| [1]Buser D,Dula K,Belser U,et al.Localized ridge augmentation using guided bone regeneration. Int J Periodontics Restorative Dent.1993; 13:29-45.[2]Dimitriou R,Mataliotakis GI,Calori GM,et al.The role of barrier membranes for guided bone regeneration and restoration of large bone defects: current experimental and clinical evidence. BMC Med.2012;10(1):81-104.[3]Crump TB,Rivera-Hidalgo F,Harrison JW,et al.Influence of three membrane type on healing of bone defects.Oral Surg Oral Med Oral Histol.1996;82(4):365-374.[4]Bottino MC,Thomas V,Schmidt G,et al.Recent advances in the development of GTR/GBR membranes for periodontal regeneration—A materials perspective.Dent Mater. 2012;28:703-721.[5]Cucchi A,Vignudelli E,Napolitano A,et al.Evaluation of complication rates and vertical bone gain after guided bone regeneration with non-resorbable membranes versus titanium meshes and resorbable membranes. A randomized clinical trial. Clin Implant Dent Relat Res. 2017;19(5):821-832.[6]Miron RJ,Fujioka-Kobayashi M,Buser D,et al.Combination of Collagen Barrier Membrane with Enamel Matrix Derivative-Liquid Improves Osteoblast Adhesion and Differentiation. Int J Oral Maxillofac Implants. 2017;32(1):196-203.[7]Kaushal S,Kumar A,Khan MA,et al.Comparative study of nonabsorbable and absorbable barrier membranes in periodontal osseous defects by guided tissue regeneration.J Oral Biol Craniofac Res.2016;6(2):111-117.[8]Jung RE,Fenner N,Hämmerle CH,et al.Long-term outcome of implants placed with guided bone regeneration (GBR) using resorbable and non-resorbable membranes after 12–14 years.Clin Oral Implants Res. 2013;24(10):1065-1073.[9]Caballé-Serrano J,Munar-Frau A,Ortiz-Puigpelat O,et al.On the search of the ideal barrier membrane for guided bone regeneration. J Clin Exp Dent.2018;10(5):e477-e483.[10]李栎,张恒,唐历波.膜生物材料及在组织工程中的应用:“引导膜再生理论”的展望[J].中国组织工程研究, 2018,22(22):3595-3601.[11]Gentile P,Chiono V,Tonda-Turo C,et al.Polymeric membranes for guided bone regeneration. Biotechnol J. 2011;6(10):1187-1197.[12]Wang J,Wang L,Zhou Z,et al.Biodegradable polymer membranes applied in guided bone/tissue regeneration: a review.Polymers. 2016;8(4):115.[13]Behring J,Junker R,Walboomers XF,et al.Toward guided tissue and bone regeneration: morphology, attachment, proliferation, and migration of cells cultured on collagen barrier membranes. A systematic review.Odontology. 2008;96(1):1-11.[14]Sheikh Z,Qureshi J,Alshahrani AM,et al.Collagen based barrier membranes for periodontal guided bone regeneration applications. Odontology.2017;105(1):1-12.[15]达静姝,陈武.异种脱细胞真皮基质对新生血管作用的研究[J].口腔生物医学,2016,7(4):187-190.[16]张丽娜.不同口腔修复膜材料在牙种植中引导骨再生的应用效果对比[J].系统医学,2017,2(23):117-119.