Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research ›› 2026, Vol. 30 ›› Issue (1): 50-57.doi: 10.12307/2025.578
Previous Articles Next Articles
Effect of dimethylglyoxal glycine on osteogenic, adipogenesis differentiation, and mitophagy of human bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells
Chen Qiheng1, 2, Weng Tujun1, Peng Jiang1
- 1Institute of Orthopedics, Fourth Medical Center, Chinese People’s Liberation Army General Hospital, Beijing 100853, China; 2Chinese People’s Liberation Army Medical School, Beijing 100853, China
-
Received:2024-10-31Accepted:2024-12-23Online:2026-01-08Published:2025-06-17 -
Contact:Peng Jiang, Chief physician, Researcher, Institute of Orthopedics, Fourth Medical Center, Chinese People’s Liberation Army General Hospital, Beijing 100853, China; Co-corresponding author: Weng Tujun, Associate researcher, Institute of Orthopedics, Fourth Medical Center, Chinese People’s Liberation Army General Hospital, Beijing 100853, China -
About author:Chen Qiheng, Master candidate, Institute of Orthopedics, Fourth Medical Center, Chinese People’s Liberation Army General Hospital, Beijing 100853, China; Chinese People’s Liberation Army Medical School, Beijing 100853, China -
Supported by:National Key Research and Development Plan Project, No. 2022YFB3804303 (to WTJ); Youth Independent Innovation Science Fund Project of Chinese People’s Liberation Army General Hospital, No. 22QNCZ032 (to WTJ)
CLC Number:
Cite this article
Chen Qiheng, Weng Tujun, Peng Jiang. Effect of dimethylglyoxal glycine on osteogenic, adipogenesis differentiation, and mitophagy of human bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(1): 50-57.
share this article
Add to citation manager EndNote|Reference Manager|ProCite|BibTeX|RefWorks
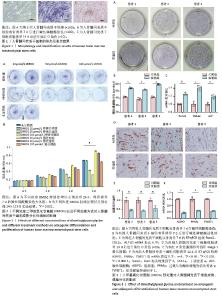
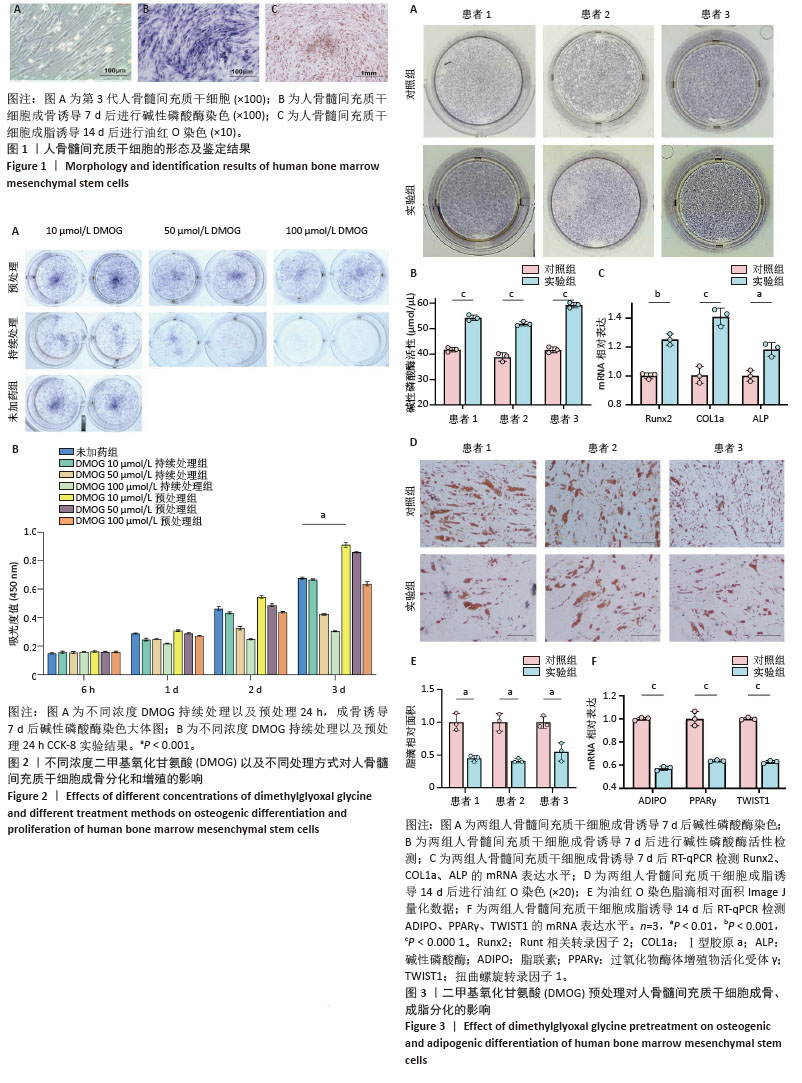
2.1 人骨髓间充质干细胞的形态及鉴定结果 倒置显微镜下观察,第3 代人骨髓间充质干细胞贴壁生长,部分呈漩涡状生长,排列紧密,细胞形态为梭形,见图1A。第3代人骨髓间充质干细胞成骨诱导7 d后进行碱性磷酸酶染色,倒置显微镜下观察细胞胞膜及胞浆蓝染,染色呈阳性反应,见图1B。第3代人骨髓间充质干细胞成脂诱导14 d后进行油红O染色,倒置显微镜下观察可见大量红染脂滴形成,见图1C。 2.2 不同浓度DMOG以及不同处理方式对人骨髓间充质干细胞成骨分化及增殖的影响 碱性磷酸酶染色显示,持续处理组随着DMOG浓度上升,其对人骨髓间充质干细胞成骨分化抑制越明显。在预处理组中,10 μmol/L DMOG具有明显的成骨促进作用,而50,100 μmol/L DMOG并没有促进成骨的效果,100 μmol/L组甚至表现为轻微抑制作用,见图2A。CCK-8实验显示10 μmol/L DMOG预处理24 h对人骨髓间充质干细胞无细胞毒性且促进增殖最明显,见图2B。在后续实验中将10 μmol/L DMOG预处理24 h设置为实验组,未经DMOG处理设置为对照组。 2.3 DMOG预处理对人骨髓间充质干细胞成骨、成脂分化的影响 碱性磷酸酶染色显示,与对照组相比,10 μmol/L DMOG预处理24 h促进了人骨髓间充质干细胞的成骨分化,见图3A。碱性磷酸酶活性显示,与对照组相比,实验组碱性磷酸酶活性更强,见图3B。RT-qPCR结果显示,在成骨诱导7 d后,与对照组相比,实验组成骨相关基因表达更高,见图3C。与成骨分化相反,油红O染色显示实验组脂滴形成明显弱于对照组,见图3D,E。RT-qPCR结果与油红O染色结果相同,实验组成脂相关基因表达明显弱于对照组,见图3F。上述这些结果表明,10 μmol/L DMOG预处理24 h可以改变人骨髓间充质干细胞的成骨、成脂分化平衡,使其更加偏向成骨分化,从而在理论上能够增强骨髓间充质干细胞在股骨头坏死治疗中的疗效。 "
