Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research ›› 2026, Vol. 30 ›› Issue (4): 917-925.doi: 10.12307/2026.530
Previous Articles Next Articles
Effect of macrophage polarization on osteogenesis-angiogenesis coupling in type 2 diabetic osteoporosis
Cao Wenqi1, Feng Xiuzhi1, Zhao Yi1, Wang Zhimin2, Chen Yiran1, Yang Xiao3, Ren Yanling1
- 1Liaoning University of Traditional Chinese Medicine, Shenyang 110847, Liaoning Province, China; 2Affiliated Hospital of Liaoning University of Traditional Chinese Medicine, Shenyang 110033, Liaoning Province, China; 3The Second Affiliated Hospital of Liaoning University of Traditional Chinese Medicine, Shenyang 110034, Liaoning Province, China
-
Received:2024-11-25Accepted:2025-01-25Online:2026-02-08Published:2025-05-20 -
Contact:Ren Yanling, PhD, Professor, Liaoning University of Traditional Chinese Medicine, Shenyang 110847, Liaoning Province, China -
About author:Cao Wenqi, PhD candidate, Liaoning University of Traditional Chinese Medicine, Shenyang 110847, Liaoning Province, China -
Supported by:the National Natural Science Foundation of China, No. 82174260 (to RYL); the Joint Fund for Doctoral Research Initiation Project of Liaoning Provincial Science and Technology Department, No. 2023-BSBA-224 (to FXZ)
CLC Number:
Cite this article
Cao Wenqi, Feng Xiuzhi, Zhao Yi, Wang Zhimin, Chen Yiran, Yang Xiao, Ren Yanling. Effect of macrophage polarization on osteogenesis-angiogenesis coupling in type 2 diabetic osteoporosis[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(4): 917-925.
share this article
Add to citation manager EndNote|Reference Manager|ProCite|BibTeX|RefWorks
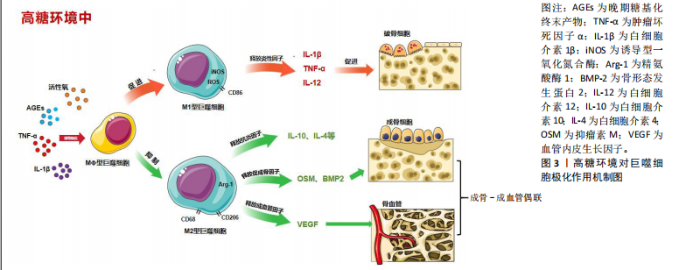
2.1 M1/M2巨噬细胞极化与T2DOP相关机制研究 目前,研究发现多种因素导致2型糖尿病患者骨脆性增加、骨质恶化,例如慢性高血糖、氧化应激、晚期糖基化终末产物(advanced glycation end products,AGEs)的形成、免疫失衡等。巨噬细胞作为人体的主要免疫细胞,在吞噬异物和消除病原体方面起着至关重要的作用。当巨噬细胞暴露在脂多糖、慢性高血糖环境中,可诱导巨噬细胞极化为M1表型(促炎型),主要特征是大量释放白细胞介素1β、肿瘤坏死因子α、白细胞介素12、活性氧和诱导型一氧化氮合酶等炎症因子。而在白细胞介素4、白细胞介素10和白细胞介素13的诱导下可极化为M2表型(抗炎型),释放抗炎因子,如白细胞介素4和白细胞介素10等来预防炎症发生[12-13]。 2.1.1 活性氧与M1/M2巨噬细胞极化 慢性高血糖状态下,糖酵解发生改变,慢性高血糖中单核细胞和巨噬细胞中活性氧形成加剧,并通过释放促炎细胞因子和蛋白酶促进炎症发生,导致巨噬细胞极化异常和免疫反应紊乱。活性氧的过量产生是巨噬细胞M1表型极化和随后促炎因子释放的重要机制[14]。在糖尿病大鼠牙周病研究中,用高糖培养基培养RAW264.7细胞,结果发现巨噬细胞浸润增强以及向M1巨噬细胞极化(诱导型一氧化氮合酶、肿瘤坏死因子α和白细胞介素6表达增加),活性氧水平升高;M2巨噬细胞标志物精氨酸酶1和CD206表达降低[15]。 活性氧是激活促炎信号通路的重要递质,与炎症和骨质流失密切相关[16],T2DOP属于炎症性骨质疏松症,慢性高糖状态会导致巨噬细胞的线粒体自噬受到抑制,活性氧在细胞中积累,诱导功能异常[17]。激活Apelin受体可以增强BNIP3-PINK1-PARKIN介导的线粒体自噬,减少活性氧的积累,并抑制NLRP3炎性小体的产生,最终抑制巨噬细胞M1极化,减轻炎症性骨质流失[18]。 2.1.2 AGEs与M1/M2巨噬细胞极化 AGEs是蛋白质、脂质和核酸通过美拉德反应和多元醇途径与葡萄糖形成的非酶糖基化产物[19]。AGEs在骨基质中的积累会降低胶原的柔韧性和骨骼强度[20]。有研究发现,慢性高血糖环境下,AGEs对破骨细胞、成骨细胞的分化和功能均有抑制作用,这表明AGEs可能通过降低骨转换率,导致骨质恶化而增加骨脆性[21]。AGEs参与巨噬细胞极化和破骨细胞生成的调控。用AGEs处理RAW264.7巨噬细胞,观察到M1相关细胞因子(诱导型一氧化氮合酶、白细胞介素6、白细胞介素12b)和表面抗原标记CD86表达增加;同时,抗酒石酸酸性磷酸酶染色和破骨细胞相关标志物(活化T细胞核因子1、肿瘤坏死因子受体相关因子6、核因子κB 受体激活因子、抗酒石酸酸性磷酸酶和组织蛋白酶K)检测结果显示,AGEs显著增强了M1型巨噬细胞的破骨能力,这可能与AGEs有效激活Notch信号通路的转导并促进NICD1的核转位有关。使用γ-分泌酶抑制剂DAPT和靶向沉默RBP-J的siRNA阻断Notch通路的信号传导,AGEs诱导的M1极化显著缓解,因此Notch/NICD/RBP-J信号轴是调节AGEs介导M1极化的重要机制[22]。研究表明,与对照组相比,AGEs培养的MC3T3-E1细胞矿化结节面积、胰岛素样生长因子1、骨保护素、骨保护素/核因子κB受体活化因子配体和β-catenin蛋白表达较对照组均显著降低,因此调控胰岛素样生长因子1/β-catenin/骨保护素信号通路,可能改善AGEs诱导的T2DOP[23]。 综上所述,慢性高血糖状态下巨噬细胞极化失衡,M1巨噬细胞数量增加,导致体内炎症因子积累,而这种慢性炎症状态正是骨丢失的关键驱动因素。在骨质疏松症模型中也发现M1/M2巨噬细胞的比例增加[24]。因此,改变骨免疫微环境可能成为防治T2DOP的关键点。 2.2 巨噬细胞极化对成骨-成血管偶联的影响 骨作为一种高度血管化的组织,其血管分布和血液供应对于维持骨微环境的稳态和骨重塑起着至关重要的作用[25]。骨血管为骨组织提供必要的营养、氧气和生长因子,与骨骼发育和骨生成密切相关。骨生成和血管之间的这种紧密的时空联系被称为“成骨-成血管偶联”[26-27]。其中,H型血管是骨骼独特的微血管,特点为高表达内皮黏蛋白和CD31,位于干骺端的生长板附近以及骨干的骨膜和骨内膜,周围被表达转录因子Osterix的骨祖细胞紧密包围[28]。现已有研究发现,T2DOP模型小鼠骨质流失加速以及H型血管减少,而促进H型血管形成能预防骨质疏松症发生[29-30]。