Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research ›› 2026, Vol. 30 ›› Issue (1): 218-228.doi: 10.12307/2025.554
Previous Articles Next Articles
Role of extracellular vesicle-mediated intercellular communication in female follicle reproduction, preimplantation embryo development and implantation
Liu Jing1, 2, Zhao Xiaoli1, 2, Xia Tian1, 2
- 1First Teaching Hospital of Tianjin University of Traditional Chinese Medicine, Tianjin 300193, China; 2National Clinical Research Center for Chinese Medicine Acupuncture and Moxibustion, Tianjin 300193, China
-
Received:2024-07-04Accepted:2024-09-21Online:2026-01-08Published:2025-07-02 -
Contact:Xia Tian, MD, Chief physician, Professor, Doctoral supervisor, First Teaching Hospital of Tianjin University of Traditional Chinese Medicine, Tianjin 300193, China; National Clinical Research Center for Chinese Medicine Acupuncture and Moxibustion, Tianjin 300193, China -
About author:Liu Jing, MD, First Teaching Hospital of Tianjin University of Traditional Chinese Medicine, Tianjin 300193, China; National Clinical Research Center for Chinese Medicine Acupuncture and Moxibustion, Tianjin 300193, China -
Supported by:National Natural Science Foundation of China, No. 82274570 (to XT)
CLC Number:
Cite this article
Liu Jing, Zhao Xiaoli, Xia Tian. Role of extracellular vesicle-mediated intercellular communication in female follicle reproduction, preimplantation embryo development and implantation[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(1): 218-228.
share this article
Add to citation manager EndNote|Reference Manager|ProCite|BibTeX|RefWorks

2.1 细胞外囊泡介导卵泡发育相关的卵泡内细胞间通讯 卵泡发育是一个周期性的动态过程,它的发育过程所跨越的时间较为漫长,文献中常提及的卵泡期是指卵泡发育的最后阶段。卵泡由外向内的结构包括卵泡膜、壁层颗粒细胞、卵泡腔、卵丘卵母复合体(the cumulus-oocyte complex,COC)、透明带[8]。越来越多研究证明,卵泡发育主要依赖于卵母细胞与其周围的卵泡体细胞(卵泡膜、壁层颗粒和卵丘细胞)所形成的卵泡微环境的支持,卵泡微环境中细胞之间的沟通对卵泡的发育、成熟具有重要意义[9],而卵泡液为卵泡内的这种信号传递方式提供了一个适宜的微环境,即卵泡液介导了卵泡细胞之间的分子交互[10]。例如,黄体生成素激增会刺激壁层颗粒细胞释放表皮生长因子配体,表皮生长因子配体作为旁分泌因子必须穿过卵泡液才能影响到卵丘细胞,进而诱导卵丘卵母复合体的特征性基因表达和扩张[11]。近年来,相继报道了人卵泡液和牛、马等其他哺乳动物卵泡液中存在细胞外囊泡,并揭示了细胞外囊泡作为信号媒介来传递卵泡内各类型细胞的讯息,从而影响卵泡发育[12-14]。 2.1.1 不同大小卵泡的卵泡液细胞外囊泡浓度呈动态变化 研究发现,随着卵泡发育过程中卵泡大小的变化,细胞外囊泡的浓度与卵泡液中的激素、细胞因子一样也存在着动态的变化,细胞外囊泡浓度与卵泡大小呈负相关[15]。 尽管也有文献报道称卵泡液细胞外囊泡的浓度和形态在不同大小的卵泡之间没有显著差异,但是CD81作为细胞外囊泡的生物标志物在不同大小卵泡中呈差异性富集,即在3-5 mm小卵泡细胞外囊泡中的表达水平最高,而在6-9 mm中卵泡和> 9 mm大卵泡中的表达显著下降[16]。在大小不同的卵泡中,卵泡液细胞外囊泡含量和特征的差异反映了其在卵泡发育中可能具有一定的生物学效应。卵泡液细胞外囊泡主要来源于颗粒细胞和卵丘卵母复合体[17]。因此,卵泡的任何生理性或病理性修饰均有可能会对卵泡液细胞外囊泡的浓度和特征造成影响。 2.1.2 细胞外囊泡及其内容物在卵泡发育中发挥作用 SOHEL等[14]对生长期卵母细胞和成熟卵母细胞来源的卵泡液细胞外囊泡进行miRNA测序,共发现了25个差异表达miRNA,其中16个miRNA在生长期卵母细胞卵泡液细胞外囊泡中的表达显著上调,表明在卵母细胞生长阶段存在更高程度的转录活性。生信分析提示,上调miRNA的靶点富集的最显著通路包括泛素介导的蛋白降解途径、神经营养因子受体信号通路、丝裂原活化蛋白激酶(mitogen-activated protein kinase,MAPK)信号通路和胰岛素信号通路,这些通路均与卵泡的生长和发育高度相关[14]。在另一项类似研究中,NAVAKANITWORAKUL等[16]首次检测了不同发育阶段卵泡的卵泡液细胞外囊泡数量和这些细胞外囊泡中miRNA丰度,发现在小卵泡的卵泡液细胞外囊泡中富集的miRNA与细胞增殖通路相关,而在大卵泡的卵泡液细胞外囊泡中富集的miRNA与炎症反应通路相关。不同生理状态下的卵泡液细胞外囊泡携带不同丰度的miRNA,提示卵泡液细胞外囊泡携带的分子货物可能随着卵母细胞的发育阶段而变化。从40名接受体外受精治疗女性的含有成熟卵母细胞的单个卵泡中收集卵泡液细胞外囊泡并进行miRNA表征,发现卵泡液细胞外囊泡中的miR-202-5p、miR-206、miR-16-1-3p和miR-1244与体外受精潜能相关,miR-663b、miR-766-3p、miR-132-3p和miR-16-5p与胚胎质量相关[18]。在另一项扩大样本量的研究中,发现卵泡液细胞外囊泡中的hsa-miR-130b和hsa-miR-92a在正常受精组和未受精组之间存在显著差异,而卵泡液细胞外囊泡中的hsa-miR-888、hsa-miR-214、hsa-miR-454在高质量胚胎和非高质量胚胎之间有显著差异[18]。对所有卵泡液样本中均可以检测到的22个细胞外囊泡miRNA进行KEGG通路分析显示,它们显著富集于卵泡生长发育、细胞信号传导、卵母细胞减数分裂和卵巢功能等通路[19],这进一步体现了卵泡液中细胞外囊泡miRNA可能在卵泡发育中发挥作用。 2.1.3 细胞外囊泡通过细胞间通讯途径调节卵泡发育 颗粒细胞产生的代谢产物可以经伪足样跨透明带结构(transzonal projections,TZP)转移至卵母细胞,当伪足样跨透明带结构受损时会影响卵泡发育[20]。研究发现,卵泡液细胞外囊泡与伪足样跨透明带结构的功能相似,通过介导卵泡内的细胞间通讯影响卵泡发育[21]。在马和牛的研究中已经证实,卵泡液细胞外囊泡可以被颗粒细胞和卵丘细胞摄取,并且还在牛伪足样跨透明带结构中发现了荧光染料标记的细胞外囊泡[13-14,20]。SOHEL等[14]为了验证细胞外囊泡介导卵泡内的细胞间通讯,利用体外实验证实了牛卵泡液中存在细胞外囊泡介导的miRNA递送,以及细胞外囊泡摄取导致了卵泡细胞内源性miRNA水平的升高和候选靶基因mRNA丰度的改变。根据这些研究结果,可以推测穿梭于卵母细胞与卵泡体细胞之间的卵泡液细胞外囊泡成为了卵泡内细胞之间信号传递的一种新机制,并且可能参与调控卵泡发育。 