Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research ›› 2026, Vol. 30 ›› Issue (1): 68-77.doi: 10.12307/2025.982
Previous Articles Next Articles
Scaffold-free three-dimensional human umbilical cord mesenchymal stem cell secretome repairs mouse skin injury
Ma Wenjing1, Zhang Jinyu1, Jiang Mingxia2, Xiu Bingshui2, Bai Rui3, Liu Yuhan4, Chen Xuyi4, Yuan Zengqiang1, Liu Zhiqiang1
- 1Hengyang Medical School, University of South China, Postgraduate Cooperative Training Base of Institute of Military Cognition and Brain Sciences, Hengyang 421001, Hunan Province, China; 2Yantai Laiyang Central Hospital, Affiliated Hospital of Weifang Medical College, Yantai 265299, Shandong Province, China; 3Cardiovascular Medicine Department of Sixth Medical Center of People's Liberation Army, Beijing 100853, China; 4Armed Police Characteristic Medical Center, Tianjin 300162, China
-
Received:2024-10-15Accepted:2024-12-06Online:2026-01-08Published:2025-06-19 -
Contact:Liu Zhiqiang, MD, Researcher, Hengyang Medical School, University of South China, Postgraduate Cooperative Training Base of Institute of Military Cognition and Brain Sciences, Hengyang 421001, Hunan Province, China; Co-corresponding author: Yuan Zengqiang, MD, Researcher, Hengyang Medical School, University of South China, Postgraduate Cooperative Training Base of Institute of Military Cognition and Brain Sciences, Hengyang 421001, Hunan Province, China -
About author:Ma Wenjing, Master candidate, Hengyang Medical School, University of South China, Postgraduate Cooperative Training Base of Institute of Military Cognition and Brain Sciences, Hengyang 421001, Hunan Province, China -
Supported by:National Natural Science Foundation of China, No. 82200295 (to BR)
CLC Number:
Cite this article
Ma Wenjing, Zhang Jinyu, Jiang Mingxia, Xiu Bingshui, Bai Rui, Liu Yuhan, Chen Xuyi, Yuan Zengqiang, Liu Zhiqiang. Scaffold-free three-dimensional human umbilical cord mesenchymal stem cell secretome repairs mouse skin injury[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(1): 68-77.
share this article
Add to citation manager EndNote|Reference Manager|ProCite|BibTeX|RefWorks
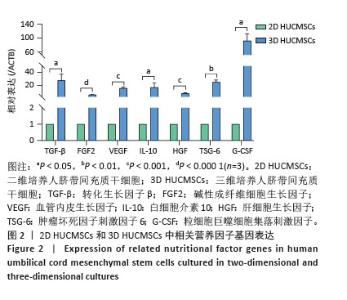
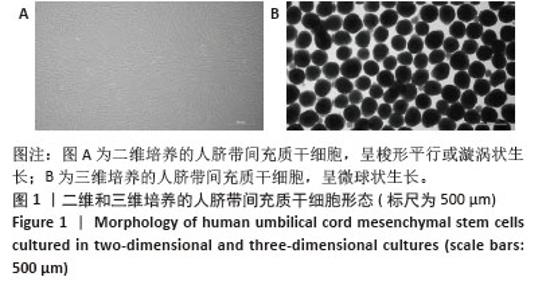
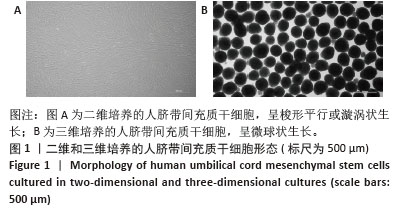
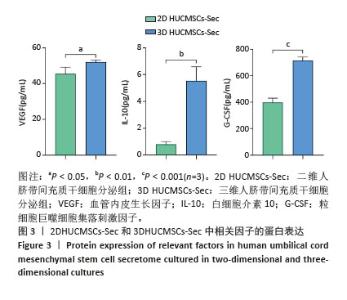
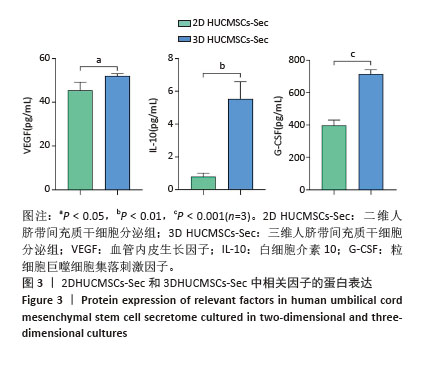
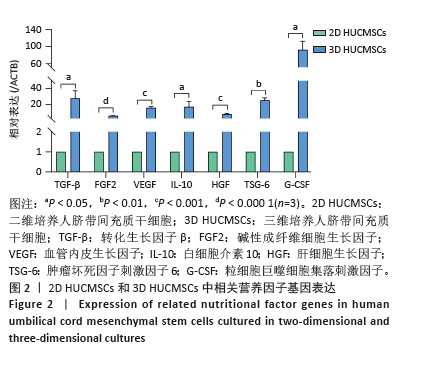