因此,H型血管成为研究骨质疏松症发病机制的新焦点,在成骨-成血管偶联中起到重要作用。 M1、M2巨噬细胞自身及分泌的细胞因子、亚型可能影响成骨-成血管偶联,见图3。下文中将分别介绍M1巨噬细胞、M2巨噬细胞对成骨-成血管偶联的影响。 2.2.1 M1巨噬细胞对成骨-成血管偶联的影响 前文已论述2型糖尿病引起的高糖炎性环境促进巨噬细胞向M1极化,并对成骨诱导起到抑制作用。在慢性高血糖培养皿中提取巨噬细胞的上清液,检测发现肿瘤坏死因子α和白细胞介素1β炎性细胞因子分泌增多,M1型巨噬细胞极化增加,且破骨细胞的数量和大小增加[31]。 骨缺损模型中发现M1巨噬细胞在修复过程中对血管生成具有抑制作用[32]。M1巨噬细胞外泌体内高表达miRNA-155-5p。对miRNA-155-5p靶基因进行KEGG注释和GO富集分析,结果显示它参与管形态发生和上皮细胞增殖的调节;进一步体内、外实验发现,miRNA-155-5p可以通过靶向生长分化因子6抑制糖尿病伤口愈合来抑制血管生成[33]。 2.2.2 M2巨噬细胞对成骨-成血管偶联的影响 首先,M2巨噬细胞可以直接作用于骨髓间充质干细胞,对其分化具有积极影响,通过调节抑瘤素M和骨形态发生蛋白2的表达促进软骨和骨的形成;其次,M2巨噬细胞通过分泌外泌体、细胞因子或改变亚型等方式影响成骨-成血管偶联。 M2巨噬细胞来源外泌体通过增加骨髓间充质干细胞中miR-690、IRS-1和TAZ2的表达,抑制脂肪生成并促进骨髓间充质干细胞的成骨[34],并且发现miR-690能提高胰岛素敏感性[35]。一项研究发现,M2巨噬细胞来源外泌体通过降低M1巨噬细胞比例来调节2型糖尿病中骨免疫微环境。通过PIK3/AKT途径诱导M1巨噬细胞向M2巨噬细胞转化,形成“RM2巨噬细胞”。这种“RM2巨噬细胞”可以表达M2特异性标志蛋白精氨酸酶1、CD206;成骨相关基因(Runt相关转录因子2、Osterix和骨钙素)表达上调及碱性磷酸酶、茜素红染色显示出优越的成骨能力[36]。目前,尚不清楚M2型巨噬细胞外泌体中的哪些"


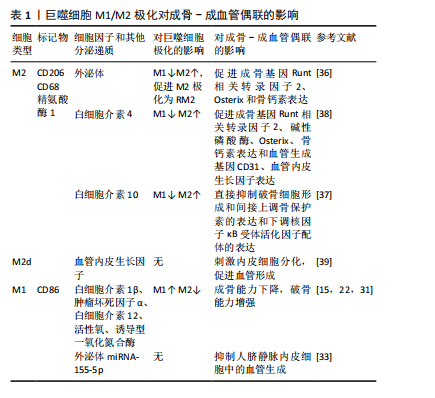
活性物质特异性地促进成骨分化,这可能归因于miRNA或蛋白质的作用,具有进一步研究的价值。 M2巨噬细胞分泌白细胞介素10、白细胞介素4等抗炎因子。白细胞介素10可以直接抑制破骨细胞形成、间接上调骨保护素的表达以及下调核因子κB受体活化因子配体的表达对破骨细胞生成具有抑制作用[37]。在一项以2型糖尿病小鼠作为模型来研究拔牙窝愈合延迟的实验中发现,通过白细胞介素4递送增强系统可促进巨噬细胞向M2极化,并增加2型糖尿病小鼠成骨基因Runt相关转录因子2、碱性磷酸酶、Osterix、骨钙素表达和血管生成基因CD31、血管内皮生长因子表达[38]。 M2巨噬细胞主要分为4种亚型,分别为M2a、M2b、M2c、M2d[39],其中M2d巨噬细胞是由Toll样受体配体与A2腺苷受体激动剂或白细胞介素6联合诱导的肿瘤相关M2巨噬细胞亚型,分泌白细胞介素10和血管内皮生长因子,而血管内皮生长因子是血管形成的关键递质。一些细胞因子和转录因子参与血管内皮生长因子A的转录和分泌,如缺氧诱导因子1α、血小板衍生生长因子BB、Noggin、Runt相关转录因子2等,这些因子与骨组织H型血管的形成密切相关[40]。成骨细胞也衍生血管内皮生长因子,可刺激血管生成和成骨细胞分化,这种促血管生成的作用也由巨噬细胞介导[41],但此项研究中并未对调控血管生成的巨噬细胞类型做进一步研究。 综上所述,在2型糖尿病的慢性炎症环境中M1/M2巨噬细胞比例失衡,M1向M2巨噬细胞转化率降低,这可能导致破骨细胞激活,M2巨噬细胞分泌的促进成骨-成血管偶联相关调节因子降低,导致成骨-成血管偶联受到抑制,提高M1向M2巨噬细胞的转化率,可能成为改善T2DOP的关键点。表1总结了巨噬细胞M1/M2极化对成骨-成血管偶联的影响。 2.3 相关治疗药物调控巨噬细胞极化对成骨-成血管偶联的影响 2.3.1 抗糖类药物 (1)双胍类:二甲双胍是一种被广泛认可的治疗2型糖尿病的药物,已被证明除控制血糖之外,还可以调节炎症反应和成骨活性[42]。研究发现,二甲双胍作用于巨"
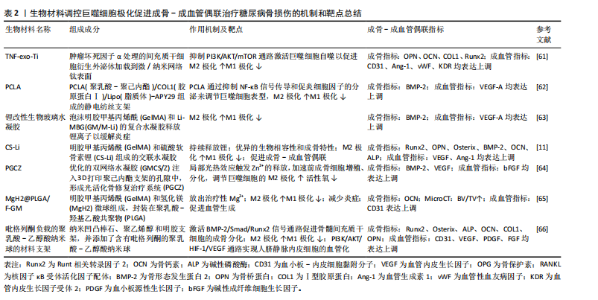
噬细胞和人脐带间充质干细胞的共培养体系,通过增加M2巨噬细胞和减少M1巨噬细胞来影响免疫系统,并且经二甲双胍处理的M2巨噬细胞更具有骨诱导能力,相应的成骨基因和蛋白表达(碱性磷酸酶、Runt相关转录因子2、骨钙素和Ⅰ型胶原)增加,这可能与二甲双胍刺激M2巨噬细胞、激活PI3K/AKT/mTOR通路促进成骨相关[43]。另一项关于二甲双胍对巨噬细胞极化和炎症反应影响的研究发现,二甲双胍对骨髓间充质干细胞具有促进成骨分化作用,并且能调节巨噬细胞极化为抗炎表型,促进抗炎因子(白细胞介素10、CD206、精氨酸酶1)的释放,抑制促炎因子(白细胞介素1β、肿瘤坏死因子α、白细胞介素6和诱导型一氧化氮合酶)来改善免疫微环境[44]。 以上实验表明,二甲双胍可以通过调控巨噬细胞极化,促进M2型巨噬细胞形成,以诱导成骨作用。此外,二甲双胍还可加速骨质疏松和正常小鼠的骨折愈合,作用机制可能为二甲双胍通过抑制损伤组织和缺氧培养的人微血管内皮细胞中YAP1/TAZ的表达来增加缺氧诱导因子1的表达,而缺氧诱导因子1为H型血管形成的重要正调节因子[45]。目前,关于二甲双胍对成骨-成血管偶联影响的直接证据较少。根据现有研究论述推测,二甲双胍对骨血管的形成有促进作用。然而在一项关于高脂饮食诱导骨关节炎的研究发现,二甲双胍诱导巨噬细胞极化的作用如前,但减少了软骨下骨中H型血管的生成[42]。 (2)二肽基肽酶4(dipeptidyl peptidase-4,DPP-4)抑制剂:DPP-4抑制剂是一种新型的降糖疗法,它通过抑制DPP-4的酶活性,从而抑制可刺激胰腺β细胞分泌胰岛素的高血糖素样肽1(glucagon-like peptide-1,GLP-1)降解来维持血糖水平[46],代表药物主要有:西格列汀、维格列汀等。 西格列汀可以调节免疫反应。在体外实验中,将西格列汀作用于M?巨噬细胞后,M2表型增加,表现为CD206和精氨酸酶1的表达增加以及肿瘤坏死因子α的表达降低,机制可能为西格列汀干扰M2巨噬细胞的线粒体动力学,降低了膜电位和线粒体活性氧的产生,并观察到M2吞噬能力降低[47]。另一项研究发现,高糖培养皿中巨噬细胞向M1型极化(诱导型一氧化氮合酶表达增加),人脐静脉内皮细胞在与巨噬细胞共培养过程中,损伤进一步加重。西格列汀干预后,可促进M1巨噬细胞向M2巨噬细胞复极化(CD206表达增加),但未能缓解人脐静脉内皮细胞的损伤;当两种细胞共培养时,西格列汀显著减轻了内皮损伤[48]。因此,西格列汀可能通过介导巨噬细胞极化失衡,改善糖尿病患者骨损伤后的血管生成和骨愈合。维格列汀也是一种常用于治疗2型糖尿病的DPP-4抑制剂。通过细胞实验发现维格列汀显著诱导RAW264.7巨噬细胞向M2型极化,促进成骨因子骨形态发生蛋白2和转化生长因子β1的分泌;在成骨细胞-RAW264.7共培养系统中观察到成骨分化增加;成骨细胞-骨髓间充质干细胞共培养系统中促进骨髓间充质干细胞向成骨形态转化,并抑制RAW 264.7细胞向破骨细胞分化[49]。现未有直接研究关于维格列汀对成骨-成血管偶联的影响,但因其促进M2巨噬细胞极化,推断对骨血管具有保护作用。 (3) 胰高血糖素样肽1受体激动剂(glucagon-like peptide-1 receptor agonist,GLP-RAs):GLP-1是一种肠促胰岛素激素,由肠道在食物刺激下分泌到血液中,通过特异性激活GLP-1受体发挥作用。艾塞那肽是临床上首个批准上市使用的GLP-1类似物,通过改善胰岛β细胞功能促进胰岛素分泌,抑制胰高血糖素分泌来降低血糖。一项关于艾塞那肽联合艾地骨化醇治疗T2DOP的研究发现二者联合能降低db/db小鼠血糖,并通过介导PI3K/AKT通路促使巨噬细胞向M2巨噬细胞极化,F4/80+CD206+细胞比例以及相关生物标志物(精氨酸酶1、Chil3、Retnla)表达显著增加;Micro-CT观察骨形态,与对照组相比,治疗组骨小梁数量、厚度增加,骨小梁间隙降低,骨体积分数升高;能诱导骨髓间充质干细胞成骨分化,相关成骨因子碱性磷酸酶、Ⅰ型胶原表达上调[50]。