Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research ›› 2014, Vol. 18 ›› Issue (12): 1944-1950.doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-4344.2014.12.023
Previous Articles Next Articles
Application of intelligent hydrogel in the tissue engineering
Zhang Ding-wen1, Liu Yan-fei2, Qi Peng1, Liu Jian-guo1, 3
- 1School of Stomatology, Zunyi Medical University, Zunyi 563000, Guizhou Province, China
2The Key Laboratory of Cell Engineering in Guizhou Province, Zunyi 563000, Guizhou Province, China
3The Special Key Laboratory of Oral Diseases Research, Higher Education Institution in Guizhou Province, Zunyi 563000, Guizhou Province, China
-
Revised:2014-02-11Online:2014-03-19Published:2014-03-19 -
Contact:Liu Jian-guo, Professor, School of Stomatology, Zunyi Medical University, Zunyi 563000, Guizhou Province, China; the Special Key Laboratory of Oral Diseases Research, Higher Education Institution in Guizhou Province, Zunyi 563000, Guizhou Province, China -
About author:Zhang Ding-wen, Studying for master’s degree, School of Stomatology, Zunyi Medical University, Zunyi 563000, Guizhou Province, China -
Supported by:the Scientific Talent Cultivation of Guizhou Province, No. (2005)0509; Science and Technology Innovation Team Fund of Guizhou Province, No. (2013) 4026; the Key Discipline Construction Project of Guizhou Province, No. SZXK-201207-04; the Excellent Research Team Cultivation Project of Zunyi Medical University, No. [2012]12
CLC Number:
Cite this article
Zhang Ding-wen, Liu Yan-fei, Qi Peng, Liu Jian-guo. Application of intelligent hydrogel in the tissue engineering[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2014, 18(12): 1944-1950.
share this article
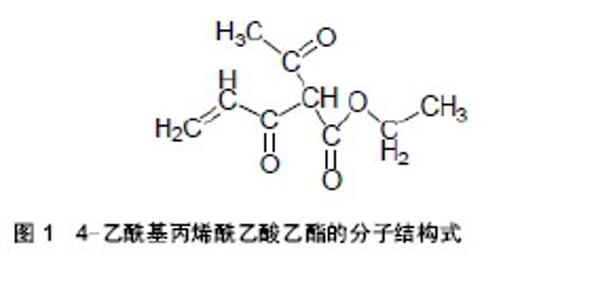
2.1 智能水凝胶的分类 2.1.1 温度敏感性水凝胶 温度敏感性水凝胶是指随着环境温度变化引起电阻变化(温阻性)的一类水凝胶。温敏性水凝胶研发的可注射水凝胶在包被细胞、药物释放、组织工程生物学等方面的应用相当广泛[7-9]。林松柏等[10]用4-乙酰基丙烯酰乙酸乙酯(其分子结构式见图1)、丙烯酸及聚乙烯醇为原料,通过自由基溶液聚合法,加入聚乙烯醇制备了PVA-P(AAEA-co-AA)半穿网络型水凝胶(图2),聚乙烯醇与P(AAEA-co-AA)形成的半穿网络结构能有效提高凝胶的抗压缩强度,其最大抗压缩强度可达8.4 MPa,对凝胶的温度敏感性研究发现:当外界温度低于体积相转变温度时,凝胶能保持溶胀状态;而当温度高于体积相转变温度(半穿网络型水凝胶的体积相转变温度一般在54.0-57.8 ℃)时,凝胶的平衡溶胀度迅速下降,表现为温度敏感性。"
Ho等[11]以N-异丙基丙烯酰胺接枝聚合反应制备了两种温敏性的可注入型水凝胶,所得到理化性质表明,其在34 ℃水溶液中时具有低临界溶液温度。Pochan等[12]设计了一种双亲性的多肽(VKVKVKTKVDPPTKVKVKVKV- NH2),当升高温度时,在疏水作用和氢键的推动下,赖氨酸残基形成亲水面,缬氨酸残基形成疏水面,从而折叠形成双层夹心结构,最终自助装成纳米纤维凝胶;当低温的时候,赖氨酸静电排斥使得自组装的凝胶溶解,此体系是一种典型的温度敏感热可逆水凝胶。 2.1.2 pH敏感性水凝胶 1980年,Tanaka等[13]首次报道陈化后的丙烯酰胺凝胶,因具有pH值敏感性而引起了人们极大的兴趣,随后有关pH值敏感性水凝胶的报道越来越多。pH敏感性实验表明,凝胶的溶胀率在pH=1.0的介质中较大,在pH=4.0的介质中次之,在中性或pH=9.0的碱性介质中较低,表明凝胶具有明显的pH敏感性。