HUNG等[22]发现从不同发育阶段牛卵泡(3-5 mm,小;6-9 mm,中;> 9 mm,大)中分离的细胞外囊泡对颗粒细胞的增殖有着不同程度的影响,与大卵泡细胞外囊泡相比,小卵泡细胞外囊泡对颗粒细胞增殖的促进程度更强,而非受体酪氨酸激酶(sarcoma,Src)、磷脂酰肌醇3-激酶(phosphoinositide 3-kinase,PI3K)和MAPK信号通路抑制剂可以明显抑制细胞外囊泡诱导颗粒细胞增殖的能力。此外,颗粒细胞对不同大小卵泡来源细胞外囊泡的摄取能力也存在显著差异,相较于大卵泡细胞外囊泡,小卵泡细胞外囊泡能够被颗粒细胞优先摄取[22],这可能是由于小卵泡细胞外囊泡对颗粒细胞增殖具有更高的促进程度,从而导致细胞外囊泡可以被更有效的摄取。黄体生成素激增会引起支持卵丘扩张的基因表达上调,例如前列腺素内过氧化物合成酶2(prostaglandin-endoperoxide synthase 2,Ptgs2)、五聚蛋白3 (pentraxin-related protein 3,Ptx3)和肿瘤坏死因子α诱导蛋白6 (tumor necrosis factor alpha-induced protein 6,Tnfaip6)[10]。 有研究将小鼠和牛的卵丘卵母复合体与牛卵泡液细胞外囊泡共培养,发现卵泡液细胞外囊泡被卵丘细胞摄取会特异性诱发卵丘扩张,同时,与卵丘扩张相关的Ptgs2、Ptx3和Tnfaip6基因表达水平也显著增加[10]。此外,与大卵泡细胞外囊泡相比,小卵泡细胞外囊泡在诱发卵丘扩张和相关基因表达上表现出更强的活性[10]。 激活素A受体1型(activin A receptor type 1,ACVR1)和DNA结合抑制因子2(inhibitor of DNA binding 2,ID2)是转化生长因子β受体超家族成员,ACVR1是一种参与调节ID2表达和骨形态发生蛋白(bone morphogenetic protein,BMP)反应通路的受体,其在卵泡发育中发挥重要作用[23]。研究发现,在卵泡成熟过程中,来自马发情中期和排卵前卵泡液中的细胞外囊泡可能通过递送ACVR1来调节颗粒细胞中ID2的功能,从而在调节卵泡成熟中发挥作用[23]。卵母细胞的发育和成熟对胚胎发育至关重要,在牛卵母细胞成熟和胚胎发育期间补充小卵泡细胞外囊泡后,可以显著提高囊胚率,同时还可以部分改变囊胚期胚胎的代谢与发育相关基因的表达[20],这表明卵泡液细胞外囊泡在卵母细胞发育、成熟和早期胚胎发育过程中均发挥重要作用。研究发现,在成熟卵母细胞周围的卵丘细胞和颗粒细胞中高表达的miR-202-5p在卵泡液细胞外囊泡中也被检测出来,miR-202-5p的靶基因参与MAPK通路,而MAPK通路对减数分裂过程的恢复至关重要[18]。这些研究表明,细胞外囊泡通过介导卵泡内细胞之间的信号传导参与调控卵泡发育、成熟和卵母细胞质量,见表1。 "

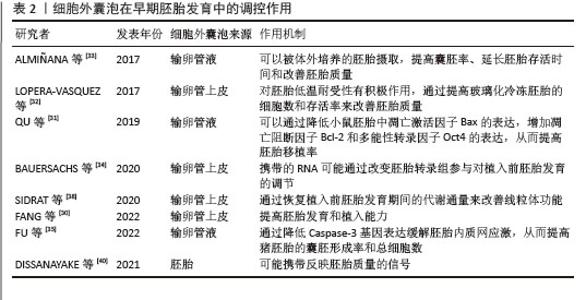
2.2 细胞外囊泡介导输卵管内的胚胎-母体沟通调控胚胎发育 卵母细胞的最终成熟、受精和胚胎的早期发育等重要生殖过程均是发生在输卵管内,输卵管为这些发育过程提供了良好的动态微环境。与子宫内膜一样,输卵管也受到卵巢类固醇激素的调控,包括输卵管形态和输卵管液[24]。在体外胚胎培养过程中常会面临胚胎发育停滞的情况,当使用输卵管上皮细胞(oviduct epithelial cells,OECs)共培养时可以克服这一情况,并且还会增加体外培养胚胎的存活率[25]。越来越多研究证实,这是由于植入前胚胎与输卵管之间的信号沟通利于胚胎发育和成功妊娠[26-27]。然而,目前关于输卵管内“母胎沟通”的具体机制仍不清楚。输卵管液是由与早期生殖发育过程相关的底物和辅酶因子组成,包括细胞因子、生长因子、激素、蛋白酶、糖类和脂类等,这些成分的浓度会因卵巢周期和输卵管解剖特征而存在差异[24]。细胞外囊泡也是输卵管液的重要成分之一,并且介导了植入前胚胎与输卵管间的沟通[28]。研究发现,在牛动情周期的不同阶段(包括排卵后、黄体早期、黄体晚期和排卵前)的输卵管液中均分离出了细胞外囊泡,这些细胞外囊泡的含量及其分子货物(蛋白质、mRNA和小非编码RNA)的丰度也均受到了类固醇激素的调节[29]。 2.2.1 输卵管源性细胞外囊泡 研究发现,猪输卵管上皮细胞来源细胞外囊泡可以提高胚胎发育和植入能力,补充输卵管液细胞外囊泡可以显著提高小鼠的活产率[30-31]。 体外培养的牛输卵管上皮细胞来源细胞外囊泡对胚胎低温耐受性有积极作用,能够通过提高玻璃化冷冻胚胎的细胞数和存活率来改善胚胎质量[28,32]。这些研究表明输卵管源性细胞外囊泡在支持胚胎发育方面发挥重要作用。ALMI?ANA等[33]研究发现,体内产生的输卵管源性细胞外囊泡可以被体外培养的胚胎摄取,并在体外培养过程中通过提高囊胚率、延长胚胎存活时间和改善胚胎质量发挥功能作用。使用质谱分析鉴定出了186种蛋白质在体内和体外输卵管源性细胞外囊泡中差异表达,功能分析揭示了参与精卵结合、受精和胚胎发育的关键蛋白,而其中一些蛋白仅在体内输卵管源性细胞外囊泡中表达[33],这为输卵管源性细胞外囊泡支持胚胎发育和介导输卵管-胚胎交互的作用提供了强有力的证据。 此外,LOPERA-VáSQUEZ等[32]研究发现,在体外培养过程中补充输卵管源性细胞外囊泡除了影响胚胎发育,还改变了一些参与胚胎发育、代谢和表观遗传调控的基因表达,使体外培养的胚胎更接近于体内状态,表明输卵管源性细胞外囊泡具有调控植入前胚胎基因表达的能力,进一步证实了输卵管内由细胞外囊泡介导的早期“母胎对话”。研究发现,体外培养过程中添加和不添加输卵管源性细胞外囊泡的两组胚胎之间存在221个差异表达基因,基于对输卵管源性细胞外囊泡中RNA的综合生物信息学分析表明,输卵管源性细胞外囊泡携带的RNA货物可能通过改变胚胎转录组参与对植入前胚胎发育的调节[34]。输卵管源性细胞外囊泡可以通过降低小鼠胚胎中凋亡激活因子Bax的表达,增加凋亡阻断因子Bcl-2和多能性转录因子Oct4的表达,从而提高胚胎移植率[31]。FU等[35]研究表明,猪输卵管液细胞外囊泡可能通过降低Caspase-3基因的表达缓解胚胎内质网应激,从而提高猪胚胎的囊胚形成率和总细胞数。在人和小鼠的研究中均证实了丙酮酸盐对体外胚胎发育的重要性,并且强调了培养基对植入前胚胎发育过程中的能量代谢有显著影响[36-37]。丙酮酸是线粒体三羧酸循环中生成ATP的必需分子,阻断丙酮酸盐进入三羧酸循环会扰乱代谢通量,导致线粒体功能障碍[38]。SIDRAT等[38]研究发现,在体外培养过程中补充牛输卵管上皮细胞源性细胞外囊泡可以通过重新建立丙酮酸盐通量并极大地影响胚胎的代谢反应,改善线粒体功能,从而消除了致密桑椹胚阶段的发育障碍。 2.2.2 植入前胚胎源性细胞外囊泡 在植入前胚胎发育过程中,胚胎本身也可以通过不同的旁分泌信号机制向输卵管发送信号。MAZZARELLA等[27]研究发现,输卵管中多胚胎的存在导致了输卵管上皮细胞转录组的改变。RODRíGUEZ-ALONSO等[39]也证实了胚胎的存在改变了输卵管的蛋白质组学特征。细胞外囊泡在输卵管微环境中介导的是胚胎-输卵管的双向沟通,植入前胚胎来源细胞外囊泡可能参与胚胎对输卵管的调控。DISSANAYAKE等[40]从优质胚胎和退化胚胎的条件培养基中分离纯化的细胞外囊泡与原代牛输卵管上皮细胞共培养并进行基因表达谱的检测,与对照组相比,在添加优质胚胎来源细胞外囊泡的牛输卵管上皮细胞中共检测25个差异基因,而在添加退化胚胎来源细胞外囊泡的牛输卵管上皮细胞中只检测到1个差异基因。DISSANAYAKE等[40]认为输卵管的不同反应依赖于胚胎质量,并且胚胎来源细胞外囊泡可能携带反映胚胎质量的信号。这项研究表明胚胎来源细胞外囊泡通过介导胚胎与母体在输卵管内的信号沟通,从而参与胚胎质量信号的递送。 细胞外囊泡在早期胚胎发育中的调控作用,见表2。 "

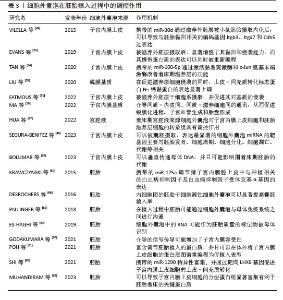
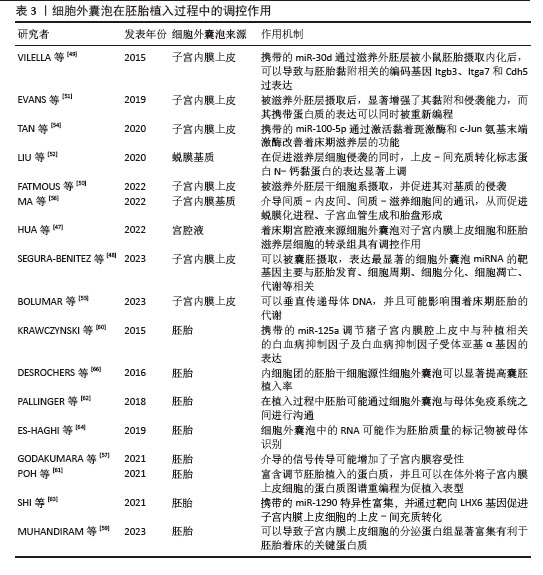
