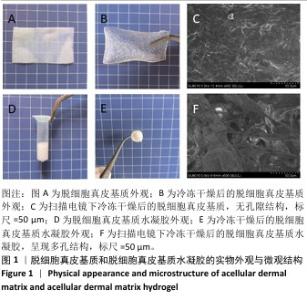
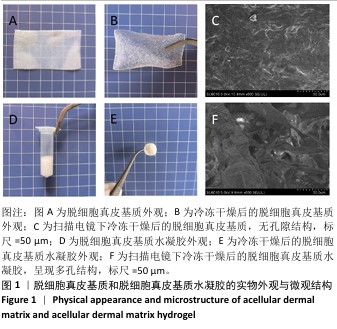
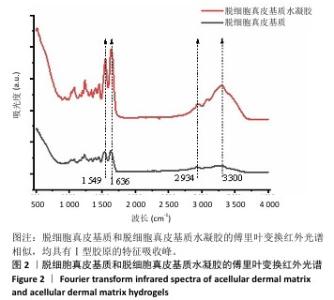
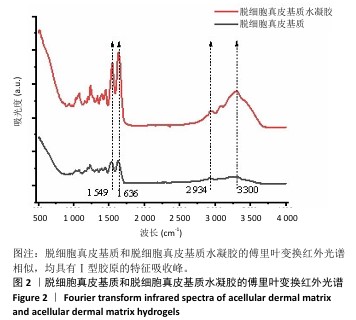
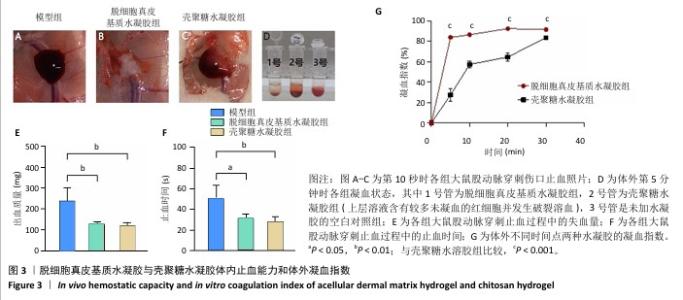
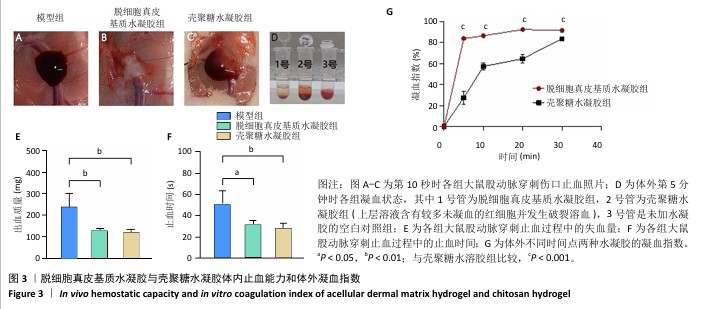
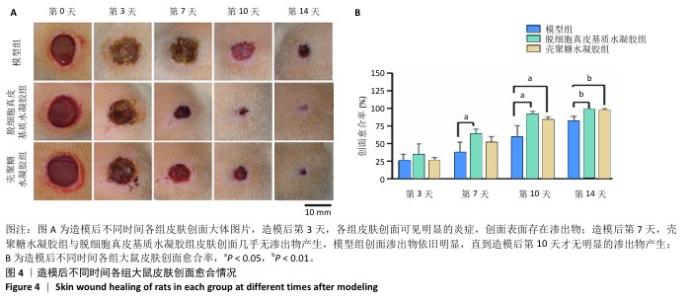
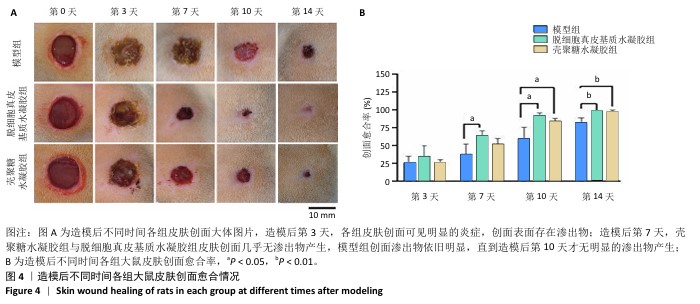
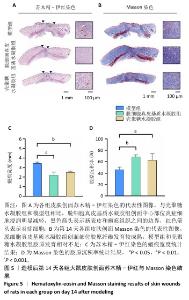
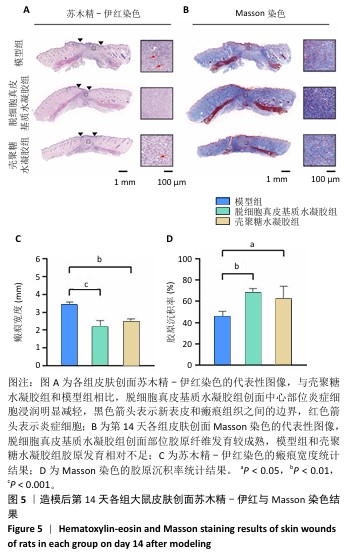
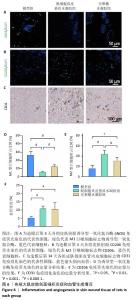
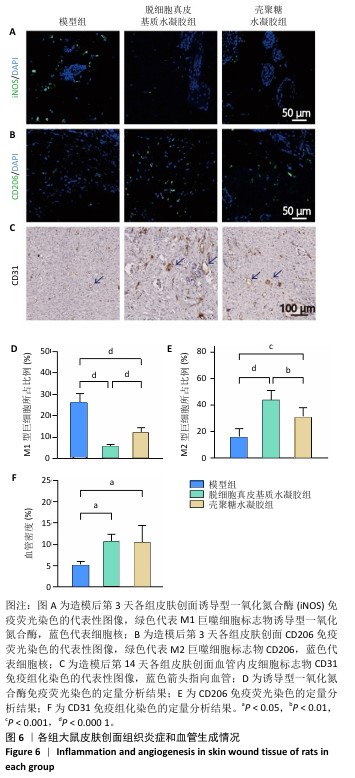
[1] XING D, XIA G, TANG X, et al. A multifunctional nanocomposite hydrogel delivery system based on dual-loaded liposomes for scarless wound healing. Adv Healthc Mater. 2024;16:e2401619.
[2] LIANG W, NI N, HUANG Y, et al. An advanced review: polyurethane-related dressings for skin wound repair. Polymers (Basel). 2023;15(21): 4301.
[3] DUARTE J, MELO FM, PIRES PC, et al. Multifunctional hydrogels-based therapies for chronic diabetic wound healing. Int J Biol Macromol. 2022;15(210):377-393.
[4] FU D, HUANG J, WU X, et al. Shape-fixing hydrogel promotes scarless healing of wounds under tension. Acta biomater. 2024;15(183): 173-190.
[5] JIANGTAO Y, DINGWEI W, JIANPING L, et al. An injectable composite hydrogel of verteporfin-bonded carboxymethyl chitosan and oxidized sodium alginate facilitates scarless full-thickness skin regeneration. Macromol Biosci. 2024;24(2):e2300165.