另外,利拉鲁肽可以直接或通过抑制M1巨噬细胞极化和炎症因子CXCL9分泌来增强骨髓间充质干细胞的成骨,机制可能与利拉鲁肽能部分逆转M1巨噬细胞调节信号,调节腺苷单磷酸活化蛋白激酶和核因子κB通路相关[51]。 2.3.2 抗骨质疏松类药物 双膦酸盐类药物是广泛使用的抑制破骨细胞的抗骨质疏松药物,这类药物可强烈抑制骨吸收,但也能减少骨形成[52]。唑来膦酸作为双膦酸盐的代表药物广泛用于治疗骨质疏松症和其他骨疾病。糖尿病患者早期使用唑来膦酸可以预防骨质减少,潜在机制可能是唑来膦酸治疗后逆转了糖尿病对成骨细胞调节转录因子骨形态发生蛋白2、Runt相关转录因子2和Osterix的表达[53]。另有研究表明,唑来膦酸在体内能抑制血管发芽成胶原蛋白基质[54],与骨微血管系统下降相关[55]。在一项研究中,通过建立双膦酸盐相关的颌骨坏死小鼠模型,发现唑来膦酸在体内损害拔牙窝骨骼血管的生成。与对照组小鼠相比,唑来膦酸组小鼠H型血管的丰度显著减少(标记物CD31、Emcn表达减少),骨祖细胞的Osterix表达降低,分子机制可能与唑来膦酸激活核因子κB信号传导,并诱导巨噬细胞中的P65核转位,导致骨髓来源巨噬细胞中miR-149-5p转录增多。而miR-149-5p通过骨髓来源巨噬细胞衍生的外泌体穿梭到内皮细胞,随后通过Rap1a/Rap1b/VEGFR2通路抑制内皮细胞的生物学功能。同时,发现拔牙槽中巨噬细胞向M1极化(F4/80+CD86+),抑制M2(F4/80+CD206+)极化[56]。因此,唑来膦酸可能对骨骼成骨-成血管偶联产生抑制作用。 另外,抗骨质疏松类药物带来的不良反应——药物相关性颌骨坏死(medication-related osteonecrosis of the jaw,MRONJ)与M1/M2巨噬细胞极化相关。当临床患者存在以下所有特征,则可能患有MRONJ:①当前或以前使用抗骨吸收或抗血管生成药物治疗;②暴露的骨骼或通过颌面部区域的口内或口外瘘管探查的骨骼持续超过8周;③无颌骨放射治疗史或颌骨明显转移性疾病[57]。为了探讨接受双膦酸盐或地诺单抗治疗MRONJ患者M1和M2巨噬细胞极化与临床分期的关系,临床收集30例MRONJ 1-3期患者坏死骨周围黏膜组织,活检评估M1和M2巨噬细胞密度以及白细胞介素6和白细胞介素10的表达,结果显示早期MRONJ巨噬细胞主要向M2巨噬细胞极化(CD68+CD206+M2巨噬细胞密度增加),M1/M2比值下降,白细胞介素10显著上调;而晚期MRONJ患者则表现出巨噬细胞向M1表型转变(CD68+iNOS+M1巨噬细胞密度增加),M1/M2比值升高,白细胞介素6显著过表达[58]。由此推测,介导巨噬细胞向M2极化,不仅可以改善双膦酸盐引起的骨血管内皮损伤,而且还能阻止抗骨质疏松药物带来的MRONJ进一步恶化。 2.4 骨生物修复材料 生物修复材料植入骨损伤部位后,宿主对生物材料的反应可以影响材料的功能并调节组织修复和重塑[59]。巨噬细胞是宿主对生物材料反应的关键细胞,通过极化作用影响生物材料的骨整合过程。而促进成骨和损伤部位血管重建是骨损伤愈合中最重要的两个因素。在骨损伤植入材料的过程中,通过改变植入材料的组成、表面形态以及药物负载来影响巨噬细胞极化,调节骨微环境炎症,减少氧化应激,促进植入物周围成骨-成血管偶联,这已经成为T2DOP患者骨折后骨植入材料整合的重要干预手段。在一项关于糖尿病足溃疡小鼠创面愈合的实验发现,通过介导转化生长因子β/Smad通路激活增加M2巨噬细胞标志物精氨酸酶1、几丁质酶3样分子、白细胞介素4的表达,同时降低M1巨噬细胞标志物诱导型一氧化氮合酶的表达[60],以促进糖尿病足溃疡面愈合。因此,促进M2巨噬细胞的表达除了促进成骨-成血管偶联,还可能有利于糖尿病患者伤口的愈合。表2中总结了糖尿病骨损伤后生物材料的植入对巨噬细胞极化及成骨-成血管偶联的影响[11,61-66]。 2.5 中药及其有效成分 2.5.1 黄芪 黄芪来源于豆科植物蒙古黄芪或膜荚黄芪的干燥根[67]。黄芪中主要的活性成分包括多糖类、皂苷类和黄酮类以及其他各种微量元素[68],黄芪中提取的生物活性成分具有免疫调节、抗高血糖、抗氧化、抗糖尿病等作用,并因不良反应小的优点而广泛应用于临床糖尿病的治疗[69],与骨质疏松治疗相关的有效成分主要集中在黄芪多糖、黄芪总皂苷、黄芪总黄酮[70]。研究发现,黄芪多糖和黄芪甲苷在治疗糖尿病相关并发症中起着重要作用。 黄芪多糖是从膜荚黄芪中提取的一种大分子活性物质。实验证据证实了黄芪多糖可减轻内皮功能障碍,改善内皮细胞损伤[71-72]。研究发现,黄芪多糖能够抑制脂多糖/慢性高血糖刺激的THP-1巨噬细胞向M1分化,降低活性氧和促炎因子(肿瘤坏死因子α、白细胞介素6、白细胞介素12)释放;黄芪多糖处理的THP-1/巨噬细胞向M2极化,并通过增强Nrf2/HO-1信号通路释放抗炎因子白细胞介素4、白细胞介素10和精氨酸酶1。在体内、外慢性高血糖环境中,黄芪多糖处理后内皮细胞增殖和凋亡得到改善,黄芪多糖促进人脐静脉内皮细胞和巨噬细胞共培养的人脐静脉内皮细胞迁移和血管形成,从而改善糖尿病血管内皮功能障碍[73]。 另外,在黄芪的活性成分中,黄芪甲苷是一种环阿烷型三萜的糖苷,具有多种生物活性,包括刺激血管生成和减轻缺血缺氧损伤。经黄芪甲苷治疗后能抑制破骨细胞生成,保留破骨前细胞,提高骨髓间充质干细胞活力,增强血小板衍生生长因子BB诱导的血管生成,并通过激活 AKT/GSK-3β/β-catenin 通路来增强成骨-成血管偶联。因此,推测中药黄芪可能通过调控M1/M2巨噬细胞极化,改善2型糖尿病引起的血管损伤,促进成骨-成血管偶联,从而治疗T2DOP[74]。 2.5.2 姜黄素 姜黄素是一种主要从姜黄根中提取的生物活性化合物,具有抗氧化、抗炎、抗癌和营养神经等多种药理学特性[75]。在T2DOP小鼠模型中观察到,姜黄素通过恢复高血糖状态下骨髓间充质干细胞的成骨-成血管偶联来改善2型糖尿病骨质疏松症[76];通过增加白细胞介素4、白细胞介素10和CD206的表达,减少白细胞介素1β、肿瘤坏死因子α、C-C趋化因子受体7、诱导型一氧化氮合酶的表达使巨噬细胞向抗炎表型M2极化,并观察到姜黄素能促进成骨相关细胞因子骨形态发生蛋白2和转化生长因子β的表达来改善骨免疫微环境[77]。 2.5.3 罗汉果酯苷V 罗汉果酯苷V为一种三萜皂苷,是中药罗汉果的主要生物活性成分,具有抗氧化能力,可以减轻巨噬细胞的炎症反应以及细胞内活性氧的产生[78]。 一项研究表明,罗汉果酯苷V可以通过NK-κB和p38 MAPK信号通路抑制慢性高血糖条件下脂多糖和干扰素γ诱导的骨髓来源巨噬细胞中M1型巨噬细胞极化和炎症反应,表现为CD11b+F4/80+CD86+细胞、炎症相关因子白细胞介素1β和白细胞介素6蛋白水平以及p65和p38的磷酸化水平升高,而经罗汉果酯苷V处理后降低[78]。另一项研究表明,罗汉果酯苷V显著增强慢性高血糖条件下骨髓间充质干细胞的活力和成骨分化能力,缓解了钙结节沉积,提高碱性磷酸酶、骨钙素和Runt相关转录因子"
| [1] KUMAR S, BEHL T, SACHDEVA M, et al. Implicating the effect of ketogenic diet as a preventive measure to obesity and diabetes mellitus. Life Sci. 2021;264:118661. [2] MOHSIN S, BANIYAS MM, ALDARMAKI RS, et al. An update on therapies for the treatment of diabetes-induced osteoporosis. Expert Opin Biol Ther. 2019;19(9):937-948. [3] Orthogeriatrics: The Management of Older Patients with Fragility Fractures, Second Edition. Med Sci Sports Exerc. 2022;54(3):536. [4] HOFBAUER LC, BUSSE B, EASTELL R, et al. Bone fragility in diabetes: novel concepts and clinical implications. Lancet Diabetes Endocrinol. 