Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research ›› 2026, Vol. 30 ›› Issue (1): 194-203.doi: 10.12307/2025.570
Previous Articles Next Articles
Isolation, identification, and application of exosomes derived from mesenchymal stem cells
Liu Yu1, Gong Senyi1, Yang Lihua1, Li Weifeng1, Hu Yuwen1, Yan Qinbiao1, 2, Guo Meijin1
- 1State Key Laboratory of Bioreactor Engineering, 2School of Business, East China University of Science and Technology, Shanghai 200237, China
-
Received:2024-09-25Accepted:2024-11-22Online:2026-01-08Published:2025-07-02 -
Contact:Guo Meijin, PhD, Professor, State Key Laboratory of Bioreactor Engineering, East China University of Science and Technology, Shanghai 200237, China -
About author:Liu Yu, Master candidate, State Key Laboratory of Bioreactor Engineering, East China University of Science and Technology, Shanghai 200237, China -
Supported by:Strategic Priority Research Program of Chinese Academy of Sciences, No. XDA16030702 (to GMJ)
CLC Number:
Cite this article
Liu Yu, Gong Senyi, Yang Lihua, Li Weifeng, Hu Yuwen, Yan Qinbiao, Guo Meijin. Isolation, identification, and application of exosomes derived from mesenchymal stem cells[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(1): 194-203.
share this article
Add to citation manager EndNote|Reference Manager|ProCite|BibTeX|RefWorks
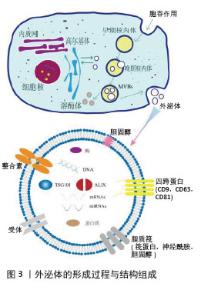
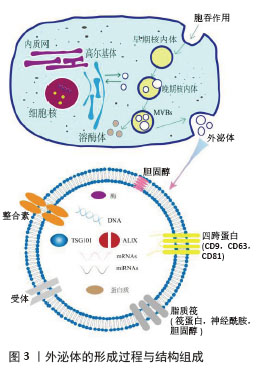
2.1 外泌体的结构与生成 外泌体的发现首次报道于1987年[5],是一种细胞外囊泡,由蛋白脂质双层膜结构组成的脂质小泡[6], 具有球形外观、直径在30-150 nm,且包含多种小分子生物活性物质[7],见图3。因其特殊的物理化学结构,外泌体可以携载核酸及蛋白质等活性成分从供体细胞转移到受体细胞,介导细胞间的信息交换[8],这与外泌体形成密切相关。外泌体的形成早期是通过质膜向内出芽得到早期内小体,这是一种膜结构的囊腔;游离的泛素化蛋白质和其他核酸分子通过特定膜融合途径进入早期小体的囊腔中形成晚期小体,此时为了进一步释放外泌体,晚期小体向细胞膜移动并对囊体膜进行修饰以更好地与细胞膜融合释放外泌体。在此过程中,不同细胞环境中存在的特有标志蛋白也被包裹在外泌体中,作为标志物应用于特定靶点的研究[9]。 "

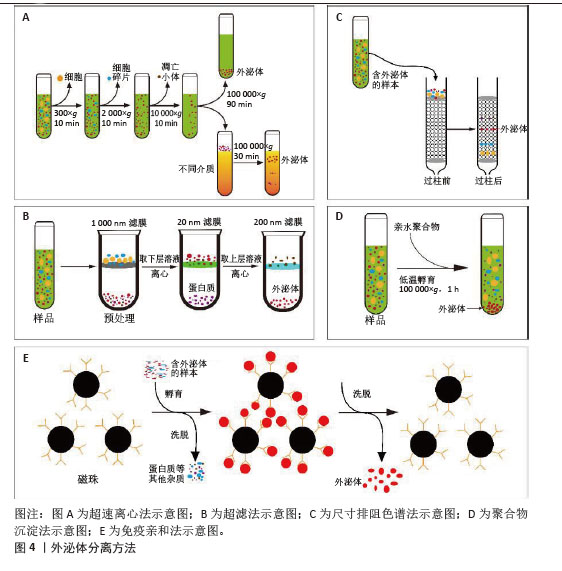
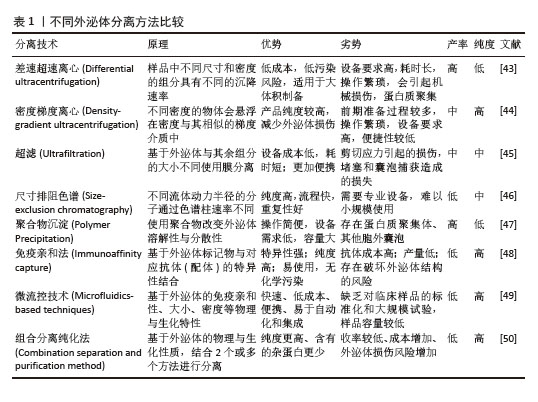
2.2.1 超速离心法 超速离心法因能够稳定地从几乎所有的样品中分离出纯度较高的外泌体而被当作外泌体分离的“金标准”[10],因其适用范围非常广泛、设备与操作的要求较为单一和外泌体纯度高,已成为实验人员首选的外泌体分离方案。超速离心法一般可以分为2类:差速超速离心法和密度梯度离心法。差速超速离心通过不同离心力和持续循环数,将外泌体与样品中其他密度和大小差异的成分分开[11];而密度梯度离心则是在其基础上使用2种或2种以上不同密度的分离介质(如蔗糖和碘二醇)进行逐层分离[12]。然而研究发现,长时间离心处理会使外泌体受到明显的机械损伤,虽然超速离心可以得到高浓度的外泌体,但它耗时较长,难以在短时间内处理多个生物样品[13],且对外泌体的损伤也不容忽视。此外,超速离心法的富集功能可能会使外泌体在制备过程中受到可溶性蛋白污染[14]。 2.2.2 超滤法 超滤的基本原理与传统的膜过滤相同,其中悬浮颗粒或聚合物的分离主要取决于它们的大小或分子质量。因此,根据外泌体的大小,可以使用具有确定分子质量或粒径大小限制的膜过滤器分离外泌体[15]。但是小规格的滤器很容易发生囊泡堵塞,降低膜的使用寿命并导致分离率降低[16]。除了用蛋白酶预处理以降低样品黏度外[17],切向流过滤技术是解决这一问题的理想方法[18]。在切向流过滤过程中,进料流与膜平行流动[19],通过操纵流体动力,施加在流体上的压力使只有一部分流体穿过膜,可以有效地减少潜在的堵塞问题,剩余的滞留物可以通过再循环回到进料储罐中进行重复过滤,从而实现自动化过程和高产量[20]。虽然基于这些优点,切向流技术已经广泛用来过滤分离外泌体,但在重复循环过程中也使得更多的杂质有机会通过滤膜,降低最终产物的纯度。因此,进一步优化切向流过滤中多次循环导致的纯度降低问题有望实现该方法的规模化应用。 2.2.3 尺寸排阻色谱法 与超滤法原理相似,尺寸排阻色谱(Size exclusion chromatography,SEC)是一种基于重力差异的分离技术。将样品加入到含有多孔珠的分离柱中,较大的颗粒无法进入凝胶孔,洗脱速度更快[21];相反,小颗粒可以进入孔隙,洗脱速度较慢,最终达到分离的目的。与超速离心法和超滤法不同,尺寸排阻色谱是通过被动重力流进行的,不影响囊泡结构和完整性[22],还可以通过选择具有生理渗透压和黏度的洗脱缓冲液进一步稳定外泌体的自然状态[23]。然而,目前常见的尺寸排阻色谱设备均存在较长的处理时间和低回收率等问题,明显限制了尺寸排阻色谱技术的大规模使用。 2.2.4 聚合物沉淀法 聚合物诱导沉淀法也是常用的外泌体分离策略之一。高度亲水性聚合物与外泌体周围的水分子相互作用,形成疏水微环境,导致外泌体沉淀[24]。聚乙二醇是一种良好的无毒聚合物,具有重塑周围材料水溶性的能力,已被广泛用于外泌体分离[25]。聚合物沉淀法实验步骤简单、成本低,适合处理大体积样品同时提高收率,曾被许多实验人员优先采纳[26]。但随着外泌体应用研究的进一步深入,对外泌体纯度的要求越来越高,而沉淀法富集的不仅包含外泌体,还有其他高分子杂质,缺乏样品选择性。当然,在实验室小规模的外泌体分离中,沉淀法的简便稳定与高产量依旧在广泛应用。 2.2.5 免疫亲和法 免疫亲和法依赖于外泌体表面表达的特异性蛋白抗体来进行捕获而分离。针对外泌体的特异性蛋白抗体可以附着在平板、磁珠、树脂和微流体装置等不同基质上,进而从样品中捕获含有特异性蛋白的外泌体[27]。与其他技术相比,免疫法虽然特异性高,捕获的外泌体纯度更高,但产量相对更低[28]。由于生物液体的复杂性,免疫亲和捕获技术常用于外泌体超速离心或超滤富集后,非常适合临床诊断等少量样品的应用场景,既获得高纯度的同时,还可以保留外泌体的活性[29]。在实际应用研究中,发现高特异性且低成本的标志蛋白抗体是免疫法分离外泌体的主要困难。此外,外泌体含有多个标志蛋白,且不一定同时同体表达,通过抗原抗体结合捕获提取液中的所有外泌体效率不高。未来有望通过寻找外泌体表面高表达蛋白抗体或优化捕获效率提高抗体使用频率的方法加大免疫法在外泌体分离的应用。 2.2.6 微流控技术 微流控技术是将样品处理、分析、检测等过程集成到一个芯片上,具有小型化、集成化、高通量、低耗时等特点[30]。目前,微流控芯片正逐渐成为简便、高效地分离外泌体的有力工具,最大特点是将外泌体分离和表征转变为一步过程[31]。其中,外泌体分离部分主要是通过免疫亲合法结合一种根据物理性质分离方法而进行分离[32]。此外,微流控装置的另一个作用是外泌体的分析鉴定,它通过一种高灵敏度、高通量的微流体装置对单个外泌体精度分析和表征,即在有效地分离高纯度的外泌体并及时地表征外泌体数据,从而利于提高不同亚群外泌体的鉴定[33]。虽然该方法的成本较高和处理量较小,但目前小剂量的处理在临床诊断领域非常适用。随着微流控技术的发展,大规模制备外泌体的微流控系统也会成为可能。 