Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research ›› 2026, Vol. 30 ›› Issue (1): 43-49.doi: 10.12307/2025.927
Previous Articles Next Articles
Effect of miR-196b-5p in adipose-derived stem cell exosomes on burn wound healing in rats
Zuo Na, Tang Qi, Yu Meng, Tao Kai
- Department of Burn Plastic Microsurgery, Fourth Affiliated Hospital of China Medical University, Shenyang 110000, Liaoning Province, China
-
Received:2024-10-11Accepted:2024-12-03Online:2026-01-08Published:2025-06-16 -
Contact:Tao Kai, MD, Chief physician, Department of Burn Plastic Microsurgery, Fourth Affiliated Hospital of China Medical University, Shenyang 110000, Liaoning Province, China -
About author:Zuo Na, MS, Attending physician, Department of Burn Plastic Microsurgery, Fourth Affiliated Hospital of China Medical University, Shenyang 110000, Liaoning Province, China -
Supported by:Liaoning Provincial Science and Technology Plan, No. 2021JH2/10300108 (to TK)
CLC Number:
Cite this article
Zuo Na, Tang Qi, Yu Meng, Tao Kai. Effect of miR-196b-5p in adipose-derived stem cell exosomes on burn wound healing in rats[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(1): 43-49.
share this article
Add to citation manager EndNote|Reference Manager|ProCite|BibTeX|RefWorks
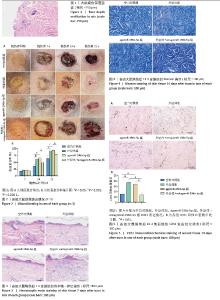
2.1 实验动物数量分析 40只SD大鼠全部进入结果分析。 2.2 烧伤深度验证 烧伤后24 h取创面行病理检测,病理切片证实为深Ⅱ度烧伤(图1),表现为表皮部分脱落,结构不清,局部坏死、变形,真皮间质充血、疏松。 2.3 大鼠创面愈合情况 如图2所示,外泌体组和agomiR-196b-5p组创面愈合率较空白对照组和外泌体+antagomiR-196b-5p组明显加快,有统计学差异(P < 0.000 1),在外泌体中加入antagomiR-196b-5p后逆转了外泌体对创面的促愈合作用(P < 0.05)。 2.4 苏木精-伊红染色结果 烧伤后7 d创面组织行苏木精-伊红染色,检测各组创面炎症浸润情况。如图3所示,外泌体组和agomiR-196b-5p组创面炎性细胞浸润较少,而空白对照组和外泌体+antagomiR-196b-5p组炎性细胞浸润较多,在外泌体中加入antagomiR-196b-5p后逆转了外泌体减轻炎症浸润的作用。 2.5 Masson染色结果 烧伤后14 d创面组织行Masson染色,检测各组创面胶原表达。如图4所示,外泌体组和agomiR-196b-5p组胶原表达明显增多,排列较为规整,而空白对照组和外泌+antagomiR-196b-5p组胶原排列较乱,在外泌体中加入antagomiR-196b-5p后逆转了外泌体促进胶原生成的作用。 2.6 免疫组化结果 烧伤后14 d取创面组织行免疫组化分析,检测各组创面中CD31表达。如图5所示,与空白对照组相比,外泌体组和agomiR-196b-5p组CD31表达明显增加,差异有显著性意义(P < 0.01),而与外泌体组和agomiR-196b-5p组相比,外泌体+antagomiR-196b-5p组CD31表达较少,差异有显著性意义(P < 0.01),说明外泌体组和agomiR-196b-5p组血管生成增加,在外泌体中加入antagomiR-196b-5p后逆转了外泌体促进血管生成的作用。 "
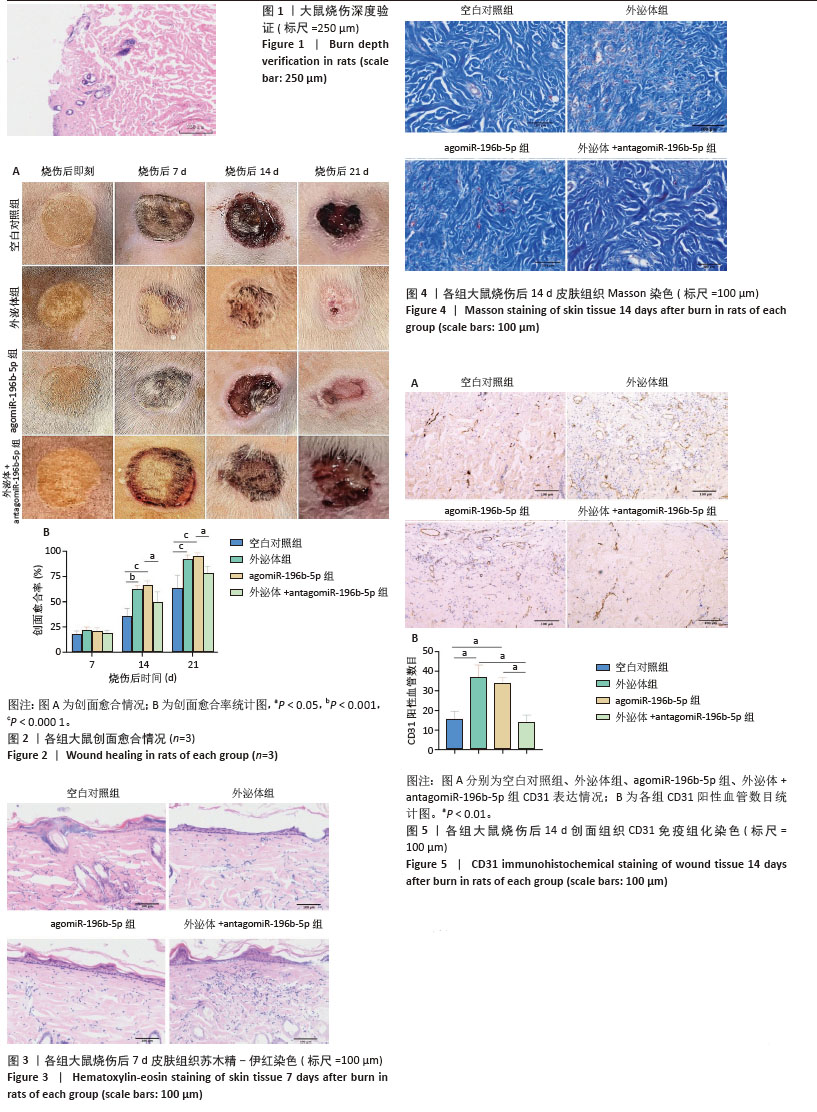
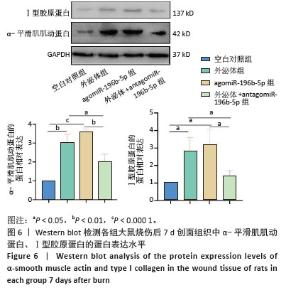
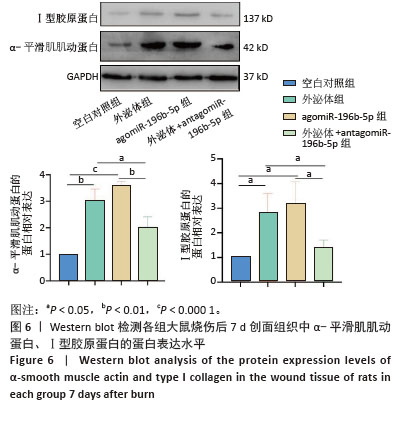
2.7 Western blot结果 烧伤后7 d取创面组织行Western blot实验,检测各组α-平滑肌肌动蛋白和Ⅰ型胶原蛋白的蛋白表达水平。如图6所示,与空白对照组相比,外泌体组和agomiR-196b-5p组α-平滑肌肌动蛋白的蛋白表达水平增高(P < 0.01和P < 0.001),在外泌体中加入antagomiR-196b-5p后逆转了外泌体促进α-平滑肌肌动蛋白表达的作用,α-平滑肌肌动蛋白的蛋白表达水平降低 (P < 0.05)。与空白对照组相比,外泌体组和agomiR-196b-5p组Ⅰ型胶原蛋白的蛋白表达水平增高(均P < 0.05),在外泌体中加入antagomiR-196b-5p后逆转了外泌体促进Ⅰ型胶原蛋白表达的作用,Ⅰ型胶原蛋白的蛋白表达水平降低(P < 0.05)。以上结果说明,miR-196b-5p在创面愈合中具有促进创口收缩、胶原生成的作用。 "
