中国组织工程研究 ›› 2019, Vol. 23 ›› Issue (20): 3148-3152.doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-4344.1180
• 骨与关节生物力学 bone and joint biomechanics • 上一篇 下一篇
载荷速率对股骨颈骨折裂纹扩展影响的有限元分析
郑利钦1,林梓凌2,3,陈心敏1,梁子毅1,李木生1,郑永泽1
- 1广州中医药大学第一临床医学院,广东省广州市 510405;2广州中医药大学第一附属医院创伤骨科,广东省广州市 510405;3广州中医药大学岭南医学研究中心,广东省广州市 510405
A finite element analysis of loading velocity affecting femoral neck fracture propagation
Zheng Liqin1, Lin Ziling2, 3, Chen Xinmin1, Liang Ziyi1, Li Musheng1, Zheng Yongze1
- 1First School of Clinical Medicine of Guangzhou University of Chinese Medicine, Guangzhou 510405, Guangdong Province, China; 2Department of Traumatic Orthopedics, First Affiliated Hospital of Guangzhou University of Chinese Medicine, Guangzhou 510405, Guangdong Province, China; 3Lingnan Medical Research Center of Guangzhou University of Chinese Medicine, Guangzhou 510405, Guangdong Province, China
摘要:
文章快速阅读:
.jpg)
文题释义:
断裂力学:材料在不断负荷作用下发生微裂纹,导致材料刚度和强度等降低,微裂纹积累到一定程度就出现裂纹扩展,继而发生大面积的裂纹,进而导致材料的折断和失效。断裂是连续的,断裂力学可直接分析构件的受力和破坏过程,因此可将脆性骨折的发生过程细化为“骨密度降低-骨小梁微损伤-裂纹拓展-微骨折-骨质断裂”的一个完整过程。
载荷速率与骨折的关系:载荷速率对松质骨的极限应力、弹性模量、破坏能及最小应力的影响,是结合了各向异性度与表面密度后的综合结果,其中与极限应力的相关性最高,其次是弹性模量、最小应力,最后才是破坏能、载荷速率对骨折裂纹的影响,实际上是载荷速率改变骨的各种材料属性后在宏观上的表现。
摘要
背景:骨折发生发展是个动态过程,传统有限元方法不能很好地预测及展示骨折发生的确切起点、骨质断裂过程及该过程的应力、应变、裂纹扩展情况。
目的:模拟不同跌倒载荷速率对股骨颈骨折裂纹扩展的影响。
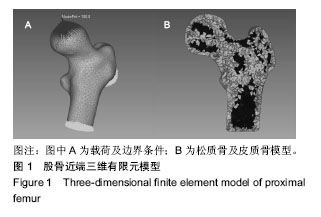
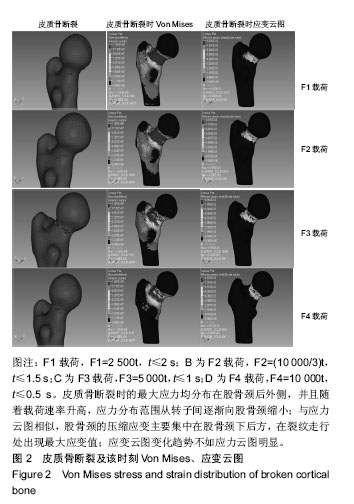
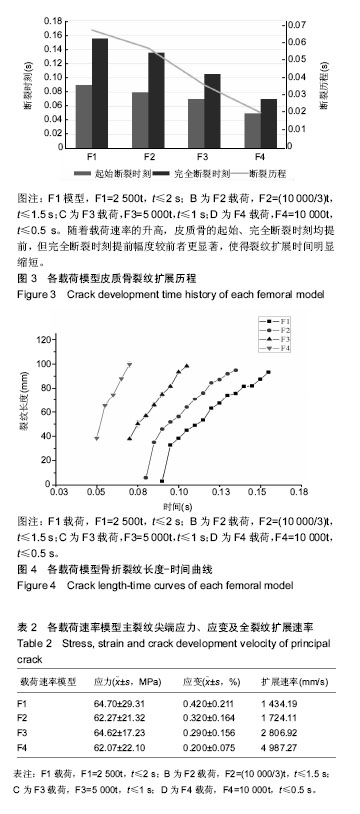
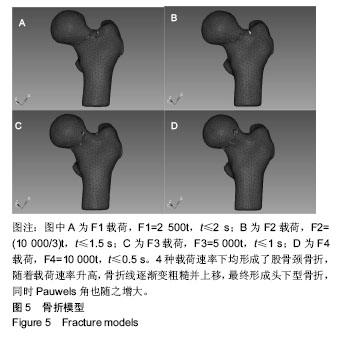
方法:将1名健康志愿者的股骨原始CT数据导入Mimics19.0软件,经区域增长、编辑笼罩、光滑、包裹等重建股骨近端三维有限元模型,并在Hypermesh14.0中进行松质骨、皮质骨网格划分、定义材料属性、设定边界条件、模拟股骨内旋、内收位跌倒状态、加载载荷-时间函数[F1=2 500t、F2=(10 000/3)t、F3= 5 000t、F4=10 000t]等前处理,将生成的K文件导入LS-DYNA求解器中运算。
结果与结论:①骨折起始裂纹均出现在股骨颈下后方,初始裂纹长度呈载荷速率依赖性;②皮质骨断裂时的最大应力均分布在股骨颈后外侧,随着载荷速率升高,应力分布从转子间逐渐向股骨颈缩小;③股骨颈的压缩应变主要集中在股骨颈下后方,在裂纹走行处出现最大应变值;④载荷速率越高皮质骨越早发生断裂,断裂历程越短,裂纹扩展速率越高,骨折线逐渐变粗糙并上移,形成头下型骨折,同时Pauwels角也随之增大;⑤结果说明,载荷速率会改变股骨颈骨折裂纹扩展行为,进而影响髋部骨折类型。
中国组织工程研究杂志出版内容重点:人工关节;骨植入物;脊柱;骨折;内固定;数字化骨科;组织工程
ORCID: 0000-0001-5241-1096(郑利钦)
中图分类号:
.jpg)
.jpg)