Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research ›› 2026, Vol. 30 ›› Issue (7): 1850-1857.doi: 10.12307/2026.527
Previous Articles Next Articles
Role and mechanism of stem cells from human exfoliated deciduous teeth in tissue regeneration and disease treatment
Fan Yongjing1, Jin Wulong1, Bai Haoyu2, Ma Ping1, Wang Shu1
- 1Department of Stomatology, Affiliated Hospital of Inner Mongolia Medical University, Hohhot 010010, Inner Mongolia Autonomous Region, China; 2Inner Mongolia Medical University, Hohhot 010050, Inner Mongolia Autonomous Region, China
-
Received:2024-12-06Revised:2025-03-17Accepted:2025-04-03Online:2026-03-08Published:2025-08-21 -
Contact:Ma Ping, MD, Associate chief physician, Department of Stomatology, Affiliated Hospital of Inner Mongolia Medical University, Hohhot 010010, Inner Mongolia Autonomous Region, China Wang Shu, PhD, Chief physician, Department of Stomatology, Affiliated Hospital of Inner Mongolia Medical University, Hohhot 010010, Inner Mongolia Autonomous Region, China -
About author:Fan Yongjing, MS, Attending physician, Department of Stomatology, Affiliated Hospital of Inner Mongolia Medical University, Hohhot 010010, Inner Mongolia Autonomous Region, China -
Supported by:General Project of Inner Mongolia Medical University, No. YKD2022MS056 (to MP); Research Project of Affiliated Hospital of Inner Mongolia Medical University, No. 2022NYFYTS014 (to FYJ); Joint Project of Inner Mongolia Medical University, No. YKD2022LH043 (to WS)
CLC Number:
Cite this article
Fan Yongjing, Jin Wulong, Bai Haoyu, Ma Ping, Wang Shu. Role and mechanism of stem cells from human exfoliated deciduous teeth in tissue regeneration and disease treatment [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(7): 1850-1857.
share this article
Add to citation manager EndNote|Reference Manager|ProCite|BibTeX|RefWorks
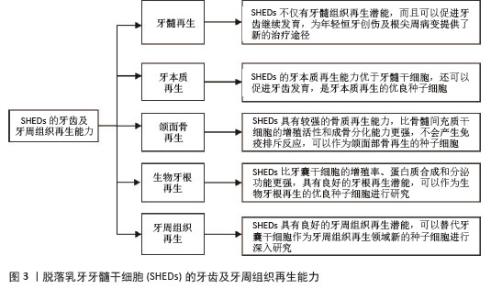
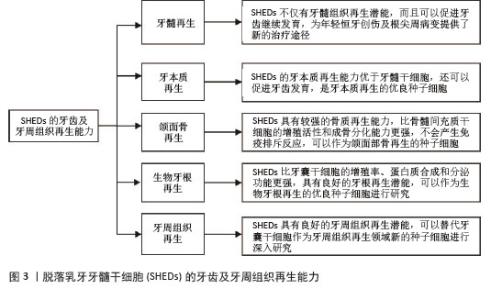
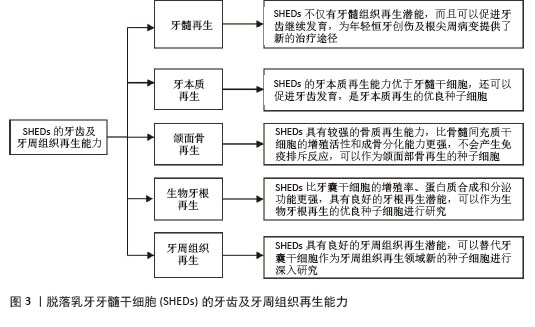
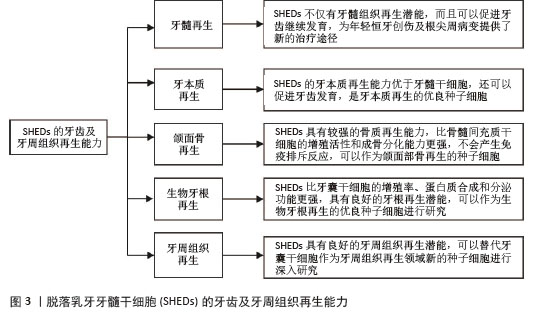
2.1 SHEDs的牙齿及牙周组织再生能力 2.1.1 牙髓再生 利用SHEDs分化能力使牙本质、血管及神经再生,进而促进患牙的牙髓活力恢复和牙根继续发育。ROSA等[4]通过鼠动物模型发现,在根管内注射SHEDs三维蛋白支架,经过一段时间后可以成功再生全根髓样组织,证明SHEDs具有牙髓再生潜能。SUI等[5]通过建立猪动物模型,发现SHEDs可在根管内再生神经组织和血管等,而传统的根尖诱导成形术仅能形成钙化组织,故SHEDs在牙髓组织再生方面更具有优势。GUO等[1]通过猪动物模型进行体内实验,不仅证明了SHEDs具有牙髓再生能力,而且在牙髓组织再生过程中,SHED可以促进血管生成。以上研究均表明SHEDs不仅可以促进牙髓组织再生,并且有促进牙齿继续发育的潜能,为年轻恒牙根尖周病变及创伤的治疗提供新途径和新思路。 2.1.2 牙本质再生 SHEDs和牙髓干细胞相似,均具有牙髓和牙本质再生潜能,SHEDs也可以分泌矿化基质,形成成牙本质细胞和管状牙本质,进而使牙本质壁增厚、牙根继续发育,促进牙齿的发育。李彩玉[6]通过成牙本质诱导,发现SHEDs的碱性磷酸酶活性、茜素红染色矿化结节、成牙本质相关基因和蛋白的表达水平均显著高于牙髓干细胞,证明了SHEDs的成牙本质分化能力比牙髓干细胞更强。SUI等[5]通过建立猪动物模型发现SHEDs在根管内可以再生成牙本质细胞,是理想的牙本质再生种子细胞。