2022;10(3):207-220. [5] ZHANG E, MIRAMINI S, ZHANG L. The impact of osteoporosis and diabetes on fracture healing under different loading conditions. Comput Methods Programs Biomed. 2024;244:107952. [6] SELLMEYER DE, CIVITELLI R, HOFBAUER LC, et al. Skeletal Metabolism, Fracture Risk, and Fracture Outcomes in Type 1 and Type 2 Diabetes. Diabetes. 2016;65(7):1757-1766. [7] CHATTERJEE S, KHUNTI K, DAVIES MJ. Type 2 diabetes. Lancet. 2017; 389(10085):2239-2251. [8] STARUP-LINDE J, HYGUM K, LANGDAHL BL. Skeletal Fragility in Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus. Endocrinol Metab (Seoul). 2018;33(3):339-351. [9] KUSUMBE AP, RAMASAMY SK, ADAMS RH. Coupling of angiogenesis and osteogenesis by a specific vessel subtype in bone. Nature. 2014; 507(7492):323-328. [10] JIAO H, XIAO E, GRAVES DT. Diabetes and Its Effect on Bone and Fracture Healing. Curr Osteoporos Rep. 2015;13(5):327-335. [11] XU C, LI W, MAO J, et al. Using chondroitin sulfate lithium hydrogel for diabetic bone regeneration via regulation of macrophage polarization. Carbohydr Polym. 2025;347:122787. [12] ABE C, BHASWANT M, MIYAZAWA T, et al. The Potential Use of Exosomes in Anti-Cancer Effect Induced by Polarized Macrophages. Pharmaceutics. 2023;15(3):1024. [13] ATRI C, GUERFALI FZ, LAOUINI D. Role of Human Macrophage Polarization in Inflammation during Infectious Diseases. Int J Mol Sci. 2018;19(6):1801. [14] WILLENBORG S, SANIN DE, JAIS A, et al. Mitochondrial metabolism coordinates stage-specific repair processes in macrophages during wound healing. Cell Metab. 2021;33(12):2398-2414.e9. [15] ZHANG B, YANG Y, YI J, et al. Hyperglycemia modulates M1/M2 macrophage polarization via reactive oxygen species overproduction in ligature-induced periodontitis. J Periodontal Res. 2021;56(5):991-1005. [16] MICHALSKI MN, MCCAULEY LK. Macrophages and skeletal health. Pharmacol Ther. 2017;174:43-54. [17] TIAN P, ZHAO L, KIM J, et al. Dual stimulus responsive borosilicate glass (BSG) scaffolds promote diabetic alveolar bone defectsrepair by modulating macrophage phenotype. Bioact Mater. 2023;26:231-248. [18] WANG W, WANG Q, LI W, et al. Targeting APJ drives BNIP3-PINK1-PARKIN induced mitophagy and improves systemic inflammatory bone loss. J Adv Res. 2024. doi: 10.1016/j.jare.2024.12.033. [19] TWARDA-CLAPA A, OLCZAK A, BIAŁKOWSKA AM, et al. Advanced Glycation End-Products (AGEs): Formation, Chemistry, Classification, Receptors, and Diseases Related to AGEs. Cells. 2022;11(8):1312. [20] KANAZAWA I, SUGIMOTO T. Diabetes Mellitus-induced Bone Fragility. Intern Med. 2018;57(19):2773-2785. [21] PARK SY, CHOI KH, JUN JE, et al. Effects of Advanced Glycation End Products on Differentiation and Function of Osteoblasts and Osteoclasts. J Korean Med Sci. 2021;36(37):e239. [22] TAN H, XU W, DING X, et al. Notch/NICD/RBP-J signaling axis regulates M1 polarization of macrophages mediated by advanced glycation end products. Glycoconj J. 2022;39(4):487-497. [23] YANG Y, LI R, WANG P, et al. Osteoking prevents bone loss and enhances osteoblastic bone formation by modulating the AGEs/IGF-1/β-catenin/OPG pathway in type 2 diabetic db/db mice. Cell Biol Int. 2024;48(10):1507-1519. [24] DOU C, DING N, ZHAO C, et al. Estrogen Deficiency-Mediated M2 Macrophage Osteoclastogenesis Contributes to M1/M2 Ratio Alteration in Ovariectomized Osteoporotic Mice. J Bone Miner Res. 2018;33(5):899-908. [25] RAMASAMY SK. Structure and Functions of Blood Vessels and Vascular Niches in Bone. Stem Cells Int. 2017;2017:5046953. [26] GROSSO A, BURGER MG, LUNGER A, et al. It Takes Two to Tango: Coupling of Angiogenesis and Osteogenesis for Bone Regeneration. Front Bioeng Biotechnol. 