2.2 二维和三维培养人脐带间充质干细胞中相关分泌因子基因表达差异 为了验证三维培养模式下人脐带间充质干细胞分泌皮肤损伤修复因子的能力是否发生改变,收集了不同条件培养3 d的二维人脐带间充质干细胞和三维人脐带间充质干细胞,通过RT-qPCR检测相关分泌因子的基因表达水平,发现三维人脐带间充质干细胞中与皮肤损伤修复相关营养因子的mRNA表达水平显著上调,如图2所示,转化生长因子β上调约28.2倍、碱性成纤维细胞生长因子上调约6.4倍、血管内皮生长因子上调约16.2倍、白细胞介素10上调约17.4倍、肝细胞生长因子上调约8.7倍、肿瘤坏死因子刺激因子6上调约25.7倍、粒细胞巨噬细胞集落刺激因子上调约92.2倍。"
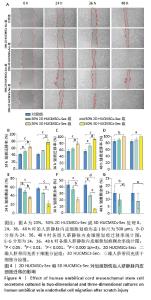
2.4 二维和三维HUCMSCs-Sec对人脐静脉内皮细胞迁移的影响 将HUCMSCs-Sec用于人脐静脉内皮细胞划痕损伤培养,以使用DMEM完全培养基为对照组,对比二维和三维HUCMSCs-Sec对人脐静脉内皮细胞迁移的影响,结果显示与对照组和同体积分数的二维HUCMSCs-Sec组相比,划痕损伤后24 h时三维HUCMSCs-Sec组细胞迁移率已超过50%,36 h时三维HUCMSCs-Sec组划痕几乎愈合,细胞迁移率[20%三维HUCMSCs-Sec为(79.3±3.4)%,50%三维HUCMSCs-Sec为(93.5±0.5)%]显著高于其他两组[对照组为(56.6±4.2)%,20%二维HUCMSCs-Sec为(63.9±3.8)%、50%二维HUCMSCs-Sec为(72.8±2.2)%];损伤后48 h时三维HUCMSCs-Sec组划痕完全愈合,愈合率为100%,显著高于其他两组[对照组为(85.5±5.3)%,20%二维HUCMSCs-Sec组为(90.3±4.1)%,50%二维HUCMSCs-Sec为(91.2±5.6)%],见图4A-D;为了更加直观地对比各组人脐静脉内皮细胞的迁移能力,对各个时间点的划痕剩余率进行了定量统计,见图4A,图4E-G,与对照组和二维HUCMSCs-Sec组相比,划痕损伤后24,36,48 h时三维HUCMSCs-Sec组划痕缩小的速率更快。 "

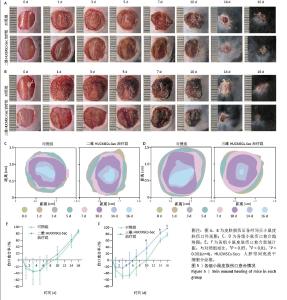
2.5 二维和三维HUCMSCs-Sec对小鼠皮肤损伤愈合的影响 小鼠皮肤损伤造模后,在0,1,3,5,7,10,14,16 d对伤口恢复情况进行拍照记录,如图5A,B所示,大体观察伤口外观发现,二维HUCMSCs-Sec治疗组小鼠伤口的炎性浸润程度、伤口结痂程度等与无处理对照组无显著差异,7-16 d伤口愈合程度无明显差异;而三维HUCMSCs-Sec治疗组小鼠在损伤后3 d内的炎性浸润程度较轻、伤口表面渗出液少,损伤后5 d时伤口结痂平整,损伤后7-16 d伤口开始快速缩小,损伤后16 d时创面几乎完全愈合,可见上皮化皮肤。将各个时间点的伤口边缘绘制成伤口愈合趋势图,见图5C,D,也同样显示三维HUCMSCs-Sec治疗组小鼠各个时间点伤口缩小更快。二维HUCMSCs-Sec治疗组小鼠伤口愈合率在术后各个时间节点与对照组相比无显著差异,见图5E,而三维HUCMSCs-Sec治疗组小鼠伤口愈合率在术后10,14,16 d时均显著高于对照组,见图5F。 "

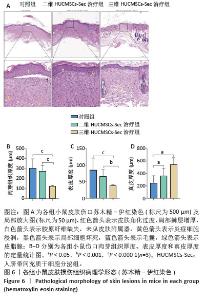
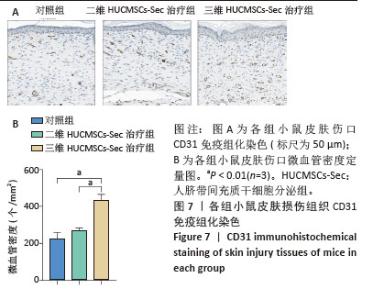
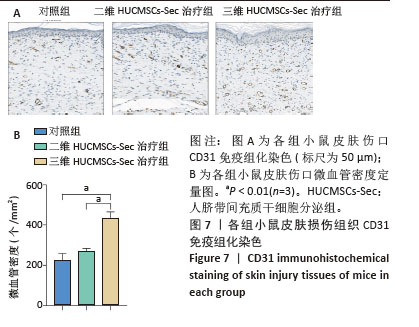
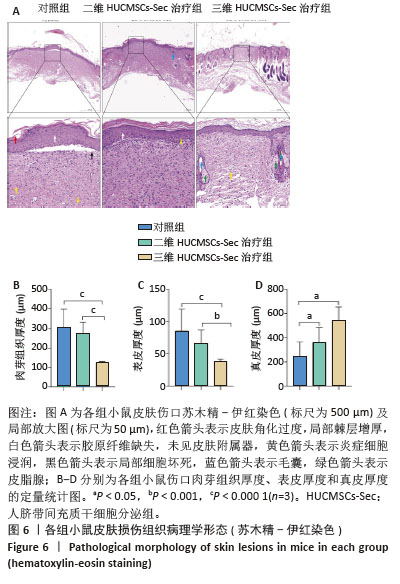
2.6 二维和三维HUCMSCs-Sec对小鼠皮肤损伤组织病理学的影响 2.6.1 苏木精-伊红染色结果 小鼠皮肤损伤后16 d,取伤口及其周围1.0-2.0 mm处的皮肤进行病理染色,如图6A显示对照组小鼠皮肤角化过度如红色箭头所示,伴有局部棘层增厚如白色箭头所示,胶原纤维缺失,未见皮肤附属器,同时可见少量炎症细胞浸润如黄色箭头所示。此外,局部区域还出现细胞坏死现象,表现为胞核碎裂、固缩及深染,如黑色箭头所示。二维HUCMSCs-Sec治疗组小鼠皮肤损伤程度较对照组稍有改善,肉芽组织区域有所减少,皮肤附属器官稍有增多,如黄色箭头所示毛囊;棘层较厚,未见明显变化,真皮层胶原纤维排列疏松,仍可见大量炎症细胞及成纤维细胞。与对照组相比,三维HUCMSCs-Sec治疗组小鼠皮肤表皮层结构保持相对完整,未见明显增厚,可观察到少量皮肤附属器,包括毛囊和皮脂腺,分别为蓝色和绿色箭头所示。更重要的是,三维HUCMSCs-Sec治疗组小鼠皮肤的炎症和坏死症状有所减轻,如黄色箭头所示,三维HUCMSCs-Sec治疗组小鼠皮肤中有较少的炎症细胞。进一步定量分析显示各小鼠在表皮、肉芽组织、真皮厚度方面有显著差异。如图6B-D所示,三维HUCMSCs-Sec治疗组小鼠的表皮厚度(38.1±15.3) μm显著低于对照组的(85.6±33.7) μm和二维HUCMSCs-Sec治疗组的(66.5±20.5) μm;三维HUCMSCs-Sec治疗组小鼠肉芽组织厚度(124.0±34.2) μm同样低于对照组的(302.3±95.0) μm和二维HUCMSCs-Sec治疗组的(275.3±54.6) μm,而三维HUCMSCs-Sec治疗组小鼠的真皮厚度(544.6±424.1) μm显著高于对照组的(246.6±117.5) μm和二维HUCMSCs-Sec治疗组的(360.6±121.6) μm,表明三维HUCMSCs-Sec组治疗后小鼠损伤皮肤结构恢复更为完整。"