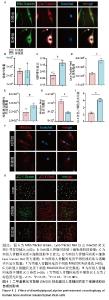
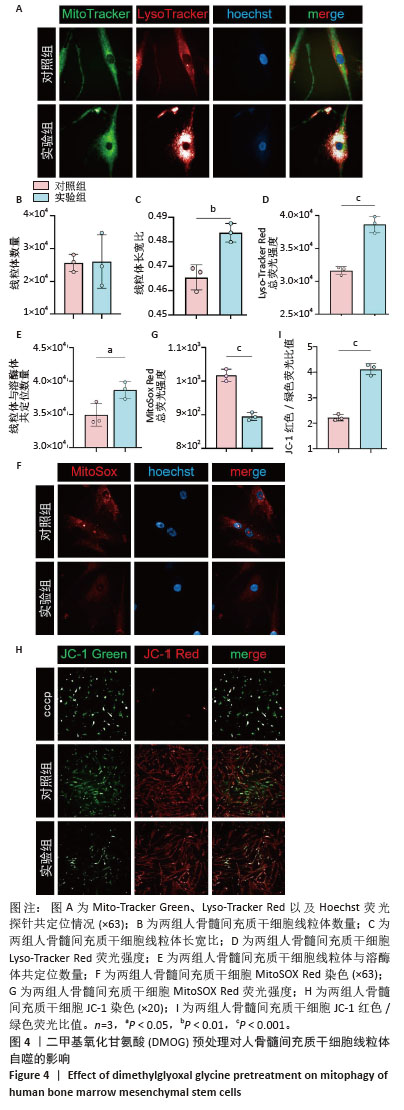
2.4 DMOG预处理对人骨髓间充质干细胞线粒体自噬的影响 Mito-Tracker Green、Lyso-Tracker Red以及Hoechst共定位实验,见图4A。与对照组相比,实验组虽然在线粒体数量上与对照组没有统计学差异,但是实验组线粒体长宽比更大,提示实验组细胞中的线粒体形态更加细长,更加健康,见图4B,C。实验组Lyso-Tracker Red荧光强度以及线粒体和溶酶体共定位的数量明显优于对照组,见图4D,E。MitoSOX Red染色显示实验组线粒体活性氧水平稍低于对照组,见图4F,G。JC-1染色显示,实验组绿色荧光的不健康线粒体明显少于对照组,而健康的红色荧光线粒体两组大致相同,实验组红色荧光与绿色荧光的比值更大,见图4H,I。上述这些结果表明,10 μmol/L DMOG预处理24 h增强了人骨髓间充质干细胞的线粒体自噬。 "
| [1] ZHAO D, ZHANG F, WANG B, et al. Guidelines for clinical diagnosis and treatment of osteonecrosis of the femoral head in adults (2019 version). J Orthop Translat. 2020;21:100-110. [2] XU Y, JIANG Y, XIA C, et al. Stem cell therapy for osteonecrosis of femoral head: Opportunities and challenges. Regen Ther. 2020;15: 295-304. [3] LI Y, FU G, GONG Y, et al. BMP-2 promotes osteogenic differentiation of mesenchymal stem cells by enhancing mitochondrial activity. J Musculoskelet Neuronal Interact. 2022;22(1):123-131. [4] YAN C, SHI Y, YUAN L, et al. Mitochondrial quality control and its role in osteoporosis. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2023;14:1077058. [5] WU J, NIU J, LI X, et al. Hypoxia induces autophagy of bone marrow-derived mesenchymal stem cells via activation of ERK1/2. Cell Physiol Biochem. 2014;33(5):1467-1474. [6] WANG K, PENG X, ZHANG R, et al. COL6A3 enhances the osteogenic differentiation potential of BMSCs by promoting mitophagy in the osteoporotic microenvironment. Mol Biol Rep. 2024;51(1):206. [7] MA S, LI S, ZHANG Y, et al. BMSC-Derived Exosomal CircHIPK3 Promotes Osteogenic Differentiation of MC3T3-E1 Cells via Mitophagy. Int J Mol Sci. 2023;24(3):2785. [8] LIU F, YUAN Y, BAI L, et al. LRRc17 controls BMSC senescence via mitophagy and inhibits the therapeutic effect of BMSCs on ovariectomy-induced bone loss. Redox Biol. 2021;43:101963. [9] BAI H, WANG Y, ZHAO Y, et al. HIF signaling: A new propellant in bone regeneration. Biomater Adv. 2022;138:212874. [10] NOWAK-STĘPNIOWSKA A, OSUCHOWSKA PN, FIEDOROWICZ H, et al. Insight in Hypoxia-Mimetic Agents as Potential Tools for Mesenchymal Stem Cell Priming in Regenerative Medicine. Stem Cells Int. 2022;2022: 8775591. [11] YI L, JU Y, HE Y, et al. Intraperitoneal injection of Desferal® alleviated the age-related bone loss and senescence of bone marrow stromal cells in rats. Stem Cell Res Ther. 2021;12(1):45. [12] SONG S, ZHANG G, CHEN X, et al. HIF-1α increases the osteogenic capacity of ADSCs by coupling angiogenesis and osteogenesis via the HIF-1α/VEGF/AKT/mTOR signaling pathway. J Nanobiotechnology. 