| [1] CAPRIE Steering Committee. A randomized, blinded, trial of clopidogrel versus aspirin in patients at risk of ishaemic events (CAPRIE).Lancet. 1996;348(9038): 1329-1339.
[2] Yusuf S,Mehta SR,Zhao F,et al.Early and late effects of clopidogrel in patients with acute coronary syndromes. Circulation.2003;107(7): 966-972.
[3] Chen ZM,Jiang LX,Chen YP,et al.Addition of clopidogrel to aspirin in 45,852 patients with acute myocardial infarction: randomised placebo-controlled trial.Lancet.2005;366(9497): 1607-1621.
[4] Sabatine MS,Cannon CP,Gibson CM,et al.Addition of clopidogrel to aspirin and fibrinolytic therapy for myocardial infarction with ST-segment elevation.N Engl J Med.2005; 352(12): 1179-1189.
[5] Sabatine MS,Cannon CP,Gibson CM,et al.Effet of clopidogrel pretreatment before percutaneous coronary intervention in patients with ST-elevation myocardial infarction treated with fibrinolytics: the PCI-CLARITY study. JAMA.2005;294(10): 1224-1232.
[6] Verheugt FW,Montalescot G,Sabatine MS,et al.Prehospital fibrinolysis with dual antiplatelet therapy in ST-elevation acute myocardial infarction: a substudy of the randomized double blind CLARITY-TIMI 28 trial.J Thromb Thrombolysis.2007; 23(3):173-179.
[7] Bertrand ME,Rupprecht HJ,Urban P,et al.Double-blind study of the safety of clopidogrel with and without a loading dose in combination with aspirin compared with ticlopidine in combination with aspirin after coronary stenting : the clopidogrel aspirin stent international cooperative study (CLASSICS).Circulation.2000;102(6): 624-629.
[8] Mehta SR,Yusuf S,Peters RJ,et al. Effects of pretreatment with clopidogrel and aspirin followed by long-term therapy in patients undergoing percutaneous coronary intervention: the PCI-CURE study. Lancet.2001;358(9281): 527-533.
[9] Steinhubl SR,Berger PB,Mann JT 3rd,et al.Clopidogrel for the Reduction of Events During Observation. Early and sustained dual oral antiplatelet therapy following percutaneous coronary intervention: a randomized controlled trial. JAMA.2002;288 (19): 2411-2420.
[10] Mehta SR,Bassand JP,Chrolavicius S,et al.CURRENT-OASIS 7 Investigators. Dose comparisons of clopidogrel and aspirin in acute coronary syndromes. N Engl J Med.2010;363(10): 930-942
[11] 中华医学会心血管病学分会/中华心血管病杂志编辑委员会. 经皮冠状动脉介入治疗指南2009[J].中华心血管病杂志,2009, 37(1): 4-25.
[12] 柏瑾,李志善,戚文航,等.国产硫酸氯吡格雷片降低血小板聚集率的临床观察[J].中国临床药学杂志2001,10(2): 67-69.
[13] 陈凌,李志善,戚文航,等.硫酸氯吡格雷的抗血小板聚集临床研究[J].中国新药杂志2000,9(10): 715-717.
[14] Kushner FG,Hand M,Smith SC Jr,et al.2009 Focused Updates: ACC/AHA Guidelines for the Management of Patients With ST-Elevation Myocardial Infarction.Circulation.2009;120(22): 2271-2306.
[15] Silber S,Albertsson P,Avilés FF,et al.Task Force for Percutaneous Coronary Interventions of the European Society of Cardiology. Guidelines for percutaneous coronary interventions.Eur Heart J.2005;26(8):804-847.
[16] Anderson JL,Adams CD,Antman EM,et al.ACC/AHA 2007 guidelines for the management of patients with unstable angina/non ST-elevation myocardial infarction.Circulation. 2007;116(7): e148-304.
[17] Holmes DR,Kereiakes DJ,Kleiman NS,et al.Combining antiplatelet and anticoagulant therapies.J Am Coll Cardiol. 2009;54(2): 95-109.
[18] 李志娟,董平栓,杨旭明,等.国产和进口氯吡格雷对经皮冠状动脉介入术后血小板功能的影响[J].中国介入心脏病学杂志,2006, 14(4):208-210.
[19] 顾俊,胡伟,肖红兵,等.国产和进口氯吡格雷对PCI近中期预后的影响[J].上海交通大学学报:医学版,2008,28(5): 608-609.
[20] 卢春山,周志强,柳景华,等.冠状动脉支架术后进口氯吡格雷(波立维)与国产氯吡格雷(泰嘉)抗血小板治疗的对照研究[J].中国介入心脏病学杂志,2009,17(2): 67-70.
[21] 李鹏,王文红,刘勇.国产氯吡格雷(泰嘉)与进口氯吡格雷(波立维)PCI术后应用的有效性和安全性对照研究[J].中国心血管病研究,2010,8(7): 506-508.