| [1] REZAEI YAZDI F, GHAHARY A, MIRDORAGHI M, et al. Promotion of Burn Wound Healing by Local Application of Adipose-Derived Mesenchymal Stem Cells: An Experimental Study. Med J Islam Repub Iran. 2021;35:172. [2] WU LL, ZHANG XY, LI X, et al. miR-196b-5p promotes myoblast proliferation and differentiation. Yi Chuan. 2023;45(5):435-446. [3] ZHU W, YU Y, YE Y, et al. MiR-196b-5p activates NF-κB signaling in non-small cell lung cancer by directly targeting NFKBIA. Transl Oncol. 2023;37:101755. [4] WANG QZ, ZHAO ZL, LIU C, et al. Exosome-derived miR-196b-5p facilitates intercellular interaction in infantile hemangioma via down-regulating CDKN1B. Ann Transl Med. 2021;9(5):394. [5] 丁毅,吾拉尔•阿德力,李敏,等.一种简便的大鼠Ⅱ度烫伤模型制备方法[J].临床与病理杂志,2021,41(3):517-522. [6] ABDUL KAREEM N, AIJAZ A, JESCHKE MG. Stem Cell Therapy for Burns: Story so Far. Biologics. 2021;15:379-397. [7] 王宏宇,刘玲英,巴特.间充质干细胞在烧伤创面修复中的研究进展[J].中华损伤与修复杂志(电子版),2020,15(6):495-498. [8] WANG X, JIAO Y, PAN Y, et al. Fetal Dermal Mesenchymal Stem Cell-Derived Exosomes Accelerate Cutaneous Wound Healing by Activating Notch Signaling. Stem Cells Int. 2019;2019:2402916. [9] 刘忠钰,李文娅,范永鸿,等.甲基丙烯酰化改性真皮细胞外基质水凝胶促进腹壁缺损修复[J].中国组织工程研究,2025,29(10): 2074-2082. [10] ZENG QL, LIU DW. Mesenchymal stem cell-derived exosomes: An emerging therapeutic strategy for normal and chronic wound healing. World J Clin Cases. 2021;9(22):6218-6233. [11] JO H, BRITO S, KWAK BM, et al. Applications of Mesenchymal Stem Cells in Skin Regeneration and Rejuvenation. Int J Mol Sci. 2021;22(5):2410. [12] HSIEH MW, WANG WT, LIN CY, et al. Stem Cell-Based Therapeutic Strategies in Diabetic Wound Healing. Biomedicines. 2022;10(9):2085. [13] HOSSEINI M, DALLEY AJ, SHAFIEE A. Convergence of Biofabrication Technologies and Cell Therapies for Wound Healing. Pharmaceutics. 2022;14(12):2749. [14] KOLANTHAI E, FU Y, KUMAR U, et al. Nanoparticle mediated RNA delivery for wound healing. Wiley Interdiscip Rev Nanomed Nanobiotechnol. 2022;14(2):e1741. [15] HEO JS, KIM S, YANG CE, et al. Human Adipose Mesenchymal Stem Cell-Derived Exosomes: A Key Player in Wound Healing. Tissue Eng Regen Med. 2021;18(4):537-548. [16] TRAMS EG, LAUTER CJ, SALEM N JR, et al. Exfoliation of membrane ecto-enzymes in the form of micro-vesicles. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1981;645(1):63-70. [17] WANG ZY, WEN ZJ, XU HM, et al. Exosomal noncoding RNAs in central nervous system diseases: biological functions and potential clinical applications. Front Mol Neurosci. 2022;15:1004221. [18] 郑明魁,薛晨晖,关晓明,等.人脐带间充质干细胞来源外泌体降低脊髓损伤后血脊髓屏障的通透性[J].