2023;21(1):257. [13] SHAO W, LI Z, WANG B, et al. Dimethyloxalylglycine Attenuates Steroid-Associated Endothelial Progenitor Cell Impairment and Osteonecrosis of the Femoral Head by Regulating the HIF-1α Signaling Pathway. Biomedicines. 2023;11(4):992. [14] ZHANG F, PENG W, WANG T, et al. Lnc Tmem235 promotes repair of early steroid-induced osteonecrosis of the femoral head by inhibiting hypoxia-induced apoptosis of BMSCs. Exp Mol Med. 2022;54(11): 1991-2006. [15] ABU-SHAHBA AG, GEBRAAD A, KAUR S, et al. Proangiogenic Hypoxia-Mimicking Agents Attenuate Osteogenic Potential of Adipose Stem/Stromal Cells. Tissue Eng Regen Med. 2020;17(4):477-493. [16] ZHANG P, HA N, DAI Q, et al. Hypoxia suppresses osteogenesis of bone mesenchymal stem cells via the extracellular signal‑regulated 1/2 and p38‑mitogen activated protein kinase signaling pathways. Mol Med Rep. 2017;16(4):5515-5522. [17] JIANG Y, FAN X, YU Y, et al. USP13 Overexpression in BMSCs Enhances Anti-Apoptotic Ability and Guards Against Methylprednisolone-Induced Osteonecrosis in Rats. Stem Cells. 2024;43(1):sxae069. [18] ZHENG C, WU Y, XU J, et al. Exosomes from bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells ameliorate glucocorticoid-induced osteonecrosis of femoral head by transferring microRNA-210 into bone microvascular endothelial cells. J Orthop Surg Res. 2023;18(1):939. [19] YANG N, LI M, LI X, et al. MAGL blockade alleviates steroid-induced femoral head osteonecrosis by reprogramming BMSC fate in rat. Cell Mol Life Sci. 2024;81(1):418. [20] LIAO Z, JIN Y, CHU Y, et al. Single-cell transcriptome analysis reveals aberrant stromal cells and heterogeneous endothelial cells in alcohol-induced osteonecrosis of the femoral head. Commun Biol. 2022;5(1):324. [21] LEE JS, LEE JS, ROH HL, et al. Alterations in the differentiation ability of mesenchymal stem cells in patients with nontraumatic osteonecrosis of the femoral head: comparative analysis according to the risk factor. J Orthop Res. 2006;24(4):604-609. [22] HOUDEK MT, WYLES CC, PACKARD BD, et al. Decreased Osteogenic Activity of Mesenchymal Stem Cells in Patients With Corticosteroid-Induced Osteonecrosis of the Femoral Head. J Arthroplasty. 