Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research ›› 2025, Vol. 29 ›› Issue (18): 3906-3914.doi: 10.12307/2025.655
Previous Articles Next Articles
AMP-activated protein kinase mediates macrophage fatty acid oxidation: an approach to prevent and treat atherosclerosis with traditional Chinese medicine
Cao Panxia1, Peng Zining2, Liu Shanshan3, Fei Tiantian1, Liang Tengyun1, Zhang Mengwen1, Wu Hong1
- 1The Second Clinical College of Henan University of Chinese Medicine, Zhengzhou 450000, Henan Province, China; 2The First Clinical College of Yunnan University of Chinese Medicine, Kunming 650000, Yunnan Province, China; 3Henan University of Chinese Medicine, Zhengzhou 450000, Henan Province, China
-
Received:2024-07-03Accepted:2024-08-12Online:2025-06-28Published:2024-11-29 -
Contact:Wu Hong, Professor, Doctoral supervisor, The Second Clinical College of Henan University of Chinese Medicine, Zhengzhou 450000, Henan Province, China -
About author:Cao Panxia, MD candidate, The Second Clinical College of Henan University of Chinese Medicine, Zhengzhou 450000, Henan Province, China -
Supported by:Henan Province Key Science and Technology Project, No. 242102311208 (to LSS); Henan Province “Double First-Class” Initiative for Traditional Chinese Medicine Scientific Research, No. HSRP-DFCTCM-2023-8-43 (to LTY); Henan Academy of Environmental Sciences Innovation Ecosystem Project, No. 219 (to CPX); University-Level Research Innovation Project, No. 2023KYCX046 (to CPX)
CLC Number:
Cite this article
Cao Panxia, Peng Zining, Liu Shanshan, Fei Tiantian, Liang Tengyun, Zhang Mengwen, Wu Hong. AMP-activated protein kinase mediates macrophage fatty acid oxidation: an approach to prevent and treat atherosclerosis with traditional Chinese medicine[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(18): 3906-3914.
share this article
Add to citation manager EndNote|Reference Manager|ProCite|BibTeX|RefWorks

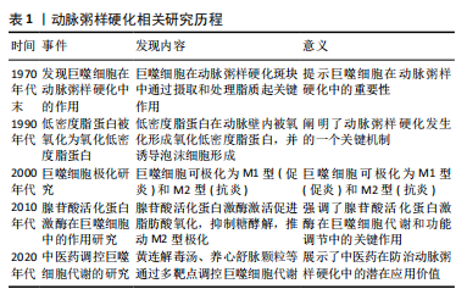
2.2 动脉粥样硬化与巨噬细胞能量代谢调控的主要途径 动脉粥样硬化是冠心病发生的主要原因,而脂质代谢紊乱是动脉粥样硬化的基础[9]。巨噬细胞作为循环中脂质的处理者和调节者,其代谢状态可以显著影响极化状态,从而改变动脉粥样硬化的病理进程[10]。文章主要探讨巨噬细胞能量代谢调控的几个主要途径。 2.2.1 低密度脂蛋白与泡沫细胞形成 低密度脂蛋白在氧化后形成氧化低密度脂蛋白,积聚在动脉壁内。氧化低密度脂蛋白与巨噬细胞表面的清道夫受体(如CD36和清道夫受体A)结合,诱导泡沫细胞形成,并激活炎症信号通路,导致巨噬细胞的激活和极化[11]。 2.2.2 血脂水平与炎性因子 冠心病患者的血脂水平明显高于健康人,血液中出现更多游离脂肪酸、超敏 C- 反应蛋白等有害脂质和炎性因子[12]。这些因子与疾病严重程度、病变血管数呈正相关,而与载脂蛋白A1呈负相关[13]。 2.2.3 巨噬细胞极化状态 巨噬细胞极化状态在斑块的稳定性和破裂风险中发挥重要作用。研究发现,斑块中M1型和M2型巨噬细胞数量均显著增加。M1型巨噬细胞在不稳定斑块中占优势,释放更多促炎因子,加剧炎症反应,导致斑块破裂和血栓形成[14-15]。 2.2.4 代谢状态与极化状态 巨噬细胞的代谢状态显著影响其极化状态,进而改变动脉粥样硬化的病理进程。在动脉粥样硬化进程中,巨噬细胞的能量代谢方式从依赖氧化磷酸化转变为糖酵解,其在炎症环境中快速反应和活化[16]。 2.2.5 糖酵解与泡沫细胞形成 激活的巨噬细胞通过吞噬氧化低密度脂蛋白转变为泡沫细胞,加速斑块的形成与扩大[17]。动物实验显示,当巨噬细胞的代谢方式被诱导为糖酵解时,细胞内脂质的吸收与积累增加,促炎细胞因子表达增多,导致动脉粥样硬化模型小鼠的斑块面积扩大[18]。 2.2.6 代谢改变与炎症反应 巨噬细胞代谢状态的改变加剧局部炎症反应,增加斑块不稳定和破裂的风险,可能触发急性冠状动脉事件。临床研究表明,激活的巨噬细胞是评估冠心病斑块稳定性的关键指标[19]。糖酵解代谢的转变促进泡沫细胞形成,使患者的冠状动脉粥样硬化负荷加重,高危斑块特征及心血管事件风险增高;相反,抑制糖酵解代谢可减少新斑块形成,提高斑块稳定性,降低心血管风险事件的发生率[20]。 综上所述,能量代谢的改变直接影响巨噬细胞的活化状态和功能,从而在动脉粥样硬化的进展中起到决定性作用,见图3。"