2.2.7 组合分离纯化法 目前常用的外泌体分离方法在单一使用时难以同时达到大规模、高纯度的要求,因此不同方法之间的联用可以有效弥补各自的不足。如将超速离心、超滤、尺寸排阻色谱、聚合物沉淀和免疫亲和法中的2种或多种方法结合[34-36],建立更高效的外泌体生产工艺。例如:聚合物沉淀与切向流过滤及尺寸排阻色谱法的结合可以降低提取过程中脂蛋白的含量而提高最终产物的纯度[37];免疫亲和法与尺寸排阻色谱法联合分离,更精确地从血清中分离出外泌体[38];超滤结合尺寸排阻色谱法更高效地分离出柑橘柠檬汁中的外泌体[39]。虽然不同方法的组合增加了实验成本、分离时间以及操作步骤,但对于制备特殊纯度需求的外泌体,工艺联用的组合有望稳定简便地分离大量高纯度外泌体。 2.2.8 其他分离方法 除了上述常用的外泌体分离方法外,近来流体力学和阴阳离子结合也被应用于外泌体的纯化中,这些新方法的尝试提高了外泌体分离的多样性,为未来开发出高效稳定地外泌体分离工艺提供了新方法。 非对称流场流动分馏法(AsFIFFF4, AF4)通过2块平板形成通道,上壁为不透水的聚碳酸酯玻璃板,下通道板为透气的由多孔不锈钢熔块材料制成,中间设有聚酯梯形分离器和超滤膜,底流道板与超滤膜可形成团聚壁[40]。该技术是一种温和的分离策略,没有强大的剪切力,因此有利于保持外泌体的天然结构和生物完整性,并允许分离外泌体亚型。然而,该技术需要特定的设备和专业人员来调节和优化横流速度、通道高度和膜类型等各种参数。 此外,AF4不适合大体积样品,需要超速离心、超滤等方法进行预浓缩[41]。 离子交换法依赖于外泌体膜的Zeta负电位与带正电荷的阴离子交换基质的相互作用进行结合,再通过提高盐浓度等方法增加缓冲离子强度进行分离[42]。该方法具有较高的可操作性和可扩展性,且产物纯度可以联合超滤等预处理方法进行提升。然而,因许多生物样本含有复杂的成分和带电物质不明确,离子交换法目前主要用于细胞培养基的样本处理。 各种外泌体分离方法的优势与局限性列于表1。 "
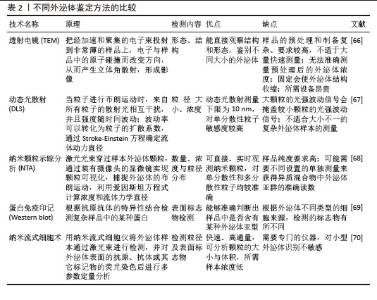
2.3 外泌体鉴定方法 深入研究外泌体的生物特性与作用机制,对其形态特征与组成成分的分析至关重要。目前对于外泌体的分析方法分为2类:物理分析与生化分析。物理分析通过观察外泌体的形态分布、颗粒大小与浓度,使用的设备和方法包括透射电子显微镜(TEM)、纳米颗粒跟踪分析(NTA)和动态光散射(DLS)等。生化分析通过使用纳米流式细胞术、蛋白免疫印迹法(Western blotting)、qPCR及蛋白质组学等分析外泌体的组成。 2.3.1 物理分析 外泌体的形貌是其基本形态表征之一,透射电子显微镜是对外泌体整体形态进行清晰和直观观察最常用的方法[51]。透射电子显微镜是利用高能电子束充当照明光源而进行放大成像的大型显微分析设备,可以观察纳米级细微结构,分辨率可达到0.2 nm。外泌体的形状是杯状或茶托形,透射电子显微镜可以直观地看到粒子的形态,鉴定外泌体的存在和完整性[52]。但电镜只能展示局部景象,无法区分与外泌体形态相近的纳米粒子,因此不能反映样品中的外泌体数量,需要与其他测试仪器相互验证进行判断。 纳米颗粒跟踪分析是检测外泌体粒径与颗粒浓度最高效的方法[53],其原理是利用光散射和布朗运动的特性获得悬浮液中的样本粒度分布。将一束能量集中的激光穿过玻璃棱镜,激光光束从较小角度入射进入样品溶液,照亮溶液中的颗粒,再通过收集散射的激光束,获得样品粒度分布的信息[54]。它能对悬浮液中粒径分布范围较宽的颗粒进行全方位表征,具有分辨率高、检测速度快、准确度高等优点。然而,纳米颗粒跟踪分析的结果仅仅是样品中的粒子信息,无法判断粒子的具体种类。因此,在实际应用过程中由于分离的外泌体样品纯度不一,只通过纳米颗粒跟踪分析很难分析外泌体的具体单位体积浓度。 动态光散射法是用于确定溶液样品中悬浮体或聚合物中颗粒尺寸和半径分布最常用的分析方法之一[55]。单色光束照射到含有以布朗运动形式移动的球形粒子的溶液中,当光击中移动的粒子时会引起多普勒频移,可以计算出颗粒的尺寸分布并详细描述颗粒在被测介质中的运动[56]。与纳米颗粒跟踪分析相比,动态光散射只能提供大概的粒径范围,不能检测溶液中的具体颗粒数,因此在外泌体表征过程中不被优先考虑。但动态光散射具有检测精度高、样品制备容易、操作简单和检测范围广等优点。研究发现先用动态光散射比较样品间的差异,再使用纳米颗粒跟踪分析得出详细粒子分布与浓度,可以有效节约时间、降低成本。 2.3.2 生化分析 在进行外泌体的表征时,仅仅通过物理分析方法难以准确判断外泌体的浓度,因此对外泌体的蛋白组成分析是很有必要的。根据《Minimal information for studies of extracellular vesicles 2018》(MISEV2018)指南推荐,Particle(粒子数)/蛋白可以作为外泌体纯度的指标,且这一标准在实际研究当中得到广泛运用。 蛋白免疫印迹是鉴定外泌体特征蛋白最常用和成熟的技术,其将蛋白样本通过聚丙烯酰胺电泳按分子质量大小分离,再转移到硝化纤维素或聚偏氟乙烯(PVDF)膜上,然后通过相应抗体对靶蛋白进行特异性检测[57]。研究发现,人源外泌体的标志性蛋白一般选择CD9、CD63以及CD81等标记物,它们是外泌体膜上常见的四跨蛋白,在膜融合、信号传导和蛋白质运输中发挥作用[58];此外,Alix、Tsg101蛋白也参与外泌体有关生物发生[59]。但是目前已经鉴定到的这些标志物蛋白并不是外泌体所特有的,诸如CD63、Alix等在细胞中广泛存在,在一些细胞碎片、溶酶体、胞内体中也大量存在。因此,蛋白免疫印迹仅能证实外泌体成分的存在,无法确认外泌体的数量和完整性。 流式细胞术常常用于表征细胞等大颗粒,通过识别荧光标记可以准确计算出样品中目的颗粒的含量。然而,传统的流式细胞术在检测直径< 500 nm的小颗粒时灵敏度和分辨率有限,造成外泌体颗粒识别不全,导致误差非常大[60]。为了使传统的流式细胞术适应外泌体分析,使用微米大小的乳胶珠来结合多个外泌体,并用荧光抗体对结合的外泌体进行染色,对其蛋白质标记物进行表征可以解决这一问题[61]。然而这种方法缺乏对单个外泌体分析能力,难以做到对外泌体亚群的准确区分。因此在此基础上开发了纳米流式仪,其可以区分直径小至100 nm的颗粒,从而提高了外泌体分析的准确性[62]。不过纳米流式仪识别能力非常依赖外泌体的相应蛋白表达,由于大多数外泌体的特征蛋白不会在所有的外泌体上同时表达,且表达量太少的蛋白会导致外泌体难以被识别,即使先进的纳米流式也很难做到真正意义上的准确区分不同亚型的外泌体。 除了鉴定外泌体中已知的特征蛋白外,外泌体中不同丰度的未知蛋白也可以通过蛋白质组学进行检测。纳升液质联用仪融合了双压离子阱的速度和灵敏度以及Orbitrap技术的高分辨率和出色质量精度,能够对复杂生物样品进行高分辨率的深度分析,可用于蛋白质组学高通量蛋白定性定量检测解析[63]。基于质谱的蛋白质组学技术有助于揭示外泌体中不同蛋白质的目的和活性,以及它们与亲本细胞中的蛋白质的相似和不同之处。 外泌体除了丰富的蛋白质外,也含有多种RNA和miRNA,通过表面蛋白与靶点的结合,释放体内遗传信息到特定受体细胞,进行表达蛋白的转录和翻译。琼脂糖凝胶电泳是一种电泳形式,用于根据核酸片段的大小进行分离。在研究外泌体对表达基因的影响时,还需要用到qPCR[64]、RT-qPCR等技术对核酸进行分离鉴定[65]。 总的来说,现今的外泌体鉴定方法缺乏统一和标准化检测要求,在越来越多的研究当中发现,无论是外泌体表观形貌的鉴定还是跨膜蛋白的检测,都不能通过单一方法进行判断是否为外泌体,尤其是外泌体的浓度和纯度。但是,总结目前的研究可以发现颗粒分布大小、表观形貌和特征蛋白是现在常用的外泌体鉴定的基本组合,能有效确定外泌体的存在并进行基本定量分析。表2比较了外泌体鉴定方法。"
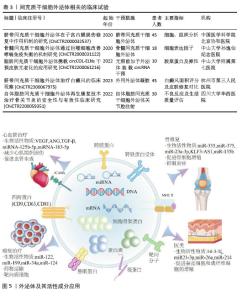
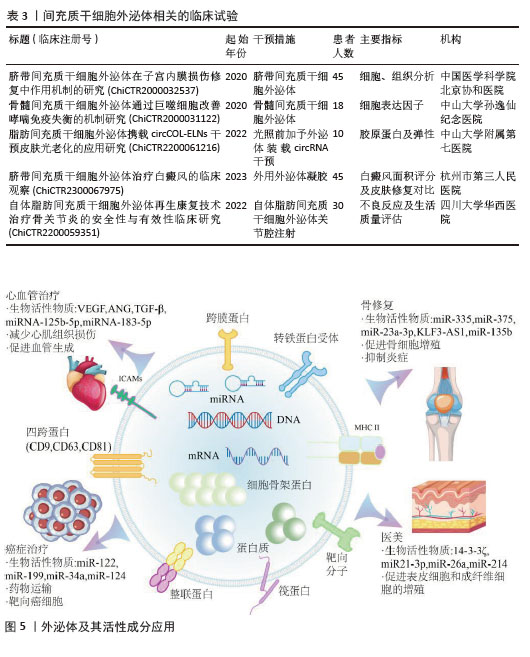
2.4 间充质干细胞外泌体的临床应用 即使外泌体的分离与分析方法尚不完善,但相关应用的研究已逐步开展,从中国临床试验注册中心查询到16个与间充质干细胞外泌体(MSCs-Exo)相关的临床试验,部分代表性临床试验见表3。与直接应用间充质干细胞的治疗方案相比,其分泌的外泌体在再生医学领域有着独特的优势。首先,间充质干细胞外泌体具有显著的免疫调节能力[71],可以影响免疫细胞的活性、抑制炎症,避免了间充质干细胞治疗过程中的免疫原性相关的问题[72]。受限于细胞培养本身的复杂性,外泌体更容易完成标准化与规模化生产,从而促进临床转化的进程[73]。此外,与干细胞在治疗过程中存在的致瘤性与细胞分化的风险相比,外泌体发生免疫排斥或引发肿瘤的可能性更小[74],而且外泌体的靶向效果更强,可以装载药物并跨越生物屏障[75]。这些优势为间充质干细胞外泌体治疗方案的开发奠定了基础,目前已在部分疾病领域得到应用,见图5。 "
