Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research ›› 2026, Vol. 30 ›› Issue (1): 163-174.doi: 10.12307/2025.571
Previous Articles Next Articles
Therapeutic potential of bioactive substances secreted by dental mesenchymal stem cells for bone repair
Zhang Zhaowei, Chen Ouzile, Bai Mingru, Wang Chenglin
- State Key Laboratory of Oral Diseases & National Center for Stomatology & National Clinical Research Center for Oral Diseases, West China School of Stomatology, Sichuan University, Chengdu 610041, Sichuan Province, China
-
Received:2024-11-12Accepted:2025-01-17Online:2026-01-08Published:2025-07-02 -
Contact:Wang Chenglin, MD, Associate professor, State Key Laboratory of Oral Diseases & National Center for Stomatology & National Clinical Research Center for Oral Diseases, West China School of Stomatology, Sichuan University, Chengdu 610041, Sichuan Province, China -
About author:Zhang Zhaowei, Master candidate, State Key Laboratory of Oral Diseases & National Center for Stomatology & National Clinical Research Center for Oral Diseases, West China School of Stomatology, Sichuan University, Chengdu 610041, Sichuan Province, China -
Supported by:Sichuan Natural Science Foundation Project, No. 2024NSFSC0551 (to WCL); Clinical Research Project of West China Hospital of Stomatology of Sichuan University, No. LCYJ2029-18 (to WCL); National Natural Science Foundation Project, No. 82470962 (to BMR)
CLC Number:
Cite this article
Zhang Zhaowei, Chen Ouzile, Bai Mingru, Wang Chenglin. Therapeutic potential of bioactive substances secreted by dental mesenchymal stem cells for bone repair[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(1): 163-174.
share this article
Add to citation manager EndNote|Reference Manager|ProCite|BibTeX|RefWorks
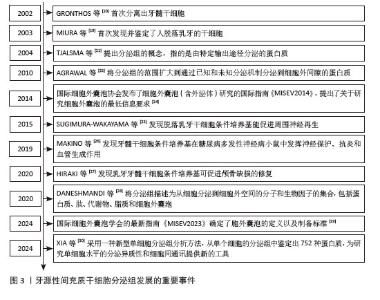
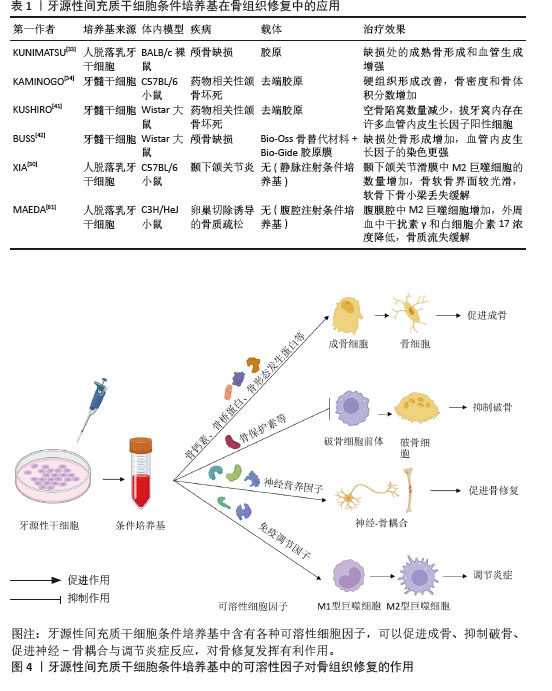
2.2 牙源性间充质干细胞条件培养基对骨组织修复的作用 2.2.1 牙源性间充质干细胞条件培养基中促进骨形成的生物活性物质对骨组织修复的作用 近来有研究表明,牙源性间充质干细胞条件培养基中含有多种促进成骨的因子,如骨钙素、骨桥蛋白、骨形态发生蛋白和牙本质涎磷蛋白等。牙源性间充质干细胞条件培养基的直接促成骨作用可能是这些因子共同作用的结果。HIRAKI等[27]利用Luminex系统分析了脱落乳牙干细胞条件培养基中20种组织再生因子,结果显示骨保护素、骨桥蛋白、骨形态发生蛋白2和骨形态发生蛋白4含量丰富,将含脱落乳牙干细胞条件培养基的去端肽胶原置入小鼠颅骨缺损处,发现其能促进颅骨缺损修复。BAR等[31]实验显示牙髓干细胞表达Ⅰ型胶原、骨钙素、骨桥蛋白、牙本质涎磷蛋白和骨唾液蛋白,且成骨诱导分化后的牙髓干细胞中这些基因表达及蛋白分泌水平更高。KOH等[32]通过体外实验发现牙髓干细胞条件培养基能促进脐带间充质干细胞成骨向分化。KUNIMATSU等[33]在体外实验中用脱落乳牙干细胞条件培养基培养骨髓间充质干细胞和MC3T3-E1细胞(成骨细胞前体细胞),可加速细胞生长并增强碱性磷酸酶、骨钙素和Runt相关转录因子2等成骨分化标志物的mRNA表达,提示脱落乳牙干细胞条件培养基可促进这些成骨谱系细胞成骨向分化。KAMINOGO等[34]在小鼠药物相关性颌骨坏死体内模型中应用牙髓干细胞条件培养基治疗,发现牙槽窝周围组织中成骨相关分子(如成骨细胞特异性转录因子Osterix、Runt相关转录因子2、骨形态发生蛋白2和碱性磷酸酶)的表达增强,牙槽窝内编织骨形成增多;同时,在药物相关性颌骨坏死模型中受到抑制的Wnt信号分子表达得到了改善,如Wnt10b,这可能是牙髓干细胞条件培养基促进药物相关性颌骨坏死成骨的分子机制之一。NOVELLO等[35]评估牙周韧带干细胞条件培养基对成骨细胞的影响,将牙周韧带干细胞条件培养基添加到Saos-2细胞(人成骨肉瘤细胞)中,发现Saos-2细胞增殖能力增强,且一些成骨细胞分化标志物(Ⅰ型胶原、Runt相关转录因子2)的表达增加。 除了对成骨的直接作用,牙源性间充质干细胞条件培养基还含有破骨细胞的抑制因子,如骨保护素,间接对成骨或骨修复产生有利作用。骨保护素是公认的破骨细胞抑制剂,能够抑制破骨细胞分化。一项研究表明,重组骨保护素通过降低RAW264.7细胞中破骨细胞分化标志物活化T-细胞核因子1、组织蛋白酶K、抗酒石酸酸性磷酸酶、核因子κB受体激活因子和基质金属蛋白酶9的表达,抑制破骨细胞分化[36]。ISHIKAWA等[37]发现,脱落乳牙干细胞条件培养基中骨保护素的含量是骨髓间充质干细胞条件培养基的2.8倍,能更有效地抑制体外破骨细胞生成。一项体外实验发现,大鼠牙髓干细胞条件培养基可抑制破骨细胞前体向破骨细胞的分化[38]。KANJI等[36]研究进一步发现,在体外非接触系统共培养时,牙髓干细胞会通过分泌骨保护素并使骨髓细胞中的蛋白激酶B信号失活来抑制破骨细胞分化。 除了以上广泛研究的条件培养基中利于骨修复的生物活性物质,一项研究还对牙髓干细胞条件培养基进行了40个细胞因子的抗体阵列测试,共有34个因子高于检测阈值,除了以上提到的细胞因子,还包括一些对骨修复具有促进作用的营养/生长因子,如神经营养因子3、肝细胞生长因子7、成纤维细胞生长因子4、胰岛素样生长因子1等[39]。牙源性间充质干细胞条件培养基中具有多种生物活性物质,并且体外内证据支持具有促骨修复的作用,但并没有证据表明某种因子的突出效果,而可能是多种因子累积的效应,具体的作用机制也尚待进一步研究。 2.2.2 牙源性间充质干细胞条件培养基中血管内皮生长因子对骨组织修复的作用 大量研究认为,骨血管系统在骨重塑中起着重要作用,血管功能和灌注的下降会导致骨体积、骨密度、成骨细胞活性降低。血管内皮生长因子能促进骨缺损局部的血管生成,对成骨细胞的趋化和分化具有促进作用[40]。牙髓干细胞条件培养基中有高含量的血管内皮生长因子,因此可能促进骨缺损区域的血管生长进而促进骨修复。 KUSHIRO等[41]提供了牙源性间充质干细胞条件培养基和血管内皮生长因子关系的证据,通过ELISA测定发现了牙髓干细胞条件培养基含有高含量的血管内皮生长因子(601±50.46) pg/mL,在药物性相关颌骨坏死大鼠拔牙窝内置入含牙髓干细胞条件培养基的明胶海绵,拔牙创的范围减小,骨密度增高,免疫组化显示拔牙窝内存在许多血管内皮生长因子阳性细胞。BUSS等[42]将牙髓干细胞条件培养基冷冻并冻干,置入大鼠颅骨缺损处,观察到缺损中心的骨形成较快,免疫组化染色显示血管内皮生长因子表达增加,这表明牙髓干细胞条件培养基的促成骨作用可能与血管内皮生长因子有关。BURGER等[43]去除脱落乳牙干细胞条件培养基中的血管内皮生长因子,发现促进人脐静脉内皮细胞增殖和血管生成的作用消失,且重组血管内皮生长因子能改善小鼠临界大小的原位颅骨缺损中早期血管浸润、骨祖细胞存活和分化以及骨修复,表明血管内皮生长因子是脱落乳牙干细胞条件培养基中有助于血管生成的主要成分。也有研究发现,骨形态发生蛋白与血管内皮生长因子之间存在协同作用,可以促进骨细胞存活、骨形成和矿化[44]。有研究表明脱落乳牙干细胞条件培养基中血管内皮生长因子在骨组织再生中有潜在益处[45],可能是直接影响促成骨信号分子,也可能是通过促进血管生成进而发挥促成骨的间接作用。 2.2.3 牙源性间充质干细胞条件培养基中神经营养因子对骨组织修复的作用 牙源性间充质干细胞起源于神经嵴,神经嵴是源自外胚层的细胞群,与产生周围神经系统各种细胞的细胞群相同,因此与其他间充质干细胞相比,它们能够分泌更多的神经营养因子。神经营养因子是一类对神经细胞起营养作用的分泌蛋白,能够促进神经细胞生长、保护神经细胞、促进神经元存活等,主要成分包括脑源性神经营养因子、神经生长因子、神经营养因子3等。近年来许多研究表明,神经营养因子与骨修复密切相关,不仅能直接促进骨髓间充质干细胞成骨,还能通过调节骨组织的神经支配与促血管生成对骨修复产生间接的有利影响。 脑源性神经营养因子已被证明可以显著上调成骨细胞分化标志物[46]。脑源性神经营养因子及其特异性受体酪氨酸激酶受体B在促进骨骼细胞分化方面起着重要作用,表明它们在骨形成和骨重塑中具有潜在的调节功能。一项研究发现,脑源性神经营养因子(100 ng/mL)可促进接种到β-磷酸三钙支架上的骨髓间充质干细胞的成神经和成骨作用。