Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research ›› 2026, Vol. 30 ›› Issue (1): 120-129.doi: 10.12307/2026.538
Previous Articles Next Articles
Alpha-ketoglutarate engineered small extracellular vesicles delay skin aging
Wu Zhijing1, 2, Li Jiali1, 2, Zhang Jiaxin1, 2, Wang Tangrong1, 2, Zheng Yuzhou1, 2, Sun Zixuan1, 2
- 1Department of Laboratory Medicine, Medical College of Jiangsu University, Zhenjiang 212013, Jiangsu Province, China; 2Zhenjiang Key Laboratory of High Technology Research on Exosomes Foundation and Transformation Application, Zhenjiang 212013, Jiangsu Province, China
-
Received:2024-11-15Accepted:2025-01-21Online:2026-01-08Published:2025-07-02 -
Contact:Sun Zixuan, MD, Associate professor, Master’s supervisor, Department of Laboratory Medicine, Medical College of Jiangsu University, Zhenjiang 212013, Jiangsu Province, China; Zhenjiang Key Laboratory of High Technology Research on Exosomes Foundation and Transformation Application, Zhenjiang 212013, Jiangsu Province, China -
About author:Wu Zhijing, Master candidate, Department of Laboratory Medicine, Medical College of Jiangsu University, Zhenjiang 212013, Jiangsu Province, China; Zhenjiang Key Laboratory of High Technology Research on Exosomes Foundation and Transformation Application, Zhenjiang 212013, Jiangsu Province, China -
Supported by:National Natural Science Foundation of China, No. 82003379 (to SZX)
CLC Number:
Cite this article
Wu Zhijing, Li Jiali, Zhang Jiaxin, Wang Tangrong, Zheng Yuzhou, Sun Zixuan. Alpha-ketoglutarate engineered small extracellular vesicles delay skin aging[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(1): 120-129.
share this article
Add to citation manager EndNote|Reference Manager|ProCite|BibTeX|RefWorks
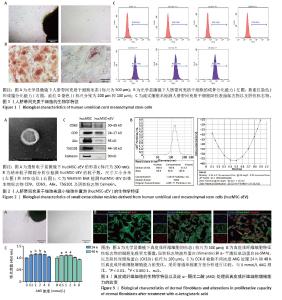
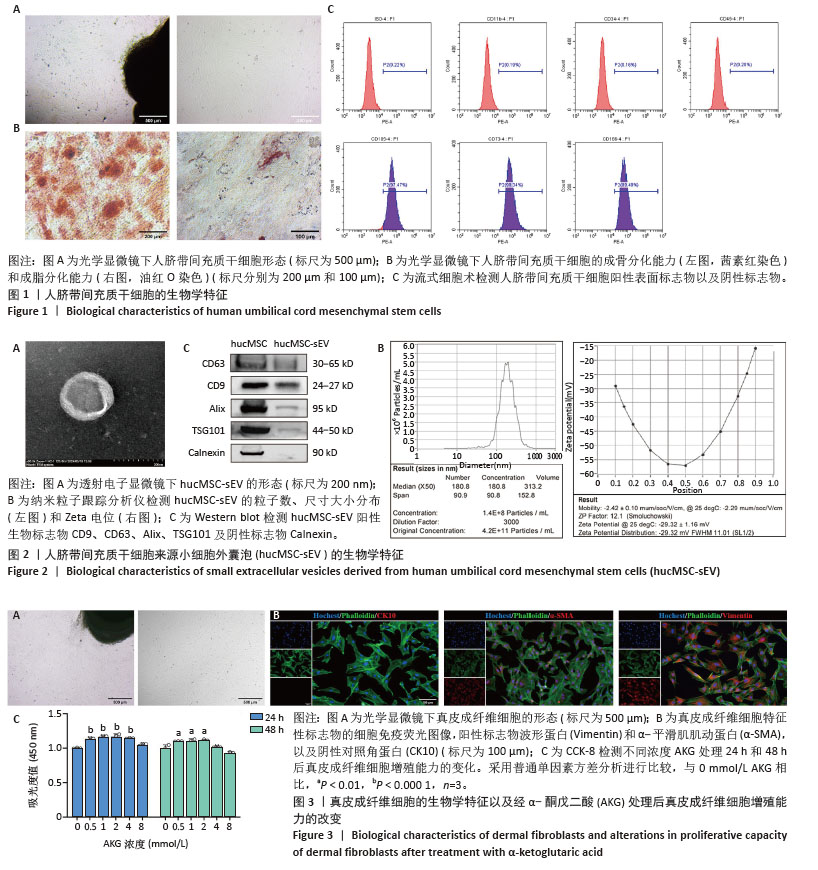
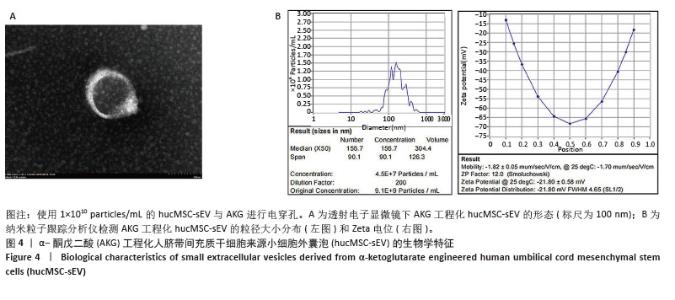
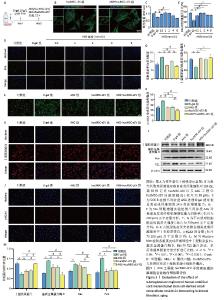
2.1 人脐带间充质干细胞及hucMSC-sEV的生物学特征 分离培养的原代人脐带间充质干细胞从组织块周围爬出,细胞形态呈梭状,细胞状态良好呈漩涡状生长,见图1A;经过成骨和成脂培养基诱导分化后进行茜素红或油红O染色,可见明显的钙结节和脂滴,表明人脐带间充质干细胞成骨、成脂分化能力良好,见图1B;流式细胞术结果表明,人脐带间充质干细胞高表达阳性标志物CD105、CD73、CD166,阴性标志物CD11b、 CD34、CD45和ISO几乎不表达,见图1C,符合间充质干细胞的生物学特征。 收集人脐带间充质干细胞上清液,进行差速-超速离心法得到hucMSC-sEV,在透射电镜下观察到hucMSC-sEV有典型的囊泡膜结构并且呈茶托状,见图2A;纳米粒子跟踪分析仪检测粒径分布在180.8 nm处,Zeta电位为(-29.32±1.16) mV,见图2B;Western blot结果显示,hucMSC-sEV表达小细胞外囊泡特征性标志物CD63、CD9、Alix、TSG101,不表达阴性标志物Calnexin,见图2C。 