中国组织工程研究,2024, 28(1):50-55. [19] TANG XH, GUO T, GAO XY, et al. Exosome-derived noncoding RNAs in gastric cancer: functions and clinical applications. Mol Cancer. 2021;20(1):99. [20] LOU R, CHEN J, ZHOU F, et al. Exosome-cargoed microRNAs: Potential therapeutic molecules for diabetic wound healing. Drug Discov Today. 2022;27(10):103323. [21] ZHANG M, HU S, LIU L, et al. Engineered exosomes from different sources for cancer-targeted therapy. Signal Transduct Target Ther. 2023;8(1):124. [22] SADEGHI S, TEHRANI FR, TAHMASEBI S, et al. Exosome engineering in cell therapy and drug delivery. Inflammopharmacology. 2023;31(1): 145-169. [23] PI L, YANG L, FANG BR, et al. LncRNA MALAT1 from human adipose-derived stem cell exosomes accelerates wound healing via miR-378a/FGF2 axis. Regen Med. 2022;17(9):627-641. [24] XU C, ZHANG H, YANG C, et al. miR-125b-5p delivered by adipose-derived stem cell exosomes alleviates hypertrophic scarring by suppressing Smad2. Burns Trauma. 2024;12:tkad064. [25] PI L, YANG L, FANG BR, et al. Exosomal microRNA-125a-3p from human adipose-derived mesenchymal stem cells promotes angiogenesis of wound healing through inhibiting PTEN. Mol Cell Biochem. 2022; 477(1):115-127. [26] ZHANG Z, YANG L, LEI X, et al. Mechanism of non-small cell lung cancer cell-derived exosome miR-196b-5p promoting pyroptosis of tumor T cells and tumor cell proliferation by downregulating ING5. J Biochem Mol Toxicol. 2024;38(1):e23629. [27] MAO X, ZHOU X, LIU J, et al. Up-regulated Linc00472 suppresses development of lung cancer cell via inhibition of MiR-196b-5p. Biosci Biotechnol Biochem. 2022;86(8):1160. [28] LI Z, GONG C, WEI H. Long non-coding RNA H19 aggravates keloid progression by upregulating SMAD family member 5 expression via miR-196b-5p. Bioengineered. 2022;13(1):1447-1458. [29] YANG J, DENG P, QI Y, et al. NEAT1 Knockdown Inhibits Keloid Fibroblast Progression by miR-196b-5p/FGF2 Axis. J Surg Res. 2021;259:261-270. [30] LI L, MA Y, HE G, et al. Pilose antler extract restores type I and III collagen to accelerate wound healing. Biomed Pharmacother. 2023; 161:114510. [31] BOLLA SR, MOHAMMED AL-SUBAIE A, YOUSUF AL-JINDAN R, et al. In vitro wound healing potency of methanolic leaf extract of Aristolochia saccata is possibly mediated by its stimulatory effect on collagen-1 expression. Heliyon. 2019;5(5):e01648. [32] EL KAHI CG, ATIYEH BS, ABDALLAH HAJJ HUSSEIN I, et al. Modulation of wound contracture alpha-smooth muscle actin and multispecific vitronectin receptor integrin alphavbeta3 in the rabbit’s experimental model. Int Wound J. 2009;6(3):214-224. [33] KWON HH, YANG SH, LEE J, et al. Combination Treatment with Human Adipose Tissue Stem Cell-derived Exosomes and Fractional CO2 Laser for Acne Scars: A 12-week Prospective, Double-blind, Randomized, Split-face Study. Acta Derm Venereol. 