脑源性神经营养因子与酪氨酸激酶受体B结合导致下游细胞外调节蛋白激酶1/2的磷酸化,并诱导成骨细胞分化的主转录因子的表达,如Runt相关转录因子2和Osterix[47]。有研究发现,周围神经损伤能激活脑源性神经营养因子产生,导致牙槽骨的硬化性变化。在大鼠下牙槽神经损伤模型中,牙槽骨表面的外源性脑源性神经营养因子有助于下牙槽神经损伤的修复和下颌皮质截骨术后的新骨形成[46]。还有研究探讨了脑源性神经营养因子在骨骺软骨中的潜在作用,发现脑源性神经营养因子在增殖区的表达比在肥大区的表达更稳定,而在矿化软骨中几乎是阴性的[48],这进一步表明脑源性神经营养因子有利于骨再生和骨缺损修复[47]。 神经生长因子在股骨发育过程中表达于初级骨化中心附近的软骨周细胞。酪氨酸激酶受体A是高亲和力的神经生长因子受体,富集于成熟骨的骨膜和骨内膜表面。有研究发现,神经生长因子-酪氨酸激酶受体A信号通过调节骨祖细胞和血管形成来指导发育中股骨的神经支配。在长时间骨折愈合过程中,神经生长因子反应性酪氨酸激酶受体A阳性感觉神经纤维受到积极支配,促进骨软骨祖细胞扩增[49]。 神经营养因子3及酪氨酸激酶受体C也与骨修复密切相关,在骨损伤部位高表达[50]。神经营养因子3处理后的骨髓间充质干细胞具有更高的增殖能力,并通过细胞外调节蛋白激酶1/2和蛋白激酶B磷酸化上调成骨细胞分化相关基因。神经营养因子3还能在脂多糖诱导的炎症下保护骨髓间充质干细胞免受炎症损伤和凋亡[51]。此外,神经营养因子3可诱导大鼠原代骨髓间充质干细胞中血管内皮生长因子的表达[52]。在损伤修复过程中,神经营养因子3和酪氨酸激酶受体C在成骨细胞和骨髓间充质干细胞等骨修复细胞中表达,加速了骨折愈合过程。因此,神经营养因子3-酪氨酸激酶受体C信号通过促进血管生成和成骨来促进骨骼修复和骨折愈合[43,45]。 一项体外研究采用干细胞共培养、定量RT-PCR分析芯片、ELISA等方法比较了牙髓干细胞、骨髓间充质干细胞和脂肪间充质干细胞的神经营养活性,结果显示,与骨髓间充质干细胞/脂肪间充质干细胞相比,牙髓干细胞分泌的神经营养因子包括神经生长因子、脑源性神经营养因子等多种生长因子水平高3-10倍[53]。AHMED等[54]的体外实验表明,牙髓干细胞表达高水平的神经营养因子mRNA和蛋白质,牙髓干细胞条件培养基刺激神经元细胞的神经突形成和延伸,添加神经营养因子受体阻断剂能消除这些效果。在体内实验中,牙髓干细胞使受损面神经延伸更大的轴突并恢复更好的功能。与之相似,SULTAN等[55]采用ELISA方法在牙髓干细胞条件培养基中检测到高含量的神经生长因子、神经营养因子3和脑源性神经营养因子(分别为191.6,161.1,85.5 pg/mL),促进了三叉神经节神经元细胞的存活和再生。还有一项研究应用多重ELISA抗体阵列分析牙髓干细胞条件培养基中的活性成分,发现胰岛素样生长因子1的水平最高,占总蛋白的42.64%。胰岛素样生长因子1是一种重要的生长因子,具有多种作用,包括免疫调节、促进骨骼肌肉生长、调节代谢、维护神经系统功能等。在体内实验中,胰岛素样生长因子1能部分缓解大鼠动脉瘤性蛛网膜下腔出血引起的神经炎 症[56]。相较于其他来源的间充质干细胞,牙源性间充质干细胞条件培养基中的神经营养因子含量更高,这些因子不仅在神经细胞修复中表现出重要作用,同时也通过调控骨组织中的神经-骨信号传递机制,促进成骨细胞活化与分化。 2.2.4 牙源性间充质干细胞条件培养基中抗炎因子及免疫调节作用对骨组织修复的作用 骨愈合是一个复杂的过程,大致可分为3个部分重叠的阶段:炎症期、修复期和重塑期[57]。最终骨愈合的质量在很大程度上取决于初始炎症阶段,因此抗炎因子及对免疫细胞的调节作用对于骨愈合十分重要。有研究显示,牙髓干细胞条件培养基比骨髓间充质干细胞条件培养基含有更多的抗炎细胞因子[58-60],例如白细胞介素10,高34倍;白细胞介素13,高63倍;转化生长因子β1,高7倍。在XIA等[30]的体外实验中,脱落乳牙干细胞条件培养基可诱导M0型巨噬细胞向M2型极化,并分泌更多的分泌型卷曲相关蛋白1,且脱落乳牙干细胞条件培养基在小鼠颞下颌关节炎模型中发挥显著的骨再生活性。MAEDA等[61]发现小鼠腹腔注射脱落乳牙干细胞条件培养基可预防卵巢切除术引起的骨质疏松,进一步通过流式细胞术分析腹腔内巨噬细胞的组成,发现脱落乳牙干细胞条件培养基促进M2巨噬细胞活化,而使用白细胞介素4中和抗体抑制M2巨噬细胞的功能后,小鼠骨质减少。 综上所述,牙源性间充质干细胞条件培养基在骨修复中展现出诸多优势,见表1。与其他来源的干细胞相比,牙源性干细胞来源条件培养基不仅在促进成骨和抑制破骨方面表现突出,而且在抗炎和血管生成能力方面具备更强的适应性。尽管这些研究主要基于体外和动物实验,但它们共同揭示了牙源性干细胞来源条件培养基在组织再生医学中的潜力。 牙源性间充质干细胞条件培养基中的可溶性因子对骨组织修复的作用,见图4。 "
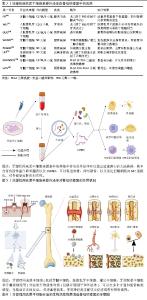
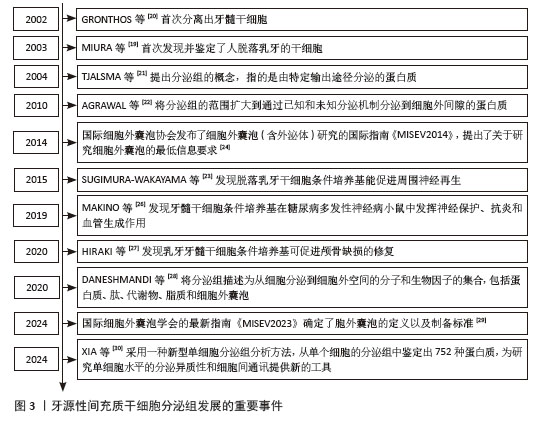
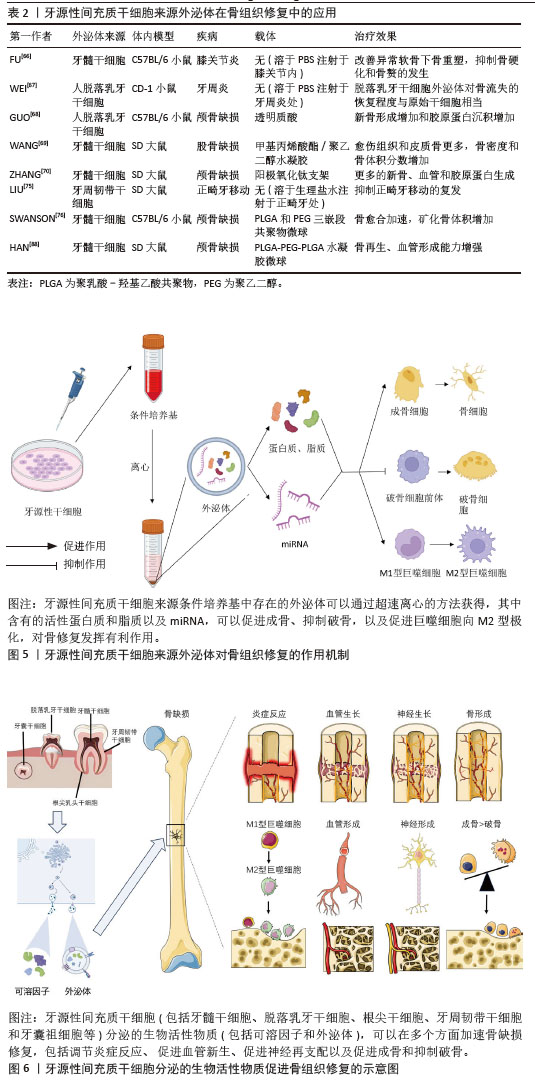
2.3 牙源性间充质干细胞衍生外泌体对骨组织修复的作用 2.3.1 牙源性间充质干细胞衍生外泌体对骨组织修复的作用 近年来有研究表明,牙源性间充质干细胞衍生外泌体中除了含有促成骨的细胞因子,还含有能促进成骨的miRNA,能通过靶向结合对应mRNA,增强成骨相关信号传导,例如牙髓干细胞来源外泌体中Hsa-miR-29c-5p能上调经典Wnt信号通路[62]、Hsa-miR-378a-5p能上调骨形态发生蛋白信号通路[63]、Hsa-miR-10b-5p能上调转化生长因子β/SMAD2信号通路等[64],对骨组织修复发挥有利作用。此外,牙源性间充质干细胞衍生外泌体还能抑制破骨细胞的活化,对成骨发挥间接作用。 LEE等[65]的体外实验中,牙髓干细胞衍生外泌体能显著促进颌骨骨髓源性干细胞的Runt相关转录因子2、碱性磷酸酶、骨钙素等成骨基因的表达,其在体外诱导的促成骨作用与骨形态发生蛋白2诱导的促成骨作用相当;将牙髓干细胞衍生外泌体搭载在胶原膜上植入大鼠下颌骨缺损模型中,表现出相对快速的伤口愈合和缺损处新骨密度的增加。FU等[66]在小鼠膝关节炎模型的关节内注射牙髓干细胞来源外泌体,发现有效促进了异常的软骨下骨重塑,抑制了骨硬化和骨赘的发生,缓解了软骨退化和滑膜炎症,其机制与外泌体抑制瞬时感受器电位香草酸受体4调节的破骨细胞活化有关。WEI等[67]的体外实验发现在不影响骨髓间充质干细胞增殖的情况下,脱落乳牙干细胞衍生外泌体轻度抑制骨髓间充质干细胞凋亡,显著增加骨髓间充质干细胞的成骨关键转录因子Runt相关转录因子2和p-Smad5、碱性磷酸酶的活性;注射脱落乳牙干细胞衍生外泌体对小鼠牙周炎骨流失的恢复程度与脱落乳牙干细胞近似,低剂量的脱落乳牙干细胞衍生外泌体能抑制炎性细胞因子白细胞介素6和肿瘤坏死因子α的表达。GUO等[68]从脱落乳牙干细胞中分离出外泌体,研究其对脱落乳牙干细胞成骨分化的影响,并将外泌体与牙髓干细胞一起混入透明质酸后植入颅骨缺损模型中,结果显示外泌体在体外促进牙髓干细胞的成骨分化,外泌体与牙髓干细胞混合后促进颅骨缺损修复。进一步研究作用机制,发现外泌体中含有线粒体转录因子A mRNA,通过转移线粒体转录因子A mRNA增加牙髓干细胞中线粒体转录因子A的表达,激活线粒体有氧代谢来加强牙髓干细胞的骨再生。 牙源性间充质干细胞衍生外泌体内含有多种促成骨的生物活性物质和miRNA,可靶向运输到靶细胞,调节靶细胞的转录、翻译和分泌,从而发挥促成骨作用。WANG等[69]用成骨诱导培养基培养牙髓干细胞,并分离得到外泌体,外泌体中有较高含量的骨钙素、骨唾液蛋白2和Runt相关转录因子2,能促进骨髓间充质干细胞迁移和成骨分化,促进皮下异位成骨模型的矿化和血管生成,且在大鼠股骨髁部缺损模型中促进骨形成。相较于牙源性间充质干细胞条件培养基,外泌体的独特之处还在于其中含有多种miRNA,这些miRNA能够进入靶细胞中,调节靶细胞的基因表达。最近许多研究发现,牙源性间充质干细胞衍生外泌体含有多种促进成骨的miRNA,对成骨发挥有利作用。ZHANG等[70]将牙髓干细胞成骨诱导后分泌的外泌体进行RNA测序,发现成骨诱导能上调成骨相关miRNA(Hsa-miR-29c-5p、Hsa-miR-378a-5p、Hsa-miR-10b-5p和Hsa-miR-9-3p),并下调抗成骨相关miRNA(Hsa-miR-31-3p、Hsa-miR-221-3p、Hsa-miR-183-5p和Hsa-miR-503-5p),将外泌体搭载阳极氧化的钛支架植入大鼠颅骨缺损模型中,实现了比未搭载外泌体的钛支架更强的骨再生效果。QU等[71]对牙周韧带细胞施加拉伸负荷后,提取外泌体并与成骨细胞共培养,通过免疫荧光和碱性磷酸酶染色发现拉伸诱导的牙周韧带细胞外泌体可被成骨细胞吸收并促进成骨细胞成骨分化,Western blot检测发现Runt相关转录因子2、骨形态发生蛋白2蛋白表达水平增加。同时,通过对外泌体microRNA测序发现,拉伸诱导的牙周韧带干细胞外泌体中miR-181d-5p显著上调。而转染miR-181d-5p的成骨细胞中成骨相关因子水平和碱性磷酸酶染色程度也升高,但是缺乏体内实验的验证。XIE等[72]分离来自成骨诱导不同时间点的牙髓干细胞外泌体,并针对环状RNA表达谱进行测序,发现circLPAR1表达增加,且与成骨分化程度相吻合。同时,牙髓干细胞衍生外泌体对受体同型牙髓干细胞具有促成骨作用。进一步研究作用机制,发现circLPAR1可以与hsa-miR-31结合,消除hsa-miR-31对成骨的抑制作用,从而促进受体同型牙髓干细胞的成骨分化。LU等[73]体外实验发现牙周韧带干细胞衍生外泌体通过miR-31-5p/内皮型一氧化氮合成酶信号通路抑制破骨细胞生成。在患有实验性牙周炎的小鼠中,牙周韧带干细胞衍生外泌体减少了牙槽骨破坏和牙槽骨表面破骨细胞的数量。WANG等[74]用脱落乳牙干细胞外泌体处理牙周韧带细胞,发现脱落乳牙干细胞外泌体可以改善牙周韧带细胞增殖、迁移、细胞周期、细胞凋亡和成骨分化。此外,对外泌体中的miRNA测序分析显示,脱落乳牙干细胞外泌体中miR-7-1-3p、miR-147b、miR-152-5p、miR-3152-3p和miR-4657高表达,miR-3622a-3p和miR-582-3p低表达。GO分析显示MAPK9、PARP6和Smad7等潜在靶基因可能受这些miRNA调节,然后修饰相应的调节信号通路,如MAPK和Wnt信号通路,导致细胞存活、增殖、凋亡和分化的改变。