王芳平等[14]用自由基交联共聚法合成了具有pH敏感性的聚丙烯酸-co-甲基丙烯酸辛基酚聚氧乙烯醚酯水凝胶(图3),发现在不同pH缓冲溶液中的溶胀性、溶胀动力学和退溶胀动力学单体配比不相同。通过浸泡法在水凝胶中载入L-抗坏血酸,初步研究了模拟胃肠液中凝胶对L-抗坏血酸的释放行为,结果表明凝胶兼具快速的溶胀和退溶胀速率,良好的pH敏感性等特征。 另有学者采用溶液共聚法合成了聚(N-异丙基丙烯酰胺-co-衣康酸)pH敏感性阴离子型水凝胶。图4为聚(N-异丙基丙烯酰胺-co-衣康酸)凝胶的红外光谱图。通过正交设计实验发现pH对凝胶溶胀率的影响十分显著,当pH在1-13之间变化时溶胀率可快速地从34 g/g变化到760 g/g[15]。郑施施等[16]研制一种新型羧甲基壳聚糖基pH敏感性水凝胶(图5),发现其具有明显的孔洞结构和良好的pH响应性能,在中性磷酸盐缓冲溶液(pH=7.4)中吸水率显著大于在酸性溶液(pH=2)中的吸水率。载有磺胺嘧 啶钠的羧甲基壳聚糖水凝胶在中性磷酸盐缓冲溶液(pH=7.4)中的4 h药物累计释放率可达到95%,而在酸性溶液(pH=2)中的4 h药物累计释放率却只有50%,在口服药物传输体系中有一定的应用前景。Park等[17]制备口服可控的壳聚糖交联γ-PGA合成水凝胶,其吸水率在pH=3-6之间有显著的变化,通过可溶于水的四唑实验证明:水凝胶具有良好生物相容性,并且在结肠中药物扩散速率主要依赖于pH,具有显著pH敏感性。 2.1.3 光敏感性水凝胶 光敏感性水凝胶可分为可见光敏感性水凝胶与紫外光敏感性水凝胶两种,含有光敏发色团的PNIAAm水凝胶具有可见光敏感性,另外紫外光敏感性水凝胶可以通过含有二(4-二甲氨基)苯基甲烷氰化物的聚合物网状结构制得。张海璇[18]利用曲酸二棕榈酸酯为模型药物、偶氮 苯-Ⅳ-琥珀酰壳聚糖聚合物和偶氮苯、壳聚糖聚合物为主要光敏感性智能载体,研究曲酸二棕榈酸酯光敏感性水凝胶智能给药系统,采用离子胶凝化法、电镜扫描法观察优选凝胶小球的表面,形态结构表征及凝胶小球的包封率、载药量、溶胀度、光敏感性等,发现在紫外光存在的条件下,该凝胶小球吸收一定波长的紫外光后释放药物,从而抑制酪氨酸酶的活性,阻断皮肤黑色素的形成,达到防治紫外线对皮肤损伤的目的。Yamamoto等[19]报道了一种光交联的聚(L-赖氨酸)多肽,此多肽的部分L-赖氨酸残基中光敏基团可以发生光交联反应获得凝胶。他们进一步报道了含有光敏基团的聚(L-鸟氨酸)多肽通过光交联反应制备凝胶[20]。"
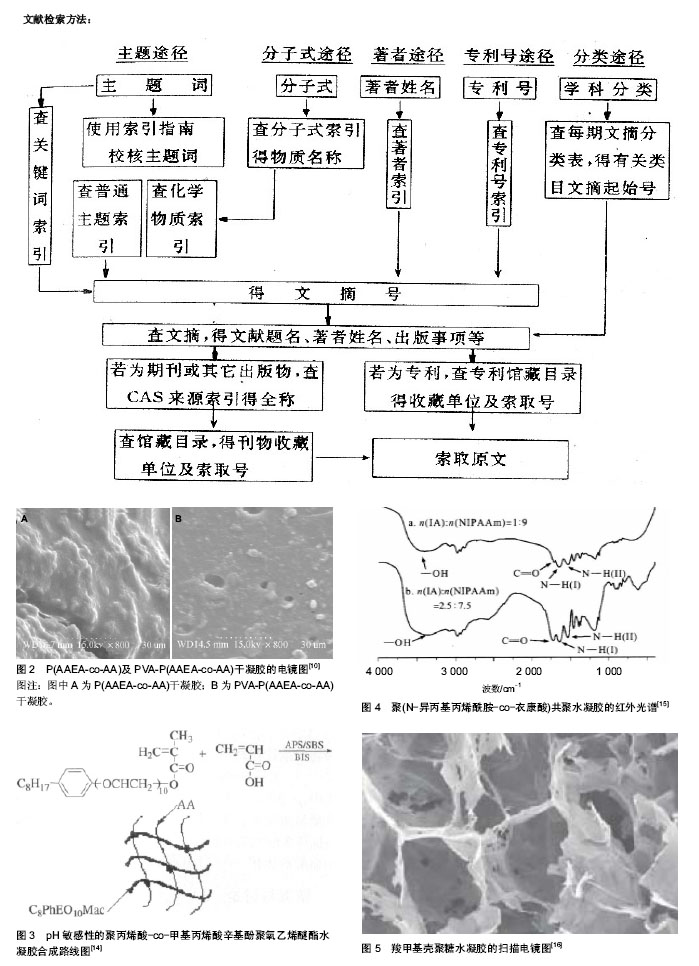
2.1.4 磁敏感性水凝胶 磁敏感性水凝胶是指具有磁响应性的一类环境敏感性水凝胶。张书第等[21]采用循环冷 冻-解冻方法制备了聚乙烯醇/Fe2O3磁敏感性水凝胶,其干凝胶的扫描电镜照片见图6,观察水凝胶各个方面性能发现:当Fe2O3含量在1%(ω)时水凝胶的力学性能相对较好;当水凝胶的磁场强度在30 000 e时表现出来的顺磁性说明其具有较好的磁敏感性。Satarkar等[22]用外光辐照引发聚合制备了PNIPAAm/Fe3O4磁敏感性水凝胶。他们将一定浓度的NIPAAm溶液与交联剂二甲基丙烯酸聚乙二醇(400)酯(PEG400DMA)、Fe3O4(粒径为20-30 nm) 按照一定比例混合,加入光引发剂安息香双甲醚,用紫外光辐照使其凝胶化。产物在去离子水中浸泡,经多次洗涤除去杂质,得到具有温度/磁场双重敏感性的水凝胶。通过改变磁性粒子的含量可以对这种磁性超分子水凝胶的力学性能进行调控。Paulino等[23]以交联壳聚糖/共聚合反应和丙烯酸在N,N’-亚甲基双丙烯酰胺下与柠檬酸盐包裹的Fe3O4进行交联,通过X射线衍射证实水凝胶的溶胀率与离子强度相关联。"

2.1.5 温度/pH双重敏感性水凝胶 同时对两种或两种以上外界刺激产生反应的智能凝胶已成为高分子缓释载体的发展方向,因pH和温度是生理生化系统中的两个重要因素,研究具有pH和温度双重敏感的水凝胶作为新型高分子材料已备受关注。Shim等[24]通过添加pH/温度敏感部分嵌段共聚物制备了一种新型的pH/温度双重敏感水凝胶,pH值在7.4-8.0变化。该溶液在pH=7.4(人体)、37 ℃形成凝胶时,可作为疏水性药物和蛋白注射的载体,并且可用来作为一个注射输送系统模板技术。陆遥遥等[25]以N-异丙基丙烯酰胺与海藻酸钠为原料,运用水溶液聚合法研制了具有温度和pH值双重敏感性的海藻酸钠/聚(N-异丙基丙烯酰胺)水凝胶。考察了在不同温度和pH值条件下,反应温度、单体浓度、交联剂用量等对该凝胶溶胀度的影响,实验表明凝胶具有良好的温度和pH敏感性能。Sun等[26]将N-异丙基丙烯酰胺和聚乙二醇(相对分子质量2 000)共混制备了具有温度和pH性双重敏感性的水凝胶薄膜,差示扫描量热法研究表明,物理共混膜表现出较低的临界溶液温度及pH值敏感性。余娟等[27]以甲基丙烯酸-2-二甲基胺基乙酯为单体,N,N’-亚甲基双丙烯酰胺为交联剂,过硫酸钾为引发剂,在35 ℃(接近人体温度)条件下,采用自由基水溶液聚合合成了聚甲基丙烯酸-2-二甲基胺基乙酯均聚物水凝胶,所合成的水凝胶具有温度和pH双重敏感性(图7)。Khurma等[28]用壳聚糖水凝胶和聚乙二醇为原料制备pH和温度双重敏感水凝胶,观察温度25,37,45 ℃时在去离子水中水凝胶的溶胀行为,利用差示扫描量热法测定了37 ℃下水凝胶在去离子水中的状态,发现其溶胀率随着凝胶中聚乙二醇浓度的增加而增加。"