| [1] HSU YC, FUCHS E. Building and Maintaining the Skin. Cold Spring Harb Perspect Biol. 2022;14(7):a040840. [2] QI L, ZHANG C, WANG B, et al. Progress in Hydrogels for Skin Wound Repair. Macromol Biosci. 2022;22(7):e2100475. [3] DING JY, CHEN MJ, WU LF, et al. Mesenchymal stem cell-derived extracellular vesicles in skin wound healing: roles, opportunities and challenges. Mil Med Res. 2023;10(1):36. [4] VAZQUEZ-ZAPIEN GJ, MARTINEZ-CUAZITL A, GRANADOS-JIMENEZ A, et al. Skin wound healing improvement in diabetic mice through FTIR microspectroscopy after implanting pluripotent stem cells. APL Bioeng. 2023;7(1):016109. [5] LUO R, DAI J, ZHANG J, et al. Accelerated Skin Wound Healing by Electrical Stimulation. Adv Healthc Mater. 2021;10(16):e2100557. [6] SADEGHI-AGHBASH M, RAHIMNEJAD M, ADELI H, et al. Wound Healing: An Overview of Wound Dressings on Health Care. Curr Pharm Biotechnol. 2023;24(9):1079-1093. [7] WILKINSON HN, HARDMAN MJ. Wound healing: cellular mechanisms and pathological outcomes. Open Biol. 2020;10(9):200223. [8] JU C, LIU D. Exosomal microRNAs from Mesenchymal Stem Cells: Novel Therapeutic Effect in Wound Healing. Tissue Eng Regen Med. 2023;20(5):647-660. [9] ZHOU C, ZHANG B, YANG Y, et al. Stem cell-derived exosomes: emerging therapeutic opportunities for wound healing. Stem Cell Res Ther. 2023;14(1):107. [10] TERATANI T, KASAHARA N, FUJIMOTO Y, et al. Mesenchymal Stem Cells Secretions Enhanced ATP Generation on Isolated Islets during Transplantation. Islets. 2022;14(1):69-81. [11] LI JY, REN KK, ZHANG WJ, et al. Human amniotic mesenchymal stem cells and their paracrine factors promote wound healing by inhibiting heat stress-induced skin cell apoptosis and enhancing their proliferation through activating PI3K/AKT signaling pathway. Stem Cell Res Ther. 2019;10(1):247. [12] FANG Z, CHEN P, TANG S, et al. Will mesenchymal stem cells be future directions for treating radiation-induced skin injury? Stem Cell Res Ther. 2021;12(1):179. [13] KOLIMI P, NARALA S, NYAVANANDI D, et al. Innovative Treatment Strategies to Accelerate Wound Healing: Trajectory and Recent Advancements. Cells. 