以上这些实验研究均证明SHEDs具有良好的牙本质再生潜能,而且牙本质再生能力优于牙髓干细胞,同时还可以促进牙齿发育,是牙本质再生的优良种子细胞。 2.1.3 颌面骨再生 文献报道与牙髓干细胞和骨髓间充质干细胞(bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells,BMSCs)相比,SHEDs的增殖活性和成骨分化能力更强,SHEDs在成骨分化过程中形成的新生类骨质和胶原纤维更多,而且在牙槽骨重建过程中,SHEDs早期类骨质生成速度快,晚期骨矿化程度高,证明SHEDs具有更强的成骨分化能力[7]。有研究者通过比较牙髓干细胞与SHEDs的增殖和成骨分化能力,发现SHEDs在各个观察时间点的细胞密度均比牙髓干细胞高,且SHEDs自培养第9天起碱性磷酸酶活性高于牙髓干细胞,说明SHEDs的成骨分化和增殖能力比牙髓干细胞更强[8]。WEI等[9]通过建立小鼠动物模型,将胶原蛋白支架和成骨分化后的SHEDs一起植入牙槽骨缺损处,发现SHEDs诱导后形成的新骨与自体髂骨移植的治疗效果相似,证明SHEDs具有良好的骨再生能力。还有研究发现,SHED条件培养基(SHED-conditioned medium,SHED-CM)在体外可以促进种植体表面磷酸钙盐和胞外基质蛋白沉积,促进骨髓基质细胞黏附,在体内SHED-CM可以诱导种植体周围形成新骨[10],证明SHED-CM具有良好的成骨潜能。除此之外,改变一些条件,也可以增强SHEDs的成骨分化能力,例如同种异体血浆、低强度的激光疗法(5 J/cm2)、一定剂量的红外线LED照射均可以增加SHEDs的细胞活性和成骨分化能力,促进新骨形成[11]。SUN等[12]建立小型猪下颌骨缺损模型,将小型猪的SHEDs负载到β-磷酸钙上,移植到下颌骨缺损处,6个月后观察到缺损区有新骨形成,表明SHEDs可用于骨缺损的修复,并且效果较好。通过以上文献证明SHEDs具有较强的骨质再生能力,比BMSCs的增殖活性和成骨分化能力更强,产生免疫排斥反应的可能性低,可以作为颌面部骨再生领域的新策略。 2.1.4 生物牙根再生 生物牙根是将间充质干细胞与预制根状支架结合后植入牙槽骨中,用组织工程学方法形成具有生理功能的牙根,“生物牙根”的概念在2006年第一次被提出[13]。牙根再生在牙齿修复和再生方面比全牙再生更有应用前景。以往研究表明牙囊干细胞(dental follicle stem cells,DFSCs)是一种很有前景的生物牙根再生种子细胞,虽然SHEDs与牙囊干细胞具有相似的牙源性分化能力,但是牙囊干细胞必须取材于未萌出的第三磨牙或正在发育的牙根,导致其在牙根再生方面的研究条件受限[13]。因SHEDs较易获得,取材方便,所以近几年很多实验研究开始尝试将SHEDs作为生物牙根再生的新的种子细胞。YANG等[14]通过建立免疫缺陷小鼠动物模型,将SHEDs与牙本质基质结合后植入免疫缺陷小鼠皮下,可以观察到牙本质和牙周组织生成,SHEDs表现出更强的迁移能力和优异的神经发生潜力,证明SHEDs可以作为生物牙根再生的种子细胞进行深入的实验研究。SHEDs的增殖率、蛋白质合成能力和分泌功能均比牙囊干细胞更强,而且局部可形成利于组织再生及修复的微环境,故SHEDs可成为生物牙根再生的优势种子细胞之一[15]。还有实验发现自体SHEDs聚合体与牙本质基质聚合体移植能够使年轻恒牙受到创伤后牙根继续发育,牙根延长,最终使根尖孔闭合,而且患牙的血流量也会增加,患牙的感觉功能也可以恢复,证明SHEDs具有良好的牙根再生潜能,可以作为生物牙根再生的优良种子细胞进行研究[14]。 2.1.5 牙周组织再生 在牙周组织再生的既往研究中,很多文献证明牙囊干细胞是优良的种子细胞[13],但牙囊干细胞只能从未萌牙胚或正在发育的牙根中获得,不易提取,获得难度较大。而SHEDs来源于自然替换的脱落乳牙牙髓,不仅细胞来源广泛、易获得,而且组织再生能力较强。YANG等[14]通过体外实验诱导牙囊干细胞和SHEDs分别形成细胞膜片,与处理后的牙本质基质结合后移植于裸鼠皮下,通过比较它们的生物学特性,发现虽然牙囊干细胞的增殖率、成骨能力和成脂能力均较高,但是SHEDs的迁移能力和神经再生潜能比牙囊干细胞更强;除此之外,他们还通过体内实验发现,SHEDs与牙本质基质复合物结合后进行体内移植,检测到了牙周血管及韧带纤维、新生牙槽骨等牙周组织的再生。通过小鼠多剂量给药实验,发现SHEDs可以促进牙周组织中CD206+ M2巨噬细胞数量增加,减少促炎细胞因子、增加抗炎细胞因子,减少小鼠牙龈出血,并使牙周韧带附着增加,降低了破骨细胞的分化,证实了SHEDs能促进牙周组织再生,并促进牙周组织损伤的修复[16]。以上实验均证明,SHEDs能为牙周组织再生的研究提供新方向。 综上,SHEDs在牙齿及牙周组织再生方面表现优秀,见图3,表1。"

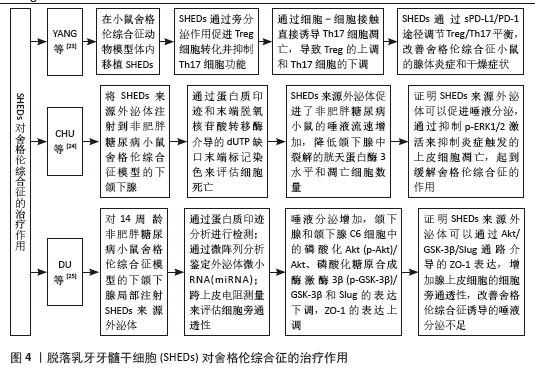
2.2 脱落乳牙牙髓干细胞对口腔疾病的治疗作用 2.2.1 牙周炎 牙周炎主要是牙菌斑中的细菌对牙周组织产生破坏,从而对牙龈、牙周膜、牙槽骨和牙骨质等牙周支持组织产生影响。牙周炎使T淋巴细胞和IgG细胞浸润增加,巨噬细胞比例增加,T细胞比例相对减少[17]。对牙周炎的治疗以及对牙周支持组织的修复一直是近几年研究的热点,SHEDs也被引入到牙周炎治疗中进行研究。GAO等[16]通过建立大鼠牙周炎动物模型,评估SHEDs在牙周组织中的存活率和分布,生物荧光成像显示SHEDs在牙周组织内存活了约7 d,发现SHEDs能够促进单核细胞-巨噬细胞向CD206+M2样表型转化,龈沟液中促炎因子减少,抗炎因子增加,大鼠牙周韧带附着增加,牙龈出血减少和破骨细胞分化减少,这个实验证明SHEDs可通过诱导M2巨噬细胞极化起到减轻牙周组织炎症的作用,进一步证明了SHEDs对牙周炎具有免疫调节作用,进而发挥治疗牙周炎的作用,SHEDs可以作为治疗牙周炎的切入点进行深入研究。 2.2.2 颞下颌关节炎 颞下颌关节炎是一种关节退行性疾病,主要特征是进行性软骨退变、软骨下骨异常改建和滑膜炎性病变,表现为颞下颌关节区疼痛、咀嚼困难及其他颞下颌关节反射区的不适[18]。