然而,脱落乳牙干细胞外泌体中MAPK9、PARP6和Smad7等靶基因的作用仍然是基于微阵列结果分析和以往文献分析的假设,仍有待进一步探索。 牙源性间充质干细胞衍生外泌体除了能不经改造直接发挥作用,还可以通过组织工程的方式包埋入其他药物或搭载新型生物材料,提高骨/牙再生效果。LIU等[75]将外泌体包埋辛伐他汀,注射到大鼠正畸牙移动模型的牙槽骨,阻止正畸牙移动后的复发。通过提取正畸牙附近总RNA和蛋白,发现骨相关基因(Runt相关转录因子2和碱性磷酸酶)和蛋白(Runt相关转录因子2、碱性磷酸酶、Osterix和Ⅰ型胶原)的表达水平升高。SWANSON等[76]设计了一个聚乳酸-羟基乙酸共聚物和聚乙二醇三嵌段共聚物微球,使其中搭载的牙髓干细胞外泌体受控释放,结果显示牙髓干细胞外泌体促进了骨髓间充质干细胞的成骨分化,且在小鼠颅骨缺损模型中加速骨愈合,其机制可能与骨髓间充质干细胞中Erk通路的激活有关。该研究团队另设计了一种聚乳酸-羟基乙酸共聚物基三嵌段共聚物载体,通过观察荧光染料的释放情况,发现该载体能实现牙髓干细胞衍生外泌体在8-12周的缓释,且洗脱出的牙髓干细胞衍生外泌体在扫描电镜下观察仍保持其特有的球形、大小和膜完整性,通过纳米颗粒跟踪分析外泌体洗脱液以确定释放量与颗粒数的函数关系,发现从外泌体洗脱液中提取的RNA量与外泌体颗粒数非常匹配,这说明该载体使牙髓干细胞衍生外泌体在8-12周的释放过程中保持生物活性,在大鼠磨牙牙髓暴露模型中可诱导牙髓干细胞迁移并分化为成牙细胞,分泌形成牙本质桥并防止牙髓坏死[77]。LIU等[78]的体外实验发现,脱落乳牙干细胞衍生外泌体可部分逆转糖皮质激素对骨髓间充质干细胞活力和成骨分化的抑制作用;转录组测序分析显示,脱落乳牙干细胞衍生外泌体调控的差异表达mRNA主要富集于细胞凋亡通路、PI3K-Akt信号通路、Hippo信号通路和p53信号通路等。脱落乳牙干细胞外泌体逆转了地塞米松诱导的肝细胞生长因子和整合素β8表达上调以及肝配蛋白A1表达下调,且进一步促进地塞米松诱导的白细胞介素7表达下调。 2.3.2 牙源性间充质干细胞衍生外泌体中的成血管因子对骨组织修复的作用 有研究显示,除了利于成骨的细胞因子,牙源性间充质干细胞衍生外泌体中还含有许多促血管生成的因子[79],如肝细胞生长因子、血管内皮生长因子,对骨修复发挥间接有利作用。肝细胞生长因子是一种可调节多种细胞生长、运动和形态发生的多功能因子,有体内实验显示,血管内皮生长因子和肝细胞生长因子对血管生成具有协同作用[80],除了具有促进血管内皮细胞增生和新生血管形成的作用外[81],也被报道有促成骨分化的作用。PARK等[82]的体外实验表明,肝细胞生长因子能促进脂肪来源干细胞的成骨分化。虽然血管内皮生长因子对成骨的促进作用更多的被认为是通过促进血管系统生长来实现的[83],但是牙髓干细胞衍生外泌体的促成骨作用也可能是通过肝细胞生长因子和血管内皮生长因子实现血管生成和成骨的耦合,从而促进骨再生。例如,HU等[84]研究发现,成骨细胞来源的血管内皮生长因子可耦合血管生成和成骨,调节骨修复过程中的成骨细胞分化和骨形成。也有研究显示,肝细胞生长因子可通过促进脂肪来源干细胞分泌血管内皮生长因子,促进骨形成[85]。 还有许多研究显示,将牙源性干细胞进行脂多糖或缺氧刺激后,其分泌的外泌体中促血管生成因子的含量增加。也有研究将外泌体与生物材料连用,实现更强的血管生成和成骨作用。HUANG等[86]的体外实验发现,脂多糖刺激后牙髓干细胞分泌的外泌体与正常牙髓干细胞分泌的外泌体相比,促进人脐静脉内皮细胞增殖、迁移和血管形成的能力更强。将这两种外泌体中的miRNA测序后进行GO分析和KEGG分析,发现脂多糖刺激组中有10个血管形成相关miRNA发生变化,其中血管内皮生长因子 mRNA表达水平显著高于正常对照组。GAO等[87]发现低氧环境诱导了脱落乳牙干细胞外泌体的释放增加,通过蛋白质组学分析和高通量测序比较了常氧和缺氧条件下产生的脱落乳牙干细胞外泌体,证明缺氧诱导的脱落乳牙干细胞能释放更多的外泌体,对缺氧诱导的脱落乳牙干细胞外泌体中的高通量RNA测序并进行KEGG分析,发现血管内皮生长因子信号通路显著上调,表现出更强的细胞募集和血管生成潜力。体外实验显示脱落乳牙干细胞外泌体可调节人脐静脉内皮细胞的血管生成潜力,而将脱落乳牙干细胞外泌体搭载一种缓释材料后能促进大鼠颅骨缺损的修复。HAN等[88]设计了一种双药程序释放水凝胶,能先后释放血管内皮生长因子和牙髓干细胞衍生外泌体,促进人脐血管内皮细胞的血管生成,并增强前成骨细胞的成骨分化;此外,将这种水凝胶体内移植到颅骨缺损中可促进骨形成。BRUNELLO等[89]的体外实验发现来自老年供体和年轻供体的牙髓干细胞衍生外泌体都能增加间充质干细胞旁分泌物的产生,与从老年供体获得的牙髓干细胞衍生外泌体相比,来自年轻供体的牙髓干细胞衍生外泌体诱导了更多的血管生成因子的产生,特别是血管内皮生长因子和肝细胞生长因子。ZHA等[90]用外泌体封装血管内皮生长因子基因来构建基因激活的工程外泌体,发现其作为基因载体能够可控释放血管内皮生长因子基因以重塑血管系统,有效诱导血管化骨再生。 2.3.3 牙源性间充质干细胞衍生外泌体通过调节免疫炎症对骨组织修复的作用 许多实验表明在炎症免疫细胞对颅颌面骨组织的修复有影响。牙源性间充质干细胞衍生外泌体能通过促进巨噬细胞向M2表型极化,从而抑制炎症反应,调节骨组织再生。QIAO等[91]发现牙髓干细胞衍生外泌体在体外不仅促进牙周韧带干细胞的增殖、迁移和成骨,还通过抑制脂多糖刺激的牙周韧带干细胞中白细胞介素6/Janus激酶2(Janus kinase 2,JAK2)/信号转导和转录活化因子3(signal transducer and activator of transcription 3,STAT3)信号通路来发挥抗炎作用。此外,牙髓干细胞衍生外泌体可以将巨噬细胞从M1表型极化为M2表型。在体内,牙髓干细胞衍生外泌体可以有效减少实验性牙周炎大鼠牙槽骨流失,促进牙周上皮愈合。一项研究通过在透明质酸水凝胶内掺入铜离子(Cu2+)和脱落乳牙干细胞衍生外泌体(Shed-Cu-HA)来开发一种用于牙周袋注射的新型药物,发现其可以增强人牙周膜干细胞的细胞活力和细胞增殖能力,并能上调成骨分化相关基因和蛋白的表达,进一步研究发现该药物通过白细胞介素6/JAK2/STAT3通路抑制巨噬细胞炎症反应。小鼠牙周炎模型的实验结果表明,Shed-Cu-HA有效降低了牙龈组织中炎性细胞浸润和细菌感染的程度,并促进了牙周骨组织的再生[92]。BAI等[93]研究了牙周韧带干细胞衍生外泌体对破骨细胞分化的影响,通过检测CD86、白细胞介素6等M1型巨噬细胞标志物,CD206和精氨酸酶1等M2型巨噬细胞标志物评估巨噬细胞极化方向,结果显示牙周韧带干细胞衍生外泌体促进破骨细胞分化和M2巨噬细胞极化,但抑制M1巨噬细胞极化,进一步研究发现,M1巨噬细胞抑制破骨细胞分化,而M2巨噬细胞促进破骨细胞分化,牙周韧带干细胞衍生外泌体通过抑制M1和促进M2巨噬细胞极化来促进破骨细胞分化。 还有实验表明,牙源性间充质干细胞衍生外泌体能够促进巨噬细胞向M1表型极化,然而这可能是在实验模型未处于炎症状态时发生。ZHAO等[94]收集压缩力刺激的牙周韧带成纤维细胞分泌的外泌体,发现外泌体显著诱导THP-1巨噬细胞的M1极化,用外泌体分泌抑制剂GW4869处理则消除了这种诱导效应。Western blot分析显示压缩力刺激组外泌体中Yes 相关蛋白含量升高,用外泌体处理的THP-1巨噬细胞中Yes 相关蛋白靶基因上调,当用Yes 相关蛋白抑制剂维替泊芬处理THP-1巨噬细胞时,Yes 相关蛋白靶基因的表达和M1极化显著下调。这些结果表明,压缩力刺激下牙周韧带成纤维细胞分泌的外泌体促进了THP-1巨噬细胞的M1极化。外泌体中Yes 相关蛋白水平升高可能是这种反应的关键因素。 还有实验表明,处于正常和炎症状态下的牙源性间充质干细胞衍生外泌体的内容物成分存在不同,发挥的免疫炎症微环境调控作用也不同。戴振宁等[95]分别从正常牙和慢性牙周炎患牙的牙周膜组织中提取牙周韧带干细胞衍生外泌体,通过蛋白质谱检测2种外泌体的蛋白组分,发现牙周炎组富集的差异表达蛋白主要与破骨细胞分化的肿瘤坏死因子信号通路、核转录因子κB信号通路相关;ELISA实验证实了牙周炎组外泌体中高表达肿瘤坏死因子α、核因子κB受体活化因子配体、白细胞介素1α,低表达转化生长因子β1、骨形态发生蛋白2。经牙周炎组外泌体处理后的RAW264.7细胞,破骨细胞分化相关基因及蛋白的表达水平升高。这些结果显示,慢性牙周炎的病理性骨吸收可能由炎性牙周韧带干细胞衍生外泌体中的核因子κB受体活化因子配体和肿瘤坏死因子α促进破骨细胞分化引起。 牙源性间充质干细胞来源外泌体在骨组织修复中的应用及机制,见表2和图5。牙源性间充质干细胞分泌的生物活性物质促进骨组织修复的示意图,见图6。 "
| [1] BAKKAR M, LIU Y, FANG D, et al. A Simplified and Systematic Method to Isolate, Culture, and Characterize Multiple Types of Human Dental Stem Cells from a Single Tooth. Methods Mol Biol. 2017;1553:191-207. [2] CHALISSERRY EP, NAM SY, PARK SH, et al. Therapeutic potential of dental stem cells. J Tissue Eng. 2017;8:2041731417702531. [3] NAKAMURA S, YAMADA Y, KATAGIRI W, et al. Stem cell proliferation pathways comparison between human exfoliated deciduous teeth and dental pulp stem cells by gene expression profile from promising dental pulp. J Endod. 2009;35(11):1536-1542. [4] LIU J, YU F, SUN Y, et al. Concise reviews: Characteristics and potential applications of human dental tissue-derived mesenchymal stem cells. Stem Cells. 