2.3 细胞外囊泡介导宫内的胚胎-母体沟通调控植入 在植入过程中,成功的妊娠除了需要具有植入潜能的胚胎和容受性子宫内膜,还依赖于子宫内膜的各类型细胞与胚胎的各类型细胞之间的分子信息交换,以促进胚胎与子宫内膜同步发育[41]。因此,了解胚胎植入过程中囊胚与子宫内膜间的协同作用对妊娠的建立至关重要。研究发现,植入前阶段宫腔液来源细胞外囊泡携带大量参与细胞凋亡的蛋白质,而植入阶段宫腔液来源细胞外囊泡则携带大量参与细胞黏附的蛋白质[7]。此外,鉴于细胞间通讯是母胎界面不同类型细胞之间相互作用的关键过程,学者们认为来源于胚胎和母体子宫内膜的细胞外囊泡是植入过程中信号传导的有效递质,并且参与对植入过程的调控。 2.3.1 子宫源性细胞外囊泡 (1)受到卵巢类固醇激素的调控:目前,已经从宫腔液和子宫内膜细胞(包括子宫内膜上皮细胞、子宫内膜基质细胞、蜕膜细胞、间充质干细胞等)中分离出了细胞外囊泡,并且对其生理性特征进行了一系列的探究。NG等[42]对人整个月经周期的子宫内膜进行免疫染色,发现细胞外囊泡的蛋白标记物CD9和CD63在子宫内膜上皮细胞的顶端表面表达,其中CD63在腺体顶端染色较强,从增殖期到分泌中期总体染色增强。后来,在小鼠的研究中也发现了类似的现象,子宫内膜中细胞外囊泡数量在“着床窗”期间明显增加,CD63表达于小鼠的子宫内膜腔上皮和腺上皮[43]。这些研究表明子宫内膜来源细胞外囊泡受到卵巢类固醇激素的调节。使用雌激素(estrogen,E)或雌激素+孕激素(estrogen plus progesterone,E+P)处理人子宫内膜腺癌上皮细胞系(endometrial adenocarcinoma epithelial cell line,EEC1),分离条件培养基中的细胞外囊泡(即E-EVs和EP-EVs),并对这些细胞外囊泡中携带的蛋白质进行表征,发现E-EVs和EP-EVs中分别有917种、789种蛋白,其中254种蛋白质特异性存在于E-EVs中,126种蛋白质特异性存在于EP-EVs中[44],这揭示了蛋白质在子宫内膜上皮细胞来源细胞外囊泡中可能具有分选机制。 在体外,利用雌孕激素诱导原代人子宫内膜上皮细胞并分离条件培养基中的细胞外囊泡,蛋白质组学分析鉴定出细胞外囊泡中含有218种蛋白质,这些蛋白质参与了与子宫内膜容受性、胚胎着床和早期胚胎发育相关的生物学过程[45]。在另一项类似研究中,模拟月经周期不同阶段(E:增殖期;P:分泌期;EP:容受期)的子宫内膜上皮细胞(RL95-2),分离条件培养基中的细胞外囊泡并进行蛋白质组学分析,发现细胞外囊泡中的蛋白质组因激素治疗而产生变化,即孕激素处理组比雌激素及雌激素+孕激素处理组产生更高浓度的细胞外囊泡[46],这可能是因为此时期子宫内膜需要为胚胎着床做准备,从而导致母胎界面的细胞间通讯信号增强。对雌孕激素模拟的容受期子宫内膜上皮细胞(endometrial epithelial cell,ECC1)及其来源的细胞外囊泡进行miRNA表征,发现227种miRNA中有13种特异性存在于细胞外囊泡中,生信分析提示细胞外囊泡中特有的miRNA在与胚胎着床高度相关的通路中具有潜在靶点[42]。子宫内膜来源细胞外囊泡及其内容物因卵巢类固醇激素引起的周期性变化而变化,并且可能在一定程度上反映了子宫内膜的生理性特征。此外,细胞外囊泡在母胎界面所介导的信号传导多是通过其携带的蛋白质和核酸的递送。 (2)调节胚胎黏附过程:研究发现,将来源于猪妊娠第13天宫腔液中的细胞外囊泡补充到子宫内膜上皮细胞和胚胎滋养层(PTr2)细胞的共培养体系中,经荧光染料标记的宫腔液细胞外囊泡被子宫内膜上皮细胞和胚胎滋养层细胞摄取[47]。转录组测序分析显示,经宫腔液细胞外囊泡处理前后的子宫内膜上皮细胞和胚胎滋养层细胞中分别有1 793和6 279个差异表达基因,这些差异表达基因参与了免疫调节、细胞迁移、细胞黏附[47],表明宫腔液中的细胞外囊泡通过介导胚胎与母体子宫内膜间的沟通在胚胎着床中起着至关重要的作用。SEGURA-BENíTEZ等[48]证实了囊胚可以摄取原代人子宫内膜上皮细胞来源细胞外囊泡,原代人子宫内膜上皮细胞来源细胞外囊泡中表达量最高的miRNA的靶基因主要与胚胎发育、细胞周期、细胞分化、细胞凋亡、代谢等相关。子宫内膜上皮细胞来源细胞外囊泡miRNA可能调控了胚胎滋养层细胞的功能。研究发现,人子宫内膜上皮细胞来源细胞外囊泡中的miR-30d可以修饰着床前胚胎的转录组[49]。miR-30d是“着床窗”期间人子宫内膜中表达最丰富的miRNA,然而,当miR-30d存在于人子宫内膜上皮细胞来源细胞外囊泡中并通过滋养外胚层被小鼠胚胎摄取内化后,可以导致与胚胎黏附相关分子的编码基因Itgb3、Itga7和Cdh5的间接过表达[49]。研究发现,经雌孕激素处理的人子宫内膜上皮细胞来源细胞外囊泡被人滋养层细胞摄取后,增强了滋养层细胞的黏附能力[44]。此外,在与人子宫内膜上皮细胞来源细胞外囊泡共培养4 h之后,滋养层细胞中黏着斑激酶(adhesion kinase,FAK)蛋白和FAK(pTyr397)磷酸化蛋白的表达均显著上调[44]。在细胞通过整合素结合蛋白黏附到细胞外基质之后,黏着斑激酶会被激活,并且同时被定位于黏附灶,进而会触发FAK-pTyr397的磷酸化[44]。因此,人子宫内膜上皮细胞来源细胞外囊泡可能是通过激活黏着斑信号来调节滋养层细胞的黏附。 (3)调节胚胎侵袭过程:除了促进胚胎黏附,子宫内膜细胞来源细胞外囊泡还促进了滋养外胚层细胞的侵袭。研究发现,人子宫内膜上皮细胞来源细胞外囊泡被滋养外胚层干细胞系摄取,并促进其对基质的侵袭[50]。基于质谱的蛋白质组学分析表明,人子宫内膜上皮细胞来源细胞外囊泡是通过上调与黏着斑(NRP1、PTPRK、ROCK2、TEK)、胚胎植入(FBLN1、NIBAN2、BSG)和激酶受体(EPHB4/B2、ERBB2、STRAP)相关的促侵袭调节因子重新编程了滋养外胚层细胞蛋白质组,从而支持这一侵袭表型[50]。在滋养外胚层L2-TSC细胞与子宫内膜上皮细胞构建的模拟胚胎植入的实验中,L2-TSc细胞球可以摄取子宫内膜上皮细胞来源细胞外囊泡,并且L2-TSC细胞球的黏附和侵袭能力均显著增强[51]。利用定量蛋白质组学揭示了经子宫内膜上皮细胞来源细胞外囊泡处理后滋养外胚层细胞的黏附网络、代谢和基因表达网络均发生了关键性变化[51],表明L2-TSC细胞的蛋白质表达可以同时被子宫内膜上皮细胞来源细胞外囊泡重编程,而滋养外胚层发生功能性改变可能是由子宫内膜上皮细胞来源细胞外囊泡的蛋白质介导的。在另一项研究中,原代人蜕膜基质细胞(human decidual stromal cells,HDSC)来源细胞外囊泡在促进滋养层细胞HTR-8/SVneo侵袭的同时,上皮-间充质转化标志蛋白N-钙黏蛋白的表达被显著上调[52]。上皮-间充质转化是胚胎植入的关键,子宫内膜上皮与滋养外胚层之间的异常上皮-间充质转化会导致胚胎植入失败[53]。当使N-钙黏蛋白沉默时,人蜕膜基质细胞来源细胞外囊泡诱导的N-钙黏蛋白表达和滋养细胞的侵袭会被阻断,而当敲低SMAD家族成员2(SMAD family member 2,SMAD2)和SMAD家族成员3(SMAD family member 3,SMAD3)时则抑制了滋养细胞中N-钙黏蛋白的上调[52],表明人蜕膜基质细胞来源细胞外囊泡可能通过SMAD2/3-N-钙黏蛋白信号通路调节滋养细胞的侵袭。研究发现,容受性子宫内膜上皮细胞来源细胞外囊泡中的miR-100-5p可以通过激活黏着斑激酶和c-Jun氨基末端激酶促进滋养细胞的迁移和侵袭,并且miR-100-5p还参与血管生成,从而增强了植入能力[54]。最近,BOLUMAR等[55]研究发现子宫内膜细胞来源细胞外囊泡还可以将核编码DNA和线粒体DNA转移到植入前胚胎,而这种母体DNA垂直转移机制可能会影响围着床期胚胎的代谢,进一步证明了母体通过细胞外囊泡递送途径向胚胎发送信号来促进胚胎的植入。 (4)调节蜕膜化进程:细胞外囊泡还介导了不同类型子宫内膜细胞之间的通讯。研究发现,人子宫内膜基质细胞在体外蜕膜化过程中会大量分泌细胞外囊泡,携带葡萄糖转运蛋白1的细胞外囊泡被邻近人子宫内膜基质细胞摄取后,形成了一个正反馈通路并加快了人子宫内膜基质细胞对葡萄糖的摄取速率,为支持和推进蜕膜化进程提供了必要的能量[56]。此外,当人子宫内膜基质细胞来源细胞外囊泡被内皮细胞摄取后,促进了内皮细胞的增殖和血管网的形成,而当蜕膜化的人子宫内膜基质细胞分泌的细胞外囊泡被滋养细胞摄取后,促进了滋养干细胞向绒毛外滋养细胞谱系的分化[56],表明人子宫内膜基质细胞来源细胞外囊泡介导了间质-内皮间、间质-滋养细胞间的通讯,从而促进蜕膜化进程、子宫血管生成和胎盘形成。这些研究表明,在围着床期,子宫内膜来源细胞外囊泡通过被胚胎滋养层细胞摄取来传递来自母体的生物分子信号,调节一系列参与黏附、侵袭和迁移的基因,从而影响胚胎植入,而细胞外囊泡携带的miRNA和蛋白质是调控胚胎植入的重要信息分子。 2.3.2 胚胎源性细胞外囊泡 (1)调节子宫内膜容受性:近年来,相继报道了植入前胚胎在体内和体外均可以分泌细胞外囊泡,并通过旁分泌的方式被子宫内膜细胞摄取,同时胚胎来源的分子信号会对子宫内膜进行功能修饰。研究发现,经荧光染料标记的胚胎滋养层细胞来源细胞外囊泡被容受性子宫内膜上皮细胞摄取并诱导其转录组发生显著变化,基因富集分析提示子宫内膜上皮细胞的反应主要体现在细胞外基质重塑和G蛋白偶联受体的信号传导上,表明细胞外囊泡介导的这种信号传导增加了子宫内膜容受性[57]。胚胎来源细胞外囊泡对子宫内膜转录组的影响在4 h左右达到峰值,主要是对胚胎着床至关重要的生物学通路产生尤为显著的改变,例如细胞外基质-受体间相互作用和细胞因子-受体间相互作用[58]。