OGASAWARA等[19]通过建立强迫张口诱导的小鼠颞下颌关节炎模型,发现经尾静脉注射 SHED-CM后,可以下调促炎降解因子白细胞介素1β、诱导型一氧化氮合酶和基质金属蛋白酶13等的表达,上调增殖细胞核抗原阳性细胞的数量,一定程度恢复颞下颌关节炎髁突软骨的完整性和表面光滑度,从而促进颞下颌的再生修复。何睿[20]应用碘乙酸钠诱导建立大鼠髁突软骨退变模型,然后在大鼠颞下颌关节腔内分别注射SHEDs及其衍生物SHED-CM和SHED外泌体,发现SHEDs及其衍生物均可以有效逆转碘乙酸钠所致的大鼠髁突软骨退变。LUO等[21]用SHED外泌体的miRNA(miR-100-5p)处理颞下颌关节软骨细胞,发现SHED外泌体可以下调白细胞介素6、白细胞介素8、基质金属蛋白酶1、基质金属蛋白酶3和血小板反应蛋白基序5等炎性因子的表达,证明SHED外泌体可以降低颞下颌关节炎导致的软骨细胞炎症反应,SHED外泌体未来可能成为治疗颞下颌关节炎症的一种新药物。MUHAMMED等[22]通过体外诱导建立人软骨细胞颞下颌关节炎模型,发现经SHED-CM 治疗后,软骨细胞的抗炎能力提高,并且上调聚集蛋白、胶原12型蛋白及白细胞介素10 的表达,显著抑制软骨降解和炎症因子白细胞介素1α、白细胞介素6、肿瘤坏死因子α 和一氧化氮的表达,从而保护颞下颌软骨组织,减少炎症因子对颞下颌造成的损伤。 2.2.3 舍格伦综合征 舍格伦综合征是一种外分泌腺的慢性炎症自身免疫性疾病,导致腺体分泌减少及淋巴细胞灶性浸润,组织学特征是唾液腺和泪腺的高淋巴细胞浸润导致的干燥症状[23]。目前研究发现,SHEDs具有强大的免疫调节能力,它可以作为新的切入点为舍格伦综合征患者提供新的治疗思路。YANG等[23]通过建立小鼠动物模型,发现在尾静脉内注射SHEDs后,可以调节Treg/Th17平衡,使唾液流速增加,从而改善舍格伦综合征。CHU等[24]将人SHED外泌体注射到非肥胖糖尿病小鼠舍格伦综合征模型的下颌下腺,通过蛋白质印迹和末端脱氧核苷酸转移酶介导的dUTP缺口末端标记染色来评估细胞死亡,发现人SHED外泌体促进了非肥胖糖尿病小鼠的唾液流速增加,同时降低了下颌下腺中裂解的胱天蛋白酶3水平和凋亡细胞数量,证明人SHED外泌体可以促进唾液分泌,通过抑制p-ERK1/2激活来抑制炎症触发的上皮细胞凋亡,起到缓解舍格伦综合征的作用。DU等[25]对14周龄非肥胖糖尿病小鼠舍格伦综合征模型的下颌下腺局部注射人SHED外泌体,发现小鼠唾液分泌增加,下颌下腺和下颌下腺C6细胞中的磷酸化Akt(p-Akt)/Akt、磷酸化糖原合成酶激酶3β(p-GSK-3β)/GSK-3β和Slug的表达下调,ZO-1的表达上调,证明SHEDs可以成为治疗舍格伦综合征的新方法,为舍格伦综合征的治疗提供新途径,见图4。"

2.3 SHEDs对非口腔疾病的治疗作用 2.3.1 神经系统疾病 神经系统疾病包括脑血管疾病、周期性麻痹、进行性肌营养不良、强直性肌营养不良、共济失调等。目前研究显示SHEDs对中枢神经系统疾病如阿尔茨海默病、帕金森病、慢性脑缺血、多发性硬化症、缺血缺氧性脑病、脊髓损伤,周围神经损伤疾病如面神经、喉上神经和坐骨神经损伤等均有治疗效果[26]。 实验研究发现,SHEDs经过神经特异性诱导培养后,可以表达神经干细胞、神经元以及神经胶质细胞标志物[27]。SHED-CM不仅能提供多种神经修复作用,而且能将疾病微环境从促炎转为抗炎,减弱β-淀粉样蛋白肽诱导的促炎症反应,利于阿尔茨海默病的治疗[28]。有学者通过建立帕金森病大鼠模型,检测SHED-CM在鱼藤酮诱导的帕金森病大鼠模型中的治疗效果,发现通过SHED-CM静脉给药,可以增加大鼠纹状体中酪氨酸羟化酶的含量,降低大鼠黑质和纹状体中α-突触核蛋白水平,显著改善帕金森病症状[29]。还有研究发现,在慢性脑缺血大鼠模型的海马区移植SHEDs,不仅可以减少神经元细胞的凋亡,增强大鼠神经功能相关蛋白的表达水平,而且还能恢复大鼠神经元数量,提高大鼠的认知能力[30]。 除此之外,SHEDs还具有分化为光感受器样细胞的潜力,有研究者使用因子混合物方案诱导SHEDs向视网膜光感受器分化达24 d,并从形态学变化、生物标志物表达和亚细胞分布以及钙内流等方面鉴定诱导细胞的特征。用萤火虫萤光素酶标记SHEDs,通过生物发光成像进行体内跟踪,将标记后的SHEDs移植到小鼠视网膜下间隙,发现SHEDs表现出类似神经元的形态,并可以表达与视网膜及光感受体前体、成熟光感受器相关的蛋白质和特定基因,最终SHEDs成功转化为光感受器样细胞。证明SHEDs或SHED-CM均可以改善小鼠视网膜电图反应及光感受器的变性程度,从而起到治疗视网膜变性的作用[31]。有学者在大鼠面神经下颌支切断模型中移植SHEDs和聚乙醇酸导管联合自体神经,6周后在体内检测到施万样细胞,证明SHEDs可以促进面神经下颌支的再生[29]。另外,SHEDs移植可以避免脊髓损伤大鼠神经元早期凋亡,使脊髓腹角处更多运动神经元存活,促进损伤后的运动功能恢复,降低肿瘤坏死因子α的表达,减少星形胶质细胞增殖,使脊髓中的线粒体组成蛋白处于正常水平,对脊髓损伤起到良好的治疗作用[32]。SHEDs对周围神经损伤的治疗作用主要是通过促进血管生成、分泌神经营养因子、促进M2型巨噬细胞极化及免疫调节、诱导SHEDs向施万细胞分化而起作用[33]。 综上所述,SHEDs对神经系统疾病的治疗作用潜力巨大,可以进行深入研究,为神经系统疾病的治疗带来新的希望,见表2。"