2022;11(15):2439. [14] PITTENGER MF, DISCHER DE, PÉAULT BM, et al. Mesenchymal stem cell perspective: cell biology to clinical progress. NPJ Regen Med. 2019;4:22. [15] FUGGLE NR, COOPER C, OREFFO ROC, et al. Alternative and complementary therapies in osteoarthritis and cartilage repair. Aging Clin Exp Res. 2020;32(4): 547-560. [16] YAO H, YUAN X, WU Z, et al. Fabrication and Performance Evaluation of Gelatin/Sodium Alginate Hydrogel-Based Macrophage and MSC Cell-Encapsulated Paracrine System with Potential Application in Wound Healing. Int J Mol Sci. 2023;24(2):1240. [17] L PK, KANDOI S, MISRA R, et al. The mesenchymal stem cell secretome: A new paradigm towards cell-free therapeutic mode in regenerative medicine. Cytokine Growth Factor Rev. 2019;46:1-9. [18] ZHANG C, XIAO J, FA L, et al. Advances in the applications of mesenchymal stem cell-conditioned medium in ocular diseases. Exp Eye Res. 2023;233:109560. [19] CHEN W, SUN Y, GU X, et al. Conditioned medium of human bone marrow-derived stem cells promotes tendon-bone healing of the rotator cuff in a rat model. Biomaterials. 2021;271:120714. [20] ALIDOUST L, AKHOONDIAN M, ATEFI AH, et al. Stem cell-conditioned medium is a promising treatment for Alzheimer’s disease. Behav Brain Res. 2023;452:114543. [21] LI X, ZHANG D, YU Y, et al. Umbilical cord-derived mesenchymal stem cell secretome promotes skin regeneration and rejuvenation: From mechanism to therapeutics. Cell Prolif. 2024;57(4):e13586. [22] WANG X, WANG Q, YIN P, et al. Secretome of human umbilical cord mesenchymal stem cell maintains skin homeostasis by regulating multiple skin physiological function. Cell Tissue Res. 2023;391(1): 111-125. [23] SON YH, YANG DH, URICOLI B, et al. Three-Dimensional Cell Culture System for Tendon Tissue Engineering. Tissue Eng Regen Med. 2023; 20(4):553-562. [24] BIAŁKOWSKA K, KOMOROWSKI P, BRYSZEWSKA M, et al. Spheroids as a Type of Three-Dimensional Cell Cultures-Examples of Methods of Preparation and the Most Important Application. Int J Mol Sci. 2020; 21(17):6225. [25] MAEDA Y, MITSUHARA T, TAKEDA M, et al. Repeated human cranial bone-derived mesenchymal stem cell transplantation improved electrophysiological recovery in a spinal cord injury rat model. Neurosci Lett. 2025;844:138031. [26] CHENG Y, SONG G. Mesenchymal stem cells and skin injury repair. Sheng Wu Yi Xue Gong Cheng Xue Za Zhi. 2021;38(2):387-392. [27] 程延思危,宋关斌.间充质干细胞与皮肤的损伤修复[J].生物医学工程学杂志,2021,38(2):387-392. [28] KIM JH, GREEN DS, JU YM, et al. Identification and characterization of stem cell secretome-based recombinant proteins for wound healing applications. Front Bioeng Biotechnol. 2022;10:954682. [29] LASOCKA I, JASTRZĘBSKA E, SZULC-DĄBROWSKA L, et al. The effects of graphene and mesenchymal stem cells in cutaneous wound healing and their putative action mechanism. Int J Nanomedicine. 