2.2 AKG对真皮成纤维细胞增殖能力的影响 分离培养的真皮成纤维细胞从大鼠乳鼠的皮肤组织块中爬出,细胞形态呈短梭状,细胞状态良好呈漩涡状生长,见图3A;细胞免疫荧光结果显示,真皮成纤维细胞表达特征性标志物波形蛋白和α-平滑肌肌动蛋白,不表达阴性标志物即表皮标志物角蛋白10,见图3B,符合真皮成纤维细胞的生物学特征。分别将0.5,1,2,4,8 mmol/L的AKG与真皮成纤维细胞共孵育24 h和48 h,CCK-8结果显示AKG没有抑制真皮成纤维细胞的增殖,表明AKG对真皮成纤维细胞无毒性,见图3C,由于在传统的电穿孔过程中投入的药物量会有一定的损失,同时通过参考相关文献[35],最终选择2 mmol/L浓度进行后续实验。 "
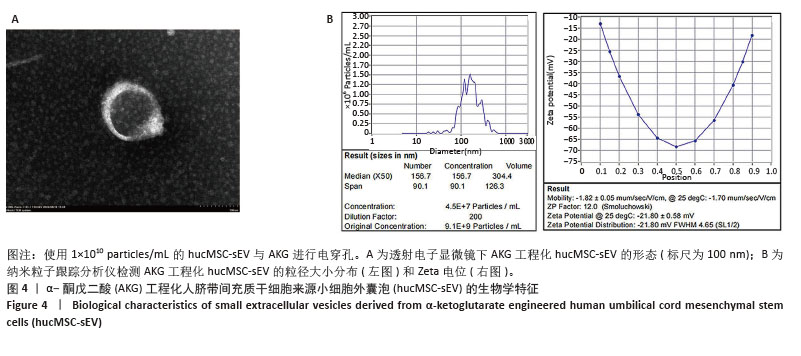
2.3 AKG工程化hucMSC-sEV的构建与鉴定 使用电穿孔技术,分别将2 mmol/L的AKG载入5×109 particles/mL,1×1010 particles/mL和5×1010 particles/mL的hucMSC-sEV中,在透射电镜下观察到AKG工程化hucMSC-sEV囊泡膜结构完整并呈茶托状,见图4A;纳米粒子跟踪分析仪检测AKG工程化hucMSC-sEV的粒子分布和Zeta电位,与hucMSC-sEV相比均无明显变化,表明电穿孔对小细胞外囊泡几乎无损伤作用,见图4B。使用高效液相色谱技术检测AKG工程化hucMSC-sEV的包封率,得到标准曲线为Y=1 613 593.088X+ 21 958.278,R2=0.999 9,表明AKG的浓度在0-5 mmol/L范围内线性关系良好。通过公式计算5×109,1×1010,5× 1010 particles/mL的hucMSC-sEV与AKG进行电穿孔后相应的包封率分别为(44.93±0.97)%,(45.38±4.36)%和(40.13±2.31)%,结果显示当小细胞外囊泡粒子数在1×1010 particles/mL时包封率最高,因此选择此浓度进行后续实验。 "
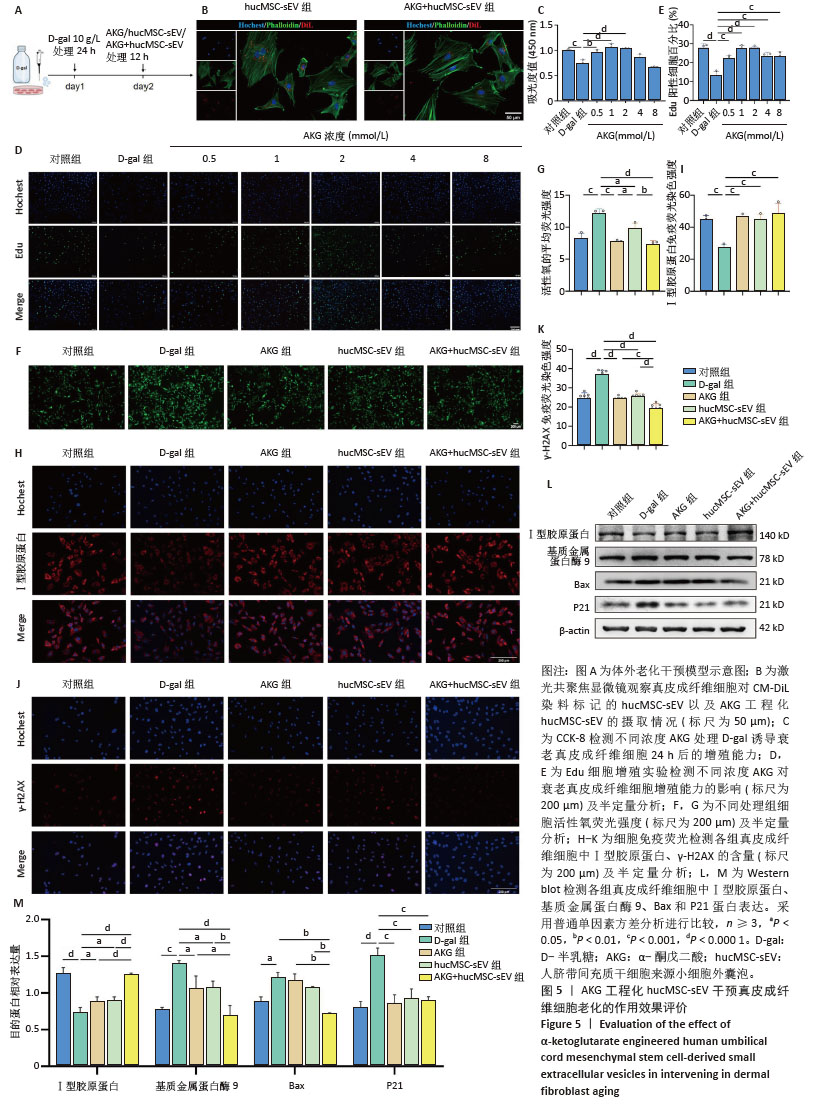
2.4 AKG工程化hucMSC-sEV延缓D-半乳糖诱导的真皮成纤维细胞衰老进程 建立真皮成纤维细胞老化模型,见图5A,在D-半乳糖处理24 h后,向细胞中分别加入AKG或hucMSC-sEV或AKG工程化hucMSC-sEV处理12 h进行后续实验。在共聚焦显微镜下观察到hucMSC-sEV与真皮成纤维细胞共孵育12 h后能被有效摄取,而AKG工程化hucMSC-sEV组的摄取效率要略低于hucMSC-sEV组,可能与电穿孔造成小细胞外囊泡数量上的损失有关,见图5B。 2.4.1 AKG工程化hucMSC-sEV促进衰老真皮成纤维细胞的增殖 通过CCK-8法来评估不同浓度AKG对D-半乳糖诱导的衰老真皮成纤维细胞增殖的影响。使用0.5,1,2,4,8 mmol/L AKG与真皮成纤维细胞共孵育,CCK-8结果显示AKG浓度在2 mmol/L以内时,对衰老的真皮成纤维细胞有促增殖作用,且当浓度为1 mmol/L和2 mmol/L时效果最为显著,Edu细胞增殖实验也具有相同的结果,见图5C-E,结合AKG对真皮成纤维细胞的毒性实验,以及药物在电穿孔过程中存在损失,最终选取2 mmol/L进行后续实验。 2.4.2 AKG工程化hucMSC-sEV降低衰老真皮成纤维细胞氧化应激水平 使用活性氧评估不同处理组衰老真皮成纤维细胞内氧化应激水平,结果显示,与D-半乳糖组相比,各处理组显著抑制了细胞内活性氧的产生,降低了氧化应激水平,其中AKG工程化hucMSC-sEV组效果更优,见图5F-G。 2.4.3 AKG工程化hucMSC-sEV减少真皮成纤维细胞的胶原蛋白流失并降低DNA损伤水平 Western blot结果显示,与D-半乳糖组相比,AKG工程化hucMSC-sEV组能有效增加Ⅰ型胶原蛋白表达,并下调基质金属蛋白酶9表达,在一定程度上抑制了胶原蛋白的降解,同时下调Bax蛋白表达,有效抑制了细胞凋亡,此外衰老相关标志物P21表达水平也显著下调。细胞免疫荧光结果也证实,AKG组、hucMSC-sEV组和AKG工程化hucMSC-sEV组均能提升Ⅰ型胶原蛋白表达水平,下调DNA双链断裂标志物γ-H2AX表达水平,表明经处理后,衰老真皮成纤维细胞的胶原蛋白含量有所恢复,DNA断裂引起的损伤减轻,其中AKG工程化hucMSC-sEV组的效果最好,见图5H-M。"
| [1] FRANCO AC, AVELEIRA C, CAVADAS C. Skin senescence: mechanisms and impact on whole-body aging. Trends Mol Med. 2022;28(2):97-109. [2] CSEKES E, RAČKOVÁ L. Skin Aging, Cellular Senescence and Natural Polyphenols. Int J Mol Sci. 2021;22(23):12641. [3] GRIFFITHS TW, WATSON REB, LANGTON AK. Skin ageing and topical rejuvenation strategies. Br J Dermatol. 