此外,MUHANDIRAM等[59]发现胚胎来源细胞外囊泡还会导致子宫内膜上皮细胞的分泌蛋白质组显著富集有利于胚胎着床的关键蛋白质。这些研究表明,胚胎信号以细胞外囊泡的形式被递送至子宫内膜,并启动容受性子宫内膜,从而为胚胎着床做准备。研究发现,胚胎来源细胞外囊泡miR-125a可以调节猪子宫内膜腔上皮中与种植相关的白血病抑制因子及白血病抑制因子受体亚基α基因的表达[60],表明胚胎来源细胞外囊泡具有改变子宫内膜基因表达的能力。在另一项研究中发现,人滋养外胚层细胞来源细胞外囊泡富含调节胚胎植入的蛋白质,并且可以在体外将子宫内膜上皮细胞的蛋白质图谱重编程为促植入表型,导致一些容受性标记物显著上调[61]。 (2)传递胚胎信号、调节子宫内膜微环境:胚胎来源细胞外囊泡携带的miRNA和蛋白质是调控胚胎-子宫内膜相互作用的关键因素。研究发现,孕激素诱导封闭因子1(progesterone-induced-blocking factor 1,PIBF1)在小鼠胚胎来源细胞外囊泡中表达,并且通过磷酯酰丝氨酸结合作用于CD4+和CD8+外周T淋巴细胞表面,进而诱导细胞外囊泡中产生更多的白细胞介素10,而这一现象被PIBF1抗体预处理后的细胞外囊泡所阻断[62],这表明在植入过程中胚胎可能通过细胞外囊泡与母体免疫系统之间进行沟通。在前文中已经叙述了细胞外囊泡在滋养层上皮-间充质转化过程中尤为重要。研究发现,miR-1290在滋养层细胞来源细胞外囊泡中特异性富集,而这些细胞外囊泡被转移至子宫内膜上皮细胞,并且通过靶向LHX6基因促进子宫内膜上皮细胞的上皮-间充质转化过程[63]。细胞外囊泡中miR-1290还促进炎症因子白细胞介素6、白细胞介素8的表达和子宫内膜上皮细胞的迁移,从而在宫腔内为植入创造所必需的炎症微环境[63]。此外,ES-HAGHI等[64]证实在“母胎对话”的体外模型中,人类胚胎RNA转录物通过细胞外囊泡转移到子宫内膜,并且只有优质胚胎来源细胞外囊泡具有改变子宫内膜转录本的潜力,因此推测胚胎来源细胞外囊泡中的RNA可能是作为胚胎质量的标记物被母体识别。这些研究表明,胚胎来源细胞外囊泡及其携带的分子货物通过被母体子宫内膜细胞摄取来传递胚胎信号,并对子宫内膜进行修饰,包括使子宫内膜对着床前胚胎质量的感应和对子宫内膜的免疫调节。 (3)调节胚胎植入能力:研究发现,体外多胚胎共培养时可以获得更高的孵化率和着床率,这是因为胚胎可以通过自分泌或旁分泌因子并构成“胚胎分泌组”来影响它的微环境,而这些自分泌和旁分泌信号可能正向调节了胚胎的发育和着床能力[65]。研究发现,来自内细胞团(the inner cell mass,ICM)的胚胎干细胞分泌的细胞外囊泡在植入过程中影响了滋养层的行为,这些细胞外囊泡携带的蛋白质(包括层粘连蛋白和纤维连接蛋白)与滋养层细胞表面的整合素相互作用,通过激活两种信号激酶(包括c-Jun氨基末端激酶和黏着斑激酶)刺激了滋养层细胞迁移[66]。进一步研究发现,将来自内细胞团的胚胎干细胞细胞外囊泡注射到囊胚中可以显著提高囊胚的植入效率[66]。这项研究揭示了细胞外囊泡还介导了内细胞团与囊胚滋养层之间的沟通,以提高囊胚的植入率。多能性相关转录因子POU5F1最初是在受精后3 d的8-细胞胚胎中表达,在第5天早期囊胚的内细胞团和滋养外胚层中保持高表达,并且在第6天主要局限于内细胞团,而多能性相关转录因子NANOG在植入前的表达始终局限于内细胞团。研究发现,在不同发育阶段的人类胚胎来源细胞外囊泡中均检测出了NANOG和POU5F1转录本[67],表明植入前胚胎分泌的细胞外囊泡既可以源于内细胞团,也可以来源于滋养外胚层,而这些细胞外囊泡不仅可以介导在胚胎与母体间传递信息,还有助于囊胚内的细胞间通讯。此外,细胞外囊泡还存在于囊胚腔液,存在于囊胚腔液中的细胞外囊泡可能有助于囊胚内的细胞间通讯[68]。 细胞外囊泡在胚胎植入过程中的调控作用,见表3。 "
| [1] LIU YJ, WANG C. A review of the regulatory mechanisms of extracellular vesicles-mediated intercellular communication. Cell Commun Signal. 2023;21(1):77. [2] VAN NIEL G, CARTER DRF, CLAYTON A, et al. Challenges and directions in studying cell-cell communication by extracellular vesicles. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 2022;23(5):369-382. [3] POPOWSKI KD, MOATTI A, SCULL G, et al. Inhalable dry powder mRNA vaccines based on extracellular vesicles. Matter. 2022;5(9): 2960-2974. [4] MARAR C, STARICH B, WIRTZ D. Extracellular vesicles in immunomodulation and tumor progression. Nat Immunol. 2021;22(5): 560-570. [5] LIANG Y, DUAN L, LU J, et al. Engineering exosomes for targeted drug delivery. Theranostics. 2021;11(7):3183-3195. [6] ALEKSEJEVA E, ZAROVNI N, DISSANAYAKE K, et al. Extracellular vesicle research in reproductive science: Paving the way for clinical achievements†. Biol Reprod. 2022;106(3):408-424. [7] HART AR, KHAN NLA, GODAKUMARA K, et al. The role of extracellular vesicles in endometrial receptivity and their potential in reproductive therapeutics and diagnosis. Reprod Biol. 2022;22(2):100645. [8] DOMPE C, KULUS M, STEFAŃSKA K, et al. Human Granulosa Cells-Stemness Properties, Molecular Cross-Talk and Follicular Angiogenesis. Cells. 2021;10(6):1396. [9] KOWALCZYK A, WRZECIŃSKA M, CZERNIAWSKA-PIĄTKOWSKA E, et al. Exosomes - Spectacular role in reproduction. Biomed Pharmacother. 2022;148:112752. [10] HUNG WT, HONG X, CHRISTENSON LK, et al. Extracellular Vesicles from Bovine Follicular Fluid Support Cumulus Expansion. Biol Reprod. 2015;93(5):117. [11] OWEN CM, JAFFE LA. Luteinizing hormone stimulates ingression of mural granulosa cells within the mouse preovulatory follicle. Biol Reprod. 2024;110(2):288-299. [12] SHOMALI N, HEMMATZADEH M, YOUSEFZADEH Y, et al. Exosomes: Emerging biomarkers and targets in folliculogenesis and endometriosis. J Reprod Immunol. 2020;142:103181. [13] GABRYŚ J, KIJ-MITKA B, SAWICKI S, et al. Extracellular vesicles from follicular fluid may improve the nuclear maturation rate of in vitro matured mare oocytes. Theriogenology. 