2015;33(3):627-638. [5] YOUNG F, SLOAN A, SONG B. Dental pulp stem cells and their potential roles in central nervous system regeneration and repair. J Neurosci Res. 2013;91(11):1383-1393. [6] YAMADA Y, NAKAMURA S, ITO K, et al. Injectable bone tissue engineering using expanded mesenchymal stem cells. Stem Cells. 2013;31(3):572-580. [7] KIM HJ, CHO YA, LEE YM, et al. PIN1 Suppresses the Hepatic Differentiation of Pulp Stem Cells via Wnt3a. J Dent Res. 2016;95(12):1415-1424. [8] MEAD B, LOGAN A, BERRY M, et al. Concise Review: Dental Pulp Stem Cells: A Novel Cell Therapy for Retinal and Central Nervous System Repair. Stem Cells. 2017;35(1):61-67. [9] MORTADA I, MORTADA R. Dental pulp stem cells and osteogenesis: an update. Cytotechnology. 2018;70(5):1479-1486. [10] TABATABAEI FS, TORSHABI M. In vitro proliferation and osteogenic differentiation of endometrial stem cells and dental pulp stem cells. Cell Tissue Bank. 2017;18(2):239-247. [11] LAINO G, D’AQUINO R, GRAZIANO A, et al. A new population of human adult dental pulp stem cells: a useful source of living autologous fibrous bone tissue (LAB). J Bone Miner Res. 2005;20(8):1394-1402. [12] MATHEUS HR, ÖZDEMIR ŞD, GUASTALDI FPS. Stem cell-based therapies for temporomandibular joint osteoarthritis and regeneration of cartilage/osteochondral defects: a systematic review of preclinical experiments. Osteoarthritis Cartilage. 2022; 30(9):1174-1185. [13] EL MOSHY S, RADWAN IA, RADY D, et al. Dental Stem Cell-Derived Secretome/Conditioned Medium: The Future for Regenerative Therapeutic Applications. Stem Cells Int. 2020; 2020:7593402. [14] BERMUDEZ MA, SENDON-LAGO J, EIRO N, et al. Corneal epithelial wound healing and bactericidal effect of conditioned medium from human uterine cervical stem cells. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 2015;56(2):983-992. [15] TAN F, LI X, WANG Z, et al. Clinical applications of stem cell-derived exosomes. Signal Transduct Target Ther. 2024;9(1):17. [16] VIZOSO FJ, EIRO N, CID S, et al. Mesenchymal Stem Cell Secretome: Toward Cell-Free Therapeutic Strategies in Regenerative Medicine. Int J Mol Sci. 2017;18(9):1852. [17] BASU J, LUDLOW JW. Exosomes for repair, regeneration and rejuvenation. Expert Opin Biol Ther. 2016;16(4):489-506. [18] LIANG Y, DUAN L, LU J, et al. Engineering exosomes for targeted drug delivery. Theranostics. 2021;11(7):3183-3195. [19] MIURA M, GRONTHOS S, ZHAO M, et al. SHED: stem cells from human exfoliated deciduous teeth. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2003;100(10):5807-5812. [20] GRONTHOS S, BRAHIM J, LI W, et al. Stem cell properties of human dental pulp stem cells. J Dent Res. 2002;81(8):531-535. [21] TJALSMA H, ANTELMANN H, JONGBLOED JD, et al. Proteomics of protein secretion by Bacillus subtilis: separating the “secrets” of the secretome. Microbiol Mol Biol Rev. 2004; 68(2):207-233. [22] AGRAWAL GK, JWA NS, LEBRUN MH, et al. Plant secretome: unlocking secrets of the secreted proteins. Proteomics. 2010; 10(4):799-827. [23] SUGIMURA-WAKAYAMA Y, KATAGIRI W, OSUGI M, et al. Peripheral Nerve Regeneration by Secretomes of Stem Cells from Human Exfoliated Deciduous Teeth. Stem Cells Dev. 2015;24(22):2687-2699. [24] LÖTVALL J, HILL AF, HOCHBERG F, et al. Minimal experimental requirements for definition of extracellular vesicles and their functions: a position statement from the International Society for Extracellular Vesicles. J Extracell Vesicles. 2014;3:26913. [25] YU S, ZHAO Y, MA Y, et al. Profiling the Secretome of Human Stem Cells from Dental Apical Papilla. Stem Cells Dev. 2016;25(6):499-508. [26] MAKINO E, NAKAMURA N, MIYABE M, et al. Conditioned media from dental pulp stem cells improved diabetic polyneuropathy through anti-inflammatory, neuroprotective and angiogenic actions: Cell-free regenerative medicine for diabetic polyneuropathy. J Diabetes Investig. 2019;10(5):1199-1208. [27] HIRAKI T, KUNIMATSU R, NAKAJIMA K, et al. Stem cell-derived conditioned media from human exfoliated deciduous teeth promote bone regeneration. Oral Dis. 2020;26(2):381-390. [28] DANESHMANDI L, SHAH S, JAFARI T, et al. Emergence of the Stem Cell Secretome in Regenerative Engineering. Trends Biotechnol. 2020;38(12):1373-1384. [29] WELSH JA, GOBERDHAN DCI, O’DRISCOLL L, et al. Minimal information for studies of extracellular vesicles (MISEV2023): From basic to advanced approaches. J Extracell Vesicles. 