[6] HAN Z, XIANG L, XINYUE C, et al. Developing natural polymers for skin wound healing. Bioact Mater. 2023;26(33):355-376.
[7] WANG Y, ZHANG Y, YANG YP, et al. Versatile dopamine-functionalized hyaluronic acid-recombinant human collagen hydrogel promoting diabetic wound healing via inflammation control and vascularization tissue regeneration. Bioact Mater. 2024;14(35):330-345.
[8] ZHAO F, ZHANG M, NIZAMOGLU M, et al. Fibroblast alignment and matrix remodeling induced by a stiffness gradient in a skin-derived extracellular matrix hydrogel. Acta biomater. 2024;182:67-80.
[9] WU Q, YANG R, FAN W, et al. Spermidine-functionalized injectable hydrogel reduces inflammation and enhances healing of acute and diabetic wounds In situ. Adv Sci (Weinh). 2024;11(22):e2310162.
[10] XUEWEI Z, XI C, HUA H, et al. Decellularized extracellular matrix scaffolds: recent trends and emerging strategies in tissue engineering. Bioact Mater. 2021;23(10):15-31.
[11] ZHOU Z, BU Z, WANG S, et al. Extracellular matrix hydrogels with fibroblast growth factor 2 containing exosomes for reconstructing skin microstructures. J Nanobiotechnology. 2024;22(1):438.