2020;100(18):adv00310. [34] ZHU YG, SHI MM, MONSEL A, et al. Nebulized exosomes derived from allogenic adipose tissue mesenchymal stromal cells in patients with severe COVID-19: a pilot study. Stem Cell Res Ther. 2022;13(1):220. [35] CHU M, WANG H, BIAN L, et al. Nebulization Therapy with Umbilical Cord Mesenchymal Stem Cell-Derived Exosomes for COVID-19 Pneumonia. Stem Cell Rev Rep. 2022;18(6):2152-2163. [36] PAK H, HADIZADEH A, HEIRANI-TABASI A, et al. Safety and efficacy of injection of human placenta mesenchymal stem cells derived exosomes for treatment of complex perianal fistula in non-Crohn’s cases: Clinical trial phase I. J Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2023;38(4):539-547. [37] SHAFEI S, KHANMOHAMMADI M, HEIDARI R, et al. Exosome loaded alginate hydrogel promotes tissue regeneration in full-thickness skin wounds: An in vivo study. J Biomed Mater Res A. 2020;108(3): 545-556. [38] ZHANG K, ZHAO X, CHEN X, et al. Enhanced Therapeutic Effects of Mesenchymal Stem Cell-Derived Exosomes with an Injectable Hydrogel for Hindlimb Ischemia Treatment. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces. 2018;10(36):30081-30091. [39] ZHU D, HU Y, KONG X, et al. Enhanced burn wound healing by controlled-release 3D ADMSC-derived exosome-loaded hyaluronan hydrogel. Regen Biomater. 2024;11:rbae035. |
| [1] | Chen Qiang, Wu Wenjuan, Jiang Shuhua, Huang Da. Physical exercise improves physical function in burn patients: a systematic review and meta-analysis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(5): 1269-1281. |
| [2] | Cao Wenqi, Feng Xiuzhi, Zhao Yi, Wang Zhimin, Chen Yiran, Yang Xiao, Ren Yanling. Effect of macrophage polarization on osteogenesis-angiogenesis coupling in type 2 diabetic osteoporosis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(4): 917-925. |
| [3] | Yang Xiao, Bai Yuehui, Zhao Tiantian, Wang Donghao, Zhao Chen, Yuan Shuo. Cartilage degeneration in temporomandibular joint osteoarthritis: mechanisms and regenerative challenges [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(4): 926-935. |
| [4] | Huang Xinxu, Zhang Xin, Wang Jian. Living microecological hydrogels promote skin wound healing [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(2): 489-498. |
| [5] | Wang Zhuo, Sun Panpan, Cheng Huanzhi, Cao Tingting. Application of chitosan in repair and regeneration of oral hard and soft tissues [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(2): 459-468. |