2016; 31(4):893-898. [23] FENG X, XIANG Q, JIA J, et al. CircHGF suppressed cell proliferation and osteogenic differentiation of BMSCs in ONFH via inhibiting miR-25-3p binding to SMAD7. Mol Ther Nucleic Acids. 2022;28:99-113. [24] MAS-BARGUES C, SANZ-ROS J, ROMÁN-DOMÍNGUEZ A, et al. Relevance of Oxygen Concentration in Stem Cell Culture for Regenerative Medicine. Int J Mol Sci. 2019;20(5):1195. [25] HU Y, LOU B, WU X, et al. Comparative Study on In Vitro Culture of Mouse Bone Marrow Mesenchymal Stem Cells. Stem Cells Int. 2018; 2018:6704583. [26] ZHAO F, VELDHUIS JJ, DUAN Y, et al. Low oxygen tension and synthetic nanogratings improve the uniformity and stemness of human mesenchymal stem cell layer. Mol Ther. 2010;18(5):1010-1018. [27] ZHAO D, LIU L, CHEN Q, et al. Hypoxia with Wharton’s jelly mesenchymal stem cell coculture maintains stemness of umbilical cord blood-derived CD34+ cells. Stem Cell Res Ther. 2018;9(1):158. [28] DONG Q, FEI X, ZHANG H, et al. Effect of Dimethyloxalylglycine on Stem Cells Osteogenic Differentiation and Bone Tissue Regeneration-A Systematic Review. Int J Mol Sci. 2024;25(7):3879. [29] LU Y, LI Z, ZHANG S, et al. Cellular mitophagy: Mechanism, roles in diseases and small molecule pharmacological regulation. Theranostics. 2023;13(2):736-766. [30] SAMAL JRK, RANGASAMI VK, SAMANTA S, et al. Discrepancies on the Role of Oxygen Gradient and Culture Condition on Mesenchymal Stem Cell Fate. Adv Healthc Mater. 2021;10(6):e2002058. [31] CHEN W, WU P, YU F, et al. HIF-1α Regulates Bone Homeostasis and Angiogenesis, Participating in the Occurrence of Bone Metabolic Diseases. Cells. 2022;11(22):3552. [32] WU D, LIU L, FU S, et al. Osteostatin improves the Osteogenic differentiation of mesenchymal stem cells and enhances angiogenesis through HIF-1α under hypoxia conditions in vitro. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2022;606:100-107. [33] SUN K, JING X, GUO J, et al. Mitophagy in degenerative joint diseases. Autophagy. 2021;17(9):2082-2092. [34] XIANG K, REN M, LIU F, et al. Tobacco toxins trigger bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells aging by inhibiting mitophagy. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf. 2024;277:116392. [35] YANG Q, ZOU Y, WEI X, et al. PTP1B knockdown alleviates BMSCs senescence via activating AMPK-mediated mitophagy and promotes osteogenesis in senile osteoporosis. Biochim Biophys Acta Mol Basis Dis. 2023;1869(7):166795. [36] LI G, JIAN Z, WANG H, et al. Irisin Promotes Osteogenesis by Modulating Oxidative Stress and Mitophagy through SIRT3 Signaling under Diabetic Conditions. Oxid Med Cell Longev. 