2024;13(2):e12404. [30] XIA L, KANO F, HASHIMOTO N, et al. Conditioned Medium From Stem Cells of Human Exfoliated Deciduous Teeth Alleviates Mouse Osteoarthritis by Inducing sFRP1-Expressing M2 Macrophages. Stem Cells Transl Med. 2024;13(4):399-413. [31] BAR JK, LIS-NAWARA A, KOWALCZYK T, et al. Osteogenic Potential of Human Dental Pulp Stem Cells (hDPSCs) Growing on Poly L-Lactide-Co-Caprolactone and Hyaluronic Acid (HYAFF-11TM) Scaffolds. Int J Mol Sci. 2023;24(23):16747. [32] KOH B, AB RAHMAN FH, MATLAN NA, et al. Potential role of dental pulp stem cells conditioned medium for odontoblastic differentiation. Biol Res. 2022;55(1):11. [33] KUNIMATSU R, HIRAKI T, RIKITAKE K, et al. Effects of Human Deciduous Dental Pulp-Derived Mesenchymal Stem Cell-Derived Conditioned Medium on the Metabolism of HUVECs, Osteoblasts, and BMSCs. Cells. 2022; 11(20):3222. [34] KAMINOGO K, YAMAGUCHI S, CHEN H, et al. Preventive Effects of Dental Pulp Stem Cell-conditioned Media on Anti-RANKL Antibody-Related Osteonecrosis of the Jaw. Calcif Tissue Int. 2024;115(2):185-195. [35] NOVELLO S, TRICOT-DOLEUX S, NOVELLA A, et al. Influence of Periodontal Ligament Stem Cell-Derived Conditioned Medium on Osteoblasts. Pharmaceutics. 2022;14(4):729. [36] KANJI S, SARKAR R, PRAMANIK A, et al. Dental pulp-derived stem cells inhibit osteoclast differentiation by secreting osteoprotegerin and deactivating AKT signalling in myeloid cells. J Cell Mol Med. 2021;25(5):2390-2403. [37] ISHIKAWA J, TAKAHASHI N, MATSUMOTO T, et al. Factors secreted from dental pulp stem cells show multifaceted benefits for treating experimental rheumatoid arthritis. Bone. 2016;83:210-219. [38] MORI H, HAMAMURA K, YO S, et al. Conditioned medium from rat dental pulp reduces the number of osteoclasts via attenuation of adhesiveness in osteoclast precursors. J Oral Sci. 2018;60(3): 352-359. [39] CHOUAIB B, COLLART-DUTILLEUL PY, BLANC-SYLVESTRE N, et al. Identification of secreted factors in dental pulp cell-conditioned medium optimized for neuronal growth. Neurochem Int. 2021;144:104961. [40] TARKKA T, SIPOLA A, JÄMSÄ T, et al. Adenoviral VEGF-A gene transfer induces angiogenesis and promotes bone formation in healing osseous tissues. J Gene Med. 2003;5(7): 560-566. [41] KUSHIRO H, TAKAHASHI H, TANAKA A. Effects of the prevention of medication-related osteonecrosis of the jaw by local administration of a dental pulp stem cell-conditioned medium to the rat tooth extraction socket. Odontology. 2021;109(4):836-844. [42] BUSS LF, DE MARTIN GS, MARTINEZ EF, et al. Conditioned Media from Human Pulp Stem Cell Cultures Improve Bone Regeneration in Rat Calvarial Critical-Size Defects. J Funct Biomater. 2023;14(8):396. [43] BURGER MG, GROSSO A, BRIQUEZ PS, et al. Robust coupling of angiogenesis and osteogenesis by VEGF-decorated matrices for bone regeneration. Acta Biomater. 2022; 149:111-125. [44] PENG H, WRIGHT V, USAS A, et al. Synergistic enhancement of bone formation and healing by stem cell-expressed VEGF and bone morphogenetic protein-4. J Clin Invest. 2002; 110(6):751-759. [45] ZHANG R, LIU Y, QI Y, et al. Self-assembled peptide hydrogel scaffolds with VEGF and BMP-2 enhanced in vitro angiogenesis and osteogenesis. Oral Dis. 2022;28(3):723-733. [46] IDA-YONEMOCHI H, YAMADA Y, YOSHIKAWA H, et al. Locally Produced BDNF Promotes Sclerotic Change in Alveolar Bone after Nerve Injury. PLoS One. 2017;12(1):e0169201. [47] LIU Q, LEI L, YU T, et al. Effect of Brain-Derived Neurotrophic Factor on the Neurogenesis and Osteogenesis in Bone Engineering. Tissue Eng Part A. 2018;24(15-16):1283-1292. [48] YAMASHIRO T, FUKUNAGA T, YAMASHITA K, et al. Gene and protein expression of brain-derived neurotrophic factor and TrkB in bone and cartilage. Bone. 2001;28(4):404-409. [49] LI Z, MEYERS CA, CHANG L, et al. Fracture repair requires TrkA signaling by skeletal sensory nerves. J Clin Invest. 2019;129(12):5137-5150. [50] SU YW, CHIM SM, ZHOU L, et al. Osteoblast derived-neurotrophin‑3 induces cartilage removal proteases and osteoclast-mediated function at injured growth plate in rats. Bone. 2018;116:232-247. [51] 谢斌,常睿.神经营养因子-3干预对骨髓间充质干细胞成骨分化及细胞增殖、凋亡的影响[J].