| [1] Luangphakdy V,Walker E,Shinohara K,et al.Evaluation of osteoconductive scaffolds in the canine femoral multi-defect model.Tissue Eng Part A.2013;19(5-6):634. [2] Kreja L,Liedert A,Schlenker H,et al.Effects of mechanical strainon human mesenchymal stem cells and ligament fibroblasts in a texturedpoly(L-lactide) scaffold for ligament tissue engineering.J Mater Sci Mater Med.2012; 23(10): 2575. [3] Han Q,Jin W,Xiao Z,et al.The promotion of neural regeneration in an extreme rat spinal cord injury model using a collagen scaffold containing a collagen binding neuroprotective protein and an EGFR neutralizing antibody. Biomaterials.2013;31(35):9212. [4] Zhao Q,Wang S,Tian J,et al.Combination of bone marrow concentrate and PGA scaffolds enhance bone marrow stimulation in rabbit articular cartilage repair.J Mater Sci Mater Med.2013;24(3):793. [5] Hong Y,Gong Y,Gao C,et al.Collagen-coated polylactide microcarriers/chitosan hydrogel composite: injectable scaffold for cartilageregeneration.J Biomed Mater Res A. 2008; 85(3): 628. [6] 韩倩倩,何晨光,赵莉,等.组织工程支架材料聚乙醇酸的体外细胞贴壁性和降解性能研究[J].药物分析杂志,2013,33(8): 1331-1335. [7] Ho E,Lowman A,Marcolongo M.Synthesis and characterization of an injectable hydrogel with tunable mechanical properties for soft tissue repair. Biomacromolecules. 2006;7(11):3223-3228. [8] Shome A,Debnath S,Das PK.Head group modulated pH-responsive hydrogel of amino acid-based amphiphiles: entrapment and release of cytochrome c and vitamin B12. Langmuir.2008;24(8):4280-4288. [9] Zhang XZ, Yang YY, Wang FJ, et al.Thermosensitive Poly(N-isopropylacrylamide-co-acrylic acid) hydrogels with expanded network structures and improved oscillating swelling-deswelling operties.Langmuir. 2002;18(6): 2013-2018. [10] 林松柏,丛辉,柯爱茹,等.PVA增强P(AAEA-co-AA)温度敏感性水凝胶的合成及其性能研究[J].化学学,2011,69(22): 2710-2716. [11] Ho J,Jin W,Hyung D,et al.Thermosensitive Chitosans as Novel Injectable Biomaterials. Macromol Symp. 2005;224(1): 275-286. [12] Pochan DJ,Schneider JP,Kretsinger J,et al.Thermally reversible hydrogels via intramolecular folding and consequent self-assembly of a denovo designed peptide. JACS.2003;125(39):11802-11803. [13] Tanaka T,Fillmore D,Sun S,et a1.Phasetransitions inionicgels.Phys Rev Lett.1980;45(20):1636-l639. [14] 王芳平,牟琥珀,张珺瑛,等.pH响应性P(AA-co-C8PhEO10Mac) 水凝胶的制备及其对L-抗坏血酸的控释性能[J].精细化工,2013, 30(2):134-138. [15] 陈旭日,陈学刚.新型P(NIPAAm-co-IA)pH敏感智能水凝胶的合成与性能研究[J].化学推进剂与高分子材料,2011,9(2):253. [16] 郑施施,王增寿.pH敏感型羧甲基壳聚糖水凝胶的制备及体外释药考察[J].中国药师,2013,16(4):535-536. [17] Park BG,Kang HS,Lee W,et al.Reinforcement of pH-responsive γ-poly(glutamic acid)/chitosan hydrogel for orally administrable colon-targeted drug delivery.J Appl Polym Sci.2013;127(1):832-836. [18] 张海璇.曲酸二棕榈酸酯光敏感性水凝胶智能给药系统的研究[D].