Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research ›› 2015, Vol. 19 ›› Issue (15): 2425-2430.doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-4344.2015.15.025
Previous Articles Next Articles
Neuronal mitochondria and apoptosis signaling pathways play an important role in cell death during transient cerebral ischemia
Dai Hai-bin, Miao Xiao-lei, Ji Qing, Duan Man-lin
- Department of Anesthesiology, Nanjing Clinical Hospital of Second Military Medical University (Nanjing General Hospital of Nanjing Military Region), Nanjing 210002, Jiangsu Province, China
-
Revised:2015-03-13Online:2015-04-09Published:2015-04-09 -
Contact:Ji Qing, M.D., Chief physician, Department of Anesthesiology, Nanjing Clinical Hospital of Second Military Medical University (Nanjing General Hospital of Nanjing Military Region), Nanjing 210002, Jiangsu Province, China -
About author:Dai Hai-bin, Studying for doctorate, Department of Anesthesiology, Nanjing Clinical Hospital of Second Military Medical University (Nanjing General Hospital of Nanjing Military Region), Nanjing 210002, Jiangsu Province, China -
Supported by:the National Natural Science Foundation of China, No. 81102514
CLC Number:
Cite this article
Dai Hai-bin, Miao Xiao-lei, Ji Qing, Duan Man-lin. Neuronal mitochondria and apoptosis signaling pathways play an important role in cell death during transient cerebral ischemia[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2015, 19(15): 2425-2430.
share this article
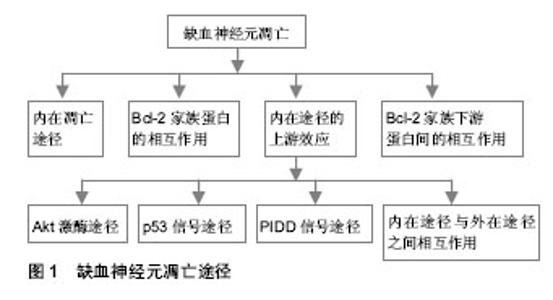
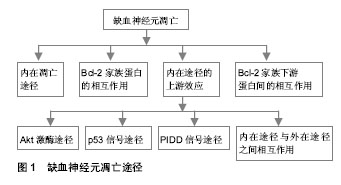
2.1 纳入资料基本概况 按入选标准筛选,并排除研究目的与文章无关及内容重复的研究,最后保留其中50篇归纳总结[1-50]。 2.2 纳入资料的研究结果特征 2.2.1 线粒体活性氧的产生和作用 生理条件下活性氧产生和清除:在生理情况下,线粒体在呼吸过程中可产生超氧阴离子(O2-)和过氧化氢(H2O2)[1],因而,氧代谢过程既是细胞生存所必须的,也是引起细胞损伤的潜在因素。促氧化的酶,例如一氧化氮合酶、环氧合酶、黄嘌呤脱氢酶、黄嘌呤氧化酶、NADPH氧化酶、髓过氧化物酶及单胺氧化酶等都可产生活性氧,其包括O2-,H2O2,一氧化氮和脂质过氧化物等。与此同时,细胞内也存在活性氧清除系统,例如超氧化物歧化酶、谷胱甘肽过氧化物酶和过氧化氢酶等。超氧化物歧化酶分为3种亚型:Cu2+/Zn2+超氧化物歧化酶(超氧化物歧化酶1)、Mn2+超氧化物歧化酶(超氧化物歧化酶2)和细胞外超氧化物歧化酶(超氧化物歧化酶3)。这3种亚型,均能使O2-歧化成H2O2及分子氧。谷胱甘肽过氧化物酶能在谷胱甘肽作用下,使H2O2转变为H2O。过氧化氢酶能催化H2O2转变为水[2]。其他一些小分子,非酶抗氧化物如维生素E和维生素C等也可在自由基清除中发挥一定的作用[7]。细胞的氧化应激,本身是细胞内活性氧的产生超过了其清除能力,从而导致细胞损伤的病理过程。脑缺血性损伤后其细胞内活性氧的产生与清除失衡,产生远大于清除,导致氧化应激相关信号通路的激活和细胞损伤。 活性氧与再灌注损伤:在恢复血液灌流后脑损伤进一步加重,表现为进行性的血管性水肿、出血、梗死面积增加等,称为再灌注损伤。活性氧在再灌注损伤中的作用,早在1980年已有学者阐述[8]。其后,大量的实验证实了活性氧与再灌注损伤的密切关系。缺血脑组织中,细胞质内促氧化酶、线粒体和抗氧化剂的过度消耗,并且补充不足和还原系统的失活都能促进活性氧的生成[2]。过量生成的活性氧引起了多种大分子的损伤,并激活多种途径产生一系列病理效应。 活性氧的检测与定量:检测缺血的脑组织中活性氧含量,一般采用间接的方法,原因是大多数种类的活性氧半衰期都很短。一种方法是通过检测活性氧靶分子的氧化产物的含量,例如脂质过氧化产物、蛋白质及DNA的氧化产物的含量来进行活性氧的定量。另外一种方法,是应用被活性氧氧化后产生发光物质的指示剂,如Hydroethidine (HEt)已用于检测组织及细胞中O2-的存在[9]。HEt被O2-氧化后,可发出红色荧光即“乙啡啶荧光”,用于O2-的追踪研究[9]。但是,近来一项研究显示,其他种类的活性氧也可产生乙啡啶。2-羟基乙胺(2-HE)是HEt的两电子氧化产物,比HEt更适用于O2-的专一性测量[10]。虽然2-羟基乙胺和乙啡啶产生的荧光谱有重叠,并且2-羟基乙胺产生的荧光不能被荧光显微镜分离,但是HEt氧化后产生的红色荧光,仍是检测活性氧,尤其是O2-的重要方法。在脑缺血性损伤后,这种红色荧光亮度上调,显示O2-影响信号转导和造成细胞损伤[11]。应用HEt进行检测的缺陷是,普通荧光显微镜不能提供可靠的定量检测,要辅助高性能的液体色谱/荧光分析进行O2-的定性和定量检测[10]。 超氧化物歧化酶的转基因和基因敲除研究:虽然对活性氧检测及定量技术的发展,使研究活性氧在脑缺血性损伤中的作用更为便利,可是关于活性氧导致缺血性脑损伤的确切机制仍未阐明。最近,转基因和基因敲除技术被用于研究活性氧在缺血性脑损伤中的分子机制。