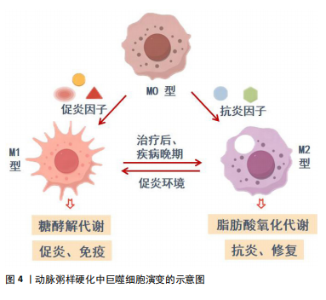
2.3 动脉粥样硬化中巨噬细胞演变的关键机制 动脉粥样硬化是一个复杂且渐进的疾病过程,巨噬细胞作为免疫系统的重要组成部分,会在不同病理阶段发挥不同作用。而巨噬细胞在动脉粥样硬化中演变的关键机制包括以下几个方面: 2.3.1 巨噬细胞的初始招募和激活 在动脉粥样硬化的起始阶段,受损的内皮细胞释放一系列趋化因子和促炎细胞因子,招募巨噬细胞聚集[21]。在这些促炎因子的刺激下,巨噬细胞转变为M1型巨噬细胞,具有高糖酵解代谢活性,分泌大量促炎细胞因子,并形成泡沫细胞,促进斑块的形成和发展[10]。随着疾病的发展,M1型巨噬细胞继续主导局部炎症反应,分泌更多促炎因子,进一步损伤内皮细胞并加剧脂质沉积。这种促炎环境增加斑块的不稳定性,导致斑块破裂和血栓形成的风险增加,可能引发心肌梗死、心绞痛等急性冠状动脉事件[22]。 2.3.2 巨噬细胞极化状态的变化 在动脉粥样硬化的不同阶段和斑块的不同区域,巨噬细胞的极化状态可以发生变化。在斑块边缘区域、纤维帽区域以及坏死核心周围,更多M2型巨噬细胞出现,这些细胞在抗炎因子的刺激下,表现出脂肪酸氧化代谢活性,分泌抗炎细胞因子,促进组织修复和炎症消退[23]。 2.3.3 治疗干预后的环境变化 在动脉粥样硬化的晚期阶段,尤其是经过治疗干预后,局部微环境中的促炎因子水平降低,抗炎因子水平升高,这种环境变化促进M1型巨噬细胞向M2型巨噬细胞的转变[24]。这一转变不仅有助于减轻炎症反应,还能增强斑块的稳定性,从而减少发生急性冠状动脉事件的风险。 明确动脉粥样硬化中巨噬细胞演变的相关机制,有助于临床上更有效地管理和治疗动脉粥样硬化相关疾病,特别是通过代谢方式调控巨噬细胞的极化状态,提供新的干预措施以改善患者的预后和生活质量,动脉粥样硬化中巨噬细胞演变的示意图见图4。"

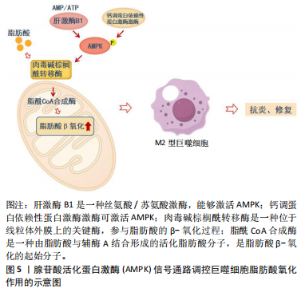
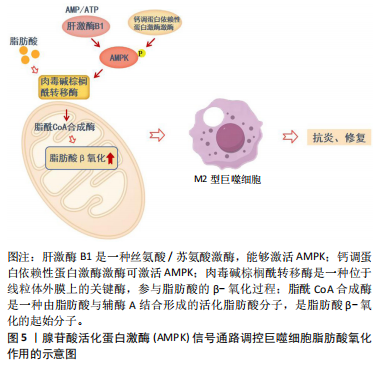
2.4 AMPK在巨噬细胞脂肪酸氧化中的作用机制 动脉粥样硬化中的巨噬细胞能量代谢调控主要通过脂肪酸氧化实现。脂肪酸氧化主要是指线粒体内脂肪酸氧化供能的过程。巨噬细胞脂肪酸氧化在动脉粥样硬化中的作用机制包括以下几个方面: 2.4.1 脂肪酸氧化在M1型和M2型巨噬细胞中的作用 对于M1型巨噬细胞,脂肪酸可作为炎症递质的前体,促进M1型巨噬细胞NOD样受体热蛋白结构域相关蛋白3炎症小体的生成,发挥促炎作用[25]。而在M2型巨噬细胞内,脂肪酸氧化为抗炎和修复作用提供能量基础。通过肉毒碱棕榈酰转移酶1,长链脂肪酸被转运到线粒体中进行代谢分解,增加脂肪酸氧化率的同时减少炎性细胞因子的表达[26]。 2.4.2 脂肪酸氧化对巨噬细胞极化的影响 脂肪酸氧化的增强倾向于支持M2型抗炎巨噬细胞的极化。葡萄糖代谢增强则倾向于支持M1型促炎巨噬细胞的极化。 2.4.3 脂肪酸氧化与冠心病 巨噬细胞脂肪酸氧化具有动脉粥样硬化的保护作用,增强脂肪酸氧化可能减缓动脉粥样硬化的进展。动物实验表明,敲除肉毒碱棕榈酰转移酶1后,巨噬细胞脂肪酸氧化受到抑制,清道夫受体CD36的表达升高,增加氧化低密度脂蛋白的摄取和泡沫细胞的转化,促进动脉粥样硬化的发展[27]。同时,临床研究发现冠心病中巨噬细胞的促炎活化抑制了脂肪酸氧化,导致脂质代谢紊乱和持续性炎症反应,对血管功能和血液流变学指标造成不利影响[28]。因此,巨噬细胞脂肪酸氧化能促进M2型极化,改善脂质代谢紊乱,减少炎症因子的产生,抑制动脉斑块的形成,对冠心病有一定的治疗作用。 2.4.4 AMPK在巨噬细胞中的调控作用 AMPK是一种关键的能量感应酶,其活性受多种因素调控,包括ATP/AMP比值、上游激酶(如LKB1、CaMKKβ)的磷酸化和代谢应激信号。当细胞内ATP水平下降,AMP/ATP比值增加时,AMPK被激活,启动一系列代谢反应以恢复能量平衡[29]。文章主要探讨AMPK在巨噬细胞脂肪酸氧化中的作用机制。 (1)AMPK对脂肪酸氧化的影响:①调节乙酰辅酶A羧化酶(Acetyl CoA carboxylase,ACC)。AMPK通过磷酸化和抑制ACC,降低丙二酸单酰辅酶A的生成,进而增加肉毒碱棕榈酰转移酶1的表达,促进脂肪酸向线粒体的转运和氧化[30]。②促进过氧化物酶体增殖物激活受体γ共激活因子1α(peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor γ coactivator-1α,PGC-1α)的表达。AMPK的激活还能促进PGC-1α的表达和活性。PGC-1α是线粒体生物合成的关键调控因子,能够增强线粒体的数量和功能,提高脂肪酸氧化的能力[31]。 (2)AMPK对脂肪酸氧化基因的调控:AMPK激活上调了一系列与脂肪酸氧化相关的基因,如肉毒碱棕榈酰转移酶和乙酰辅酶A脱氢酶,增强脂肪酸氧化的酶促反应[30]。 因此,AMPK的激活通过促进脂肪酸氧化,推动巨噬细胞向M2型极化,促进组织修复和抗炎反应。明确AMPK在巨噬细胞脂肪酸氧化中的作用机制,有助于通过代谢调控巨噬细胞的极化状态,为动脉粥样硬化的防治提供新的干预措施和理论依据,见图5。 2.5 中医药防治动脉粥样硬化的研究现状 中医学认为,动脉粥样硬化是一种由气滞血瘀、痰浊内阻、阴阳失调等多种病理因素引起的慢性疾病,归属于“脉痹”“脉"
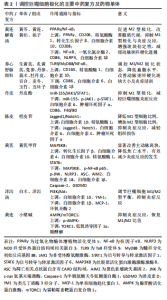
浊”“心痹”等证候类型。巨噬细胞通过调整自身极化状态,参与动脉粥样硬化过程中的血液循环障碍、代谢紊乱和炎症反应。这种机制为中医药提供了潜在的治疗途径,通过干预巨噬细胞的极化机制,中医药在治疗动脉粥样硬化方面取得了显著效果。 2.5.1 中医药调控巨噬细胞极化的机制 传统医学认为,动脉粥样硬化中的巨噬细胞异常表现,如促炎或抗炎的极化状态,是体内环境失衡的结果。黄连解毒汤具有清热解毒、活血化瘀、调节气血的作用。研究表明,黄连解毒汤能降低动脉粥样硬化模型小鼠血脂水平和外周血炎性单核细胞亚群比例,促进巨噬细胞M2型极化、减少M1型细胞极化和泡沫细胞分化,增强动脉斑块的稳定性,从而抑制高脂血症引发的动脉粥样硬化。体外实验显示,黄连解毒汤含药血清能够促进单核细胞向M2型巨噬细胞分化,增加M2型特异性受体CD206和精氨酸酶1基因的表达,降低M1型基因一氧化氮合酶2的表达[32]。此外,黄连解毒汤还通过激活过氧化物酶体增殖物激活受体γ (peroxisome proliferators-activated receptors-γ,PPARγ),在改善脂质代谢的基础上促进RAW264.7源泡沫细胞向M2表型极化,从而发挥抗炎和抗动脉粥样硬化的作用[33]。