2019;14: 2281-2299. [30] LI Z, WANG Y, WANG H, et al. Self-Assembled DNA Composite-Engineered Mesenchymal Stem Cells for Improved Skin-Wound Repair. Small. 2024;20(31):e2310241. [31] DAMAYANTI RH, RUSDIANA T, WATHONI N. Mesenchymal Stem Cell Secretome for Dermatology Application: A Review. Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol. 2021;14:1401-1412. [32] RAJESH A, JU EDE, OXFORD KA, et al. The mesenchymal stromal cell secretome promotes tissue regeneration and increases macrophage infiltration in acute and methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus-infected skin wounds in vivo. Cytotherapy. 2024;26(11):1400-1410. [33] SUN J, ZHANG Y, SONG X, et al. The Healing Effects of Conditioned Medium Derived from Mesenchymal Stem Cells on Radiation-Induced Skin Wounds in Rats. Cell Transplant. 2019;28(1):105-115. [34] LIN H, CHEN H, ZHAO X, et al. Advances in mesenchymal stem cell conditioned medium-mediated periodontal tissue regeneration. J Transl Med. 2021;19(1):456. [35] LIU G, DAVID BT, TRAWCZYNSKI M, et al. Advances in Pluripotent Stem Cells: History, Mechanisms, Technologies, and Applications. Stem Cell Rev Rep. 2020;16(1):3-32. [36] KIM MH, WU WH, CHOI JH, et al. Galectin-1 from conditioned medium of three-dimensional culture of adipose-derived stem cells accelerates migration and proliferation of human keratinocytes and fibroblasts. Wound Repair Regen. 2018;26 Suppl 1:S9-S18. [37] RAJA IS, JANG HJ, KANG MS, et al. Role of Graphene Family Nanomaterials in Skin Wound Healing and Regeneration. Adv Exp Med Biol. 2022;1351:89-105. [38] BRUNCHUKOV V, ASTRELINA T, USUPZHANOVA D, et al. Evaluation of the Effectiveness of Mesenchymal Stem Cells of the Placenta and Their Conditioned Medium in Local Radiation Injuries. Cells. 2020;9(12):2558. [39] ZHANG G, LI J, WANG D, et al. The mechanisms related to fibroblasts in burn surface. Skin Res Technol. 2023;29(8):e13431. [40] AKITA S, AKINO K, IMAIZUMI T, et al. Basic fibroblast growth factor accelerates and improves second-degree burn wound healing. Wound Repair Regen. 2008;16(5):635-641. [41] MANDLA S, DAVENPORT HUYER L, RADISIC M. Review: Multimodal bioactive material approaches for wound healing. APL Bioeng. 2018; 2(2):021503. [42] MŰZES G, SIPOS F. Mesenchymal Stem Cell-Derived Secretome: A Potential Therapeutic Option for Autoimmune and Immune-Mediated Inflammatory Diseases. Cells. 