已有大量此方面的研究,应用携带人类超氧化物歧化酶基因或超氧化物歧化酶基因敲除(超氧化物歧化酶+/-或超氧化物歧化酶-/-)的转基因动物,建立了脑缺血性损伤模型。 超氧化物歧化酶1基因有神经保护作用。应用携带人类超氧化物歧化酶1基因的杂合子转基因动物的研究发现,与野生型相比,超氧化物歧化酶1的活性在小鼠增加了3倍[12]、在大鼠增加了4倍[13]。超氧化物歧化酶1转基因动物,前脑缺血后脑梗死面积与野生型相比,减少了35%-50%[14]。短暂性全脑缺血后延迟性神经元死亡,在超氧化物歧化酶1转基因小鼠中减少了50%[15]。对多种信号通路的调控,都能产生神经保护作用, 如激活磷脂酰肌醇-3-激酶(phosphatidyl-inosital-3-kinase,PI3-K)相关途径[16],如抑制丝裂原活化蛋白激酶(mitogen activated protein kinase,MAPK)途径[17]、p53信号途径[11]、核转录因子κB[18]和线粒体依赖的凋亡途径等[19]。而且,在超氧化物歧化酶1基因敲除(超氧化物歧化酶-/-)小鼠,前脑缺血后脑梗死面积及水肿都降低[20],但短暂性全脑缺血后细胞死亡增加[21]。 超氧化物歧化酶2基因同样有重要的神经保护作用。应用携带人类超氧化物歧化酶2基因的杂合子转基因小鼠的研究发现,前脑缺血中脑损伤[22] 及血管内皮细胞死亡程度[23]都降低。在超氧化物歧化酶2基因敲除鼠前脑缺血模型中,脑梗死面积[24]、水肿[23]、O2-的产量[11]、基质金属蛋白酶9的活性[23]、caspase-9的活性[25]以及细胞色素C的释放[26],与野生型相比都升高。而且超氧化物歧化酶2基因敲除小鼠,短暂性前脑缺血后出血性转化增加[23]。 目前,仅有少量的超氧化物歧化酶3转基因或基因敲除鼠,用于脑缺血模型研究,这些研究也显示了超氧化物歧化酶3 有神经保护作用。在前脑缺血后,与野生型相比超氧化物歧化酶3转基因小鼠脑梗死面积降低了28%[27],并且超氧化物歧化酶3 含量增加了5倍[28]。可是超氧化物歧化酶3基因敲除(超氧化物歧化酶3-/-)鼠,前脑缺血后脑梗死面积增加了81%[29]。总之,应用超氧化物歧化酶转基因或基因敲除动物的研究,都显示活性氧在脑缺血性损伤中有重要作用,通过激活多种信号途径参与缺血性损伤。 线粒体一氧化氮合酶:研究发现,在哺乳动物有3种一氧化氮合酶亚型,为神经元型、诱导型和内皮细胞型一氧化氮合酶。可是,目前的研究也发现,线粒体内膜中含有其独有的亚型,即线粒体型一氧化氮合酶 [30]。线粒体型一氧化氮合酶并非由线粒体的基因编码,而由核DNA编码,推测其可能在细胞质中合成后,转运到线粒体中,其具体的转运机制现在并不清楚。线粒体内Ca2+含量升高后,可以激活线粒体型一氧化氮合酶。线粒体型一氧化氮合酶能够持续控制线粒体呼吸,因而被认为是导致再灌注损伤的重要分子之一[30]。在缺血性损伤的鼠中,线粒体型一氧化氮合酶酶活性比正常鼠升高。线粒体型一氧化氮合酶也被认为是引起脑组织老化的指标之一。在高龄老年鼠中,线粒体型一氧化氮合酶的活性与神经行为学表现,及神经存活率呈线性相关[31]。由于线粒体型一氧化氮合酶控制线粒体呼吸,和催化一氧化氮生成,因此,可能与脑卒中后神经细胞的凋亡有关。有关线粒体型一氧化氮合酶在脑卒中中作用的进一步研究,也可能有助于提供更理想的治疗策略。 2.2.2 缺血后神经元的凋亡途径 见图1。"
| [1] Boveris A, Chance B. The mitochondrial generation of hydrogen peroxide. General properties and effect of hyperbaric oxygen. Biochem J. 1973;134(3):707-716. [2] Chan PH. Reactive oxygen radicals in signaling and damage in the ischemic brain. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab. 2001;21(1): 2-14. [3] Allen RG, Tresini M. Oxidative stress and gene regulation. Free Radic Biol Med. 2000;28(3):463-499. [4] Patel RP, McAndrew J, Sellak H, et al. Biological aspects of reactive nitrogen species.Biochim Biophys Acta.1999; 1411 (3): 385-400. [5] Bredt DS. Endogenous nitric oxide synthesis: biological functions and pathophysiology. Free Radic Res. 1999;31(6): 577-596. [6] Fiskum G, Murphy AN, Beal MF. Mitochondria in neurodegeneration: acute ischemia and chronic neurodegenerative diseases. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab. 1999;19(4):351-369. [7] Packer JE, Slater TF, Willson RL. Direct observation of a free radical interaction between vitamin E and vitamin C. Nature. 1979;278(5706):737-738. [8] Yoshida S, Abe K, Busto R, et al. Influence of transient ischemia on lipid-soluble antioxidants, free fatty acids and energy metabolites in rat brain. Brain Res. 1982;245(2):307-316. [9] Bindokas VP, Jordan J, Lee CC, et al. Superoxide production in rat hippocampal neurons: selective imaging with hydroethidine. J Neurosci. 1996;16(4):1324-1336. [10] Zhao H, Joseph J, Fales HM, et al. Detection and characterization of the product of hydroethidine and intracellular superoxide by HPLC and limitations of ?uorescence. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 2005;102(16):5727-5732. [11] Niizuma K, Endo H, Nito C, et al. Potential role of PUMA in delayed death of hippocampal CA1 neurons after transient global cerebral ischemia. Stroke. 2009;40(2):618-625. [12] Chan PH, Epstein CJ, Kinouchi H, et al. SOD-1 transgenic mice as a model for studies of neuroprotection in stroke and brain trauma. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1994;738:93-103. [13] Sugawara T, Noshita N, Lewen A, et al. Overexpression of copper/zinc superoxide dismutase in transgenic rats protects vulnerable neurons against ischemic damage by blocking the mitochondrial pathway of caspase activation. J Neurosci. 2002; 22(1):209-217. [14] Kamii H, Mikawa S, Murakami K, et al. Effects of nitric oxide synthase inhibition on brain infarction in SOD-1-transgenic mice following transient focal cerebral ischemia. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab. 1996;16(6):1153-1157. [15] Chan PH, Kawase M, Murakami K, et al. Overexpression of SOD1 in transgenic rats protects vulnerable neurons against ischemic damage after global cerebral ischemia and reperfusion. J Neurosci. 1998;18(20):8292-8299. [16] Noshita N, Sugawara T, Lewen A, et al. Copper–zinc superoxide dismutase affects Akt activation after transient focal cerebral ischemia in mice. Stroke. 2003;34(6):1513-1518. [17] Nito C, Kamada H, Endo H, et al. Role of the p38 mitogen-activated protein kinase/cytosolic phospholipase A2 signaling pathway in blood–brain barrier disruption after focal cerebral ischemia and reperfusion. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab. 2008;28(10):1686-1696. [18] Song YS, Lee YS, Narasimhan P, et al. Reduced oxidative stress promotes NF-kappaB-mediated neuroprotective gene expression after transient focal cerebral ischemia: lymphocytotrophic cytokines and antiapoptotic factors. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab. 2007;27(4):764-775. [19] Saito A, Hayashi T, Okuno S, et al. Overexpression of copper/zinc superoxide dismutase in transgenic mice protects against neuronal cell death signaling pathway. J Neurosci. 2003;23(5):1710-1718. [20] Kondo T, Reaume AG, Huang TT, et al. Reduction of CuZn-superoxide dismutase activity exacerbates neuronal cell injury and edema formation after transient focal cerebral ischemia. J Neurosci. 1997;17(11):4180-4189. [21] Kawase M, Murakami K, Fujimura M, et al. Exacerbation of delayed cell injury after transient global ischemia in mutant mice with CuZn superoxide dismutase de?ciency. Stroke. 1999;30(9):1962-1968. [22] Keller JN, Kindy MS, Holtsberg FW, et al. Mitochondrial manganese superoxide dismutase prevents neural apoptosis and reduces ischemic brain injury: suppression of peroxynitrite production, lipid peroxidation, and mitochondrial dysfunction. J Neurosci, 1998;18(2):687-697. [23] Maier CM, Hsieh L, Crandall T, et al. Evaluating therapeutic targets for reperfusion-related brain hemorrhage. Ann Neurol. 