[12] ESLAHI N, SOLEIMANI F, LOTFI R, et al. How biomimetic nanofibers advance the realm of cutaneous wound management: the state-of-the-art and future prospects. Prog Mater Sci. 2024;145:101293.
[13] 蒋永生,李锐,韩春婵,等.脱细胞基质水凝胶促组织再生的研究进展[J].中国生物医学工程学报,2021,40(5):628-635.
[14] HUIMIN X, XIN C, XUANZHE L, et al. Recent advances in decellularized biomaterials for wound healing. Mater Today Bio. 2023;23(19):100589.
[15] CHEN Y, HU M, HU H, et al. Fabrication of an adhesive small intestinal submucosa acellular matrix hydrogel for accelerating diabetic wound healing. ACS Omega. 2023;8(49):46653-46662.
[16] HUANG Z, CHENG J, SU W. A double cross-linked injectable hydrogel derived from muscular decellularized matrix promotes myoblast proliferation and myogenic differentiation. Materials (Basel). 2023; 16(15):5335.
[17] 刘忠钰,李文娅,范永鸿,等.甲基丙烯酰化改性真皮细胞外基质水凝胶促进腹壁缺损修复[J].中国组织工程研究,2024,29(10): 2074-2082.
[18] KUMAR V, KUMAR N, GANGWAR AK, et al. Comparative evaluation of two different xenogenic acellular matrices on full-thickness skin wound healing. J Wound Care. 2024;33(Sup3a): lxxiv-lxxx.doi: 10.12968/jowc.2024.33.Sup3a.lxxiv.
[19] BS A, GANESH SB, ESWARAMOORTHY R, et al. Hyaluronic acid hydrogel combined with ocimum sanctum and tendon-derived extracellular matrix enhances tenogenesis in periodontal ligament stem cells. Cureus. 2024;16(2):e54060.
[20] KAMEDANI M, OKAWA M, MADHAVIKUTTY AS, et al. Injectable extracellular matrix-inspired hemostatic hydrogel composed of hyaluronan and gelatin with shear-thinning and self-healing. Biomacromolecules. 2024;25(3):1790-1799.
[21] HONGYUAN X, ZENGJIE Z, QIJIANG M, et al. Injectable exosome-functionalized extracellular matrix hydrogel for metabolism balance and pyroptosis regulation in intervertebral disc degeneration. J Nanobiotechnology. 2021;19(1):264.
[22] ZHAO J, ZHANG D, LAN Q, et al. Tendon decellularized matrix modified fibrous scaffolds with porous and crimped microstructure for tendon regeneration. ACS Appl Bio Mater. 2024;7(7):4747-4759.
[23] 徐鑫,刘曜玮,穆云萍,等.脱细胞真皮基质水凝胶的制备及生物学评价[J].中国组织工程研究,2023,27(21):3325-3331.
[24] YANG Y, MA Y, WANG H, et al. Chitosan-based hydrogel dressings with antibacterial and antioxidant for wound healing. Int J Biol Macromol. 2024;280(Pt 2):135939.
[25] NORO J, VILAÇA-FARIA H, REIS RL, et al. Extracellular matrix-derived materials for tissue engineering and regenerative medicine: A journey from isolation to characterization and application. Bioact Mater. 2024; 34:494-519.
[26] LUO Y, TAO F, WANG J, et al. Development and evaluation of tilapia skin-derived gelatin, collagen, and acellular dermal matrix for potential use as hemostatic sponges. Int J Biol Macromol. 2023;253(Pt 4):127014.
[27] PANG Z, LI Q, LIU K, et al. Efficacy of melanin-loaded lipoic acid-modified chitosan hydrogel in diabetic wound healing. Carbohydr Polym. 2024;340:122215.
[28] PATEL DK, GANGULY K, HEXIU J, et al. Functionalized chitosan/spherical nanocellulose-based hydrogel with superior antibacterial efficiency for wound healing. Carbohydr Polym. 2022;284:119202.
[29] ZHANG X, HUANG Y, LUO T, et al. Advanced wound healing and scar reduction using an innovative anti-ROS polysaccharide hydrogel with recombinant human collagen type III. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces. 2024;16(38):50305-50320.
[30] CHIN SW, AZMAN AS, TAN JW. Incorporation of natural and synthetic polymers into honey hydrogel for wound healing: a review. Health Sci Rep. 2024;7(7):e2251.