| [1] HOANG DM, PHAM PT, BACH TQ, et al. Stem cell-based therapy for human diseases. Signal Transduct Target Ther. 2022;7(1):272. [2] KOU M, HUANG L, YANG JJ, et al. Mesenchymal stem cell-derived extracellular vesicles for immunomodulation and regeneration: a next generation therapeutic tool? Cell Death Dis. 2022;13(7):16. [3] LOTFY A, ABOQUELLA NM, WANG HJ. Mesenchymal stromal/stem cell (MSC)-derived exosomes in clinical trials. Stem Cell Res Ther. 2023;14(1):18. [4] LAI JJ, CHAU ZL, CHEN SY, et al. Exosome Processing and Characterization Approaches for Research and Technology Development. Adv Sci (Weinh). 2022;9(15):e2103222. [5] AGRAWAL AK, AQIL F, JEYABALAN J, et al. Milk-derived exosomes for oral delivery of paclitaxel. Nanomedicine. 2017;13(5):1627-1636. [6] ARYA SB, COLLIE SP, PARENT CA. The ins-and-outs of exosome biogenesis, secretion, and internalization. Trends Cell Biol. 2024;34(2): 90-108. [7] KRYLOVA SV, FENG DR. The Machinery of Exosomes: Biogenesis, Release, and Uptake. Int J Mol Sci. 2023;24(2):1337. [8] LI YB, HUANG P, NASSER MI, et al. Role of exosomes in bone and joint disease metabolism, diagnosis, and therapy. Eur J Pharm Sci. 2022;176:106262. [9] LIANG YJ, IQBAL Z, LU JP, et al. Cell-derived nanovesicle-mediated drug delivery to the brain: Principles and strategies for vesicle engineering. Mol Ther. 2023;31(5):1207-1224. [10] XU K, JIN YL, LI YM, et al. Recent Progress of Exosome Isolation and Peptide Recognition-Guided Strategies for Exosome Research. Front Chem. 2022:10:844124. [11] HUANG K, GARIMELLA S, CLAY-GILMOUR A, et al. Comparison of Human Urinary Exosomes Isolated via Ultracentrifugation Alone versus Ultracentrifugation Followed by SEC Column-Purification. J Pers Med. 2022;12(3):340. [12] WANG WJ, SUN H, DUAN HJ, et al. Isolation and usage of exosomes in central nervous system diseases. CNS Neurosci Ther. 2024; 30(3):e14677. [13] ZABOROWSKI MP, BALAJ L, BREAKEFIELD XO, et al. Extracellular Vesicles: Composition, Biological Relevance, and Methods of Study. Bioscience. 2015;65(8):783-797. [14] MARTINS TS, VAZ M, HENRIQUES AG. A review on comparative studies addressing exosome isolation methods from body fluids. Anal Bioanal Chem. 2023;415(7):1239-1263. [15] ANSARI FJ, TAFTI H A, AMANZADEH A, et al. Comparison of the efficiency of ultrafiltration, precipitation, and ultracentrifugation methods for exosome isolation. Biochem Biophys Rep. 2024:38:101668. [16] PETERSON MF, OTOC N, SETHI JK, et al. Integrated systems for exosome investigation. Methods. 2015;87:31-45. [17] GHEINANI AH, VöGELI M, BAUMGARTNER U, et al. Improved isolation strategies to increase the yield and purity of human urinary exosomes for biomarker discovery. Sci Rep. 2018;8(1):3945. [18] HUA X, ZHU Q, LIU Y, et al. A double tangential flow filtration-based microfluidic device for highly efficient separation and enrichment of exosomes. Anal Chim Acta. 2023:1258:341160. [19] KO M, KIM HJ, PARK J, et al. Isolation of Bovine Milk Exosome Using Electrophoretic Oscillation Assisted Tangential Flow Filtration with Antifouling of Micro-ultrafiltration Membrane Filters. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces. 2023;15(21):26069-26080. [20] VISAN KS, LOBB RJ, HAM S, et al. Comparative analysis of tangential flow filtration and ultracentrifugation, both combined with subsequent size exclusion chromatography, for the isolation of small extracellular vesicles. J Extracell Vesicles. 2022;11(9):e12266. [21] XU WM, LI A, CHEN JJ, et al. Research Development on Exosome Separation Technology. J Membr Biol. 2023;256(1):25-34. [22] ALTINTAS O, SAYLAN Y. Exploring the Versatility of Exosomes: A Review on Isolation, Characterization, Detection Methods, and Diverse Applications. Anal Chem. 2023;95(44): 16029-16048. [23] CHEN JC, LI PL, ZHANG TY, et al. Review on Strategies and Technologies for Exosome Isolation and Purification. Front Bioeng Biotechnol. 