兰州:兰州大学硕士学位论文,2009. [19] Yamamoto H,Kitsuki T,Nishida A,et al.Photoresponsive peptide and polypeptide systems. 13. Photoinduced cross-linked gel and biodegradation properties of copoly(l-lysine) containing ε-7-Coumaryloxyacetyl-L-lysine Residues. Macromolecules.1999; 32(4):1055-1061. [20] Ohkawa K,Shoumura K,Yamada M,et al.Photoresponsive Peptide and Polypeptide Systems, 14. Biodegradation of Photocrosslinkable Copolypeptide Hydrogels Containing L-Ornithine and δ-7-Coumaryloxyacetyl-L-ornithine Residues. Macromol Biosci.2001;1(4):149-156. [21] 张书第,翟玉春,张振芳.PVA/Fe2O3磁敏感性水凝胶的制备及性能[J].过程工程学报,2010,10(2):405-408. [22] Starkar NS,Hilt JZ.Magnetic hydrogel nanocomposites for remote controlled pulsatile drug release.J Control Release. 2008;130(3):246-251. [23] Paulino AT,Guilhermea MR,de Almeida EAMS,et al. One- potsynthesis of achitosanbased hydrogel as a potential device for magnetic biomaterial.J Magnet Magnet Mater. 2009;321(17):2636-2642. [24] Shim WS,Yoo JS,Lee DS,et al.Novel injectable pH and temperature sensitive block copolymer hydrogel.Biomacromolecules.2005;6(6):2930−2934.. [25] 陆遥遥,吴季怀,林建明,等.反应条件对海藻酸钠/聚N-异丙基丙烯酰胺水凝胶温度及pH敏感性能的影响研究[J].材料导报,2010, 24(5):99-104. [26] Sun GM,Zhang XZ,Chu CC.Formulation and characterization of chitosan-based hydrogel films having both temperature and pH sensitivity.J Mater Sci Mater Med. 2007;18(8):1563-1577. [27] 余娟,刘守信,房喻,等.pH/温度双重敏感的PDMAEMA水凝胶的力学性质[J].陕西师范大学学报:自然科学版, 2010,38(3): 50-55. [28] Khurma JR,Nand AV.Temperature and pH Sensitive Hydrogels Composed of Chitosan and Poly ( ethylene glycol).Polymer Bulletin.2008;59(6):805-812. [29] Canter HI,Vargel I,Korkusuz P,et al.Effect of use of slow release of bone morphogenetic protein-2 and transforming growth factor-Beta-2 in a chitosan gel matrix on cranial bone graft survival in experimental cranial critical size defect model.Ann Plastic Surg.2010;64(3):342-350. [30] Gulati K,Ramakrishnan S,Aw MS,et al.Biocompatible polymer coating of titania nanotube arrays for improved drug elution and osteoblast adhesion.Acta Biomaterialia. 2011;8(1): 449-456. [31] Coimbra P,Ferreira P,de Sousa HC,et al. Preparation and chemical and biological characterization of a pectin/chitosan polyelectrolyte complex scaffold for possible bone tissue engineering applications. Int J Biol Macromol. 2011;48(1): 112-118. [32] Anderson JM,Vines JB,Patterson JL,et al.Osteogenic differentiation of human mesenchymal stem cells synergistically enhanced by biomimetic peptide amphiphiles combined with conditioned medium.Acta Biomater. 