2023;189(Suppl 1):i17-i23. [4] BLAIR MJ, JONES JD, WOESSNER AE, et al. Skin Structure-Function Relationships and the Wound Healing Response to Intrinsic Aging. Adv Wound Care (New Rochelle). 2020;9(3):127-143. [5] HÖHN A, WEBER D, JUNG T, et al. Happily (n)ever after: Aging in the context of oxidative stress, proteostasis loss and cellular senescence. Redox Biol. 2017;11:482-501. [6] HARLEY CB, FUTCHER AB, GREIDER CW. Telomeres shorten during ageing of human fibroblasts. Nature. 1990;345(6274):458-460. [7] PEZONE A, OLIVIERI F, NAPOLI MV, et al. Inflammation and DNA damage: cause, effect or both. Nat Rev Rheumatol. 2023;19(4):200-211. [8] BHARATH LP, AGRAWAL M, MCCAMBRIDGE G, et al. Metformin Enhances Autophagy and Normalizes Mitochondrial Function to Alleviate Aging-Associated Inflammation. Cell Metab. 2020;32(1): 44-55.e6. [9] ANSARY TM, HOSSAIN MR, KAMIYA K, et al. Inflammatory Molecules Associated with Ultraviolet Radiation-Mediated Skin Aging. Int J Mol Sci. 2021;22(8):3974. [10] LOVELL CR, SMOLENSKI KA, DUANCE VC, et al. Type I and III collagen content and fibre distribution in normal human skin during ageing. Br J Dermatol. 1987;117(4):419-428. [11] WANG H, WEI S, XUE X, et al. Adipose stem cells’ antagonism in glycosylation of D-galactose-induced skin aging of nude mice and its skin recovery function. Int J Immunopathol Pharmacol. 2016;29(3): 376-385. [12] CRISAN M, TAULESCU M, CRISAN D, et al. Expression of advanced glycation end-products on sun-exposed and non-exposed cutaneous sites during the ageing process in humans. PLoS One. 2013;8(10):e75003. [13] WANG L, JIANG Y, ZHAO C. The effects of advanced glycation end-products on skin and potential anti-glycation strategies. Exp Dermatol. 2024;33(4):e15065. [14] MAURELLI M, GISONDI P, GIROLOMONI G. Advanced Glycation End Products and Psoriasis. Vaccines (Basel). 2023;11(3):617. [15] THÉRY C, WITWER KW, AIKAWA E, et al. Minimal information for studies of extracellular vesicles 2018 (MISEV2018): a position statement of the International Society for Extracellular Vesicles and update of the MISEV2014 guidelines. J Extracell Vesicles. 