2022;188:116-124. [14] SOHEL MM, HOELKER M, NOFERESTI SS, et al. Exosomal and Non-Exosomal Transport of Extra-Cellular microRNAs in Follicular Fluid: Implications for Bovine Oocyte Developmental Competence. PLoS One. 2013;8(11):e78505. [15] HASAN MM, RESHI QUA, LÄTTEKIVI F, et al. Bovine Follicular Fluid Derived Extracellular Vesicles Modulate the Viability, Capacitation and Acrosome Reaction of Bull Spermatozoa. Biology (Basel). 2021;10(11):1154. [16] NAVAKANITWORAKUL R, HUNG WT, GUNEWARDENA S, et al. Characterization and Small RNA Content of Extracellular Vesicles in Follicular Fluid of Developing Bovine Antral Follicles. Sci Rep. 2016;6:25486. [17] PU X, ZHANG L, ZHANG P, et al. Human UC-MSC-derived exosomes facilitate ovarian renovation in rats with chemotherapy-induced premature ovarian insufficiency. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2023;14: 1205901. [18] MACHTINGER R, RODOSTHENOUS RS, ADIR M, et al. Extracellular microRNAs in follicular fluid and their potential association with oocyte fertilization and embryo quality: an exploratory study. J Assist Reprod Genet. 2017;34(4): 525-533. [19] MARTINEZ RM, LIANG L, RACOWSKY C, et al. Extracellular microRNAs profile in human follicular fluid and IVF outcomes. Sci Rep. 2018;8(1):17036. [20] DA SILVEIRA JC, ANDRADE GM, DEL COLLADO M, et al. Supplementation with small-extracellular vesicles from ovarian follicular fluid during in vitro production modulates bovine embryo development. PLoS One. 2017; 12(6):e0179451. [21] WANG Y, WANG X, ZHAO Y, et al. Progress in the effect of microRNA carried by extracellular vesicles in follicular fluid on follicular atresia. Sheng Wu Gong Cheng Xue Bao. 2022;38(8): 2767-2783. [22] HUNG WT, NAVAKANITWORAKUL R, KHAN T, et al. Stage-specific follicular extracellular vesicle uptake and regulation of bovine granulosa cell proliferation. Biol Reprod. 2017;97(4):644-655. [23] DA SILVEIRA JC, CARNEVALE EM, WINGER QA, et al. Regulation of ACVR1 and ID2 by cell-secreted exosomes during follicle maturation in the mare. Reprod Biol Endocrinol. 2014; 12:44. [24] BASTOS NM, FERST JG, GOULART RS, et al. The role of the oviduct and extracellular vesicles during early embryo development in bovine. Anim Reprod. 2022;19(1):e20220015. [25] CAJAS YN, CAÑÓN-BELTRÁN K, DE LA BLANCA MGM, et al. Role of reproductive fluids and extracellular vesicles in embryo–maternal interaction during early pregnancy in cattle. Reprod Fertil Dev. 2021; 34(2):117-138. [26] HAMDI M, SÁNCHEZ JM, FERNANDEZ-FUERTES B, et al. Oviductal extracellular vesicles miRNA cargo varies in response to embryos and their quality. BMC Genomics. 2024;25(1):520. [27] MAZZARELLA R, BASTOS NM, BRIDI A, et al. Changes in Oviductal Cells and Small Extracellular Vesicles miRNAs in Pregnant Cows. Front Vet Sci. 2021;8:639752. [28] MENJIVAR NG, GAD A, THOMPSON RE, et al. Bovine oviductal organoids: a multi-omics approach to capture the cellular and extracellular molecular response of the oviduct to heat stress. BMC Genomics. 2023;24(1):646. [29] ALMIÑANA C, TSIKIS G, LABAS V, et al. Deciphering the oviductal extracellular vesicles content across the estrous cycle: implications for the gametes-oviduct interactions and the environment of the potential embryo. BMC Genomics. 2018;19(1):622. [30] FANG X, TANGA BM, BANG S, et al. Oviduct Epithelial Cell-Derived Extracellular Vesicles Improve Porcine Trophoblast Outgrowth. Vet Sci. 2022;9(11):609. [31] QU P, ZHAO Y, WANG R, et al. Extracellular vesicles derived from donor oviduct fluid improved birth rates after embryo transfer in mice. Reprod Fertil Dev. 2019;31(2):324-332. [32] LOPERA-VASQUEZ R, HAMDI M, MAILLO V, et al. Effect of bovine oviductal extracellular vesicles on embryo development and quality in vitro. Reproduction. 