2022;2022:3319056. [37] LU Z, JIANG L, LESANI P, et al. Nicotinamide Mononucleotide Alleviates Osteoblast Senescence Induction and Promotes Bone Healing in Osteoporotic Mice. J Gerontol A Biol Sci Med Sci. 2023; 78(2):186-194. [38] LIN Q, LI S, JIANG N, et al. Inhibiting NLRP3 inflammasome attenuates apoptosis in contrast-induced acute kidney injury through the upregulation of HIF1A and BNIP3-mediated mitophagy. Autophagy. 2021;17(10):2975-2990. [39] LI J, LIN Q, SHAO X, et al. HIF1α-BNIP3-mediated mitophagy protects against renal fibrosis by decreasing ROS and inhibiting activation of the NLRP3 inflammasome. Cell Death Dis. 2023;14(3):200. [40] FU ZJ, WANG ZY, XU L, et al. HIF-1α-BNIP3-mediated mitophagy in tubular cells protects against renal ischemia/reperfusion injury. Redox Biol. 2020;36:101671. |
| [1] | Wu Yanting, Li Yu, Liao Jinfeng. Magnesium oxide nanoparticles regulate osteogenesis- and angiogenesis-related gene expressions to promote bone defect healing [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(8): 1885-1895. |
| [2] | Jiang Xinghai, Song Yulin, Li Dejin, Shao Jianmin, Xu Junzhi, Liu Huakai, Wu Yingguo, Shen Yuehui, Feng Sicheng. Vascular endothelial growth factor 165 genes transfected into bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells to construct a vascularized amphiphilic peptide gel module [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(8): 1903-1911. |
| [3] | Hou Chaowen, Li Zhaojin, Kong Jianda, Zhang Shuli. Main physiological changes in skeletal muscle aging and the multimechanism regulatory role of exercise [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(6): 1464-1475. |
| [4] | Lyu Xiaofan, Huang Yi, Ding Liucheng . Mitochondrial mechanism and intervention therapy in diabetic cystopathy [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(6): 1508-1515. |
| [5] | Zhou Zixiang, Zhao Baoxiang. Research progress in the relationship between nontraumatic necrosis of the femoral head and lipid metabolism and its treatment [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(3): 680-690. |
| [6] | Lu Yongheng, Zhu Shuang, Zhao Feiyan, Ai Fujun, Liu Yanjie, Dong Yangting, Guan Zhizhong, Wei Na. Effect of fluoride exposure on endoplasmic reticulum-mitochondrial calcium transfer and apoptosis in primary nerve cells [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(1): 111-119. |