2.3.2 消化系统疾病 消化系统疾病包括食管、胃、肠、肝、胆、胰等脏器的器质性病变和功能性疾病。在动物消化系统疾病模型中,SHEDs可以再生肝内胆管系统,治疗肝脏疾病,如减轻急性肝损伤,改善肝纤维化,但是目前未见治疗其他消化系统疾病的相关报道。 YUNIARTHA等[34]通过小鼠慢性肝纤维化模型,在小鼠脾静脉内输注SHEDs,形成肝细胞样细胞(SHED-converted hepatocyte-likecells,SHED-Heps),发现SHED-Heps可以促进胆管细胞生成、胆管系统再生、改善胆汁淤积,证明在肝脏中SHEDs具有再生潜力,对肝脏疾病的治疗具有积极意义。DAL等[35]建立慢性肝纤维化小鼠模型,将SHED-Heps移植到左侧肝脏中,发现SHED-Heps不仅对左侧肝脏肝叶纤维化有治疗作用,而且对其他肝叶纤维化也有改善作用,证明SHED-Heps的治疗作用比较强大。XIONG等[36]通过建立大鼠暴发性肝功能衰竭动物模型,用Atp7b突变的Long-Evans肉桂(LEC)经铜过载诱导模拟威尔森病,将SHED-Heps输注到脾静脉内,发现SHED-Heps可以减少小鼠肝脏的氧化应激,证明SHED-Heps为治疗暴发性威尔森病提供了一种潜在的功能恢复、桥接和预防方法,对威尔森病有治疗作用。ZHOU等[37]先在小鼠尾静脉内注射SHEDs,之后再将小鼠制备成急性肝损伤模型,发现SHEDs可以抑制核因子κB表达,抑制肝细胞凋亡,减轻肝损伤。MUTO等[38]在非酒精性肝炎小鼠模型中,将SHED衍生条件培养基注射到小鼠尾静脉,检测到血液中的游离脂肪酸和三酰甘油水平降低,但对肝脏脂肪沉积没有改善作用,从而证明SHEDs对脂肪肝没有治疗作用。 SHEDs对其他消化系统疾病是否有治疗作用,还需要查阅更多的文献得以证实,同时也是进一步深入研究的新方向,见表3。"

| [1] GUO H, ZHAO W, LIU A, et al. SHED promote angiogenesis in stem cell-mediated dental pulp regeneration. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2020;529(4):1158-1164. [2] HAN Y, ZHANG L, ZHANG C, et al. Guiding Lineage Specific Differentiation of SHED for Target Tissue/Organ Regeneration. Curr Stem Cell Res Ther. 2021;16(5):518-534. [3] SABBAGH J, GHASSIBE-SABBAGH M, FAYYAD-KAZAN M, et al. Differences in osteogenic and odontogenic differentiation potential of DPSCs and SHED. J Dent. 2020;101:103413. [4] ROSA V, ZHANG Z, GRANDE RH, et al. Dental pulp tissue engineering in full-length human root canals. J Dent Res. 2013;92(11):970-975. [5] SUI B, CHEN C, KOU X, et al. Pulp Stem Cell-Mediated Functional Pulp Regeneration. J Dent Res. 2019;98(1):27-35. [6] 李彩玉.FGF2对人乳牙牙髓干细胞成牙本质向分化能力影响的研究[D].重庆:重庆医科大学,2020. [7] SUN X, MAO Y, LIU B, et al. Mesenchymal Stem Cell-Derived Exosomes Enhance 3D-Printed Scaffold Functions and Promote Alveolar Bone Defect Repair by Enhancing Angiogenesis. J Pers Med. 2023;13(2):180. [8] ZHANG N, XU L, SONG H, et al. Tracking of Stem Cells from Human Exfoliated Deciduous Teeth Labeled with Molday ION Rhodamine-B during Periodontal Bone Regeneration in Rats. Int J Stem Cells. 2023;16(1):93-107. [9] WEI J, SONG Y, DU Z, et al. Exosomes derived from human exfoliated deciduous teeth ameliorate adult bone loss in mice through promoting osteogenesis. J Mol Histol. 2020;51(4):455-466. [10] MA S, JIANG Y, QIAN Y, et al. The Emerging Biological Functions of Exosomes from Dental Tissue-Derived Mesenchymal Stem Cells. Cell Reprogram. 2023;25(2):53-64. [11] WANG T, ZHOU Y, ZHANG W, et al. Exosomes and exosome composite scaffolds in periodontal tissue engineering. Front Bioeng Biotechnol. 2024;11:1287714. [12] SUN Y, LIU J, XU Z, et al. Matrix stiffness regulates myocardial differentiation of human umbilical cord mesenchymal stem cells. Aging (Albany NY). 2020;13(2):2231-2250. [13] SONOYAMA W, LIU Y, FANG D, et al. Mesenchymal stem cell-mediated functional tooth regeneration in swine. PLoS One. 2006; 1(1):e79. [14] YANG X, MA Y, GUO W, et al. Stem cells from human exfoliated deciduous teeth as an alternative cell source in bio-root regeneration. Theranostics. 