2017;153(4):461-470. [33] ALMIÑANA C, CORBIN E, TSIKIS G, et al. Oviduct extracellular vesicles protein content and their role during oviduct-embryo cross-talk. Reproduction. 2017; 154(3):153-168. [34] BAUERSACHS S, MERMILLOD P, ALMIÑANA C. The Oviductal Extracellular Vesicles’ RNA Cargo Regulates the Bovine Embryonic Transcriptome. Int J Mol Sci. 2020;21(4): 1303. [35] FU B, MA H, ZHANG DJ, et al. Porcine oviductal extracellular vesicles facilitate early embryonic development via relief of endoplasmic reticulum stress. Cell Biol Int. 2022;46(2):300-310. [36] BOUTOURLINSKY K, ALLÈGRE N, CHAZAUD C. Ex Vivo Culture for Preimplantation Mouse Embryo to Analyze Pluripotency. Methods Mol Biol. 2021;2214:1-10. [37] KOBANAWA M. Fertilization, embryo culture, and clinical results using low lactate embryo culture medium for pre-culture, insemination, and beyond. Reprod Med Biol. 2022;21(1):e12458. [38] SIDRAT T, KHAN AA, JOO MD, et al. Bovine Oviduct Epithelial Cell-Derived Culture Media and Exosomes Improve Mitochondrial Health by Restoring Metabolic Flux during Pre-Implantation Development. Int J Mol Sci. 2020;21(20):7589. [39] RODRÍGUEZ-ALONSO B, MAILLO V, ACUÑA OS, et al. Spatial and Pregnancy-Related Changes in the Protein, Amino Acid, and Carbohydrate Composition of Bovine Oviduct Fluid. Int J Mol Sci. 2020;21(5):1681. [40] DISSANAYAKE K, NÕMM M, LÄTTEKIVI F, et al. Oviduct as a sensor of embryo quality: deciphering the extracellular vesicle (EV)-mediated embryo-maternal dialogue. J Mol Med (Berl). 2021;99(5):685-697. [41] PENNAROSSA G, ARCURI S, ZMIJEWSKA A, et al. Bioengineering-tissue strategies to model mammalian implantation in vitro. Front Bioeng Biotechnol. 2024;12:1430235. [42] NG YH, ROME S, JALABERT A, et al. Endometrial exosomes/microvesicles in the uterine microenvironment: a new paradigm for embryo-endometrial cross talk at implantation. PLoS One. 2013;8(3):e58502. [43] TAN Q, SHI S, LIANG J, et al. MicroRNAs in Small Extracellular Vesicles Indicate Successful Embryo Implantation during Early Pregnancy. Cells. 2020;9(3):645. [44] GREENING DW, NGUYEN HP, ELGASS K, et al. Human Endometrial Exosomes Contain Hormone-Specific Cargo Modulating Trophoblast Adhesive Capacity: Insights into Endometrial-Embryo Interactions. Biol Reprod. 2016;94(2):38. [45] SEGURA-BENÍTEZ M, CARBAJO-GARCÍA MC, CORACHÁN A, et al. Proteomic analysis of extracellular vesicles secreted by primary human epithelial endometrial cells reveals key proteins related to embryo implantation. Reprod Biol Endocrinol. 2022; 20(1):3. [46] HART AR, KHAN NLA, DISSANAYAKE K, et al. The Extracellular Vesicles Proteome of Endometrial Cells Simulating the Receptive Menstrual Phase Differs from That of Endometrial Cells Simulating the Non-Receptive Menstrual Phase. Biomolecules. 2023;13(2):279. [47] HUA R, LIU Q, LIAN W, et al. Transcriptome regulation of extracellular vesicles derived from porcine uterine flushing fluids during peri-implantation on endometrial epithelial cells and embryonic trophoblast cells. Gene. 2022;822:146337. [48] SEGURA-BENÍTEZ M, BAS-RIVAS A, JUÁREZ-BARBER E, et al. Human blastocysts uptake extracellular vesicles secreted by endometrial cells containing miRNAs related to implantation. Hum Reprod. 2023;38(8): 1547-1559. [49] VILELLA F, MORENO-MOYA JM, BALAGUER N, et al. Hsa-miR-30d, secreted by the human endometrium, is taken up by the pre-implantation embryo and might modify its transcriptome. Development. 2015;142(18):3210-3221. [50] FATMOUS M, RAI A, POH QH, et al. Endometrial small extracellular vesicles regulate human trophectodermal cell invasion by reprogramming the phosphoproteome landscape. Front Cell Dev Biol. 2022;10: 1078096. [51] EVANS J, RAI A, NGUYEN HPT, et al. Human Endometrial Extracellular Vesicles Functionally Prepare Human Trophectoderm Model for Implantation: Understanding Bidirectional Maternal-Embryo Communication. Proteomics. 