2022;9:811971. [24] JANG J, JEONG H, JANG E, et al. Isolation of high-purity and high-stability exosomes from ginseng. Front Plant Sci. 2023:13:1064412. [25] SHIEH TM, TSENG YH, HSIA SM, et al. Optimization Protocol of the PEG-Based Method for OSCC-Derived Exosome Isolation and Downstream Applications. Separations. 2022;9(12):11. [26] ZHANG MD, JIN K, GAO L, et al. Methods and Technologies for Exosome Isolation and Characterization. Small Methods. 2018; 2(9):10. [27] TANG Q, XIAO XY, LI RH, et al. Recent Advances in Detection for Breast-Cancer-Derived Exosomes. Molecules. 2022;27(19):6673. [28] PANWAR D, SHRIVASTAVA D, BHAWAL S, et al. Detection of exosomes in various biological fluids utilizing specific epitopes and directed multiple antigenic peptide antibodies. Rev Anal Chem. 2023;42(1):11. [29] GUO XN, HU F, ZHAO SH, et al. Immunomagnetic Separation Method Integrated with the Strep-Tag II System for Rapid Enrichment and Mild Release of Exosomes. Anal Chem. 2023;95(7): 3569-3576. [30] SINGH PK, PATEL A, KAFFENES A, et al. Microfluidic Approaches and Methods Enabling Extracellular Vesicle Isolation for Cancer Diagnostics. Micromachines (Basel). 2022;13(1):139. [31] SHEN JN, MA ZT, XU JQ, et al. Exosome Isolation and Detection: From Microfluidic Chips to Nanoplasmonic Biosensor. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces. 2024 Apr 27. doi: 10.1021/acsami.3c19396. [32] BAI JJ, WEI X, ZHANG X, et al. Microfluidic strategies for the isolation and profiling of exosomes. Trac-Trends Anal Chem. 2023; 158:12. [33] WU YS, WANG YQ, LU YJ, et al. Microfluidic Technology for the Isolation and Analysis of Exosomes. Micromachines (Basel). 2022; 13(10):1571. [34] DING T, CHENG T, ZHU XR, et al. Exosomes mediate the antibody-resistant intercellular transmission of porcine epidemic diarrhea virus. Vet Microbiol. 2023:284:109834. [35] MAHGOUB EO, ABDELLA GM. Improved exosome isolation methods from non-small lung cancer cells (NC1975) and their characterization using morphological and surface protein biomarker methods. J Cancer Res Clin Oncol. 2023;149(10):7505-7514. [36] CHEN ZH, WANG D, GU SS, et al. Size exclusion chromatography and asymmetrical flow field-flow fractionation for structural characterization of polysaccharides: A comparative review. Int J Biol Macromol. 2024;277(Pt 2):134236. [37] IANNOTTA D, A A, LAI AD, et al. Chemically-Induced Lipoprotein Breakdown for Improved Extracellular Vesicle Purification. Small. 2024; 20(18):e2307240. [38] KOKSAL AR, EKMEN N, AYDIN Y, et al. A Single-Step Immunocapture Assay to Quantify HCC Exosomes Using the Highly Sensitive Fluorescence Nanoparticle-Tracking Analysis. J Hepatocell Carcinoma. 2023:10:1935-1954. [39] STEC A, CHODKOWSKA M, KASPRZYK-POCHOPIEN J, et al. Isolation of Citrus lemon extracellular vesicles: Development and process control using capillary electrophoresis. Food Chem. 2023:424:136333. [40] CHEN X, ZHANG WH, DOU YW, et al. Applications of asymmetrical flow field-flow fractionation for separation and characterization of polysaccharides: A review. J Chromatogr A. 2021;1635:461726. [41] JIA YW, YU L, MA TL, et al. Small extracellular vesicles isolation and separation: Current techniques, pending questions and clinical applications. Theranostics. 2022;12(15): 6548-6575. [42] ZHANG WY, MENG TJ, HU J, et al. A Liquid Band-Aid with Mesenchymal Stem Cell-Derived Exosomes for Wound Healing in Mice. Curr Pharm Biotechnol. 2024 Sep 30. doi: 10.2174/0113892010331302240913114112. [43] MOGHASSEMI S, DADASHZADEH A, SOUSA MJ, et al. Extracellular vesicles in nanomedicine and regenerative medicine: A review over the last decade. Bioact Mater. 2024;36:126-156. [44] PARK SH, LEE EK, YIM J, et al. Exosomes: Nomenclature, Isolation, and Biological Roles in Liver Diseases. Biomol Ther (Seoul). 2023;31(3):253-263. [45] ZHU FK, WANG TY, WANG GJ, et al. The Exosome-Mediated Bone Regeneration: An Advanced Horizon Toward the Isolation, Engineering, Carrying Modalities, and Mechanisms. Adv Healthc Mater. 