2018;7(1):1535750. [16] ZHANG H, XIAO X, WANG L, et al. Human adipose and umbilical cord mesenchymal stem cell-derived extracellular vesicles mitigate photoaging via TIMP1/Notch1. Signal Transduct Target Ther. 2024; 9(1):294. [17] SUN Z, WANG T, HOU X, et al. Mesenchymal stromal cells-derived small extracellular vesicles protect against UV-induced photoaging via regulating pregnancy zone protein. Stem Cells Transl Med. 2024; 13(11):1129-1143. [18] RÄDLER J, GUPTA D, ZICKLER A, et al. Exploiting the biogenesis of extracellular vesicles for bioengineering and therapeutic cargo loading. Mol Ther. 2023;31(5):1231-1250. [19] 张咪,吴赛璇,董明,等.新型纳米递送系统:工程化小细胞外囊泡[J].中国组织工程研究,2022,26(27):4417-4422. [20] WU P, ZHANG B, OCANSEY DKW, et al. Extracellular vesicles: A bright star of nanomedicine. Biomaterials. 2021;269:120467. [21] HERRMANN IK, WOOD MJA, FUHRMANN G. Extracellular vesicles as a next-generation drug delivery platform. Nat Nanotechnol. 2021; 16(7):748-759. [22] YUAN Y, ZHU C, WANG Y, et al. α-Ketoglutaric acid ameliorates hyperglycemia in diabetes by inhibiting hepatic gluconeogenesis via serpina1e signaling. Sci Adv. 2022;8(18):eabn2879. [23] 吴楠.α-酮戊二酸在果蝇抗衰老中的作用及其机制研究[D].雅安:四川农业大学,2017. [24] CHIN RM, FU X, PAI MY, et al. The metabolite α-ketoglutarate extends lifespan by inhibiting ATP synthase and TOR. Nature. 2014; 510(7505):397-401. [25] YANG F, ZHOU Z, GUO M, et al. The study of skin hydration, anti-wrinkles function improvement of anti-aging cream with alpha-ketoglutarate. J Cosmet Dermatol. 2022;21(4):1736-1743. [26] SON ED, CHOI GH, KIM H, et al. Alpha-ketoglutarate stimulates procollagen production in cultured human dermal fibroblasts, and decreases UVB-induced wrinkle formation following topical application on the dorsal skin of hairless mice. Biol Pharm Bull. 2007;30(8): 1395-1399. [27] ASADI SHAHMIRZADI A, EDGAR D, LIAO CY, et al. Alpha-Ketoglutarate, an Endogenous Metabolite, Extends Lifespan and Compresses Morbidity in Aging Mice. Cell Metab. 2020;32(3):447-456.e6. [28] LIU S, HE L, YAO K. The Antioxidative Function of Alpha-Ketoglutarate and Its Applications. Biomed Res Int. 2018;2018:3408467. [29] SALMINEN A, KAARNIRANTA K. AMP-activated protein kinase (AMPK) controls the aging process via an integrated signaling network. Ageing Res Rev. 2012;11(2):230-241. [30] BAYLIAK MM, LUSHCHAK VI. Pleiotropic effects of alpha-ketoglutarate as a potential anti-ageing agent. Ageing Res Rev. 2021;66:101237. [31] KOMURO H, AMINOVA S, LAURO K, et al. Advances of engineered extracellular vesicles-based therapeutics strategy. Sci Technol Adv Mater. 