[22] 阴赪茜,李志忠,张京梅,等.国产与进口氯吡格雷在冠状动脉介入治疗中的疗效对比分析[J].中国新药杂志,2010,19(10): 849-852.
[23] Meng K, Lü SZ, Zhu HG,et al.Use of tailored loading-dose clopidogrel in patients undergoing selected percutaneous coronary intervention based on adenosine diphosphate-mediated platelet aggregation. Chin Med J. 2010;123(24): 3578-3582.
[24] 孙裕华,陶秀彬,倪芳,等.国产氯吡格雷治疗冠心病疗效及安全性的Meta分析[J].中国循证心血管医学杂志,2010,2(4): 214-218. |
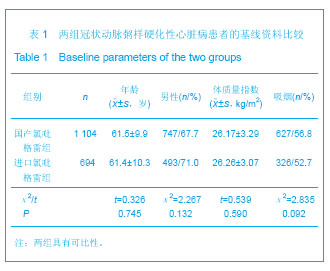
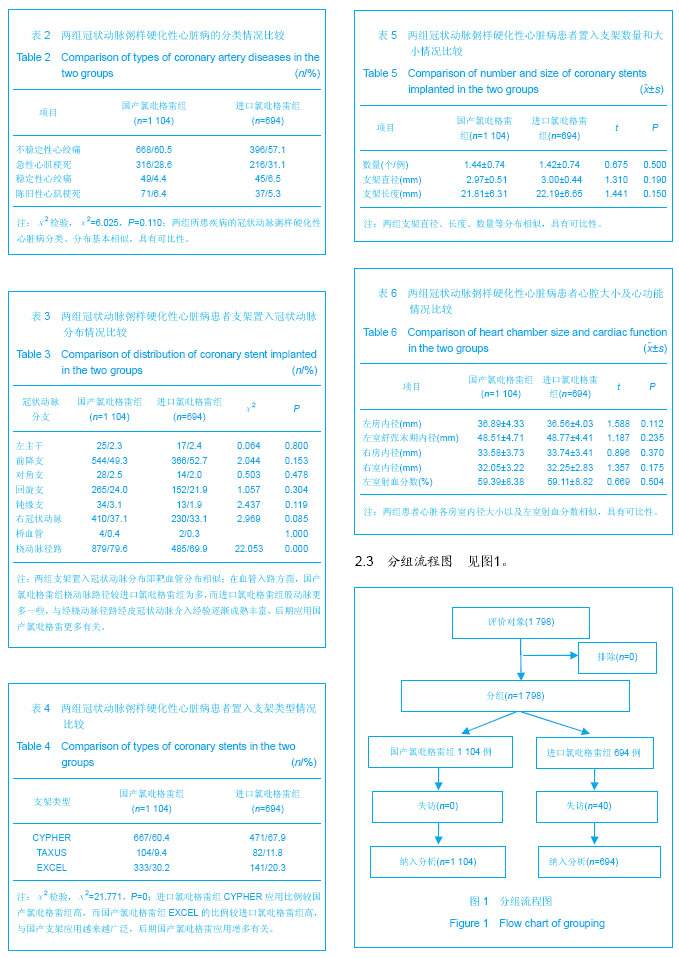
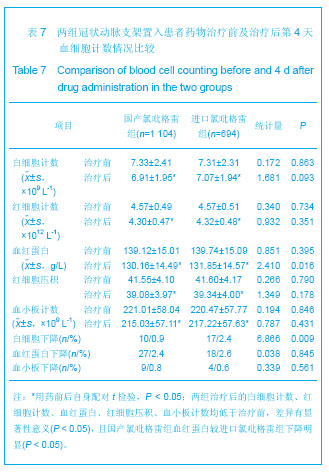
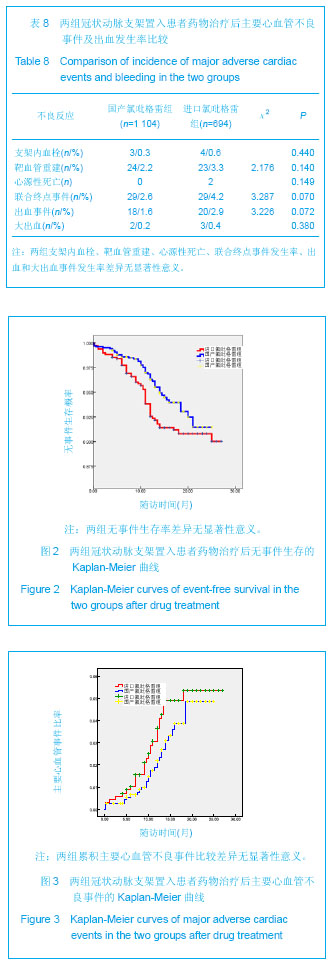
.jpg)