2022;11(15):2300. [43] JO H, BRITO S, KWAK BM, et al. Applications of Mesenchymal Stem Cells in Skin Regeneration and Rejuvenation. Int J Mol Sci. 2021;22(5):2410. [44] KWON JW, SAVITRI C, AN B, et al. Mesenchymal stem cell-derived secretomes-enriched alginate/ extracellular matrix hydrogel patch accelerates skin wound healing. Biomater Res. 2023;27(1):107. [45] WERNER S, GROSE R. Regulation of wound healing by growth factors and cytokines. Physiol Rev. 2003;83(3):835-870. [46] WU S, SUN S, FU W, et al. The Role and Prospects of Mesenchymal Stem Cells in Skin Repair and Regeneration. Biomedicines. 2024; 12(4):743. [47] WANG Y, CAO Z, WEI Q, et al. VH298-loaded extracellular vesicles released from gelatin methacryloyl hydrogel facilitate diabetic wound healing by HIF-1α-mediated enhancement of angiogenesis. Acta Biomater. 2022;147:342-355. [48] HEYDARI MB, GHANBARI-MOVAHED Z, HEYDARI M, et al. In vitro study of the mesenchymal stem cells-conditional media role in skin wound healing process: A systematic review. Int Wound J. 2022;19(8): 2210-2223. [49] NIE S, REN C, LIANG X, et al. Supramolecular Hydrogel-Wrapped Gingival Mesenchymal Stem Cells in Cutaneous Radiation Injury. Cells. 2022;11(19):3089. |
| [1] | Liu Xiaohong, Zhao Tian, Mu Yunping, Feng Wenjin, Lyu Cunsheng, Zhang Zhiyong, Zhao Zijian, Li Fanghong. Acellular dermal matrix hydrogel promotes skin wound healing in rats [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(2): 395-403. |
| [2] | Huang Xinxu, Zhang Xin, Wang Jian. Living microecological hydrogels promote skin wound healing [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(2): 489-498. |
| [3] | Wang Zhuo, Sun Panpan, Cheng Huanzhi, Cao Tingting. Application of chitosan in repair and regeneration of oral hard and soft tissues [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(2): 459-468. |
| [4] | Sun Huiwen, Guo Qiangqiang, Wang Wei, Wu Jie, Xi Kun, Gu Yong. Engineered stem cell bionic periosteum coordinates immune inflammation and vascularization to promote bone regeneration [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(1): 21-33. |
| [5] | Zuo Na, Tang Qi, Yu Meng, Tao Kai. Effect of miR-196b-5p in adipose-derived stem cell exosomes on burn wound healing in rats [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(1): 43-49. |