海南医学院学报,2018,24(16): 1463-1466. [52] SU YW, CHUNG R, RUAN CS, et al. Neurotrophin-3 Induces BMP-2 and VEGF Activities and Promotes the Bony Repair of Injured Growth Plate Cartilage and Bone in Rats. J Bone Miner Res. 2016;31(6): 1258-1274. [53] MEAD B, LOGAN A, BERRY M, et al. Paracrine-mediated neuroprotection and neuritogenesis of axotomised retinal ganglion cells by human dental pulp stem cells: comparison with human bone marrow and adipose-derived mesenchymal stem cells. PLoS One. 2014;9(10):e109305. [54] AHMED MN, SHI D, DAILEY MT, et al. Dental Pulp Cell Sheets Enhance Facial Nerve Regeneration via Local Neurotrophic Factor Delivery. Tissue Eng Part A. 2021;27(17-18): 1128-1139. [55] SULTAN N, AMIN LE, ZAHER AR, et al. Neurotrophic effects of dental pulp stem cells on trigeminal neuronal cells. Sci Rep. 2020;10(1):19694. [56] CHEN TF, CHEN KW, CHIEN Y, et al. Dental Pulp Stem Cell-Derived Factors Alleviate Subarachnoid Hemorrhage-Induced Neuroinflammation and Ischemic Neurological Deficits. Int J Mol Sci. 2019;20(15):3747. [57] CLAES L, RECKNAGEL S, IGNATIUS A. Fracture healing under healthy and inflammatory conditions. Nat Rev Rheumatol. 2012;8(3): 133-143. [58] BOUSNAKI M, BAKOPOULOU A, PICH A, et al. Mapping the Secretome of Dental Pulp Stem Cells Under Variable Microenvironmental Conditions. Stem Cell Rev Rep. 2022;18(4): 1372-1407. [59] MATSUMURA-KAWASHIMA M, OGATA K, MORIYAMA M, et al. Secreted factors from dental pulp stem cells improve Sjögren’s syndrome via regulatory T cell-mediated immunosuppression. Stem Cell Res Ther. 2021;12(1):182. [60] OGATA K, MATSUMURA-KAWASHIMA M, MORIYAMA M, et al. Dental pulp-derived stem cell-conditioned media attenuates secondary Sjögren’s syndrome via suppression of inflammatory cytokines in the submandibular glands. Regen Ther. 2021;16:73-80. [61] MAEDA A, KIKUIRI T, YOSHIMURA Y, et al. Bone resorption improvement by conditioned medium of stem cells from human exfoliated deciduous teeth in ovariectomized mice. Exp Ther Med. 2022;23(4):299. [62] KAPINAS K, KESSLER CB, DELANY AM. miR-29 suppression of osteonectin in osteoblasts: regulation during differentiation and by canonical Wnt signaling. J Cell Biochem. 2009; 108(1):216-224. [63] HUPKES M, SOTOCA AM, HENDRIKS JM, et al. MicroRNA miR-378 promotes BMP2-induced osteogenic differentiation of mesenchymal progenitor cells. BMC Mol Biol. 2014;15:1. [64] LI H, FAN J, FAN L, et al. MiRNA-10b Reciprocally Stimulates Osteogenesis and Inhibits Adipogenesis Partly through the TGF-β/SMAD2 Signaling Pathway. Aging Dis. 2018;9(6):1058-1073. [65] LEE AE, CHOI JG, SHI SH, et al. DPSC-Derived Extracellular Vesicles Promote Rat Jawbone Regeneration. J Dent Res. 2023;102(3): 313-321. [66] FU Y, CUI S, ZHOU Y, et al. Dental Pulp Stem Cell-Derived Exosomes Alleviate Mice Knee Osteoarthritis by Inhibiting TRPV4-Mediated Osteoclast Activation. Int J Mol Sci. 2023;24(5):4926. [67] WEI J, SONG Y, DU Z, et al. Exosomes derived from human exfoliated deciduous teeth ameliorate adult bone loss in mice through promoting osteogenesis. J Mol Histol. 2020;51(4):455-466. [68] GUO J, ZHOU F, LIU Z, et al. Exosome-shuttled mitochondrial transcription factor A mRNA promotes the osteogenesis of dental pulp stem cells through mitochondrial oxidative phosphorylation activation. Cell Prolif. 2022; 55(12):e13324. [69] WANG L, WEI X, HE X, et al. Osteoinductive Dental Pulp Stem Cell-Derived Extracellular Vesicle-Loaded Multifunctional Hydrogel for Bone Regeneration. ACS Nano. 2024;18(12): 8777-8797. [70] ZHANG S, WANG S, CHEN J, et al. Human dental pulp stem cell-derived exosomes decorated titanium scaffolds for promoting bone regeneration. Colloids Surf B Biointerfaces. 2024;235:113775. [71] QU F, ZHANG YF, WANG YY, et al. Cyclic stretch-induced exosomes from periodontal ligament cells promote osteoblasts osteogenic differentiation via the miR-181d-5p/TNF signaling pathway. Arch Oral Biol. 2024;157:105843. [72] XIE L, GUAN Z, ZHANG M, et al. Exosomal circLPAR1 Promoted Osteogenic Differentiation of Homotypic Dental Pulp Stem Cells by Competitively Binding to hsa-miR-31. Biomed Res Int. 2020;2020: 6319395. [73] LU J, YU N, LIU Q, et al. Periodontal Ligament Stem Cell Exosomes Key to Regulate Periodontal Regeneration by miR-31-5p in Mice Model. Int J Nanomedicine. 2023;18:5327-5342. [74] WANG M, LI J, YE Y, et al. SHED-derived exosomes improve the repair capacity and osteogenesis potential of hPDLCs. Oral Dis. 2023;29(4):1692-1705. [75] LIU X, MUHAMMED FK, LIU Y. Simvastatin encapsulated in exosomes can enhance its inhibition of relapse after orthodontic tooth movement. Am J Orthod Dentofacial Orthop. 2022;162(6):881-889. [76] SWANSON WB, ZHANG Z, XIU K, et al. Scaffolds with controlled release of pro-mineralization exosomes to promote craniofacial bone healing without cell transplantation. Acta Biomater. 2020;118: 215-232. [77] SWANSON WB, GONG T, ZHANG Z, et al. Controlled release of odontogenic exosomes from a biodegradable vehicle mediates dentinogenesis as a novel biomimetic pulp capping therapy. J Control Release. 