2019;9(9):2694-2711. [15] 张晓月,赵卿,王小聪,等.牙源性干细胞在生物牙根中的应用进展[J].临床口腔医学杂志,2022,38(8):502-504. [16] GAO P, KAJIYA M, MOTOIKE S, et al. Application of mesenchymal stem/stromal cells in periodontal regeneration: Opportunities and challenges. Jpn Dent Sci Rev. 2024;60:95-108. [17] 陈宁馨,赖光云,汪俊.脱落乳牙牙髓干细胞在口腔颌面部组织再生及免疫调节中应用的研究进展[J].中国实用口腔科杂志, 2021,14(2):220-224. [18] RASHEED Z, AKHTAR N, HAQQI TM. Advanced glycation end products induce the expression of interleukin-6 and interleukin-8 by receptor for advanced glycation end product-mediated activation of mitogen-activated protein kinases and nuclear factor-κB in human osteoarthritis chondrocytes. Rheumatology (Oxford). 2011; 50(5):838-851. [19] OGASAWARA N, KANO F, HASHIMOTO N, et al. Factors secreted from dental pulp stem cells show multifaceted benefits for treating experimental temporomandibular joint osteoarthritis. Osteoarthritis Cartilage. 2020;28(6):831-841. [20] 何睿.脱落人乳牙牙髓干细胞及其衍生物对大鼠颞下颌骨关节炎软骨退变转归的作用研究[D].合肥:安徽医科大学,2022. [21] LUO P, JIANG C, JI P, et al. Exosomes of stem cells from human exfoliated deciduous teeth as an anti-inflammatory agent in temporomandibular joint chondrocytes via miR-100-5p/mTOR. Stem Cell Res Ther. 2019;10(1):216. [22] MUHAMMAD SA, NORDIN N, HUSSIN P, et al. Protective effects of stem cells from human exfoliated deciduous teeth derived conditioned medium on osteoarthritic chondrocytes. PLoS One. 2020;15(9):e0238449. [23] YANG N, LIU X, CHEN X, et al. Stem cells from exfoliated deciduous teeth transplantation ameliorates Sjögren’s syndrome by secreting soluble PD-L1. J Leukoc Biol. 2022;111(5): 1043-1055. [24] CHU WX, DING C, DU ZH, et al. SHED-exos promote saliva secretion by suppressing p-ERK1/2-mediated apoptosis in glandular cells. Oral Dis. 2024;30(5):3066-3080. [25] DU Z, WEI P, JIANG N, et al. SHED-derived exosomes ameliorate hyposalivation caused by Sjögren’s syndrome via Akt/GSK-3β/Slug-mediated ZO-1 expression. Chin Med J (Engl). 2023;136(21):2596-2608. [26] 周绍兰,梁燕,袁媛园.脱落乳牙牙髓干细胞在神经系统疾病的应用及研究进展[J].疑难病杂志,2023,22(3):324-327. [27] 张军伟,郝晓宁,杨晓慧,等.磁共振 SWI 技术在急性脊髓损伤中 的应用及对神经功能的评价[J].疑难病杂志,2022,21( 5): 492- 496. [28] ALIDOUST L, AKHOONDIAN M, ATEFI AH, et al. Stem cell-conditioned medium is a promising treatment for Alzheimer’s disease. Behav Brain Res. 2023;452:114543. [29] CHEN YR, LAI PL, CHIEN Y, et al. Improvement of Impaired Motor Functions by Human Dental Exfoliated Deciduous Teeth Stem Cell-Derived Factors in a Rat Model of Parkinson’s Disease. Int J Mol Sci. 2020;21(11):3807. [30] GUGLIANDOLO A, MAZZON E. Dental Mesenchymal Stem Cell Secretome: An Intriguing Approach for Neuroprotection and Neuroregeneration. Int J Mol Sci. 2021; 23(1):456. [31] ASADI-GOLSHAN R, RAZBAN V, MIRZAEI E, et al. Efficacy of dental pulp-derived stem cells conditioned medium loaded in collagen hydrogel in spinal cord injury in rats: Stereological evidence. J Chem Neuroanat. 