[17]Lutz R,Neukam FW,Simion M,et al.Long-term outcomes of bone augmentation on soft and hard-tissue stability: a systematic review. Clin Oral Implants Res. 2015;26(11):103-122.[18]Parma-Benfenati S,Roncati M,Galletti P, et al. Resorbable dome device and guided bone regeneration: an alternative bony defect treatment around implants. A case series.Int J Periodontics Restorative Dent.2014;34(6):749-755.[19]Porcaro G, Busa A, Bianco E, et al. Use of a Partial-thickness Flap for Guided Bone Regeneration in the Upper Jaw. The journal of contemporary dental practice. 2017;18(12):1117-1121.[20]陈一宁,但卫华,但年华.脱细胞真皮基质的改性及应用概述[J].材料导报, 2018,32(13):2311-2319.[21]Gielkens PF,Schortinghuis J,de Jong JR,et al.Vivosorb, Bio-Gide, and Gore-Tex as barrier membranes in rat mandibular defects: an evaluation by microradiography and micro-CT.Clin Oral Implants Res.2008;19(5):516-521.[22]Ferreira AM,Gentile P,Chiono V,et al.Collagen for bone tissue regeneration. ActaBiomaterialia. 2012;8(9):3191-3200.[23]Calciolari E,Ravanetti F,Strange A,et al.Degradation pattern of a porcine collagen membrane in an in vivo model of guided bone regeneration. J Periodontal Res.2018;53(3):430-439.[24]Lu HK,Lee SY,Lin FP.Elastic modulus, permeation time and swelling ratio of a new porcine dermal collagen membrane.J Periodontal Res.1998;33(5):243-248.[25]Rothamel D,Schwarz F,Sager M, et al. Biodegradation of differently cross-linked collagen membranes: an experimental study in the rat. Clin Oral Implants Res.2005;16(3):369-378.[26]Speer DP,Chvapil M,Eskelson CD,et al.Biological effects of residual glutaraldehyde in glutaraldehyde-tanned collagen biomaterials.J Biomed Mater Res.1980;14:753-764.[27]Gilbert TW,Freund JM,Badylak SF.Quantification of DNA in biologic scaffold materials. J Surg Res.2009;152(1):135-139.[28]Crapo PM,Gilbert TW,Badylak SF.An overview of tissue and whole organ decellularization processes. Biomaterials. 2011;32(12):3233-3243.[29]Harriger MD,Supp AP,Warden GD,et al.Glutaraldehyde crosslinking of collagen substrates inhibits degradation in skin substitutes grafted to athymic mice.J Biomed Mater Res. 1997;35(2):137-145.[30]Rothamel D,Schwarz F,Sculean A,et al.Biocompatibility of various collagen membranes in cultures of human PDL fibroblasts and human osteoblast-like cells.Clin Oral Implants Res.2004;15(4):443-449.[31]Cheung HY,Brown MR.Evaluation of glycine as an inactivator of glutaraldehyde. J Pharm Pharmacol. 1982;34(4):211-214.[32]李盼盼.活性羰基化合物诱导的氧化应激致细胞能量代谢障碍和毒性的机制[D].咸阳:西北农林科技大学,2015. |
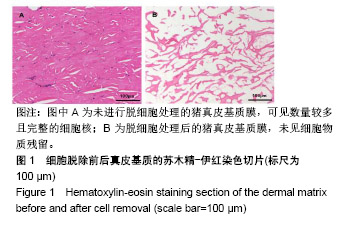
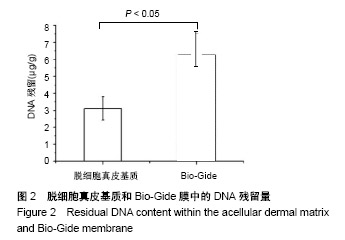
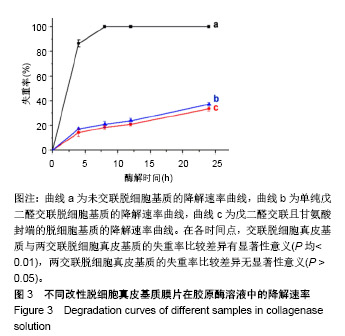
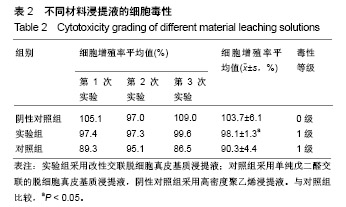
.jpg)

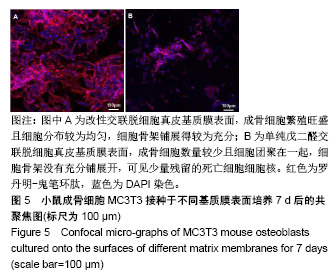
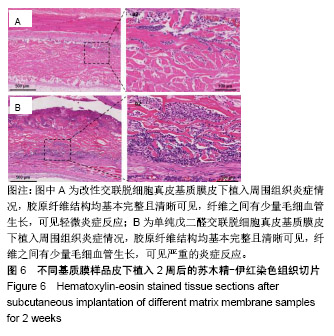

.jpg)