2020;324: 679-694. [78] LIU F, WANG X, XU J, et al. Preliminary study on the mechanism by which exosomes derived from human exfoliated deciduous teeth improve the proliferation and osteogenic inhibitory effect of glucocorticoid-induced BMSCs. Gene. 2024;923:148575. [79] GANESH V, SEOL D, GOMEZ-CONTRERAS PC, et al. Exosome-Based Cell Homing and Angiogenic Differentiation for Dental Pulp Regeneration. Int J Mol Sci. 2022;24(1):466. [80] GOLOCHEIKINE A, TIRIVEEDHI V, ANGASWAMY N, et al. Cooperative signaling for angiogenesis and neovascularization by VEGF and HGF following islet transplantation. Transplantation. 2010;90(7):725-731. [81] MADONNA R, CEVIK C, NASSER M, et al. Hepatocyte growth factor: molecular biomarker and player in cardioprotection and cardiovascular regeneration. Thromb Haemost. 2012;107(4):656-661. [82] PARK JS, KIM D, HONG HS. Priming with a Combination of FGF2 and HGF Restores the Impaired Osteogenic Differentiation of Adipose-Derived Stem Cells. Cells. 2022;11(13): 2042. [83] QIN Q, LEE S, PATEL N, et al. Neurovascular coupling in bone regeneration. Exp Mol Med. 2022;54(11):1844-1849. [84] HU K, OLSEN BR. Osteoblast-derived VEGF regulates osteoblast differentiation and bone formation during bone repair. J Clin Invest. 2016;126(2):509-526. [85] PARK JS, KIM DY, HONG HS. FGF2/HGF priming facilitates adipose-derived stem cell-mediated bone formation in osteoporotic defects. Heliyon. 2024;10(2):e24554. [86] HUANG X, QIU W, PAN Y, et al. Exosomes from LPS-Stimulated hDPSCs Activated the Angiogenic Potential of HUVECs In Vitro. Stem Cells Int. 2021;2021:6685307. [87] GAO Y, YUAN Z, YUAN X, et al. Bioinspired porous microspheres for sustained hypoxic exosomes release and vascularized bone regeneration. Bioact Mater. 2022;14:377-388. [88] HAN S, YANG H, NI X, et al. Programmed release of vascular endothelial growth factor and exosome from injectable chitosan nanofibrous microsphere-based PLGA-PEG-PLGA hydrogel for enhanced bone regeneration. Int J Biol Macromol. 2023;253(Pt 1):126721. [89] BRUNELLO G, ZANOTTI F, TRENTINI M, et al. Exosomes Derived from Dental Pulp Stem Cells Show Different Angiogenic and Osteogenic Properties in Relation to the Age of the Donor. Pharmaceutics. 2022;14(5):908. [90] ZHA Y, LI Y, LIN T, et al. Progenitor cell-derived exosomes endowed with VEGF plasmids enhance osteogenic induction and vascular remodeling in large segmental bone defects. Theranostics. 2021;11(1):397-409. [91] QIAO X, TANG J, DOU L, et al. Dental Pulp Stem Cell-Derived Exosomes Regulate Anti-Inflammatory and Osteogenesis in Periodontal Ligament Stem Cells and Promote the Repair of Experimental Periodontitis in Rats. Int J Nanomedicine. 2023;18:4683-4703. [92] YU Y, LI X, YING Q, et al. Synergistic Effects of Shed-Derived Exosomes, Cu2+, and an Injectable Hyaluronic Acid Hydrogel on Antibacterial, Anti-inflammatory, and Osteogenic Activity for Periodontal Bone Regeneration. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces. 2024;16(26):33053-33069. [93] BAI X, WANG Y, MA X, et al. Periodontal ligament cells-derived exosomes promote osteoclast differentiation via modulating macrophage polarization. Sci Rep. 2024; 14(1):1465. [94] ZHAO M, MA Q, ZHAO Z, et al. Periodontal ligament fibroblast-derived exosomes induced by compressive force promote macrophage M1 polarization via Yes-associated protein. Arch Oral Biol. 2021;132:105263. [95] 戴振宁,郑蔚晗,利时雨.核因子κB受体活化因子配体和肿瘤坏死因子α经炎性牙周膜干细胞外泌体促进破骨细胞分化[J].华西口腔医学杂志,2022,40(4):377-385. [96] WU JY, LI YJ, HU XB, et al. Preservation of small extracellular vesicles for functional analysis and therapeutic applications: a comparative evaluation of storage conditions. Drug Deliv. 2021;28(1):162-170. [97] CUI Y, LI Z, GUO Y, et al. Bioinspired Nanovesicles Convert the Skeletal Endothelium-Associated Secretory Phenotype to Treat Osteoporosis. ACS Nano. 2022;16(7):11076-11091. [98] LIANG L, WANG L, LIAO Z, et al. High-yield nanovesicles extruded from dental follicle stem cells promote the regeneration of periodontal tissues as an alternative of exosomes. J Clin Periodontol. 2024;51(10):1395-1407. [99] JOO KH, SONG JS, KIM S, et al. Cytokine Expression of Stem Cells Originating from the Apical Complex and Coronal Pulp of Immature Teeth. J Endod. 