2022;23(1):655-681. [32] MUKHOPADHYA A, TSIAPALIS D, MCNAMEE N, et al. Doxorubicin Loading into Milk and Mesenchymal Stem Cells’ Extracellular Vesicles as Drug Delivery Vehicles. Pharmaceutics. 2023;15(3):718. [33] CHEN C, LI Y, WANG Q, et al. Single-particle assessment of six different drug-loading strategies for incorporating doxorubicin into small extracellular vesicles. Anal Bioanal Chem. 2023;415(7):1287-1298. [34] TIAN J, HAN Z, SONG D, et al. Engineered Exosome for Drug Delivery: Recent Development and Clinical Applications. Int J Nanomedicine. 2023;18:7923-7940. [35] WANG Y, DENG P, LIU Y, et al. Alpha-ketoglutarate ameliorates age-related osteoporosis via regulating histone methylations. Nat Commun. 2020;11(1):5596. [36] LEE CM, WATSON REB, KLEYN CE. The impact of perceived stress on skin ageing. J Eur Acad Dermatol Venereol. 2020;34(1):54-58. [37] SHIN SH, LEE YH, RHO NK, et al. Skin aging from mechanisms to interventions: focusing on dermal aging. Front Physiol. 2023;14: 1195272. [38] KRUTMANN J, SCHIKOWSKI T, MORITA A, et al. Environmentally-Induced (Extrinsic) Skin Aging: Exposomal Factors and Underlying Mechanisms. J Invest Dermatol. 2021;141(4S):1096-1103. [39] KOHL E, STEINBAUER J, LANDTHALER M, et al. Skin ageing. J Eur Acad Dermatol Venereol. 2011;25(8):873-884. [40] MARTINI H, PASSOS JF. Cellular senescence: all roads lead to mitochondria. FEBS J. 2023;290(5):1186-1202. [41] SREEDHAR A, AGUILERA-AGUIRRE L, SINGH KK. Mitochondria in skin health, aging, and disease. Cell Death Dis. 2020;11(6):444. [42] POLJŠAK B, DAHMANE RG, GODIĆ A. Intrinsic skin aging: the role of oxidative stress. Acta Dermatovenerol Alp Pannonica Adriat. 2012; 21(2):33-36. [43] LEE H, HONG Y, KIM M. Structural and Functional Changes and Possible Molecular Mechanisms in Aged Skin. Int J Mol Sci. 2021;22(22):12489. [44] UMBAYEV B, ASKAROVA S, ALMABAYEVA A, et al. Galactose-Induced Skin Aging: The Role of Oxidative Stress. Oxid Med Cell Longev. 2020; 2020:7145656. [45] KUMAR H, BHARDWAJ K, VALKO M, et al. Antioxidative potential of Lactobacillus sp. in ameliorating D-galactose-induced aging. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol. 2022;106(13-16):4831-4843. [46] WEI H, LI L, SONG Q, et al. Behavioural study of the D-galactose induced aging model in C57BL/6J mice. Behav Brain Res. 2005;157(2):245-251. [47] AZMAN KF, ZAKARIA R. D-Galactose-induced accelerated aging model: an overview. Biogerontology. 