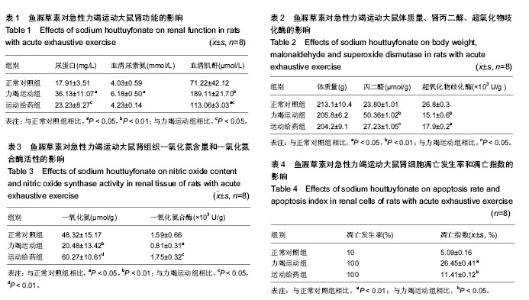
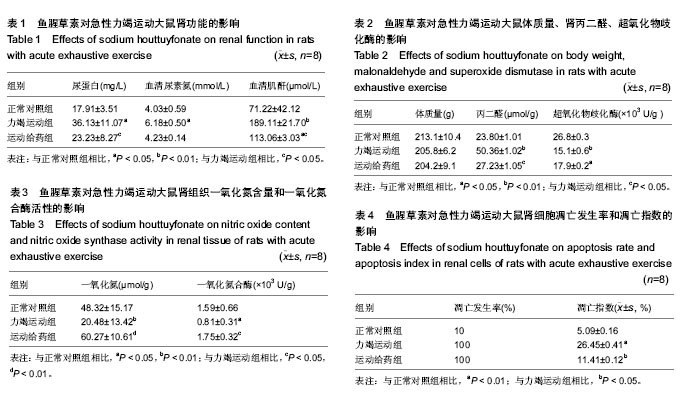
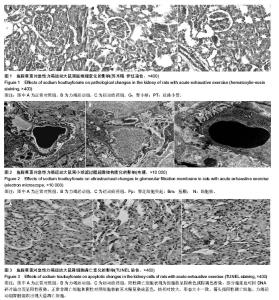
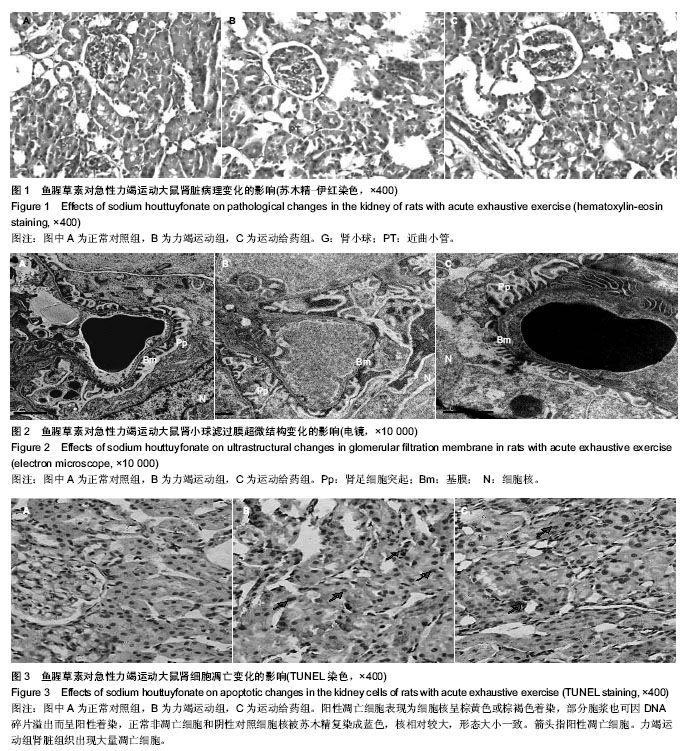
| [1] GanongWF. Review of Medical Physiology. Lange Medical publication.1995.
[2] 洪佳璇,汪柏尧,高雅文,等.鲜鱼腥草提取物对脂多糖所致小鼠肺部炎症的影响[J].中国现代应用药学杂志,2008,25(5):376-378.
[3] 王芳,陆付耳,徐丽君,等.鱼腥草对糖尿病大鼠肾脏组织中BMP -7和TGFβ1 表达的影响[J].天津中医药,2006,23(4):334-337.
[4] 王海颖,修彦凤.鱼腥草改善糖尿病模型大鼠尿白蛋白与胰岛素抵抗的实验研究[J].中药新药与临床药理,2008,19(1):12-14.
[5] Kaushal GP, Basnakian AG, Shah SV. Apoptotic pathways in ischemic acute renal failure. Kidney Int. 2004;66(2):500-506.
[6] Bonegio R, Lieberthal W. Role of apoptosis in the pathogenesis of acute renal failure. Curr Opin Nephrol Hypertens. 2002;11(3):301-308.
[7] Wijsman JH, Jonker RR, Keijzer R, et al. A new method to detect apoptosis in paraffin sections: in situ end-labeling of fragmented DNA. J Histochem Cytochem. 1993;41(1):7-12.
[8] 林喜秀,瞿树林,周桔,等.低氧训练对大鼠心、肝、肾、海马组织细胞凋亡的影响及其机制研究[J].中国运动医学杂志,2012(2): 47-57.
[9] 林喜秀,瞿树林,陈嘉勤.低氧、运动对肾脏组织细胞凋亡及凋亡相关因子HIF-1a、Bax、Bcl-2表达的影响[J].中国运动医学杂志,2008,9(27):571-574.
[10] 林喜秀.低氧训练对大鼠肾组织细胞凋亡相关因子的影响[D].长沙:湖南师范大学,2008.
[11] 林喜秀.力竭运动致大鼠慢性肾损伤机制及促红细胞生成素干预研究[D].长沙:湖南师范大学,2011.
[12] 林喜秀,周桔,罗自强,等.低氧训练与低氧大鼠心肌细胞凋亡及凋亡因子的表达[J].中国组织工程研究杂志,2013,17(11):1951- 1958.
[13] Lin X, Qu S, Hu M, et al. Protective effect of erythropoietin on renal injury induced by acute exhaustive exercise in the rat. Int J Sports Med. 2010;31(12):847-853.
[14] Lin X, Jiang C, Luo Z, et al. Protective effect of erythropoietin on renal injury induced in rats by four weeks of exhaustive exercise. BMC Nephrol. 2013;14:130.
[15] Liu Y. Cellular and molecular mechanisms of renal fibrosis. Nat Rev Nephrol. 2011;7(12):684-696.
[16] Komarievtseva IO, Orlova OA, Blahodarenko IeA. Level of nitric oxide in the kidneys during apoptosis activation. Ukr Biokhim Zh. 2002;74(4):116-119. |