2017;5:68. [27] SARAN U, GEMINI PIPERNI S, CHATTERJEE S. Role of angiogenesis in bone repair. Arch Biochem Biophys. 2014;561:109-117. [28] PENG Y, WU S, LI Y, et al. Type H blood vessels in bone modeling and remodeling. Theranostics. 2020;10(1):426-436. [29] LIN X, XU F, ZHANG KW, et al. Acacetin Prevents Bone Loss by Disrupting Osteoclast Formation and Promoting Type H Vessel Formation in Ovariectomy-Induced Osteoporosis. Front Cell Dev Biol. 2022;10:796227. [30] LU J, HU D, MA C, et al. Modified Qing’ e Pills exerts anti-osteoporosis effects and prevents bone loss by enhancing type H blood vessel formation. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2022;13:998971. [31] CHEN M, LIN W, YE R, et al. PPARβ/δ Agonist Alleviates Diabetic Osteoporosis via Regulating M1/M2 Macrophage Polarization. Front Cell Dev Biol. 2021;9:753194. [32] HUANG Y, HE B, WANG L, et al. Bone marrow mesenchymal stem cell-derived exosomes promote rotator cuff tendon-bone healing by promoting angiogenesis and regulating M1 macrophages in rats. Stem Cell Res Ther. 2020;11(1):496. [33] LOU R, CHEN J, ZHOU F, et al. Exosomal miRNA-155-5p from M1-polarized macrophages suppresses angiogenesis by targeting GDF6 to interrupt diabetic wound healing. Mol Ther Nucleic Acids. 2023;34:102074. [34] LI Z, WANG Y, LI S, et al. Exosomes Derived From M2 Macrophages Facilitate Osteogenesis and Reduce Adipogenesis of BMSCs. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2021;12:680328. [35] YING W, GAO H, DOS REIS FCG, et al. MiR-690, an exosomal-derived miRNA from M2-polarized macrophages, improves insulin sensitivity in obese mice. Cell Metab. 2021;33(4):781-790.e5. [36] WANG Y, LIN Q, ZHANG H, et al. M2 macrophage-derived exosomes promote diabetic fracture healing by acting as an immunomodulator. Bioact Mater. 2023;28:273-283. [37] ZHU Z, CHEN G, YU S, et al. Circadian clock disruption stimulates bone loss via regulatory T cell-Mediated regulation of IL-10 expression. Int Immunopharmacol. 2024;139:112589. [38] SHEN X, SHEN X, LI B, et al. Abnormal macrophage polarization impedes the healing of diabetes-associated tooth sockets. Bone. 2021; 143:115618. [39] SHAPOURI-MOGHADDAM A, MOHAMMADIAN S, VAZINI H, et al. Macrophage plasticity, polarization, and function in health and disease. J Cell Physiol. 2018;233(9):6425-6440. [40] ZHANG D, WANG Y, ZHOU Z, et al. Role of miRNA-regulated type H vessel formation in osteoporosis. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2024; 15:1394785. [41] HU K, OLSEN BR. Osteoblast-derived VEGF regulates osteoblast differentiation and bone formation during bone repair. J Clin Invest. 2016;126(2):509-526. [42] LIU X, GUO Q, WANG L, et al. Metformin attenuates high-fat diet induced metabolic syndrome related osteoarthritis through inhibition of prostaglandins. Front Cell Dev Biol. 2023;11:1184524. [43] SHEN M, YU H, JIN Y, et al. Metformin Facilitates Osteoblastic Differentiation and M2 Macrophage Polarization by PI3K/AKT/mTOR Pathway in Human Umbilical Cord Mesenchymal Stem Cells. Stem Cells Int. 2022;2022:9498876. [44] FAN S, ZHANG C, SUN X, et al. Metformin enhances osteogenic differentiation of BMSC by modulating macrophage M2 polarization. Sci Rep. 2024;14(1):20267. [45] RUAN Z, YIN H, WAN TF, et al. Metformin accelerates bone fracture healing by promoting type H vessel formation through inhibition of YAP1/TAZ expression. Bone Res. 2023;11(1):45. [46] ISHIDA M, SHEN WR, KIMURA K, et al. DPP-4 inhibitor impedes lipopolysaccharide-induced osteoclast formation and bone resorption in vivo. Biomed Pharmacother. 