2024;13(19): e2400293. [46] SHIREJINI SZ, INCI F. The Yin and Yang of exosome isolation methods: conventional practice, microfluidics, and commercial kits. Biotechnol Adv. 2022:54:107814. [47] KIMIZ-GEBOLOGLU I, ONCEL SS. Exosomes: Large-scale production, isolation, drug loading efficiency, and biodistribution and uptake. J Control Release. 2022:347:533-543. [48] KHANABDALI R, MANDREKAR M, GRYGIEL R, et al. High-throughput surface epitope immunoaffinity isolation of extracellular vesicles and downstream analysis. Biol Methods Protoc. 2024;9(1):bpae032. [49] OMRANI M, BEYRAMPOUR-BASMENJ H, JAHANBAN-ESFAHLAN R, et al. Global trend in exosome isolation and application: an update concept in management of diseases. Mol Cell Biochem. 2024;479(3):679-691. [50] BOK EY, SEO SY, LEE HG, et al. Exosomes isolation from bovine serum: qualitative and quantitative comparison between ultracentrifugation, combination ultracentrifugation and size exclusion chromatography, and exoEasy methods. J Anim Sci Technol. 2024;66(5):1021-1033. [51] ISHII N, NOGUCHI K, IKEMOTO MJ, et al. Optimizing Exosome Preparation Based on Size and Morphology: Insights From Electron Microscopy. Microsc Microanal. 2023;29(6): 2068-2079. [52] LIU Z, XUE HW, CHEN Q, et al. A method for extraction of exosomes from breast tumour cells and characterisation by transmission electron microscopy. J Microsc. 2023;292(3):117-122. [53] LOGOZZI M, OREFICE NS, DI RAIMO R, et al. The Importance of Detecting, Quantifying, and Characterizing Exosomes as a New Diagnostic/Prognostic Approach for Tumor Patients. Cancers (Basel). 2023; 15(11):2878. [54] HOFMANN L, MEDYANY V, EZIC J, et al. Cargo and Functional Profile of Saliva-Derived Exosomes Reveal Biomarkers Specific for Head and Neck Cancer. Front Med (Lausanne). 2022:9:904295. [55] XU S T, ZHANG Y X, LIU S L, et al. Exosomes derived from cardiac fibroblasts with angiotensin II stimulation provoke hypertrophy and autophagy inhibition in cardiomyocytes. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2023:682: 199-206. [56] HASSAN PA, RANA S, VERMA G. Making Sense of Brownian Motion: Colloid Characterization by Dynamic Light Scattering. Langmuir. 2015; 31(1):3-12. [57] ZHOU XH, XU H, XU C, et al. Hepatocellular carcinoma-derived exosomal miRNA-761 regulates the tumor microenvironment by targeting the SOCS2/JAK2/STAT3 pathway. World J Emerg Med. 2022;13(5):379-385. [58] NAKAMACHI Y, UTO K, HAYASHI S, et al. Exosomes derived from synovial fibroblasts from patients with rheumatoid arthritis promote macrophage migration that can be suppressed by miR-124-3p. Heliyon. 2023; 9(4):e14986. [59] LEE KM, SEO EC, LEE JH, et al. The Multifunctional Protein Syntenin-1: Regulator of Exosome Biogenesis, Cellular Function, and Tumor Progression. Int J Mol Sci. 2023; 24(11):9418. [60] HUICA R, HUICA S, MOLDOVEANU E. Flow cytometric assessment of circulating microparticles - towards a more objective analysis. Rom Biotech Lett. 2011;16(3):6271-6277. [61] ARRAUD N, GOUNOU C, TURPIN D, et al. Fluorescence Triggering: A General Strategy for Enumerating and Phenotyping Extracellular Vesicles by Flow Cytometry. Cytometry A. 2016;89A(2):184-195. [62] LIU HS, TIAN Y, XUE CF, et al. Analysis of extracellular vesicle DNA at the single-vesicle level by nano-flow cytometry. J Extracell Vesicles. 2022;11(4):e12206. [63] HAN KY, CHANG JH, AZAR DT. Proteomics-Based Characterization of the Effects of MMP14 on the Protein Content of Exosomes from Corneal Fibroblasts. Protein Pept Lett. 2020;27(10):979-988. [64] SHEN ZR, SHAO JJ, SUN JQ, et al. Exosomes released by melanocytes modulate fibroblasts to promote keloid formation: a pilot study. J Zhejiang Univ Sci B. 2022;23(8):699-704. [65] YIN SH, JIA FM, RAN LQ, et al. Exosomes derived from idiopathic gingival fibroma fibroblasts regulate gingival fibroblast proliferation and apoptosis. Oral Dis. 2021; 27(7):1789-1795. [66] WEI HX, CHEN JY, WANG SL, et al. A Nanodrug Consisting Of Doxorubicin And Exosome Derived From Mesenchymal Stem Cells For Osteosarcoma Treatment In Vitro. Int J Nanomed. 