2006;59(6):929-938. [24] Murakami K, Kondo T, Kawase M, et al. Mitochondrial susceptibility to oxidative stress exacerbates cerebral infarction that follows permanent focal cerebral ischemia in mutant mice with manganese superoxide dismutase de?ciency. J Neurosci. 1998;18(1):205-213. [25] Fujimura M, Morita-Fujimura Y, Kawase M, et al. Manganese superoxide dismutase mediates the early release of mitochondrial cytochrome c and subsequent DNA fragmentation after permanent focal cerebral ischemia in mice. J Neurosci. 1999;19(9):3414-3422. [26] Noshita N, Sugaware T, Fujimura M, et al. Manganese superoxide dismutase affects cytochrome c release and caspase-9 activation after transient focal cerebral ischemia in mice. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab. 2001;21(5):557-567. [27] Sheng H, Bart RD, Oury TD, et al. Mice overexpressing extracellular superoxide dismutase have increased resistance to focal cerebral ischemia. Neuroscience, 1999;88(1):185-191. [28] Oury TD, Ho YS, Piantadosi CA, et al. Extracellular superoxide dismutase, nitric oxide, and central nervous system O2 toxicity. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 1992;89(20):9715-9719. [29] Sheng H, Brady TC, Pearlstein RD, et al. Extracellular superoxide dismutase de?ciency worsens outcome from focal cerebral ischemia in the mouse. Neurosci Lett. 1999;267(1):13-16. [30] Finocchietto PV, Franco MC, Holod S, et al. Mitochondrial nitric oxide synthase: a master piece of metabolic adaptation, cell growth, transformation, and death. Exp Biol Med. 2009; 234(9):1020-1028. [31] Boveris A, Navarro A. Brain mitochondrial dysfunction in aging. IUBMB Life. 2008;60(5):308-314. [32] Kim H, Rafiuddin-Shah M, Tu HC, et al. Hierarchical regulation of mitochondrion-dependent apoptosis by BCL-2 subfamilies. Nat Cell Biol. 2006;8(12):1348-1358. [33] Inta I, Paxian S, Maegele I, et al. Bim and Noxa are candidates to mediate the deleterious effect of the NF-kappa B subunit RelA in cerebral ischemia. J Neurosci. 2006;26(50): 12896-12903. [34] Gillardon F, Lenz C, Waschke KF, et al. Altered expression of Bcl-2, Bcl-X, Bax, and c-Fos colocalizes with DNA fragmentation and ischemic cell damage following middle cerebral artery occlusion in rats. Brain Res Mol Brain Res. 1996;40(2):254-260. [35] Krajewski S, Mai JK, Krajewska M, et al. Upregulation of Bax protein levels in neurons following cerebral ischemia. J Neurosci. 1995;15(10):6364-6376. [36] Okuno S, Saito A, Hayashi T, et al. The c-Jun N-terminal protein kinase signaling pathway mediates Bax activation and subsequent neuronal apoptosis through interaction with Bim after transient focal cerebral ischemia. J Neurosci. 2004; 24(36): 7879-7887. [37] Yoshida H, Kong YY, Yoshida R, et al. Apaf1 is required for mitochondrial pathways of apoptosis and brain development. Cell. 1998;94(6):739-750. [38] Chaitanya GV, Babu PP. Differential PARP cleavage: an indication of heterogeneous forms of cell death and involvement of multiple proteases in the infarct of focal cerebral ischemia in rat. Cell Mol Neurobiol. 