2019;20(6):763-782. [48] DU XL, EDELSTEIN D, ROSSETTI L, et al. Hyperglycemia-induced mitochondrial superoxide overproduction activates the hexosamine pathway and induces plasminogen activator inhibitor-1 expression by increasing Sp1 glycosylation. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2000;97(22): 12222-12226. [49] GYANWALI B, LIM ZX, SOH J, et al. Alpha-Ketoglutarate dietary supplementation to improve health in humans. Trends Endocrinol Metab. 2022;33(2):136-146. [50] WIKLANDER OPB, BRENNAN MÁ, LÖTVALL J, et al. Advances in therapeutic applications of extracellular vesicles. Sci Transl Med. 2019;11(492):eaav8521. |
| [1] | Haonan Yang, Zhengwei Yuan, Junpeng Xu, Zhiqi Mao, Jianning Zhang. Preliminary study on the mechanisms and efficacy of deep brain stimulation in treating depression [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(在线): 1-9. |
| [2] | Hu Jing, Zhu Ling, Xie Juan, Kong Deying, Liu Doudou. Autophagy regulates early embryonic development in mice via affecting H3K4me3 modification [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(5): 1147-1155. |
| [3] | Yang Xiao, Bai Yuehui, Zhao Tiantian, Wang Donghao, Zhao Chen, Yuan Shuo. Cartilage degeneration in temporomandibular joint osteoarthritis: mechanisms and regenerative challenges [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(4): 926-935. |
| [4] | Dong Chao, Zhao Mohan, Liu Yunan, Yang Zeli, Chen Leqin, Wang Lanfang. Effects of magnetic nano-drug carriers on exercise-induced muscle injury and inflammatory response in rats [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(2): 345-353. |
| [5] | Wang Yaping, Gao Tianyun, Wang Bin. Senescence of human bone marrow mesenchymal stromal cells with increasing age is not dependent on the mediation of endogenous retroviruses [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(1): 10-20. |
| [6] | Xue Hui, Li Dongnan, Zhao Yadi, Chen Chao, Xie Zongyuan. Relationship between BCR/ABL gene expression and recurrence before and after allogeneic transplantation in Ph chromosome positive acute lymphoblastic leukemia [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(1): 139-144. |