2019;14:8603-8610. [67] WU SJ, ZHAO YL, ZHANG ZT, et al. The Advances and Applications of Characterization Technique for Exosomes: From Dynamic Light Scattering to Super-Resolution Imaging Technology. Photonics. 2024;11(2):21. [68] AHN SH, RYU SW, CHOI H, et al. Manufacturing Therapeutic Exosomes: from Bench to Industry. Mol Cells. 2022;45(5):284-290. [69] LIN BQ, LEI YM, WANG JX, et al. Microfluidic-Based Exosome Analysis for Liquid Biopsy. Small Methods. 2021;5(3):e2001131. [70] NOLAN JP, JONES JC. Detection of platelet vesicles by flow cytometry. Platelets. 2017; 28(3):256-262. [71] GUPTA A, KASHTE S, GUPTA M, et al. Mesenchymal stem cells and exosome therapy for COVID-19: current status and future perspective. Human Cell. 2020;33(4): 907-918. [72] NATASHA G, GUNDOGAN B, TAN A, et al. Exosomes as Immunotheranostic Nanoparticles. Clin Ther. 2014;36(6):820-829. [73] SMITH JA, DANIEL R. Human vaginal fluid contains exosomes that have an inhibitory effect on an early step of the HIV-1 life cycle. Aids. 2016;30(17):2611-2616. [74] LEE JH, PARK J, LEE JW. Therapeutic use of mesenchymal stem cell-derived extracellular vesicles in acute lung injury. Transfusion. 2019;59:876-883. [75] ZHAO AG, SHAH KR, CROMER B, et al. Mesenchymal Stem Cell-Derived Extracellular Vesicles and Their Therapeutic Potential. Stem Cells Int. 2020;2020:10. [76] YI KH, WINAYANUWATTIKUN W, KIM SY, et al. Skin boosters: Definitions and varied classifications. Skin Res Technol. 2024;30(3):e13627. [77] ZHOU Y, WEN LL, LI YF, et al. Exosomes derived from bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells protect the injured spinal cord by inhibiting pericyte pyroptosis. Neural Regen Res. 2022; 17(1):194-202. [78] KIM S, LEE S K, KIM H, et al. Exosomes Secreted from Induced Pluripotent Stem Cell-Derived Mesenchymal Stem Cells Accelerate Skin Cell Proliferation. Int J Mol Sci. 2018; 19(10):16. [79] MA T, FU B C, YANG X, et al. Adipose mesenchymal stem cell-derived exosomes promote cell proliferation, migration, and inhibit cell apoptosis via Wnt/-catenin signaling in cutaneous wound healing. J Cell Biochem. 2019;120(6):10847-10854. [80] HU P, CHIARINI A, WU J, et al. Exosomes of adult human fibroblasts cultured on 3D silk fibroin nonwovens intensely stimulate neoangiogenesis. Burns Trauma. 2021;9: tkab003. [81] SUN CK, CHEN CH, CHANG CL, et al. Melatonin treatment enhances therapeutic effects of exosomes against acute liver ischemia-reperfusion injury. Am J Transl Res. 2017;9(4):1543-1560. [82] KWON HH, YANG SH, LEE J, et al. Combination Treatment with Human Adipose Tissue Stem Cell-derived Exosomes and Fractional CO2 Laser for Acne Scars: A 12-week Prospective, Double-blind, Randomized, Split-face Study. Acta Derm Venereol. 2020;100(18):adv00310. [83] BURKE J, HUNTER M, KOLHE R, et al. Therapeutic potential of mesenchymal stem cell based therapy for osteoarthritis. Clin Transl Med. 2016;5(1):27. [84] HU HX, DONG LL, BU ZH, et al. miR-23a-3p-abundant small extracellular vesicles released from Gelma/nanoclay hydrogel for cartilage regeneration. J Extracell Vesicles. 2020;9(1):1778883. [85] JIANG SP, TIAN GZ, YANG Z, et al. Enhancement of acellular cartilage matrix scaffold by Wharton’s jelly mesenchymal stem cell-derived exosomes to promote osteochondral regeneration. Bioact Mater. 2021;6(9): 2711-2728. [86] REN SH, LIN YY, LIU WY, et al. MSC-Exos: Important active factor of bone regeneration. Front Bioeng Biotechnol. 2023:11:1136453. [87] 刘闯,谭龙旺,周禾山,等.脂肪间充质干细胞外泌体治疗创伤性中枢神经系统损伤[J].