2019;19(23):e1800423. [52] LIU M, CHEN X, CHANG QX, et al. Decidual small extracellular vesicles induce trophoblast invasion by upregulating N-cadherin. Reproduction. 2020;159(2):171-180. [53] OGHBAEI F, ZAREZADEH R, JAFARI-GHARABAGHLOU D, et al. Epithelial-mesenchymal transition process during embryo implantation. Cell Tissue Res. 2022; 388(1):1-17. [54] TAN Q, SHI S, LIANG J, et al. Endometrial cell-derived small extracellular vesicle miR-100-5p promotes functions of trophoblast during embryo implantation. Mol Ther Nucleic Acids. 2020;23:217-231. [55] BOLUMAR D, MONCAYO-ARLANDI J, GONZALEZ-FERNANDEZ J, et al. Vertical transmission of maternal DNA through extracellular vesicles associates with altered embryo bioenergetics during the periconception period. Elife. 2023;12: RP88008. [56] MA Q, BEAL JR, BHURKE A, et al. Extracellular vesicles secreted by human uterine stromal cells regulate decidualization, angiogenesis, and trophoblast differentiation. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2022;119(38):e2200252119. [57] GODAKUMARA K, ORD J, LÄTTEKIVI F, et al. Trophoblast derived extracellular vesicles specifically alter the transcriptome of endometrial cells and may constitute a critical component of embryo-maternal communication. Reprod Biol Endocrinol. 2021;19(1):115. [58] GODAKUMARA K, HEATH PR, FAZELI A. Rhythm of the First Language: Dynamics of Extracellular Vesicle-Based Embryo-Maternal Communication in the Pre-Implantation Microenvironment. Int J Mol Sci. 2023;24(7):6811. [59] MUHANDIRAM S, DISSANAYAKE K, ORRO T, et al. Secretory Proteomic Responses of Endometrial Epithelial Cells to Trophoblast-Derived Extracellular Vesicles. Int J Mol Sci. 2023;24(15):11924. [60] KRAWCZYNSKI K, NAJMULA J, BAUERSACHS S, et al. MicroRNAome of porcine conceptuses and trophoblasts: expression profile of micrornas and their potential to regulate genes crucial for establishment of pregnancy. Biol Reprod. 2015;92(1):21. [61] POH QH, RAI A, CARMICHAEL II, et al. Proteome reprogramming of endometrial epithelial cells by human trophectodermal small extracellular vesicles reveals key insights into embryo implantation. Proteomics. 2021; 21(13-14):e2000210. [62] PALLINGER E, BOGNAR Z, BOGDAN A, et al. PIBF+ extracellular vesicles from mouse embryos affect IL-10 production by CD8+ cells. Sci Rep. 2018;8(1):4662. [63] SHI S, TAN Q, LIANG J, et al. Placental trophoblast cell-derived exosomal microRNA-1290 promotes the interaction between endometrium and embryo by targeting LHX6. Mol Ther Nucleic Acids. 2021;26:760-772. [64] ES-HAGHI M, GODAKUMARA K, HÄLING A, et al. Specific trophoblast transcripts transferred by extracellular vesicles affect gene expression in endometrial epithelial cells and may have a role in embryo-maternal crosstalk. Cell Commun Signal. 2019;17(1):146. [65] HAWKE DC, WATSON AJ, BETTS DH. Extracellular vesicles, microRNA and the preimplantation embryo: non-invasive clues of embryo well-being. Reprod Biomed Online. 2021;42(1):39-54. [66] DESROCHERS LM, BORDELEAU F, REINHART-KING CA, et al. Microvesicles provide a mechanism for intercellular communication by embryonic stem cells during embryo implantation. Nat Commun. 2016;7:11958. [67] GIACOMINI E, VAGO R, SANCHEZ AM, et al. Secretome of in vitro cultured human embryos contains extracellular vesicles that are uptaken by the maternal side. Sci Rep. 2017;7(1):5210. [68] LAL A, ROUDEBUSH WE, CHOSED RJ. Embryo Biopsy Can Offer More Information Than Just Ploidy Status. Front Cell Dev Biol. 2020;8:78. [69] SUN Y, ZHANG Y, MA X, et al. Determining Diagnostic Criteria of Unexplained Recurrent Implantation Failure: A Retrospective Study of Two vs Three or More Implantation Failure. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2021; 12:619437. |