| [6] | Wu Zhijing, Li Jiali, Zhang Jiaxin, Wang Tangrong, Zheng Yuzhou, Sun Zixuan. Alpha-ketoglutarate engineered small extracellular vesicles delay skin aging [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(1): 120-129. |
| [7] | Xu Haichao, Luo Lihua, Pan Yihuai. Application and progress of dental pulp stem cells and their derivatives in dental pulp regeneration [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(1): 153-162. |
| [8] | Zhang Zhaowei, Chen Ouzile, Bai Mingru, Wang Chenglin. Therapeutic potential of bioactive substances secreted by dental mesenchymal stem cells for bone repair [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(1): 163-174. |
| [9] | Yao Lijie, Yan Yuying, Chen Siyu, Wang Yuanfei, Wu Tong. Nanofibers with gradient deposition of endothelial cell derived matrix particles modulate the behavior of Schwann cells [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(在线): 1-10. |
| [10] | Hu Taotao, Liu Bing, Chen Cheng, Yin Zongyin, Kan Daohong, Ni Jie, Ye Lingxiao, Zheng Xiangbing, Yan Min, Zou Yong. Human amniotic mesenchymal stem cells overexpressing neuregulin-1 promote skin wound healing in mice [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(7): 1343-1349. |
| [11] | Jin Kai, Tang Ting, Li Meile, Xie Yuan. Effects of conditioned medium and exosomes of human umbilical cord mesenchymal stem cells on proliferation, migration, invasion, and apoptosis of hepatocellular carcinoma cells [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(7): 1350-1355. |
| [12] | Li Dijun, Jiu Jingwei, Liu Haifeng, Yan Lei, Li Songyan, Wang Bin. Three-dimensional gelatin microspheres loaded human umbilical cord mesenchymal stem cells for chronic tendinopathy repair [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(7): 1356-1362. |
| [13] | Li Jialin, Zhang Yaodong, Lou Yanru, Yu Yang, Yang Rui. Molecular mechanisms underlying role of mesenchymal stem cell secretome [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(7): 1512-1522. |
| [14] | Dong Meilin, Du Haiyu, Liu Yuan. Quercetin-loaded carboxymethyl chitosan hydrogel promotes wound healing in diabetic rats [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(4): 692-699. |
| [15] | Wu Chen, Jiang Jiahui, Su Dou, Liu Chen, Ci Chao. Decellularized skin matrix/polyurethane blended fibrous scaffolds promote repair of skin defects in rats [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(4): 745-751. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||