罗舒文等[34]发现,黄连解毒汤抗动脉粥样硬化的作用可能与核因子κB(nuclear factor kappa-B,NF-κB)相关通路有关,其通过上调PPARγ与M2型极化因子精氨酸酶1、转化生长因子β、CD208的表达,下调磷酸化NF-κB和M1型极化因子,降低动脉粥样硬化炎症水平,延缓疾病进程,进一步阐明了黄连解毒汤治疗动脉粥样硬化的机制。养心舒脉颗粒同样通过NF-κB相关通路发挥治疗动脉粥样硬化的作用,其能抑制 TLR9/MyD88/NF-κB通路,继而改变巨噬细胞能量代谢方式,通过促进脂质代谢使M1型向 M2型极化,抑制炎症反应,达到改善动脉粥样硬化斑块的目的[35]。除此之外,中药丹皮的提取物丹皮酚能有效减少巨噬细胞表面的炎症标志物和炎症因子的分泌,其通过下调miR-155的表达,抑制JAK1-STAT1通路的活化,进一步下调细胞表面标志性因子及炎症因子,抑制巨噬细胞M1型极化[36],表明丹皮酚通过调节特定基因和蛋白质通路,为动脉粥样硬化的治疗提供了新的思路。中药陈皮中的橙皮苷通过抑制Jagged1/Notch1通路,促进巨噬细胞M2型极化,从而减轻炎症小鼠的组织损伤[37]。同样,黄芪的提取物黄芪甲苷通过调控MAP3K8介导的巨噬细胞焦亡与极化的交互作用,降低促炎因子和焦亡相关蛋白的表达,促进抗炎因子和M2型巨噬细胞标志物的表达,从而减轻动脉粥样硬化中的炎症反应,稳定动脉斑块,具有治疗动脉粥硬化的作用[38]。泽泻汤为仲景所创治疗痰饮眩晕的方剂,主要用于水湿内停、痰饮之证,具有利水健脾之效,研究发现泽泻汤通过激活PI3K/AKT信号通路,调节巨噬细胞M1/M2极化平衡,抑制炎症因子表达,促进抗炎因子表达,改善脂代谢紊乱小鼠和细胞模型的代谢状态,并具有减轻炎症和降脂的作用[39]。而中药黄连的提取物小檗碱通过AMPK依赖性调控mTORC1通路,恢复巨噬细胞的M1/M2极化平衡,并通过改变巨噬细胞的代谢方式,降低炎症反应的发生,为中药干预巨噬细胞代谢调节提供了科学依据。 综上所述,传统医学通过多种中药方剂和单味药物调控巨噬细胞的极化状态,从而发挥抗炎和抗动脉粥样硬化的作用。这些中药不仅能在体内外实验中降低炎症反应,促进巨噬细胞向M2型极化,还能通过调控多种信号通路和基因表达,改善脂质代谢,减轻动脉粥样硬化病变。这些研究为动脉粥样硬化的防治提供了新的思路和科学依据,显示了中医药在现代疾病治疗中的潜力和优势,可调控巨噬细胞极化的主要中药复方见表2。 2.5.2 中医药调控巨噬细胞脂肪酸氧化途径的研究 巨噬细胞脂肪酸氧化是指巨噬细胞通过脂肪酸氧化代谢获得能量的途径,在不同的环境中,这种代谢方式发挥着不同的作用[40-41]。中医药通过调节巨噬细胞的脂肪酸氧化途径,具有显著的治疗效果。甘草和人参的提取物能够干扰信号传导及转录激活蛋白6信号通路,增加miR-155的表达,从而抑制肿瘤中M2型巨噬细胞极化[42]。此外,甘草中的甘草苷和异甘草苷、人参中的人参皂苷Rg3和Rg1、冬虫夏草中的虫草素、刺五加中的刺五加苷B、黄芪中的黄芪甲苷等成分通过抑制精氨酸酶1的表达,影响L-精氨酸的代谢,从而干预巨噬细胞脂肪酸氧化过程,抑制肿瘤中M2型巨噬细胞的极化,说明益气类中药可能是通过抑制M2型巨噬细胞极化发挥抗肿瘤作用[43]。 黄精通过降低耗氧率和提升细胞外酸化率,使巨噬细胞的代谢从脂肪酸氧化转向糖酵解,同时它也通过抑制AMPK信号通路的磷酸化,降低M2型巨噬细胞的线粒体氧化磷酸化和ATP产量,从而抑制其极化,为黄精在抗肿瘤免疫中的应用提供了理论依据[44]。 与此相反,吴茱萸汤通过调节鞘脂代谢、脂肪酸生物合成和PPARγ信号通路干预巨噬细胞的脂肪酸氧化,降低关键代谢物如1-磷酸鞘氨醇和棕榈酸的水平,减少炎症反应和氧化应激,从而发挥抗动脉粥样硬化的作用[45]。黄芪中的黄芪多糖通过延长脂肪酸链和激发多个"
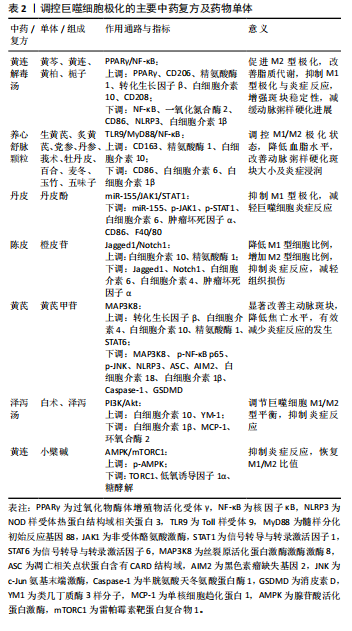

脂肪酸代谢途径的活性,提高细胞脂肪酸氧化代谢,增强巨噬细胞吞噬功能,进而发挥抗炎的作用[46]。同样,复方黄芩汤通过激活游离脂肪酸受体4/AMPK/PPARα通路,抑制脂肪酸合成酶和ACC的活性,激活沉默信息调节因子1介导的脂肪酸氧化,并通过抑制NF-κB通路减少炎症反应[47]。而洋参芎芍方可以降低巨噬细胞的葡萄糖摄取率、总胆固醇和游离胆固醇浓度,减少巨噬细胞内脂滴面积,并通过增加PPARγ的表达,促进脂肪酸氧化,减少脂质积聚和炎症反应,延缓动脉粥样硬化疾病进程[48]。 总之,上述不同的机制为靶向巨噬细胞代谢途径提供了潜在的治疗策略,可调控巨噬细胞脂肪酸氧化途径的主要中药复方见表3。 2.5.3 中医药调控巨噬细胞能量代谢AMPK途径的研究 AMPK作为能量传感器蛋白,在细胞能量状态低下时(如ATP水平下降)被激活,它在调控细胞代谢、维持能量稳态、调节细胞生长和自噬等过程中发挥关键作用。中医药通过双向调节AMPK激活途径,改善整体代谢状态,发挥抗"

炎修复作用。研究发现,雷公藤提取物雷公藤甲素通过抑制AMPK,解除对哺乳动物雷帕霉素靶蛋白(mammalian target of rapamycin,mTOR)的抑制,增强mTOR及其下游靶蛋白真核翻译起始因子4E结合蛋白1的磷酸化,促进蛋白质合成和细胞生长。另外通过调控AMPK/mTOR通路减少了巨噬细胞中炎症因子肿瘤坏死因子α、白细胞介素6、粒细胞-巨噬细胞集落刺激因子等的生成和释放,进一步降低了能量消耗,促进细胞的能量储存和利用[49]。黑果枸杞花青素同样通过抑制AMPK的活性,上调mTOR表达,从而抑制巨噬细胞自噬,减少细胞能量的消耗,展示了其调控细胞代谢和免疫功能的潜力[50]。 相反,白藜芦醇通过激活AMPK,上调AMPK和ACC的磷酸化水平,促进巨噬细胞脂肪酸氧化,并抑制内毒素诱导的NF-κB依赖性环氧合酶2信号通路,减少疾病的炎症反应[51]。另外,它还通过上调血管内皮生长因子B、激活AMPK、抑制NF-κB信号通路,实现了对巨噬细胞能量代谢的调节,并通过促进巨噬细胞向M2型极化,减轻了炎症反应,展示了白藜芦醇抑制异丙肾上腺素诱导的心肌重构的潜在治疗效果[52]。穿心莲提取物穿心莲内酯也通过激活LKB1、AMPKα、ACC和糖原合成酶激酶3β蛋白的磷酸化,抑制mTOR和p70核糖体蛋白S6激酶的磷酸化,减少促炎因子白细胞介素6、肿瘤坏死因子α、白细胞介素1β等的表达,有效抑制了巨噬细胞的炎症反应[53]。还有研究发现,黄连素通过激活AMPK,抑制mTORC1/低氧诱导因子1α通路,减少M1巨噬细胞的糖酵解代谢,切换M1巨噬细胞的糖酵解重编程,恢复M1/M2极化平衡,减轻疾病损伤[54]。同样的,中药复方也可以激活AMPK相关通路,从而调节巨噬细胞能量代谢,发挥治疗疾病的作用,如调肝导浊方、补肾活血方、三黄消炎方等[55-57],通过AMPK途径调控巨噬细胞能量代谢的主要中药复方见表4。"