中国组织工程研究,2023,27(19): 3061-3069. [88] DING M, SHEN Y, WANG P, et al. Exosomes Isolated From Human Umbilical Cord Mesenchymal Stem Cells Alleviate Neuroinflammation and Reduce Amyloid-Beta Deposition by Modulating Microglial Activation in Alzheimer’s Disease. Neurochem Res. 2018; 43(11):2165-2177. [89] LEE M, BAN JJ, YANG S, et al. The exosome of adipose-derived stem cells reduces β-amyloid pathology and apoptosis of neuronal cells derived from the transgenic mouse model of Alzheimer’s disease. Brain Res. 2018;1691: 87-93. [90] SONG JY, SUN TT, TANG Z, et al. Exosomes derived from smooth muscle cells ameliorate diabetes-induced erectile dysfunction by inhibiting fibrosis and modulating the NO/cGMP pathway. J Cell Mol Med. 2020;24(22): 13289-13302. [91] MITSIALIS V, WALL S, LIU P, et al. Single-Cell Analyses of Colon and Blood Reveal Distinct Immune Cell Signatures of Ulcerative Colitis and Crohn’s Disease. Gastroenterology. 2020; 159(2):591-608.e10. [92] NISHIDA A, INOUE R, INATOMI O, et al. Gut microbiota in the pathogenesis of inflammatory bowel disease. Clin J Gastroenterol. 2018; 11(1):1-10. [93] LI YJ, XU QW, XU CH, et al. MSC Promotes the Secretion of Exosomal miR-34a-5p and Improve Intestinal Barrier Function Through METTL3-Mediated Pre-miR-34A m6A Modification. Mol Neurobiol. 2022;59(8):5222-5235. [94] WU XR, LAN P, WU XJ, et al. Exosomes from mesenchymal stromal cells reduce murine colonic inflammation via a macrophage-dependent mechanism. JCI Insight. 2019; 4(24):e131273. [95] WANG GY, JOEL MDM, YUAN JT, et al. Human umbilical cord mesenchymal stem cells alleviate inflammatory bowel disease by inhibiting ERK phosphorylation in neutrophils. Inflammopharmacology. 2020;28(2):603-616. [96] CAI X, ZHANG ZY, YUAN JT, et al. hucMSC-derived exosomes attenuate colitis by regulating macrophage pyroptosis via the miR-378a-5p/NLRP3 axis. Stem Cell Res Ther. 2021;12(1):416. [97] KALOGERIS T, BAINES CP, KRENZ M, et al. Ischemia/Reperfusion. Compr Physiol. 2016; 7(1):113-170. [98] REN Y, WU Y, HE WS, et al. Exosomes secreted from bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells suppress cardiomyocyte hypertrophy through Hippo-YAP pathway in heart failure. Genet Mol Biol. 2023;46(1):e20220221. [99] WANG ZC, GAO D, WANG SJ, et al. Exosomal microRNA-1246 from human umbilical cord mesenchymal stem cells potentiates myocardial angiogenesis in chronic heart failure. Cell Biol Int. 2021;45(11):2211-2225. [100] LIU L, JIN X, HU CF, et al. Exosomes Derived from Mesenchymal Stem Cells Rescue Myocardial Ischaemia/Reperfusion Injury by Inducing Cardiomyocyte Autophagy Via AMPK and Akt Pathways. Cell Physiol Biochem. 2017;43(1):52-68. [101] LIN ZJ, WU YL, XU YT, et al. Mesenchymal stem cell-derived exosomes in cancer therapy resistance: recent advances and therapeutic potential. Mol Cancer. 2022;21(1):179. [102] LOU GH, SONG XL, YANG F, et al. Exosomes derived from miR-122-modified adipose tissue-derived MSCs increase chemosensitivity of hepatocellular carcinoma. J Hematol Oncol. 2015:8:122. [103] LOU GH, CHEN L, XIA CX, et al. MiR-199a-modified exosomes from adipose tissue-derived mesenchymal stem cells improve hepatocellular carcinoma chemosensitivity through mTOR pathway. J Exp Clin Cancer Res. 2020;39(1):4. [104] SHARIF S, GHAHREMANI MH, SOLEIMANI M. Delivery of Exogenous miR-124 to Glioblastoma Multiform Cells by Wharton’s Jelly Mesenchymal Stem Cells Decreases Cell Proliferation and Migration, and Confers Chemosensitivity. Stem Cell Rev Rep. 2018;14(2):236-246. [105] CHEN HY, SUN T, JIANG C. Extracellular vesicle-based macromolecule delivery systems in cancer immunotherapy. J Control Release. 2022:348:572-589. [106] YANG Q, LI SS, OU HB, et al. Exosome-based delivery strategies for tumor therapy: an update on modification, loading, and clinical application. J Nanobiotechnology. 2024;22(1):41. [107] ZHAO M, LIU SY, WANG CS, et al. Mesenchymal Stem Cell-Derived Extracellular Vesicles Attenuate Mitochondrial Damage and Inflammation by Stabilizing Mitochondrial DNA. ACS Nano. 2021;15(1): 1519-1538. [108] 王双敏,汪显耀,何志旭.工程化间充质干细胞来源外泌体在靶向递送抗肿瘤药物中的应用与问题[J].中国组织工程研究,2025, 29(23):4975-4983. [109] DEHNAVI S, KHODADADI A, ASADIRAD A, et al. Loading Ovalbumin into Mesenchymal Stem Cell-Derived Exosomes as a Nanoscale Carrier with Immunomodulatory Potential for Allergen-Specific Immunotherapy. Rep Biochem Mol Biol. 2023;11(4):626-634. |
