS, Martelotto LG, Peifer M, et al. A crucial requirement for Hedgehog signaling in small cell lung cancer. Nat Med. 2011;17(11):1504-1508.[42] Lemjabbar-Alaoui H, Dasari V, Sidhu SS, et al. Wnt and Hedgehog are critical mediators of cigarette smoke-induced lung cancer. PLoS One. 2006;1:e93.[43] 郑晓文,陈一强,孔晋亮,等. Hedgehog信号通路成分SHH和Gli-1及血管内皮生长因子在人肺癌中的表达[J].中国全科医学, 2014, 17(18): 2096-2102.[44] Wang J, Peng Y, Liu Y, et al. Berberine, a natural compound, suppresses Hedgehog signaling pathway activity and cancer growth. BMC Cancer. 2015;15:595. |
.jpg)
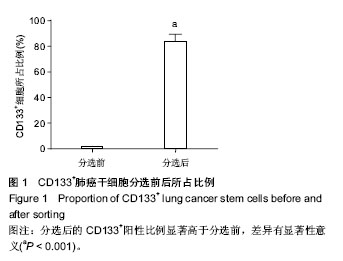

.jpg)