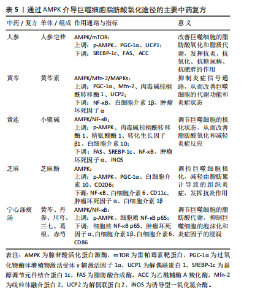
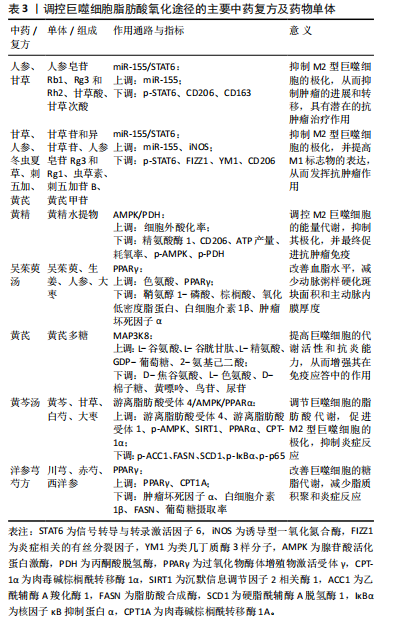
2.5.4 中医药调控AMPK介导巨噬细胞脂肪酸氧化途径的研究 AMPK激活后,会磷酸化并抑制ACC,从而抑制脂肪酸的合成并促进脂肪酸氧化,这意味着巨噬细胞在能量代谢上转向更高效的脂肪酸氧化路径,从而满足高能量需求的抗炎状态。中医药通过多种活性成分和复方配伍,能够高效、精准地激活AMPK信号通路,发挥多重药理作用,增强巨噬细胞的脂肪酸氧化能力,发挥治疗优势。人参皂苷是人参的主要活性成分之一,它可以激活AMPK信号通路,促进巨噬细胞的脂肪酸氧化,增加PGC-1α和肉毒碱棕榈酰转移酶的表达,减少脂质积累和炎症因子的产生[58]。同样的,黄芩提取物黄芩素通过激活AMPK通路,增加线粒体融合蛋白2的表达,促进巨噬细胞的脂肪酸氧化,减少炎症因子的产生,从而减轻动脉粥样硬化[59]。 黄连提取物小檗碱也通过激活AMPK,抑制NF-κB信号通路,增加巨噬细胞的脂肪酸氧化,并促进巨噬细胞从M1型向M2型转化,减少促炎性细胞因子的产生,增加抗炎性细胞因子的表达[60]。芝麻酚是一种从芝麻中提取的天然物质,研究发现它也激活AMPK信号通路,增加PGC-1α的表达,抑制NF-κB的表达,从而促进巨噬细胞脂肪酸氧化,调控巨噬细胞从M1型向M2型的极化,减轻组织炎症[61]。中药复方宁心涤痰汤同样通过激活AMPK信号通路,抑制NF-κB信号通路,促进巨噬细胞脂肪酸氧化,减少细胞内脂质积累和炎症因子表达,从而改善经皮冠状动脉介入术后血管再狭窄[62]。 综上所述,中医药通过激活AMPK信号通路,促进巨噬细胞的脂肪酸氧化,调节巨噬细胞的极化状态,减少炎症因子的产生,发挥抗炎作用,为治疗动脉粥样硬化等炎症相关疾病提供了有效的理论依据和实践指导,可通过AMPK介导巨噬细胞脂肪酸氧化途径的主要中药复方见表5。"

| [1] AGARWAL A, HUFFMAN MD. Inclusion of Polypills for Prevention of Cardiovascular Disease in the 23rd World Health Organization Model List of Essential Medicines: A Significant Step Towards Reducing Global Cardiovascular Morbidity and Mortality. Glob Heart. 2024;19(1):24. [2] LIAO Y, DONG Z, LIAO H, et al. Lipid metabolism patterns and relevant clinical and molecular features of coronary artery disease patients: an integrated bioinformatic analysis. Lipids Health Dis. 2022;21(1):87. [3] LINTON MF, MOSLEHI JJ, BABAEV VR. Akt Signaling in Macrophage Polarization, Survival, and Atherosclerosis. Int J Mol Sci. 2019;20(11): 2703. [4] YANG S, YUAN HQ, HAO YM, et al. Macrophage polarization in atherosclerosis. Clin Chim Acta. 2020;501:142-146. [5] FARAHI L, SINHA SK, LUSIS AJ. Roles of Macrophages in Atherogenesis. Front Pharmacol. 2021;12:785220. [6] MA A, WANG J, YANG L, et al. AMPK activation enhances the anti-atherogenic effects of high density lipoproteins in apoE-/- mice. J Lipid Res. 2017;58(8):1536-1547. [7] ZHAO Y, ZHAO Y, TIAN Y, et al. Metformin suppresses foam cell formation, inflammation and ferroptosis via the AMPK/ERK signaling pathway in ox‑LDL‑induced THP‑1 monocytes. Exp Ther Med. 2022; 24(4):636. [8] YANG Y, JIA Y, NING Y, et al. TAK1-AMPK Pathway in Macrophages Regulates Hypothyroid Atherosclerosis. Cardiovasc Drugs Ther. 2021; 35(3):599-612. [9] KOTLYAROV S. Involvement of Lipids and Lipid Mediators in Inflammation and Atherogenesis. Curr Med Chem. 2024. doi: 10.2174/0109298673303369240312092913. [10] DOLFI B, GALLERAND A, HASCHEMI A, et al. Macrophage metabolic regulation in atherosclerotic plaque. Atherosclerosis. 2021;334:1-8. [11] BONACINA F, DA DALT L, CATAPANO AL, et al. Metabolic adaptations of cells at the vascular-immune interface during atherosclerosis. Mol Aspects Med. 2021;77:100918. [12] 于峰.血清同型半胱氨酸、游离脂肪酸、超敏C反应蛋白以及胱抑素C在冠心病患者中的诊断作用[J].中国现代药物应用,2023, 17(17):71-73. [13] 赵忠平,刘虎,盛红专.HDL-C/ApoA1、MCP-1水平与中青年冠心病患者病变程度及炎症反应的相关性[J].