2021;116:101978. [32] LIU Y, KANO F, HASHIMOTO N, et al. Conditioned Medium From the Stem Cells of Human Exfoliated Deciduous Teeth Ameliorates Neuropathic Pain in a Partial Sciatic Nerve Ligation Model. Front Pharmacol. 2022;13:745020. [33] LUO L, HE Y, JIN L, et al. Application of bioactive hydrogels combined with dental pulp stem cells for the repair of large gap peripheral nerve injuries. Bioact Mater. 2020;6(3):638-654. [34] YUNIARTHA R, YAMAZA T, SONODA S, et al. Cholangiogenic potential of human deciduous pulp stem cell-converted hepatocyte-like cells. Stem Cell Res Ther. 2021;12(1):57. [35] DAL NE, AFAGH A, KANIT N, et al. TGF-β1 promotes cell migration in hepatocellular carcinoma by suppressing REELIN expression. Gene. 2020;724:143923. [36] XIONG X, GAO C, MENG X, et al. Research progress in stem cell therapy for Wilson disease. Regen Ther. 2024;27:73-82. [37] ZHOU YK, ZHU LS, HUANG HM, et al. Stem cells from human exfoliated deciduous teeth ameliorate concanavalin A-induced autoimmune hepatitis by protecting hepatocytes from apoptosis. World J Stem Cells. 2020;12(12):1623-1639. [38] MUTO H, ITO T, TANAKA T, et al. Conditioned medium from stem cells derived from human exfoliated deciduous teeth ameliorates NASH via the Gut-Liver axis. Sci Rep. 2021; 11(1):18778. [39] WU M, LIU X, LI Z, et al. SHED aggregate exosomes shuttled miR-26a promote angiogenesis in pulp regeneration via TGF-β/SMAD2/3 signalling. Cell Prolif. 2021;54(7): e13074. [40] LIU P, ZHANG Q, MI J, et al. Exosomes derived from stem cells of human deciduous exfoliated teeth inhibit angiogenesis in vivo and in vitro via the transfer of miR-100-5p and miR-1246. Stem Cell Res Ther. 2022;13(1):89. [41] QIU X, LIU J, ZHENG C, et al. Exosomes released from educated mesenchymal stem cells accelerate cutaneous wound healing via promoting angiogenesis. Cell Prolif. 2020; 53(8):e12830. [42] HATTORI Y, KIM H, TSUBOI N, et al. Therapeutic Potential of Stem Cells from Human Exfoliated Deciduous Teeth in Models of Acute Kidney Injury. PLoS One. 2015;10(10):e0140121. [43] RAO N, WANG X, XIE J, et al. Stem Cells from Human Exfoliated Deciduous Teeth Ameliorate Diabetic Nephropathy In Vivo and In Vitro by Inhibiting Advanced Glycation End Product-Activated Epithelial-Mesenchymal Transition. Stem Cells Int. 2019;2019:2751475. [44] 蒋志寒,徐凌.