2019;109:242-253. [47] QUADROS-PEREIRA L, NERY-NETO JAO, DA SILVA EM, et al. Treatment with sitagliptin exacerbates the M2 phenotype in macrophages in vitro. Int Immunopharmacol. 2025;145:113730. [48] XIANG G, HUANG X, WANG T, et al. The impact of sitagliptin on macrophage polarity and angiogenesis in the osteointegration of titanium implants in type 2 diabetes. Biomed Pharmacother. 2020; 126:110078. [49] HE J, ZHAO D, PENG B, et al. A novel mechanism of Vildagliptin in regulating bone metabolism and mitigating osteoporosis. Int Immunopharmacol. 2024;130:111671. [50] LU Y, LIU S, YANG P, et al. Exendin-4 and eldecalcitol synergistically promote osteogenic differentiation of bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells through M2 macrophages polarization via PI3K/AKT pathway. Stem Cell Res Ther. 2022;13(1):113. [51] HE Y, SONG W, DENG Y, et al. Liraglutide promotes osteogenic differentiation of mesenchymal stem cells by inhibiting M1 macrophage polarization and CXCL9 release in vitro. Mol Cell Endocrinol. 2025;597: 112441. [52] JENSEN PR, ANDERSEN TL, CHAVASSIEUX P, et al. Bisphosphonates impair the onset of bone formation at remodeling sites. Bone. 2021; 145:115850. [53] CUI M, YU LZ, ZHANG N, et al. Zoledronic Acid Improves Bone Quality in the Streptozotocin-Induced Diabetes Rat through Affecting the Expression of the Osteoblast-Regulating Transcription Factors. Exp Clin Endocrinol Diabetes. 2019;127(1):68-75. [54] OTTO M, WEIGEL J, ZIEBART T, et al. Significance of bisphosphonates on angiogenesis in vivo and their effect under geranyl-geraniol addition - could it alter the treatment of bisphosphonate-associated necrosis of the jaw? Oral Maxillofac Surg. 2023;27(2):263-268. [55] REYES C, HITZ M, PRIETO-ALHAMBRA D, et al. Risks and Benefits of Bisphosphonate Therapies. J Cell Biochem. 2016;117(1):20-28. [56] SHEN X, ZHU W, ZHANG P, et al. Macrophage miR-149-5p induction is a key driver and therapeutic target for BRONJ. JCI Insight. 2022; 7(16):e159865. [57] RUGGIERO SL, DODSON TB, FANTASIA J, et al. American Association of Oral and Maxillofacial Surgeons position paper on medication-related osteonecrosis of the jaw--2014 update. J Oral Maxillofac Surg. 2014;72(10):1938-1956. [58] PASCHALIDI P, GKOUVERIS I, SOUNDIA A, et al. The role of M1 and M2 macrophage polarization in progression of medication-related osteonecrosis of the jaw. Clin Oral Investig. 2021;25(5):2845-2857. [59] HUANG X, CHEN M, WU H, et al. Macrophage Polarization Mediated by Chitooligosaccharide (COS) and Associated Osteogenic and Angiogenic Activities. ACS Biomater Sci Eng. 2020;6(3):1614-1629. [60] GENG K, MA X, JIANG Z, et al. WDR74 facilitates TGF-β/Smad pathway activation to promote M2 macrophage polarization and diabetic foot ulcer wound healing in mice. Cell Biol Toxicol. 2023;39(4):1577-1591. [61] YANG Y, WANG J, LIN X, et al. TNF-α-licensed exosome-integrated titaniumaccelerated T2D osseointegration by promoting autophagy-regulated M2 macrophage polarization. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2024;727:150316. [62] QIAO Y, YU L, YANG P, et al. Spatiotemporal Immunomodulation and Biphasic Osteo-Vascular Aligned Electrospun Membrane for Diabetic Periosteum Regeneration. Adv Sci (Weinh). 2023;10(36):e2302874. [63] WU Z, BAI J, GE G, et al. Regulating Macrophage Polarization in High Glucose Microenvironment Using Lithium-Modified Bioglass-Hydrogel for Diabetic Bone Regeneration. Adv Healthc Mater. 