中国现代医学杂志,2023, 33(16):49-54. [14] CHO KY, MIYOSHI H, KURODA S, et al. The phenotype of infiltrating macrophages influences arteriosclerotic plaque vulnerability in the carotid artery. J Stroke Cerebrovasc Dis. 2013;22(7):910-918. [15] ZHANG Y, YANG X, BIAN F, et al. TNF-α promotes early atherosclerosis by increasing transcytosis of LDL across endothelial cells: crosstalk between NF-κB and PPAR-γ. J Mol Cell Cardiol. 2014;72:85-94. [16] LI L, MOU J, HAN Y, et al. Calenduloside e modulates macrophage polarization via KLF2-regulated glycolysis, contributing to attenuates atherosclerosis. Int Immunopharmacol. 2023;117:109730. [17] KING SD, CAI D, FRAUNFELDER MM, et al. Surfactant protein A promotes atherosclerosis through mediating macrophage foam cell formation. bioRxiv [Preprint]. 2023:2023.03.23.533959.
[18] ZHANG L, LI L, LI Y, et al. Disruption of COMMD1 accelerates diabetic atherosclerosis by promoting glycolysis. Diab Vasc Dis Res. 2023;20(1): 14791641231159009. [19] LIN C. Early Diagnosis and Treatment of Coronary Heart Disease with Image Features of Optical Coherence Tomography under Adaptive Segmentation Algorithm. Comput Math Methods Med. 2022;2022:1261259. [20] KARPOUZAS GA, PAPOTTI B, ORMSETH S, et al. Serum cholesterol loading capacity on macrophages is linked to coronary atherosclerosis and cardiovascular event risk in rheumatoid arthritis. RMD Open. 2022;8(2):e002411. [21] ROY A, SAQIB U, BAIG MS. NOS1-mediated macrophage and endothelial cell interaction in the progression of atherosclerosis. Cell Biol Int. 2021;45(6):1191-1201. [22] ZHANG Z, WANG Q, YAO J, et al. Chemokine Receptor 5, a Double-Edged Sword in Metabolic Syndrome and Cardiovascular Disease. Front Pharmacol. 2020;11:146. [23] MEHU M, NARASIMHULU CA, SINGLA DK. Inflammatory Cells in Atherosclerosis. Antioxidants (Basel). 2022;11(2):233. [24] PENG D, ZHUGE F, WANG M, et al. (Sangzhi) alkaloids mitigate atherosclerosis by regulating M1/M2 macrophage polarization. Phytomedicine. 2024;128:155526. [25] MOON JS, NAKAHIRA K, CHUNG KP, et al. NOX4-dependent fatty acid oxidation promotes NLRP3 inflammasome activation in macrophages. Nat Med. 2016;22(9):1002-1012. [26] YADAV S, GANTA V, SUDHAHAR V, et al. Myeloid Drp1 Deficiency Limits Revascularization in Ischemic Muscles via Inflammatory Macrophage Polarization and Metabolic Reprograming. bioRxiv [Preprint]. 2023: 2023.11.04.565656. [27] NOMURA M, LIU J, YU ZX, et al. Macrophage fatty acid oxidation inhibits atherosclerosis progression. J Mol Cell Cardiol. 2019;127:270-276. [28] REN J, CHANG D, LIU J. Pathophysiological Characteristics of Phlegm-stasis Cementation Syndrome in Coronary Heart Disease:a Review and Update.World Journal of Traditional Chinese Medicine. 2015;1(4):38-41. [29] TARASIUK O, MICELI M, DI DOMIZIO A, et al. AMPK and Diseases: State of the Art Regulation by AMPK-Targeting Molecules. Biology (Basel). 