中国组织工程研究 ›› 2019, Vol. 23 ›› Issue (4): 493-498.doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-4344.1028
• 人工假体 artificial prosthesis • 下一篇
全髋关节置换局部应用氨甲环酸术中术后失血及白细胞介素6和C-反应蛋白的变化
赵洪顺1,阿尖措1,高顺红2,李永刚3,郭立平3
- 青海红十字医院,1骨二科,3骨一科,青海省西宁市 810000;2唐山市第二人民医院手外二科,河北省唐山市 630010
Intraoperative and postoperative blood loss and levels of C-reactive protein and interleukin-6 after local application of tranexamic acid in total hip arthroplasty
Zhao Hongshun1, A Jiancuo1, Gao Shunhong2, Li Yonggang3, Guo Liping3
- 1Second Department of Orthopedics, 3First Department of Orthopedics, Qinghai Red Cross Hospital, Xining 810000, Qinghai Province, China; 2Second Department of Hand Surgery, the Second People’s Hospital of Tangshan, Tangshan 630010, Hebei Province, China
摘要:
文章快速阅读:
.jpg) 文题释义:
白细胞介素6:是由CD4+ T细胞、巨噬细胞等多种细胞产生的促炎性细胞因子,它能够对多种细胞产生促炎作用。在正常健康人群的血浆中其表达水平较低,在手术、炎症、感染等情况时,其表达水平会显著上升。
C-反应蛋白:是由肝细胞合成的急性时相蛋白,参与机体的炎症反应。人体发生炎症反应时血液中 C-反应蛋白的浓度随之升高。
文题释义:
白细胞介素6:是由CD4+ T细胞、巨噬细胞等多种细胞产生的促炎性细胞因子,它能够对多种细胞产生促炎作用。在正常健康人群的血浆中其表达水平较低,在手术、炎症、感染等情况时,其表达水平会显著上升。
C-反应蛋白:是由肝细胞合成的急性时相蛋白,参与机体的炎症反应。人体发生炎症反应时血液中 C-反应蛋白的浓度随之升高。
摘要
背景:多数研究是在全髋关节置换开始前将氨甲环酸静脉注射入患者体内,观察其对显性及隐形失血的影响,很少有研究观察氨甲环酸治疗后血液中白细胞介素6及C-反应蛋白的变化情况。
目的:探讨氨甲环酸局部应用对全髋关节置换围置换期失血以及白细胞介素6和C-反应蛋白的影响。
方法:选择2015年1月至2017年1月在青海红十字医院就诊行初次单侧全髋关节置换的75例患者作为研究对象,随机分为治疗组和对照组,治疗组37例在安置假体后给予氨甲环酸静脉点滴,对照组38例在相同时间给予等量的氯化钠静脉点滴。观察并比较2组患者术中失血量、术后引流量、总失血量、隐性出血量、输血量及输血率;测量2组患者术前及术后不同时刻的血红蛋白及红细胞压积、C-反应蛋白及白细胞介素6的表达水平;记录2组患者发热、下肢静脉血栓形成等并发症发生情况。
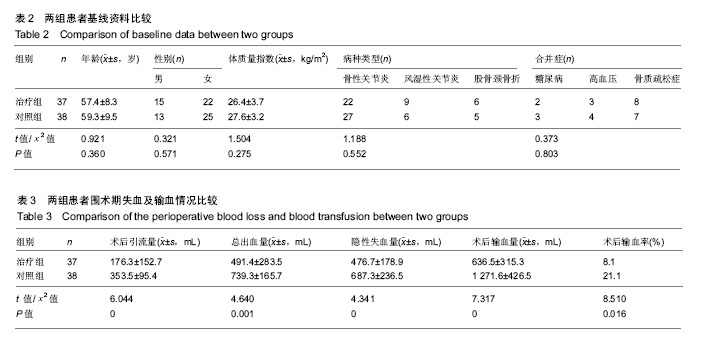
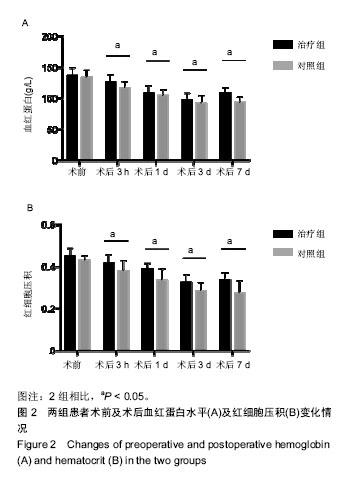
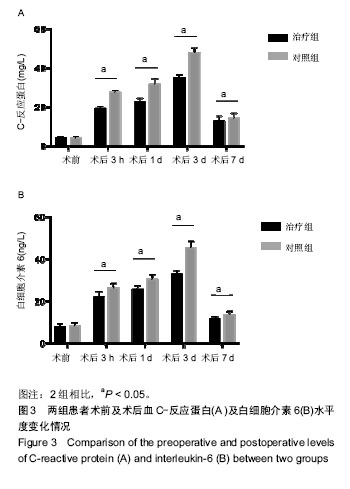
结果与结论:①治疗组术后引流量、总出血量、隐性失血量、术后输血量及术后输血率均小于对照组,差异有显著性意义(P < 0.05);②治疗组术后3 h、1 d、3 d、7 d的血红蛋白及红细胞压积均高于对照组,差异有显著性意义(P < 0.05);③术后3 h、1 d及3 d时2组患者C-反应蛋白及白细胞介素6水平均逐渐升高,且对照组升高更多(P < 0.05);④围置换期2组患者无发热、感染及下肢深静脉血栓形成;⑤提示静脉应用氨甲环酸能够安全有效的减少全髋关节置换后出血,且能够降低白细胞介素6及C-反应蛋白释放水平。
中国组织工程研究杂志出版内容重点:人工关节;骨植入物;脊柱;骨折;内固定;数字化骨科;组织工程
ORCID: 0000-0002-2945-8280(赵洪顺)
中图分类号:
.jpg)
.jpg) 文题释义:
白细胞介素6:是由CD4+ T细胞、巨噬细胞等多种细胞产生的促炎性细胞因子,它能够对多种细胞产生促炎作用。在正常健康人群的血浆中其表达水平较低,在手术、炎症、感染等情况时,其表达水平会显著上升。
C-反应蛋白:是由肝细胞合成的急性时相蛋白,参与机体的炎症反应。人体发生炎症反应时血液中 C-反应蛋白的浓度随之升高。
文题释义:
白细胞介素6:是由CD4+ T细胞、巨噬细胞等多种细胞产生的促炎性细胞因子,它能够对多种细胞产生促炎作用。在正常健康人群的血浆中其表达水平较低,在手术、炎症、感染等情况时,其表达水平会显著上升。
C-反应蛋白:是由肝细胞合成的急性时相蛋白,参与机体的炎症反应。人体发生炎症反应时血液中 C-反应蛋白的浓度随之升高。