2009;29(4):563-573. [39] Ferrer I, Planas AM. Signaling of cell death and cell survival following focal cerebral ischemia: life and death struggle in the penumbra. J Neuropathol Exp Neurol. 2003;62(4):329-339. [40] Culmsee C, Zhu C, Landshamer S, et al. Apoptosis-inducing factor triggered by poly(ADP-ribose) polymerase and Bid mediates neuronal cell death after oxygen-glucose deprivation and focal cerebral ischemia. J Neurosci. 2005; 25(44):10262-10272. [41] Lee BI, Lee DJ, Cho KJ, et al. Early nuclear translocation of endonuclease G and subsequent DNA fragmentation after transient focal cerebral ischemia in mice. Neurosci Lett. 2005; 386(1):23-27. [42] Kamada H, Nito C, Endo H, et al. Bad as a converging signaling molecule between survival PI3-K/Akt and death JNK in neurons after transient focal cerebral ischemia in rats. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab. 2007;27(3):521-533. [43] Cardone MH, Roy N, Stennicke HR, et al. Regulation of cell death protease caspase-9 by phosphorylation. Science. 1998; 282(5392):1318-1321. [44] Endo H, Kamada H, Nito C, et al. Mitochondrial translocation of p53 mediates release of cytochrome c and hippocampal CA1 neuronal death after transient global cerebral ischemia in rats. J Neurosci. 2006;26(30):7974-7983. [45] Tinel A, Tschopp J. The PIDDosome, a protein complex implicated in activation of caspase-2 in response to genotoxic stress. Science. 2004.304(5672):843-846. [46] Niizuma K, Endo H, Nito C, et al. The PIDDosome mediates delayed death of hippocampal CA1 neurons after transient global cerebral ischemia in rats. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 2008.105(42):16368-16373. [47] Robertson JD, Gogvadze V, Kropotov A, et al. Processed caspase-2 can induce mitochondria-mediated apoptosis independently of its enzymatic activity. EMBO Rep. 2004; 5(6):643-648. [48] Tinel A, Janssens S, Lippens S, et al. Autoproteolysis of PIDD marks the bifurcation between pro-death caspase-2 and pro-survival NF-kappaB pathway. EMBO J. 2007;26(1):197-208. [49] Rosenbaum DM, Gupta G, D’Amore J, et al. Fas (CD95/APO-1) plays a role in the pathophysiology of focal cerebral ischemia. J Neurosci Res. 2000;61(6):686-692. [50] Jin K, Graham SH, Mao X, et al. (CD95) may mediate delayed cell death in hippocampal CA1 sector after global cerebral ischemia. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab. 2001;21(12): 1411-1421. |
| [1] | Zhang Tongtong, Wang Zhonghua, Wen Jie, Song Yuxin, Liu Lin. Application of three-dimensional printing model in surgical resection and reconstruction of cervical tumor [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(9): 1335-1339. |
| [2] | Geng Qiudong, Ge Haiya, Wang Heming, Li Nan. Role and mechanism of Guilu Erxianjiao in treatment of osteoarthritis based on network pharmacology [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(8): 1229-1236. |
| [3] | Pei Lili, Sun Guicai, Wang Di. Salvianolic acid B inhibits oxidative damage of bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells and promotes differentiation into cardiomyocytes [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(7): 1032-1036. |