2022;11(7):1041. [30] DAY EA, TOWNSEND LK, REHAL S, et al. Macrophage AMPK β1 activation by PF-06409577 reduces the inflammatory response, cholesterol synthesis, and atherosclerosis in mice. iScience. 2023;26(11):108269. [31] GU T, ZHANG Z, LIU J, et al. Chlorogenic Acid Alleviates LPS-Induced Inflammation and Oxidative Stress by Modulating CD36/AMPK/PGC-1α in RAW264.7 Macrophages. Int J Mol Sci. 2023;24(17):13516. [32] CAI Y, WEN J, MA S, et al. Huang-Lian-Jie-Du Decoction Attenuates Atherosclerosis and Increases Plaque Stability in High-Fat Diet-Induced ApoE-/- Mice by Inhibiting M1 Macrophage Polarization and Promoting M2 Macrophage Polarization. Front Physiol. 2021;12:666449. [33] 盛蒙,许滔,于红红,等.黄连解毒汤含药血清激活PPARγ诱导RAW264.7源性泡沫细胞向M2表型极化[J].中国免疫学杂志,2020, 36(3):277-281,288. [34] 罗舒文,何金涛,王腊,等.基于PPARγ/NF-κB通路探讨黄连解毒汤干预M1/M2极化延缓AS的作用机制[J].时珍国医国药,2022, 33(9):2065-2069. [35] 黄宏.养心舒脉颗粒调控TLR9/MyD88/NF-κB通路介导巨噬细胞极化改善动脉粥样硬化的机制研究[D].南京:南京中医药大学,2022. [36] 孙颖,刘玲,施晓艳,等.丹皮酚通过下调miR-155/JAK1-STAT1通过抑制巨噬细胞M1极化[J].中国中药杂志,2020,45(9):2158-2164. [37] 赵兴艳,汤正珍,岳春,等.橙皮苷调控Jagged1/Notch1通路对巨噬细胞极化及细支气管炎小鼠肺损伤的影响[J].中国医学科学院学报,2022,44(5):777-784. [38] 何信用,张哲,贾连群,等.黄芪甲苷调控MAP3K8介导的细胞焦亡及巨噬细胞极化交互作用防治动脉粥样硬化的机制[J].中华中医药杂志,2023,38(5):2311-2316. [39] 李二稳,崔正浩,高改,等.泽泻汤基于PI3K/AKT通路调节巨噬细胞M1/M2极化平衡机制研究[J].中国免疫学杂志,2024,40(8): 1684-1691. [40] ZHANG H, WANG SQ, HANG L, et al. GRP78 facilitates M2 macrophage polarization and tumour progression. Cell Mol Life Sci. 2021;78(23): 7709-7732. [41] SHI W, HUANG Y, YANG Z, et al. Reduction of TMAO level enhances the stability of carotid atherosclerotic plaque through promoting macrophage M2 polarization and efferocytosis. Biosci Rep. 2021;41(6): BSR20204250. [42] WANG D, WANG F, KONG X, et al. The role of metabolic reprogramming in cancer metastasis and potential mechanism of traditional Chinese medicine intervention. Biomed Pharmacother. 2022;153:113376. [43] JIANG YX, CHEN Y, YANG Y, et al. Screening Five Qi-Tonifying Herbs on M2 Phenotype Macrophages. Evid Based Complement Alternat Med. 2019;2019:9549315. [44] 侯亚琴,李明,岳利多,等.黄精对白细胞介素-4诱导M2巨噬细胞能量代谢和极化的作用与机制[J].中华中医药杂志,2022,37(8): 4400-4404. [45] LI C, CHI C, LI W, et al. An integrated approach for identifying the efficacy and potential mechanisms of TCM against atherosclerosis-Wu-Zhu-Yu decoction as a case study. J Ethnopharmacol. 2022;296:115436. [46] 李树颖,李科,秦雪梅,等.基于LC-MS代谢组学技术的注射用黄芪多糖活性成分调控巨噬细胞代谢研究[J].中草药,2020,51(6): 1575-1585. [47] LI MY, WU YZ, QIU JG, et al. Huangqin Decoction ameliorates ulcerative colitis by regulating fatty acid metabolism to mediate macrophage polarization via activating FFAR4-AMPK-PPARα pathway. J Ethnopharmacol. 2023;311:116430. [48] 王红芹,徐凤芹,周庆兵,等.基于RNA-Seq技术探讨洋参芎芍方改善RAW 264.7巨噬细胞代谢及炎症反应的机制[J].中西医结合心脑血管病杂志,2023,21(14):2568-2575. [49] 李雪丽,刘钊.雷公藤甲素通过调控AMPK/mTOR通路抑制脂肪细胞和巨噬细胞炎症机制研究[J].辽宁中医药大学学报,2022, 24(12):24-29+237. [50] 武强,薛才华,王梦杰,等.基于AMPK-mTOR信号通路探讨黑果枸杞花青素对小鼠巨噬细胞RAW264.7自噬的影响[J].