人脱落乳牙牙髓干细胞治疗非口腔疾病的研究进展[J].中国全科医学,2023,26(24):3067-3073. [45] ISHIKAWA J, TAKAHASHI N, MATSUMOTO T, et al. Factors secreted from dental pulp stem cells show multifaceted benefits for treating experimental rheumatoid arthritis. Bone. 2016;83:210-219. [46] TYAGI A, SHETTY J, SHETTY S, et al. Antibacterial and Immunomodulatory Properties of Stem Cells from Human Exfoliated Deciduous Teeth: An In Vitro Study. Int J Clin Pediatr Dent. 2023; 16(Suppl 3):240-246. [47] 朱凌肃.脱落乳牙牙髓干细胞治疗小鼠自身免疫性肝炎的研究[D].郑州:郑州大学, 2019. [48] LI W, JIAO X, SONG J, et al. Therapeutic potential of stem cells from human exfoliated deciduous teeth infusion into patients with type 2 diabetes depends on basal lipid levels and islet function. Stem Cells Transl Med. 2021;10(7):956-967. [49] KANAFI MM, BHONDE RR. Diverse Approaches toward Application of Dental Pulp Stem Cells from Human Permanent and Deciduous Teeth in the Treatment of Diabetes. Curr Diabetes Rev. 2024;20(1):e210323214822. [50] LIANG TY, LU LH, TANG SY, et al. Current status and prospects of basic research and clinical application of mesenchymal stem cells in acute respiratory distress syndrome. World J Stem Cells. 2023;15(4):150-164. [51] HERRMAN H, PATEL V, KIELING C, et al. Time for united action on depression: a Lancet-World Psychiatric Association Commission. Lancet. 2022;399(10328):957-1022. [52] 沈钊舟.人脱落乳牙牙髓干细胞治疗重度抑郁症的研究[D].长沙:中南大学,2022. |
| [1] | Yang Xuetao, Zhu Menghan, Zhang Chenxi, Sun Yimin, Ye Ling. Applications and limitations of antioxidant nanomaterials in oral cavity [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(8): 2044-2053. |
| [2] | Yang Qiongqiong, Liu Wei. Comparison of performance and clinical effects of zirconia and titanium implants [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(8): 2063-2071. |
| [3] | Hu Xiongke, Liu Shaohua, Tan Qian, Liu Kun, Zhu Guanghui. Shikonin intervention with bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells improves microstructure of femur in aged mice [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(7): 1609-1615. |
| [4] | Yuan Xiaoshuang, Yang Xu, Yang Bo, Chen Xiaoxu, Tian Ting, Wang Feiqing, Li Yanju, Liu Yang, Yang Wenxiu. Effect of conditioned medium of diffuse large B-cell lymphoma cells on proliferation and apoptosis of human bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(7): 1632-1640. |
| [5] | Cui Lianxu, Li Haomin, Xu Junrong, Tan Baodong, Lu Dahong, Peng Siwei, Wang Jinhui. Effect of umbilical cord mesenchymal stem cell conditioned medium on tissue repair after traumatic craniocerebral injury in miniature pigs [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(7): 1730-1735. |