[31] THOMAS K, AHMAD A, NICOLAS F, et al. A cell-free, biomimetic hydrogel based on probiotic membrane vesicles ameliorates wound healing. J Control Release. 2024;365:969-980.
[32] MOHAMMAD S, MARZIYEH F, JALEH B, et al. Bioactive hydrogel-based scaffolds for the regeneration of dental pulp tissue. J Drug Deliv Sci Tec. 2021;64:102600.
[33] LIU M, JIN J, ZHONG X, et al. Polysaccharide hydrogels for skin wound healing. Heliyon. 2024;10(15):e35014.
[34] CHOCARRO-WRONA C, LÓPEZ DE ANDRÉS J, RIOBOÓ-LEGASPI P, et al. Design and evaluation of a bilayered dermal/hypodermal 3D model using a biomimetic hydrogel formulation. Biomed Pharmacother. 2024; 177:117051.
[35] DING Q, ZHANG S, LIU X, et al. Hydrogel tissue bioengineered scaffolds in bone repair: a review. Molecules. 2023;28(20):7039.
[36] CHABRIA Y, DUFFY GP, LOWERY AJ, et al. Hydrogels: 3D drug delivery systems for nanoparticles and extracellular vesicles. Biomedicines. 2021;9(11):1694.
[37] JIN F, LI X, CHEN J, et al. Clinical study on the role of platelet-rich plasma in human acellular dermal matrix with razor autologous skin graft repair of giant congenital pigmented nevus in children. J Plast Reconstr Aesthet Surg. 2024;90:305-314.
[38] SHUIQING Z, QIUSHENG W, AO H, et al. Advances in skin wound and scar repair by polymer scaffolds. Molecules. 2021;26(20):6110.
[39] CUI D, GUO W, CHANG J, et al. Polydopamine-coated polycaprolactone/carbon nanotube fibrous scaffolds loaded with basic fibroblast growth factor for wound healing. Mater Today Bio. 2024;6(28): 101190.
[40] ZHANG X, YANG C, ZENG X, et al. A bioactive composite sponge based on biomimetic collagen fibril and oxidized alginate for noncompressible hemorrhage and wound healing. Carbohydr Polym. 2024;1(343): 122409.
[41] WANG T, LI X, LIU S, et al. Stepwise co-assembled biomimetic hydrogel with antibacterial, angiogenesis, and tissue regeneration acceleration for diabetic wound healing. Mater Design. 2024;244:113149.
[42] YIN S, WU H, HUANG Y, et al. Structurally and mechanically tuned macroporous hydrogels for scalable mesenchymal stem cell-extracellular matrix spheroid production. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2024;121(28):e2404210121.
[43] RIJNS L, BAKER MB, DANKERS PYW. Using chemistry to recreate the complexity of the extracellular matrix: guidelines for supramolecular hydrogel-cell interactions. J Am Chem Soc. 2024;146(26):
17539-17558.
[44] YU Y, XIAO H, TANG G, et al. Biomimetic hydrogel derived from decellularized dermal matrix facilitates skin wounds healing. Mater Today Bio. 2023;7(21):100725.
[45] YANG Y, SUO D, XU T, et al. Sprayable biomimetic double mask with rapid autophasing and hierarchical programming for scarless wound healing. Sci Adv. 2024;10(33):eado9479.
[46] ZHANG S, LEI X, LV Y, et al. Recent advances of chitosan as a hemostatic material: hemostatic mechanism, material design and prospective application. Carbohydr Polym. 2024;327:121673.
[47] PENG S, NIU S, GAO Q, et al. Hydroxypropyl chitosan/ε-poly-l-lysine based injectable and self-healing hydrogels with antimicrobial and hemostatic activity for wound repair. Carbohydr Polym. 2024; 337:122135.
[48] HUANG Z, ZHANG D, TONG L, et al. Protonated-chitosan sponge with procoagulation activity for hemostasis in coagulopathy. Bioact Mater. 2024;41:174-192.
[49] LEI XX, ZOU CY, HU JJ, et al. Click-crosslinked in-situ hydrogel improves the therapeutic effect in wound infections through antibacterial, antioxidant and anti-inflammatory activities. Chem Eng J. 2023;461:142092.
[50] CHEN Z, ZOU Y, SUN H, et al. Engineered enucleated mesenchymal stem cells regulating immune microenvironment and promoting wound healing. Adv Mater. 2024;19:e2412253.
|