中国兽医学报,2021,41(11):2176-2181. [51] YI CO, JEON BT, SHIN HJ, et al. Resveratrol activates AMPK and suppresses LPS-induced NF-κB-dependent COX-2 activation in RAW 264.7 macrophage cells. Anat Cell Biol. 2011;44(3):194-203. [52] LI Y, FENG L, LI G, et al. Resveratrol prevents ISO-induced myocardial remodeling associated with regulating polarization of macrophages through VEGF-B/AMPK/NF-kB pathway. Int Immunopharmacol. 2020; 84:106508. [53] KIM N, LERTNIMITPHUN P, JIANG Y, et al. Andrographolide inhibits inflammatory responses in LPS-stimulated macrophages and murine acute colitis through activating AMPK. Biochem Pharmacol. 2019;170: 113646. [54] CHENG JW, YU Y, ZONG SY, et al. Berberine ameliorates collagen-induced arthritis in mice by restoring macrophage polarization via AMPK/mTORC1 pathway switching glycolytic reprogramming. Int Immunopharmacol. 2023;124(Pt B):111024. [55] ZHANG Y, ZENG M, ZHANG X, et al. Tiaogan daozhuo formula attenuates atherosclerosis via activating AMPK -PPARγ-LXRα pathway. J Ethnopharmacol. 2024;324:117814. [56] ZHANG Z, ZHENG Y, CHEN N, et al. San Huang Xiao Yan recipe modulates the HMGB1-mediated abnormal inflammatory microenvironment and ameliorates diabetic foot by activating the AMPK/Nrf2 signalling pathway. Phytomedicine. 2023;118:154931. [57] CHEN S, TAO L, ZHU F, et al. BushenHuoxue decoction suppresses M1 macrophage polarization and prevents LPS induced inflammatory bone loss by activating AMPK pathway. Heliyon. 2023;9(5):e15583. [58] 石莹莹,沙纪越,李志满,等.基于AMPK信号通路探讨人参皂苷对脂质代谢调控的研究进展[J/OL].特产研究,1-7[2024-07-02].https://doi.org/10.16720/j.cnki.tcyj.2023.233. [59] ZHANG X, QIN Y, RUAN W, et al. Targeting inflammation-associated AMPK//Mfn-2/MAPKs signaling pathways by baicalein exerts anti-atherosclerotic action. Phytother Res. 2021;35(8):4442-4455. [60] ZHOU J, YU Y, YANG X, et al. Berberine attenuates arthritis in adjuvant-induced arthritic rats associated with regulating polarization of macrophages through AMPK/NF-кB pathway. Eur J Pharmacol. 2019; 852:179-188. [61] 刘瞩,程明慧,张劝劝,等.芝麻酚通过AMPK信号通路调控巨噬细胞极化减轻脂肪组织炎症[J].中国药理学通报,2023,39(11): 2082-2088. [62] 曹丽娟,于玲,刘莉.宁心涤痰汤通过AMPK/NF-κB通路抑制巨噬细胞分化改善血管再狭窄的机制研究[J].中国中医急症,2023, 32(4):592-596, 623. |
| [1] | Yu Shuai, Liu Jiawei, Zhu Bin, Pan Tan, Li Xinglong, Sun Guangfeng, Yu Haiyang, Ding Ya, Wang Hongliang. Hot issues and application prospects of small molecule drugs in treatment of osteoarthritis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(9): 1913-1922. |
| [2] | Zhou Panpan, Cui Yinglin, Zhang Wentao, Wang Shurui, Chen Jiahui, Yang Tong . Role of cellular autophagy in cerebral ischemic injury and the regulatory mechanism of traditional Chinese medicine [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(8): 1650-1658. |
| [3] | Yu Jingbang, Wu Yayun. Regulatory effect of non-coding RNA in pulmonary fibrosis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(8): 1659-1666. |
| [4] | Wang Qiuyue, Jin Pan, Pu Rui . Exercise intervention and the role of pyroptosis in osteoarthritis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(8): 1667-1675. |