2022;11(13): e2200298. [64] WU M, LIU H, ZHU Y, et al. Bioinspired soft-hard combined system with mild photothermal therapeutic activity promotes diabetic bone defect healing via synergetic effects of immune activation and angiogenesis. Theranostics. 2024;14(10):4014-4057. [65] PEI M, LI P, GUO X, et al. Sustained Release of Hydrogen and Magnesium Ions Mediated by a Foamed Gelatin-Methacryloyl Hydrogel for the Repair of Bone Defects in Diabetes. ACS Biomater Sci Eng. 2024;10(7):4411-4424. [66] FAN S, TAN Y, YUAN X, et al. Regulation of the immune microenvironment by pioglitazone-loaded polylactic glycolic acid nanosphere composite scaffolds to promote vascularization and bone regeneration. J Tissue Eng. 2024;15:20417314241231452. [67] 国家药典委员会编.中华人民共和国药典一部2020年版[M].北京:中国医药科技出版社,2020. [68] 彭剑岚,朱永苹,林寿宁,等.黄芪及其活性成分治疗胃癌的作用机制研究进展[J].中华中医药学刊,2023,41(4):196-201. [69] ZHANG Y, CHEN Z, CHEN L, et al. Astragali radix (Huangqi): a time-honored nourishing herbal medicine. Chin Med. 2024;19(1):119. [70] 刘凯雯,郭成龙,张晓刚,等.黄芪有效成分治疗骨质疏松症相关信号通路的研究进展[J].中国骨质疏松杂志,2024,30(10):1487-1492. [71] TU S, SHAO A, REN L, et al. Angiogenesis effect of Astragalus polysaccharide combined with endothelial progenitor cells therapy in diabetic male rat following experimental hind limb ischemia. Chin Med J (Engl). 2014;127(11):2121-2128. [72] HAN R, TANG F, LU M, et al. Astragalus polysaccharide ameliorates H2O2-induced human umbilical vein endothelial cell injury. Mol Med Rep. 2017;15(6):4027-4034. [73] SHA W, ZHAO B, WEI H, et al. Astragalus polysaccharide ameliorates vascular endothelial dysfunction by stimulating macrophage M2 polarization via potentiating Nrf2/HO-1 signaling pathway. Phytomedicine. 2023;112:154667. [74] WANG F, QIAN H, KONG L, et al. Accelerated Bone Regeneration by Astragaloside IV through Stimulating the Coupling of Osteogenesis and Angiogenesis. Int J Biol Sci. 2021;17(7):1821-1836. [75] HE Y, ZHAO Y, LV RJ, et al. Curcumin activates the Wnt/β-catenin signaling pathway to alleviate hippocampal neurogenesis abnormalities caused by intermittent hypoxia: A study based on network pharmacology and experimental verification. Int Immunopharmacol. 2024;143(Pt 1):113299. [76] FAN D, LU J, YU N, et al. Curcumin Prevents Diabetic Osteoporosis through Promoting Osteogenesis and Angiogenesis Coupling via NF-κB Signaling. Evid Based Complement Alternat Med. 2022;2022:4974343. [77] CHEN S, LIANG H, JI Y, et al. Curcumin Modulates the Crosstalk Between Macrophages and Bone Mesenchymal Stem Cells to Ameliorate Osteogenesis. Front Cell Dev Biol. 2021;9:634650. [78] SHEN J, SHEN D, TANG Q, et al. Mogroside V exerts anti-inflammatory effects on fine particulate matter-induced inflammation in porcine alveolar macrophages. Toxicol In Vitro. 2022;80:105326. [79] LUO Y, YE Z, LI C, et al. Mogroside V Promotes Osteogenic Differentiation of Bone Marrow Mesenchymal Stem Cells from Diabetic Mice by Altering MicroRNA Profiles. Comb Chem High Throughput Screen. 2024. doi: 10.2174/0113862073299904240416114653. |
| [1] | Pan Hongfei, Zhuang Zhenbing, Xu Baiyun, Yang Zhangyang, Lin Kairui, Zhan Bingqing, Lan Jinghan, Gao Heng, Zhang Nanbo, Lin Jiayu. Inhibitory effects of different concentrations of auranofin on M1 macrophage function and its therapeutic potential in diabetic wound healing [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(6): 1390-1397. |
| [2] | You Huijuan, Wu Shuzhen, Rong Rong, Chen Liyuan, Zhao Yuqing, Wang Qinglu, Ou Xiaowei, Yang Fengying. Macrophage autophagy in lung diseases: two-sided effects [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(6): 1516-1526. |