| [1] | Yang Xiao, Bai Yuehui, Zhao Tiantian, Wang Donghao, Zhao Chen, Yuan Shuo. Cartilage degeneration in temporomandibular joint osteoarthritis: mechanisms and regenerative challenges [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(4): 926-935. |
| [2] | Yu Shiyu, Yu Sutong, Xu Yang, Zhen Xiangyan, Han Fengxuan. Advances in research and application of tissue engineering therapeutic strategies in oral submucous fibrosis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(4): 936-948. |
| [3] | Tan Fengyi, Xie Jiamin, Pan Zhenfeng, Zhang Xinxu, Zheng Zetai, Zeng Zhiying, Zhou Yanfang. Effect and mechanism of collagen combined with microneedles in treatment of skin photoaging [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(2): 451-458. |
| [4] | Yu Manya, Cui Xing. Contribution and interaction of various cells in bone marrow microenvironment to exosomal circular RNA associated with multiple myeloma bone disease [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(1): 101-110. |
| [5] | Zhang Tingting, Li Yalong, Yue Haodi, Li Yanjun, Geng Xiwen, Zhang Yuwei, Liu Xiaozhuan. Protection of exosomes derived from bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells of different mouse ages on radiation-induced lung injury [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(1): 1-9. |
| [6] | Wu Zhijing, Li Jiali, Zhang Jiaxin, Wang Tangrong, Zheng Yuzhou, Sun Zixuan. Alpha-ketoglutarate engineered small extracellular vesicles delay skin aging [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(1): 120-129. |
| [7] | Xu Haichao, Luo Lihua, Pan Yihuai. Application and progress of dental pulp stem cells and their derivatives in dental pulp regeneration [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(1): 153-162. |
| [8] | Zhang Zhaowei, Chen Ouzile, Bai Mingru, Wang Chenglin. Therapeutic potential of bioactive substances secreted by dental mesenchymal stem cells for bone repair [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(1): 163-174. |
| [9] | Liu Nian, Dong Xinyue, Wang Songpeng, Xu Yingjiang, Zhang Xiaoming. Stem cell exosomes and biomaterial-assisted exosomes in bone defect repair [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(1): 175-183. |
| [10] | Lyu Ruyue, Gu Lulu, Liu Qian, Zhou Siyi, Li Beibei, Xue Letian, Sun Peng. Regulatory mechanisms of exosome secretion and its application prospects in biomedicine [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(1): 184-193. |
| [11] | Luo Wenbin, Li Ruoyun, Pan Chaofan, Luo Changjiang. Engineered exosomes for repairing tissue damage: application potential, excellent biological stability, and targeting specificity [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(1): 204-217. |
| [12] | Liu Jing, Zhao Xiaoli, Xia Tian. Role of extracellular vesicle-mediated intercellular communication in female follicle reproduction, preimplantation embryo development and implantation [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(1): 218-228. |
| [13] | Sun Huiwen, Guo Qiangqiang, Wang Wei, Wu Jie, Xi Kun, Gu Yong. Engineered stem cell bionic periosteum coordinates immune inflammation and vascularization to promote bone regeneration [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(1): 21-33. |
| [14] | Sun Zhanpeng, Liu Sen, Shi Ling, Chen Kaiyuan, Song Meichen, Wu Yan, Yu Jing. Bone marrow mesenchymal stem cell nanovesicles fusion neutrophil apoptotic bodies promote skin wound healing in diabetic mice [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(1): 34-42. |
| [15] | Zuo Na, Tang Qi, Yu Meng, Tao Kai. Effect of miR-196b-5p in adipose-derived stem cell exosomes on burn wound healing in rats [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(1): 43-49. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||