中国组织工程研究 ›› 2017, Vol. 21 ›› Issue (4): 574-579.doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-4344.2017.04.014
• 口腔组织构建 oral tissue construction • 上一篇 下一篇
浓缩生长因子在上颌窦侧壁开窗窦底提升即刻种植中的成骨效果: 单中心、随机对照临床试验方案
程 扬1,刘 敏2
- 1德阳市口腔医院,四川省德阳市 618000;2西南医科大学附属口腔医院,四川省泸州市 646000
Osteogenic effects of concentrated growth factors applied in maxillary sinus floor elevation via a lateral window approach with simultaneous implant placement: study protocol for a single-center randomized controlled trial
Cheng Yang1, Liu Min2
- 1Deyang Stomatological Hospital, Deyang 618000, Sichuan Province, China; 2 Hospital of Stomatology, Southwest Medical University, Luzhou 646000, Sichuan Province, China
摘要:
文章快速阅读:
.jpg) 文题释义:
上颌窦侧壁开窗窦底提升:又称上颌窦外提升,通过侧壁开窗,建立进入上颌窦的开口,从上颌窦底提升上颌窦黏膜,并在现有牙槽骨之上的空间中植入骨移植物,达到提高牙槽骨高度的目的。
浓缩生长因子:是通过专用特殊设备,将自体外周血经不间断差速离心制备而成的富含多种高浓度生长因子的血液提取物。
文题释义:
上颌窦侧壁开窗窦底提升:又称上颌窦外提升,通过侧壁开窗,建立进入上颌窦的开口,从上颌窦底提升上颌窦黏膜,并在现有牙槽骨之上的空间中植入骨移植物,达到提高牙槽骨高度的目的。
浓缩生长因子:是通过专用特殊设备,将自体外周血经不间断差速离心制备而成的富含多种高浓度生长因子的血液提取物。
.jpg) 文题释义:
上颌窦侧壁开窗窦底提升:又称上颌窦外提升,通过侧壁开窗,建立进入上颌窦的开口,从上颌窦底提升上颌窦黏膜,并在现有牙槽骨之上的空间中植入骨移植物,达到提高牙槽骨高度的目的。
浓缩生长因子:是通过专用特殊设备,将自体外周血经不间断差速离心制备而成的富含多种高浓度生长因子的血液提取物。
文题释义:
上颌窦侧壁开窗窦底提升:又称上颌窦外提升,通过侧壁开窗,建立进入上颌窦的开口,从上颌窦底提升上颌窦黏膜,并在现有牙槽骨之上的空间中植入骨移植物,达到提高牙槽骨高度的目的。
浓缩生长因子:是通过专用特殊设备,将自体外周血经不间断差速离心制备而成的富含多种高浓度生长因子的血液提取物。摘要
背景:上颌窦侧壁开窗窦底提升是克服萎缩上颌后牙区骨量不足最有效的方法,且骨移植被认为是上颌窦提升成功的先决条件。富血小板血浆和血小板纤维蛋白已被用于加速新骨形成、再生和修复,但是浓缩生长因子对新骨形成的研究并不深入。
目的:探讨浓缩生长因子在上颌窦侧壁开窗窦底提升即刻种植中对骨缺损区的修复和成骨效果的影响。
方法:随机双盲对照试验将在西南医科大学附属口腔医院完成。40例上颌磨牙缺失、上颌后牙区剩余骨高度为2-5 mm的患者被纳入研究,并随机分为浓缩生长因子组(n=20)和对照组(n=20),分别于上颌窦侧壁开窗窦底提升即刻,将浓缩生长因子+羟基磷灰石+自体骨或羟基磷灰石+自体骨种植体植于骨缺损区。于种植后1,3和6个月行X射线平片检查,判断种植区骨组织再生、骨修复效果,并以优良率作为评估标准;应用锥形束CT测量上颌窦骨缺损填充区骨皮质厚度,以反映骨质密度。研究方案已取得西南医科大学附属口腔医院伦理委员会的书面批准,且符合世界医学会制订的《赫尔辛基宣言》,并已在北美临床试验注册中心注册(NCT03046173)。患者均签署知情同意书。
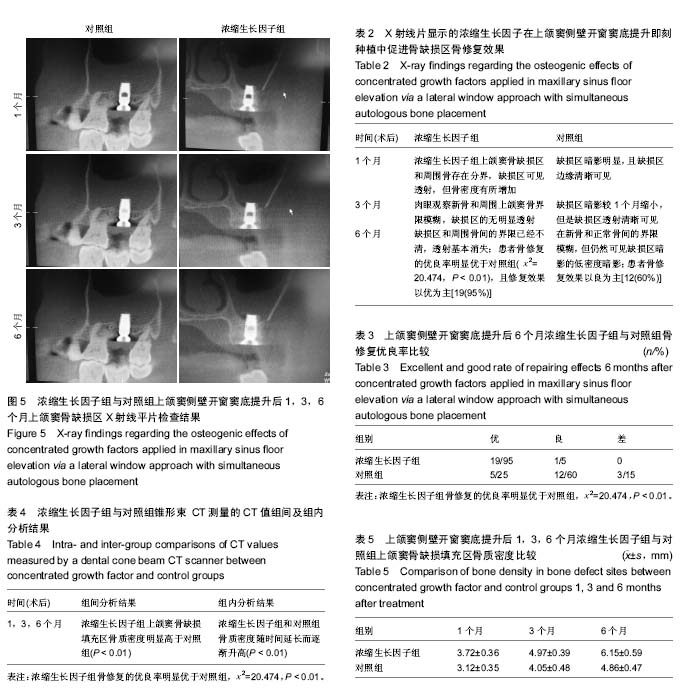
结果与结论:研究已于2016年完成。获得的研究结果:X射线平片显示,随访3和6个月时浓缩生长因子组种植体引导周围骨缺损中的骨组织再生效果较好,优于对照组(P < 0.01),且6个月时优于3个月时。随访1,3,6个月时浓缩生长因子组骨种植区骨质密度明显高于对照组(P < 0.01)。说明浓缩生长因子可促进上颌窦侧壁开窗窦底提升即刻种植体种植后的新骨形成,加快骨结合。
中国组织工程研究杂志出版内容重点:组织构建;骨细胞;软骨细胞;细胞培养;成纤维细胞;血管内皮细胞;骨质疏松;组织工程
ORCID:0000-0002-3676-7428(程扬)
中图分类号:
.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg) 文题释义:
上颌窦侧壁开窗窦底提升:又称上颌窦外提升,通过侧壁开窗,建立进入上颌窦的开口,从上颌窦底提升上颌窦黏膜,并在现有牙槽骨之上的空间中植入骨移植物,达到提高牙槽骨高度的目的。
浓缩生长因子:是通过专用特殊设备,将自体外周血经不间断差速离心制备而成的富含多种高浓度生长因子的血液提取物。
文题释义:
上颌窦侧壁开窗窦底提升:又称上颌窦外提升,通过侧壁开窗,建立进入上颌窦的开口,从上颌窦底提升上颌窦黏膜,并在现有牙槽骨之上的空间中植入骨移植物,达到提高牙槽骨高度的目的。
浓缩生长因子:是通过专用特殊设备,将自体外周血经不间断差速离心制备而成的富含多种高浓度生长因子的血液提取物。