| [1] | Hu Jing, Zhu Ling, Xie Juan, Kong Deying, Liu Doudou. Autophagy regulates early embryonic development in mice via affecting H3K4me3 modification [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(5): 1147-1155. |
| [2] | Yang Xiao, Bai Yuehui, Zhao Tiantian, Wang Donghao, Zhao Chen, Yuan Shuo. Cartilage degeneration in temporomandibular joint osteoarthritis: mechanisms and regenerative challenges [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(4): 926-935. |
| [3] | Tan Fengyi, Xie Jiamin, Pan Zhenfeng, Zhang Xinxu, Zheng Zetai, Zeng Zhiying, Zhou Yanfang. Effect and mechanism of collagen combined with microneedles in treatment of skin photoaging [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(2): 451-458. |
| [4] | Mu Yanli, Hu Anchun, Xu Wenchi, Chen Panpan, Chen hao, Zhao Shuyun, Huang Guanyou, Chen Xiaojuan. Effects of human umbilical cord blood platelet-rich plasma, mononuclear cells, and mesenchymal stem cells in repairing thin endometrium in rats [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(1): 78-92. |
| [5] | Yu Shuai, Liu Jiawei, Zhu Bin, Pan Tan, Li Xinglong, Sun Guangfeng, Yu Haiyang, Ding Ya, Wang Hongliang. Hot issues and application prospects of small molecule drugs in treatment of osteoarthritis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(9): 1913-1922. |
| [6] | Yu Jingbang, Wu Yayun. Regulatory effect of non-coding RNA in pulmonary fibrosis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(8): 1659-1666. |
| [7] | Wang Qiuyue, Jin Pan, Pu Rui . Exercise intervention and the role of pyroptosis in osteoarthritis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(8): 1667-1675. |
| [8] | Yuan Weibo, Liu Chan, Yu Limei. Potential application of liver organoids in liver disease models and transplantation therapy [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(8): 1684-1692. |
| [9] | Huang Ting, Zheng Xiaohan, Zhong Yuanji, Wei Yanzhao, Wei Xufang, Cao Xudong, Feng Xiaoli, Zhao Zhenqiang. Effects of macrophage migration inhibitory factor on survival, proliferation, and differentiation of human embryonic stem cells [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(7): 1380-1387. |
| [10] | Peng Hongcheng, Peng Guoxuan, Lei Anyi, Lin Yuan, Sun Hong, Ning Xu, Shang Xianwen, Deng Jin, Huang Mingzhi . Role and mechanism of platelet-derived growth factor BB in repair of growth plate injury [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(7): 1497-1503. |
| [11] | Liu Haoyang, Xie Qiang, Shen Mengran, Ren Yansong, Ma Jinhui, Wang Bailiang, Yue Debo, Wang Weiguo . Application, research hotspots, and shortcomings of degradable zinc-based alloys in bone defect repair and reconstruction [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(4): 839-845. |
| [12] | Zhang Xiongjinfu, Chen Yida, Cheng Xinyi, Liu Daihui, Shi Qin . Exosomes derived from bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells of young rats to reverse senescence in aged rat bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(36): 7709-7718. |
| [13] | Guo Zhao, Zhuang Haoyan, Shi Xuewen. Role of exosomes derived from mesenchymal stem cells in treatment of colorectal cancer [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(36): 7872-7879. |
| [14] | Li Zhe, Li Ping, Zhang Chao, Guo Guangling. A network meta-analysis of efficacy of mesenchymal stem cells from different sources in treatment of premature ovarian failure animal models [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(36): 7898-7908. |
| [15] | Zhou Yang, Liu Kexin, Wang Deli, Sun Zhang. Regenerative effects of engineered extracellular vesicles on repairing bone defects [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(36): 7839-7847. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||