| [4] | Zeng Yanhua, Hao Yanlei. In vitro culture and purification of Schwann cells: a systematic review [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(7): 1135-1141. |
| [5] | Li Shibin, Lai Yu, Zhou Yi, Liao Jianzhao, Zhang Xiaoyun, Zhang Xuan. Pathogenesis of hormonal osteonecrosis of the femoral head and the target effect of related signaling pathways [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(6): 935-941. |
| [6] | Xu Yinqin, Shi Hongmei, Wang Guangyi. Effects of Tongbi prescription hot compress combined with acupuncture on mRNA expressions of apoptosis-related genes,Caspase-3 and Bcl-2, in degenerative intervertebral discs [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(5): 713-718. |
| [7] | Zhang Wenwen, Jin Songfeng, Zhao Guoliang, Gong Lihong. Mechanism by which Wenban Decoction reduces homocysteine-induced apoptosis of myocardial microvascular endothelial cells in rats [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(5): 723-728. |
| [8] | Liu Qing, Wan Bijiang. Effect of acupotomy therapy on the expression of Bcl-2/Bax in synovial tissue of collagen-induced arthritis rats [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(5): 729-734. |
| [9] | Xie Chongxin, Zhang Lei. Comparison of knee degeneration after anterior cruciate ligament reconstruction with or without remnant preservation [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(5): 735-740. |
| [10] | Xu Dongzi, Zhang Ting, Ouyang Zhaolian. The global competitive situation of cardiac tissue engineering based on patent analysis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(5): 807-812. |
| [11] | Wu Zijian, Hu Zhaoduan, Xie Youqiong, Wang Feng, Li Jia, Li Bocun, Cai Guowei, Peng Rui. Three-dimensional printing technology and bone tissue engineering research: literature metrology and visual analysis of research hotspots [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(4): 564-569. |
| [12] | Chang Wenliao, Zhao Jie, Sun Xiaoliang, Wang Kun, Wu Guofeng, Zhou Jian, Li Shuxiang, Sun Han. Material selection, theoretical design and biomimetic function of artificial periosteum [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(4): 600-606. |
| [13] | Liu Fei, Cui Yutao, Liu He. Advantages and problems of local antibiotic delivery system in the treatment of osteomyelitis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(4): 614-620. |
| [14] | Li Xiaozhuang, Duan Hao, Wang Weizhou, Tang Zhihong, Wang Yanghao, He Fei. Application of bone tissue engineering materials in the treatment of bone defect diseases in vivo [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(4): 626-631. |
| [15] | Zhang Zhenkun, Li Zhe, Li Ya, Wang Yingying, Wang Yaping, Zhou Xinkui, Ma Shanshan, Guan Fangxia. Application of alginate based hydrogels/dressings in wound healing: sustained, dynamic and sequential release [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(4): 638-643. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||