| [6] | Zhang Qian, Wang Fuxia, Wang Wen, Zhang Kun. Characteristic analysis of nanogel composite system and its application strategies in visualization of diagnostic imaging and therapy [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(2): 480-488. |
| [7] | Gu Jianmei, Yuan Kunshan, Zhou Qiang, Zhang Haijun, , . Application of laser microporous decellularized scaffolds in tissue regeneration [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(2): 499-507. |
| [8] | Cheng Yanan, Yu Jiazhi, Liu Yinchang, Wu Jie, Yu Tong, Wang Lu, Li Xiaoguang. Three-dimensional finite element analysis of molar distalization with clear aligners with different thicknesses and edges [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(2): 310-318. |
| [9] | Xu Haichao, Luo Lihua, Pan Yihuai. Application and progress of dental pulp stem cells and their derivatives in dental pulp regeneration [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(1): 153-162. |
| [10] | Zhang Zhaowei, Chen Ouzile, Bai Mingru, Wang Chenglin. Therapeutic potential of bioactive substances secreted by dental mesenchymal stem cells for bone repair [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(1): 163-174. |
| [11] | Liu Yu, Gong Senyi, Yang Lihua, Li Weifeng, Hu Yuwen, Yan Qinbiao, Guo Meijin. Isolation, identification, and application of exosomes derived from mesenchymal stem cells [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(1): 194-203. |
| [12] | Sun Huiwen, Guo Qiangqiang, Wang Wei, Wu Jie, Xi Kun, Gu Yong. Engineered stem cell bionic periosteum coordinates immune inflammation and vascularization to promote bone regeneration [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(1): 21-33. |
| [13] | Chen Qiheng, Weng Tujun, Peng Jiang. Effect of dimethylglyoxal glycine on osteogenic, adipogenesis differentiation, and mitophagy of human bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(1): 50-57. |
| [14] | Ma Wenjing, Zhang Jinyu, Jiang Mingxia, Xiu Bingshui, Bai Rui, Liu Yuhan, Chen Xuyi, Yuan Zengqiang, Liu Zhiqiang. Scaffold-free three-dimensional human umbilical cord mesenchymal stem cell secretome repairs mouse skin injury [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(1): 68-77. |
| [15] | Li Dijun, Jiu Jingwei, Liu Haifeng, Yan Lei, Li Songyan, Wang Bin. Three-dimensional gelatin microspheres loaded human umbilical cord mesenchymal stem cells for chronic tendinopathy repair [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(7): 1356-1362. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||