2018;44(1):87-92.e1. [100] BHANDI S, AL KHATANI A, ABDULAZIZ SUMAYLI H, et al. Comparative analysis of cytokines and growth factors in the conditioned media of stem cells from the pulp of deciduous, young, and old permanent tooth. Saudi J Biol Sci. 2021;28(6):3559-3565. [101] BHANDI S, AL KAHTANI A, MASHYAKHY M, et al. Modulation of the Dental Pulp Stem Cell Secretory Profile by Hypoxia Induction Using Cobalt Chloride. J Pers Med. 2021;11(4):247. [102] YAMADA Y, NAKAMURA-YAMADA S, KUSANO K, et al. Clinical Potential and Current Progress of Dental Pulp Stem Cells for Various Systemic Diseases in Regenerative Medicine: A Concise Review. Int J Mol Sci. 2019;20(5):1132. [103] OGATA K, MORIYAMA M, MATSUMURA-KAWASHIMA M, et al. The Therapeutic Potential of Secreted Factors from Dental Pulp Stem Cells for Various Diseases. Biomedicines. 2022;10(5):1049. [104] GUGLIANDOLO A, MAZZON E. Dental Mesenchymal Stem Cell Secretome: An Intriguing Approach for Neuroprotection and Neuroregeneration. Int J Mol Sci. 2021; 23(1):456. |
| [1] | Cao Wenqi, Feng Xiuzhi, Zhao Yi, Wang Zhimin, Chen Yiran, Yang Xiao, Ren Yanling. Effect of macrophage polarization on osteogenesis-angiogenesis coupling in type 2 diabetic osteoporosis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(4): 917-925. |
| [2] | Zhang Tingting, Li Yalong, Yue Haodi, Li Yanjun, Geng Xiwen, Zhang Yuwei, Liu Xiaozhuan. Protection of exosomes derived from bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells of different mouse ages on radiation-induced lung injury [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(1): 1-9. |
| [3] | Yu Manya, Cui Xing. Contribution and interaction of various cells in bone marrow microenvironment to exosomal circular RNA associated with multiple myeloma bone disease [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(1): 101-110. |
| [4] | Sun Huiwen, Guo Qiangqiang, Wang Wei, Wu Jie, Xi Kun, Gu Yong. Engineered stem cell bionic periosteum coordinates immune inflammation and vascularization to promote bone regeneration [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(1): 21-33. |
| [5] | Zuo Na, Tang Qi, Yu Meng, Tao Kai. Effect of miR-196b-5p in adipose-derived stem cell exosomes on burn wound healing in rats [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(1): 43-49. |
| [6] | Yuan Weiyuan, Lei Qinhui, Li Xiuqi, Lu Tiezhu, Fu Ziwen, Liang Zhili, Ji Shaoyang, Li Yijia, Ren Yu . Therapeutic effects of adipose-derived mesenchymal stem cells and their exosomes on dexamethasone-induced sarcopenia in mice [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(1): 58-67. |
| [7] | Ma Wenjing, Zhang Jinyu, Jiang Mingxia, Xiu Bingshui, Bai Rui, Liu Yuhan, Chen Xuyi, Yuan Zengqiang, Liu Zhiqiang. Scaffold-free three-dimensional human umbilical cord mesenchymal stem cell secretome repairs mouse skin injury [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(1): 68-77. |
| [8] | Xu Haichao, Luo Lihua, Pan Yihuai. Application and progress of dental pulp stem cells and their derivatives in dental pulp regeneration [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(1): 153-162. |
| [9] | Liu Nian, Dong Xinyue, Wang Songpeng, Xu Yingjiang, Zhang Xiaoming. Stem cell exosomes and biomaterial-assisted exosomes in bone defect repair [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(1): 175-183. |
| [10] | Lyu Ruyue, Gu Lulu, Liu Qian, Zhou Siyi, Li Beibei, Xue Letian, Sun Peng. Regulatory mechanisms of exosome secretion and its application prospects in biomedicine [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(1): 184-193. |
| [11] | Liu Yu, Gong Senyi, Yang Lihua, Li Weifeng, Hu Yuwen, Yan Qinbiao, Guo Meijin. Isolation, identification, and application of exosomes derived from mesenchymal stem cells [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(1): 194-203. |
| [12] | Luo Wenbin, Li Ruoyun, Pan Chaofan, Luo Changjiang. Engineered exosomes for repairing tissue damage: application potential, excellent biological stability, and targeting specificity [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(1): 204-217. |
| [13] | Lai Pengyu, Liang Ran, Shen Shan. Tissue engineering technology for repairing temporomandibular joint: problems and challenges [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(在线): 1-9. |
| [14] | Yu Ting, Lyu Dongmei, Deng Hao, Sun Tao, Cheng Qian. Icariin pretreatment enhances effect of human periodontal stem cells on M1-type macrophages [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(7): 1328-1335. |
| [15] | Jin Kai, Tang Ting, Li Meile, Xie Yuan. Effects of conditioned medium and exosomes of human umbilical cord mesenchymal stem cells on proliferation, migration, invasion, and apoptosis of hepatocellular carcinoma cells [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(7): 1350-1355. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||