| [6] | Liu Xiaohong, Zhao Tian, Mu Yunping, Feng Wenjin, Lyu Cunsheng, Zhang Zhiyong, Zhao Zijian, Li Fanghong. Acellular dermal matrix hydrogel promotes skin wound healing in rats [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(2): 395-403. |
| [7] | Ma Wenjing, Zhang Jinyu, Jiang Mingxia, Xiu Bingshui, Bai Rui, Liu Yuhan, Chen Xuyi, Yuan Zengqiang, Liu Zhiqiang. Scaffold-free three-dimensional human umbilical cord mesenchymal stem cell secretome repairs mouse skin injury [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(1): 68-77. |
| [8] | Yuan Weiyuan, Lei Qinhui, Li Xiuqi, Lu Tiezhu, Fu Ziwen, Liang Zhili, Ji Shaoyang, Li Yijia, Ren Yu . Therapeutic effects of adipose-derived mesenchymal stem cells and their exosomes on dexamethasone-induced sarcopenia in mice [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(1): 58-67. |
| [9] | Yu Manya, Cui Xing. Contribution and interaction of various cells in bone marrow microenvironment to exosomal circular RNA associated with multiple myeloma bone disease [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(1): 101-110. |
| [10] | Zhang Tingting, Li Yalong, Yue Haodi, Li Yanjun, Geng Xiwen, Zhang Yuwei, Liu Xiaozhuan. Protection of exosomes derived from bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells of different mouse ages on radiation-induced lung injury [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(1): 1-9. |
| [11] | Zhang Zhaowei, Chen Ouzile, Bai Mingru, Wang Chenglin. Therapeutic potential of bioactive substances secreted by dental mesenchymal stem cells for bone repair [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(1): 163-174. |
| [12] | Liu Nian, Dong Xinyue, Wang Songpeng, Xu Yingjiang, Zhang Xiaoming. Stem cell exosomes and biomaterial-assisted exosomes in bone defect repair [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(1): 175-183. |
| [13] | Lyu Ruyue, Gu Lulu, Liu Qian, Zhou Siyi, Li Beibei, Xue Letian, Sun Peng. Regulatory mechanisms of exosome secretion and its application prospects in biomedicine [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(1): 184-193. |
| [14] | Liu Yu, Gong Senyi, Yang Lihua, Li Weifeng, Hu Yuwen, Yan Qinbiao, Guo Meijin. Isolation, identification, and application of exosomes derived from mesenchymal stem cells [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(1): 194-203. |
| [15] | Luo Wenbin, Li Ruoyun, Pan Chaofan, Luo Changjiang. Engineered exosomes for repairing tissue damage: application potential, excellent biological stability, and targeting specificity [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(1): 204-217. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||