| [7] | Zhang Tingting, Li Yalong, Yue Haodi, Li Yanjun, Geng Xiwen, Zhang Yuwei, Liu Xiaozhuan. Protection of exosomes derived from bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells of different mouse ages on radiation-induced lung injury [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(1): 1-9. |
| [8] | Zhao Yang, Li Jialin, Wu Xiao, Zou Yourui, Liu Yang, Ma Hui. Choline kinase alpha silencing affects proliferation and apoptosis in glioma cells by inducing mitochondrial dysfunction [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(1): 130-138. |
| [9] | Li Yiwen, Liu Feixiang, Zhang Yunke. Regulation of lysosome function by stem cells in treatment of lysosomal storage diseases [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(1): 145-152. |
| [10] | Sun Huiwen, Guo Qiangqiang, Wang Wei, Wu Jie, Xi Kun, Gu Yong. Engineered stem cell bionic periosteum coordinates immune inflammation and vascularization to promote bone regeneration [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(1): 21-33. |
| [11] | Sun Zhanpeng, Liu Sen, Shi Ling, Chen Kaiyuan, Song Meichen, Wu Yan, Yu Jing. Bone marrow mesenchymal stem cell nanovesicles fusion neutrophil apoptotic bodies promote skin wound healing in diabetic mice [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(1): 34-42. |
| [12] | Li Jiagen, Chen Yueping, Huang Keqi, Chen Shangtong, Huang Chuanhong. The construction and validation of a prediction model based on multiple machine learning algorithms and the immunomodulatory analysis of rheumatoid arthritis from the perspective of mitophagy [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(在线): 1-15. |
| [13] | Li Huayuan, Li Chun, Liu Junwei, Wang Ting, Li Long, Wu Yongli. Effect of warm acupuncture on PINK1/Parkin pathway in the skeletal muscle of rats with chronic fatigue syndrome [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(8): 1618-1625. |
| [14] | Zhu Hanmin, Wang Song, Xiao Wenlin, Zhang Wenjing, Zhou Xi, He Ye, Li Wei, . Mitophagy regulates bone metabolism [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(8): 1676-1683. |
| [15] | Yang Zhihang, Sun Zuyan, Huang Wenliang, Wan Yu, Chen Shida, Deng Jiang. Nerve growth factor promotes chondrogenic differentiation and inhibits hypertrophic differentiation of rabbit bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(7): 1336-1342. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||