| [5] | Yuan Weibo, Liu Chan, Yu Limei. Potential application of liver organoids in liver disease models and transplantation therapy [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(8): 1684-1692. |
| [6] | Wang Wentao, Hou Zhenyang, Wang Yijun, Xu Yaozeng. Apelin-13 alleviates systemic inflammatory bone loss by inhibiting macrophage M1 polarization [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(8): 1548-1555. |
| [7] | Chang Jinxia, Liu Yufei, Niu Shaohui, Wang Chang, Cao Jianchun. Visualization analysis of macrophage polarization in tissue repair process [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(7): 1486-1496. |
| [8] | Peng Hongcheng, Peng Guoxuan, Lei Anyi, Lin Yuan, Sun Hong, Ning Xu, Shang Xianwen, Deng Jin, Huang Mingzhi . Role and mechanism of platelet-derived growth factor BB in repair of growth plate injury [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(7): 1497-1503. |
| [9] | Gao Yang, Qin Hewei, Liu Dandan. ACSL4 mediates ferroptosis and its potential role in atherosclerotic cardiovascular disease [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(6): 1239-1247. |
| [10] | Liu Lingyun, He Guixin, Qin Weibin, Song Hui, Zhang Liwen, Tang Weizhi, Yang Feifei, Zhu Ziyi, Ou Yangbin . Improvement of myocardial injury by traditional Chinese medicine: mitochondrial calcium homeostasis mediates macrophage autophagy and pyroptosis pathway [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(6): 1276-1284. |
| [11] | Liu Haoyang, Xie Qiang, Shen Mengran, Ren Yansong, Ma Jinhui, Wang Bailiang, Yue Debo, Wang Weiguo . Application, research hotspots, and shortcomings of degradable zinc-based alloys in bone defect repair and reconstruction [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(4): 839-845. |
| [12] | Wang Sifan, He Huiyu, Yang Quan, Han Xiangzhen. miRNA-378a overexpression of macrophage cell line composite collagen sponge: anti-inflammation and tissue repair promotion [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(4): 789-799. |
| [13] | Guo Zhao, Zhuang Haoyan, Shi Xuewen. Role of exosomes derived from mesenchymal stem cells in treatment of colorectal cancer [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(36): 7872-7879. |
| [14] | Huang Haina, Yu Yanrong, Bi Jian, Huang Miao, Peng Weijie. Epigenetic characteristics of hepatogenic differentiation of mesenchymal stem cells in three-dimensional culture [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(36): 7848-7855. |
| [15] | Liu Lu, Zhong Chang, Yu Xin, Ren Chenyuan, Gong Yangyang, Zhou Ping, Wang Yingbin. Academic progress and clinical application of in vitro synthetic microenvironment to promote maturation of human pluripotent stem cell-derived cardiomyocytes [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(36): 7856-7862. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||