| [7] | Lyu Ruyue, Gu Lulu, Liu Qian, Zhou Siyi, Li Beibei, Xue Letian, Sun Peng. Regulatory mechanisms of exosome secretion and its application prospects in biomedicine [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(1): 184-193. |
| [8] | Luo Wenbin, Li Ruoyun, Pan Chaofan, Luo Changjiang. Engineered exosomes for repairing tissue damage: application potential, excellent biological stability, and targeting specificity [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(1): 204-217. |
| [9] | Liu Ziwei, Nijati·Tursun, Yin Rui, Li Shuhui, Zhou Jing. Effect of cannabinoid type I receptors on neuronal differentiation of human apical papilla stem cells [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(1): 93-100. |
| [10] | Li Zikai, Zhang Chengcheng, Xiong Jiaying, Yang Xirui, Yang Jing, Shi Haishan. Potential effects of ornidazole on intracanal vascularization in endodontic regeneration [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(在线): 1-7. |
| [11] | Yao Lijie, Yan Yuying, Chen Siyu, Wang Yuanfei, Wu Tong. Nanofibers with gradient deposition of endothelial cell derived matrix particles modulate the behavior of Schwann cells [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(在线): 1-10. |
| [12] | Zhang Yibo, Lu Jianqi, Mao Meiling, Pang Yan, Dong Li, Yang Shangbing, Xiao Xiang. Exploring the causal relationship between rheumatoid arthritis and coronary atherosclerosis: a Mendel randomized study involving serum metabolites and inflammatory factors [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(在线): 1-9. |
| [13] | Xu Hao, Ding Lu, Li Xiao. Investigating the effect of the mechanical wear on abutment screw in Morse taper connection implant implant system by using finite element analysis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(在线): 1-9. |
| [14] | Zhao Jiyu, Wang Shaowei. Forkhead box transcription factor O1 signaling pathway in bone metabolism [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(9): 1923-1930. |
| [15] | Jin Kai, Tang Ting, Li Meile, Xie Yuan. Effects of conditioned medium and exosomes of human umbilical cord mesenchymal stem cells on proliferation, migration, invasion, and apoptosis of hepatocellular carcinoma cells [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(7): 1350-1355. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||