2010; 7(2):675-682. [33] Miller RE,Grodzinsky AJ,Vanderploeg EJ,et al.Effect of self-assembling peptide,chondrogenic factors and bone marrow-derived stromal cells on osteochondral repair. Osteoarthritis Cartilage.2010;18(12):1608-1619. [34] 吴敏,宋鸿,陆永志,等.自组装短肽用于SD大鼠头顶骨损伤的修复[J].四川动物, 2010,29(3):386-388. [35] 盛宇,陆永志,孙丽娟,等.新型纳米材料及与前成骨细胞联合培养的实验研究[J].北京生物医学工程,2009,28(1):55-60. [36] Kim HK,Shim WS,Kim SE,et al.Injectable in situ- forming pH/ thermo- sensitive Hydrogel for bone Tissue Engineering. Tissue Eng Part A.2009;15(4):923-33. [37] Koh MY,Ohtsuki C,Miyazaki T.Modification of polyglutamic acid with silanol groups and calcium salts to induce calcification in a simulated body fluid.J Biomater Appl. 2011; 25(6):581-594. [38] Tan H,Chu CR,Payne KA,et al.Injectable in situ forming biodegradable chitosan-hyaluronic acid based hydrogels for cartilage tissue engineering.Biomaterials. 2009;30(13): 2499-2506. [39] 郝彤,刘暾,吕双红,等.采用温敏性壳聚糖水凝胶体外构建组织工程化软骨的实验研究[J].解放军医学杂志,2007,32(5):500-502. [40] Cho JH.Chondrogenic differentiation of human mesenchymal stem cells using a thermosensitive poly(N-isopropylacrylamide) and water-soluble chitosan copolymer.Biomaterials.2004;25(26):5743-5751. [41] Chao PH,Yodmuang S,Wang X,et al. Silk of Hydrogel frcartilage Tissue Eng ineering.J Biomed Mater Res B Appl Biomater.2010;95(1):84-90. [42] Tysseling-Mattiace VM,Sahni V,Niece KL,et al. Self-assembling nanofibers inhibit glial scar formation and promote axon elongation after spinal cord injury.J Neurosci. 2008;28(14):3831-3823. [43] Sun J,Zheng Q,Wu Y,et al.Culture of nucleus pulposus cells from intervertebral disc on self-assembling KLD-12 peptide hydrogel scaffold. Mater Sci Eng C.2010;30(7):975-980. |
| [1] | Pu Rui, Chen Ziyang, Yuan Lingyan. Characteristics and effects of exosomes from different cell sources in cardioprotection [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(在线): 1-. |
| [2] | Zhang Tongtong, Wang Zhonghua, Wen Jie, Song Yuxin, Liu Lin. Application of three-dimensional printing model in surgical resection and reconstruction of cervical tumor [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(9): 1335-1339. |
| [3] | Zhang Chao, Lü Xin. Heterotopic ossification after acetabular fracture fixation: risk factors, prevention and treatment progress [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(9): 1434-1439. |
| [4] | Zhou Jihui, Li Xinzhi, Zhou You, Huang Wei, Chen Wenyao. Multiple problems in the selection of implants for patellar fracture [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(9): 1440-1445. |