| [3] | Xie Peisen, Guan Zhenpeng, Wei Xianjie, Zhang Keshi, Kang Qingyuan, Xiao Wentao, Guo Xiaoshuai. Cerium dioxide nanoparticles regulate expression of inflammatory factors in M1 macrophages and affect fibroblast co-culture system [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(2): 375-383. |
| [4] | Wang Wentao, Hou Zhenyang, Wang Yijun, Xu Yaozeng. Apelin-13 alleviates systemic inflammatory bone loss by inhibiting macrophage M1 polarization [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(8): 1548-1555. |
| [5] | Chang Jinxia, Liu Yufei, Niu Shaohui, Wang Chang, Cao Jianchun. Visualization analysis of macrophage polarization in tissue repair process [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(7): 1486-1496. |
| [6] | Wang Sifan, He Huiyu, Yang Quan, Han Xiangzhen. miRNA-378a overexpression of macrophage cell line composite collagen sponge: anti-inflammation and tissue repair promotion [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(4): 789-799. |
| [7] | Zhao Jianwei, Li Xunsheng, Lyu Jinpeng, Zhou Jue, Jiang Yidi, Yue Zhigang, Sun Hongmei. Deer antler stem cell exosome composite hydrogel promotes the repair of burned skin [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(34): 7344-7352. |
| [8] | Yao Lanxuan, Wang Xuefei, Liu Yang, Yang Yujia, Zhao Yi, Qi Fangfang, Li Yinghui . Mesenchymal stem cells and their derived extracellular vesicles target macrophages to intervene in autoimmune diseases [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(31): 6772-6781. |
| [9] | Chen Yixin, Lu Yan, Zhang Xuan, Chen Xiaoli, Tan Liangyuan, Xu Zhangjie, Chen Wanglong, Su Shaoting, Liang Jiyao, Zhou Honghai. Mechanism by which Tongan Decoction regulates synovial macrophage polarization in rats with knee osteoarthritis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(26): 5621-5631. |
| [10] | Fang Jun, Wei Wei, Xue Yating, Cui Chenlong, Wei Jiasheng, Shi Xiao, Yang Lijuan, Yang Baozhong. M2 macrophage-derived exosomes promote microglia M2-type polarization [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(25): 5320-5327. |
| [11] | Zou Shunyi, Chai yuan, Li Kunjian. Involvement of macrophage polarization in osteoarticular diseases: a visual analysis based on SCI-Expanded information [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(24): 5245-5253. |
| [12] | Cao Panxia, Peng Zining, Liu Shanshan, Fei Tiantian, Liang Tengyun, Zhang Mengwen, Wu Hong. AMP-activated protein kinase mediates macrophage fatty acid oxidation: an approach to prevent and treat atherosclerosis with traditional Chinese medicine [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(18): 3906-3914. |
| [13] | Zhao Yuqing, Wang Wei, You Huijuan, Chen Liyuan, Chen Yan, Wang Qinglu, Yang Fengying. Relationship between macrophage subtypes in obese adipose tissue and metabolic diseases [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(13): 2832-2841. |
| [14] | Yang Peng, Zhang Wei, Li Wenming, Li Wenhao, Wu Zebin, Zhou Jun, Geng Dechun. Linagliptin alleviates wear particle-induced inflammatory osteolysis by regulating macrophage polarization and osteoclast formation [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(12): 2421-2428. |
| [15] | Ge Ruiyang, Ni Can, Yang Kun, Yan Fuhua. The role of macrophage polarization in the pathogenesis and treatment of periodontitis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(20): 3246-3251. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||