| [5] | Wang Debin, Bi Zhenggang. Related problems in anatomy mechanics, injury characteristics, fixed repair and three-dimensional technology application for olecranon fracture-dislocations [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(9): 1446-1451. |
| [6] | Ji Zhixiang, Lan Changgong. Polymorphism of urate transporter in gout and its correlation with gout treatment [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(8): 1290-1298. |
| [7] | Yuan Mei, Zhang Xinxin, Guo Yisha, Bi Xia. Diagnostic potential of circulating microRNA in vascular cognitive impairment [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(8): 1299-1304. |
| [8] | Wang Xianyao, Guan Yalin, Liu Zhongshan. Strategies for improving the therapeutic efficacy of mesenchymal stem cells in the treatment of nonhealing wounds [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(7): 1081-1087. |
| [9] | Wan Ran, Shi Xu, Liu Jingsong, Wang Yansong. Research progress in the treatment of spinal cord injury with mesenchymal stem cell secretome [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(7): 1088-1095. |
| [10] | Liao Chengcheng, An Jiaxing, Tan Zhangxue, Wang Qian, Liu Jianguo. Therapeutic target and application prospects of oral squamous cell carcinoma stem cells [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(7): 1096-1103. |
| [11] | Zhao Min, Feng Liuxiang, Chen Yao, Gu Xia, Wang Pingyi, Li Yimei, Li Wenhua. Exosomes as a disease marker under hypoxic conditions [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(7): 1104-1108. |
| [12] | Xie Wenjia, Xia Tianjiao, Zhou Qingyun, Liu Yujia, Gu Xiaoping. Role of microglia-mediated neuronal injury in neurodegenerative diseases [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(7): 1109-1115. |
| [13] | Li Shanshan, Guo Xiaoxiao, You Ran, Yang Xiufen, Zhao Lu, Chen Xi, Wang Yanling. Photoreceptor cell replacement therapy for retinal degeneration diseases [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(7): 1116-1121. |
| [14] | Jiao Hui, Zhang Yining, Song Yuqing, Lin Yu, Wang Xiuli. Advances in research and application of breast cancer organoids [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(7): 1122-1128. |
| [15] | Wang Shiqi, Zhang Jinsheng. Effects of Chinese medicine on proliferation, differentiation and aging of bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells regulating ischemia-hypoxia microenvironment [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(7): 1129-1134. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||